How to avoid blisters on the roof of your mouth?
Doctors consider the oral cavity to be a mirror image of the entire body, signs of infection and disturbances in the functioning of all internal organs. The presence of blisters on the palate is not only unpleasant, but also very dangerous, as they are a gateway for infection.
In addition, they can be evidence of a severe pathology in the body, and their inaccessibility (unlike skin rashes) makes its diagnosis and treatment very difficult.
Blisters on the roof of the mouth can bother both children and adults, causing pain and discomfort. They need to be dealt with only with the help of a specialist.
A blister appeared in the sky - what is it? Causes
Fans of very hot drinks and food often find slightly swollen areas of skin on the palate, which differ in color from the usual color of the mucous membrane. They may be lighter or have a scarlet, bright red tint, be pinkish or white.
Clear, even round spots with swelling and raised skin, under which a clear or white with a yellowish liquid is clearly visible, may indicate infection with an infectious disease or a relapse of a chronic disease.
With uneven swelling, which also contains contents, liquid or very dense, the situation is more complicated; such a blister can indicate both a burn and an illness.
Symptoms of burns
Thermal
- The pain appears immediately after eating food , taking a sip of tea or coffee, acute for a few seconds, it is replaced by aching, intensifying when touched.
- The swelling has a blurred shape, the areas are bright red, and in case of serious damage, the skin peels off almost immediately, forming a blister.
- Pain and discomfort do not allow you to drink and eat normally; you can only take liquid, lukewarm food.
- In a normal course, the burn heals within a week, leaving no marks or scars.
- The delicate skin of the mucous membrane of the palate is often injured, so the blister bursts, the exfoliated skin “falls off”, leaving tiny ulcers or inflamed areas with a whitish coating.
Chemical
- Sharp acute pain after acid or alkali enters the oral cavity, which almost always have a very characteristic taste and smell.
- Swelling, with clearly visible boundaries of the lesion.
- A blister or many blisters that merge with each other, or ulcerations of the palate with areas of peeling skin in the form of blisters.
- Long-term recovery is accompanied by pain almost throughout, and scars may remain.
Important. Chemical burns are dangerous because the depth of the damage is very difficult to determine; the substances often destroy not only mucous membranes, but also hard tissue and bone. Sometimes, to eliminate the consequences, not only long-term treatment is required, but also surgery to remove colloidal scars.
Other burns
Treatment of inflammation in the larynx and pharynx with ultraviolet light and quartz can cause a serious burn with the appearance of blisters if the duration of the procedure or the radiation power is incorrectly set,
High body temperature with drying of the mucous membranes, which persists for a long time, strong and prolonged thirst with a lack of water can also cause the appearance of blisters: the delicate mucous membrane dies without the required amount of saliva or moisture, this can lead to much more serious complications than just a blister on the roof of the mouth, because it is affected will be the entire oral cavity.
That is why doctors always try to moisten the lips of patients, give them a little something to drink, so that they can at least wet their mouth and rinse it.
Injuries
Injuries to the palate are no less common than burns.
A blister may be the result of mechanical damage from solid food, after eating, for example, a large amount of nuts, crackers, dried fruits.
Diseases
A hard blister appeared in the sky - what is it? The appearance of a blister on the roof of your mouth can be a symptom of a number of diseases.
- Fungal infection: the mucous membrane of the palate, as well as the tongue, cheeks, and gums, becomes inflamed and covered with a gray coating. Blisters or one large blister are clearly visible on the palate, after opening which a difficult-to-heal ulcer remains.
- Dental diseases – pulpitis, caries, others. Inflammatory processes easily spread in the oral cavity to all mucous membranes and can provoke detachment of individual areas of the skin.
- Stomatitis is an infectious lesion of the oral cavity, in which a rash of blisters appears on the mucous membrane, which open and heal within 10 to 14 days with appropriate treatment.
- Herpes is a dangerous and very unpleasant disease, highly contagious and fraught with complications. It affects not only the skin and mucous membranes. The virus can infect internal organs. It is insidious because it is almost impossible to completely destroy and makes itself felt by exacerbations at the slightest weakening of the immune system.
- Angioma is a proliferation of blood vessels that forms lump-like lumps or bright red blisters.
- A cyst is a benign neoplasm, a cavity with walls that retain fluid. It can remain the same size for a long time, enlarge, open on its own and begin to grow again. Formed on the palate when the glands are blocked. It is dangerous because inflammation may begin inside the cavity.
- Poisoning - a blister on the roof of your mouth can be a symptom of poisoning with lead and other heavy metals.
- Chickenpox - if the rules of care for patients with chickenpox are not followed or the disease is severe, blisters characteristic of this disease may appear in the oral cavity and on the palate.
- Allergies - reactions to foods, juices, and much more can be unpredictable with autoimmune diseases or a tendency for the body to have an unusual response to certain compounds.
A blister on the roof of your mouth may be what we call hives, only inside the mouth. Such blisters are very painful, easily injured, cause a lot of trouble, but disappear without a trace, as with ordinary urticaria, after 1 to 5 hours. - Sexually transmitted infections – sexually transmitted diseases can appear in the mouth after oral sex. Infected people pose a danger to others, and under certain conditions they can release the virus into the environment when they cough, sneeze, or get saliva on personal hygiene items or dishes.
Important. Any neoplasm in the palate, or in the oral cavity in general, requires consultation with specialists. Whatever its nature, the danger of infection and further spread throughout the body is very high.
A blister, either from a burn or as a result of an illness or an allergic reaction, cannot be ignored. It is necessary to clarify the reason for its appearance, strictly follow the treatment recommendations, so that complications do not arise and others do not suffer in case of infection with the virus.
What do blisters look like on the roof of your mouth?
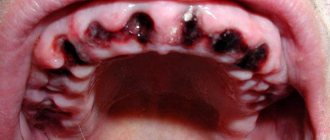
Outwardly, it looks like several transparent or white bubbles or spots that appear on the palate and other areas of the oral mucosa. Depending on the reason for their appearance, each bubble may be surrounded by a small roll of hyperemia.
Most often, such rashes are grouped in certain areas close to each other.
Symptoms and causes
The reasons for the appearance of a blister on the roof of the mouth vary greatly: the same symptoms in children and adults may indicate completely different infections and viruses. Remember that in children they can appear due to very sharp teeth or malocclusion. Let's look at the main reasons for their appearance.
Thermal burns
When drinking hot water or food (especially in children), burns to the oral mucosa may occur. There are 3 stages of damage:
- tissue inflammation;
- the appearance of transparent blisters on the palate;
- tissue death and rejection.
Mechanical injuries
There are people who like to chew nuts, hard sugar, etc., since the mechanism of blistering is similar to the formation of calluses (when the skin is rubbed).
Injury can also be caused by poor-quality dentures or uneven teeth.
Follicular tonsillitis
The most dangerous type of sore throat, accompanied by inflammation of the tonsils. During the pathology process, follicles (small lymph nodes) develop in the form of transparent blisters.
They are easily identified during a routine examination of the oral cavity using a mirror. As a rule, follicular tonsillitis is acute and is characterized by the following symptoms: severe headache, intoxication of the body, fever and cutting pain in the throat.
Dühring's disease
An autoimmune pathology that develops as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
This video explains what symptoms you should see a doctor for:
Herpetic stomatitis
An acute pathology affecting the oral cavity, during which blisters appear in large numbers on its surface. The cause of this condition is the herpes virus.
Over time, the blisters burst, leaving erosions that can become inflamed if they become infected.
Herpangina
Inflammation of the palate and back of the throat. It is characterized by the appearance of a large number of transparent blisters, more reminiscent of follicles and can be caused by the Coxsackie virus, staphylococcus or streptococcus.
This pathology is contagious and has the following symptoms: high fever, sore throat and abdominal pain, fever, intoxication and inflammation of the maxillary sinus.
Abscess and pharyngitis
These pathologies can provoke the formation of blisters, which can persist for a month even after complete recovery (depending on the state of the immune system).
Vesical vascular syndrome
Most often found in people with heart disease and looks like a large red blister. The reason for its appearance is an increase in blood pressure.
Hand-foot-mouth syndrome
A childhood disease caused by the Coxsackie virus. Its symptoms are very easy to identify: the presence of blisters on the roof of the mouth and on the limbs, fever, pain and dehydration.
Pemphigus or pemphigus
A dangerous pathology, most often observed in older people and has several varieties: vulgar, leaf-shaped, vegetative and erythematous.
The main symptoms of pemphigus are: the formation of complete blisters, a cheesy coating, deterioration in health and bad breath.
Exudative erythema (multiform)
It is characterized by a long course with repeated relapses. Main symptoms: increased body temperature, general malaise, burning in the mouth, body aches, the formation of blisters that cause pain while eating and talking.
Congenital epidermolysis
This pathology is detected from the very birth of a person and does not leave him until the end of his life. It has a simple and dystrophic form, and can also be benign or malignant.
In addition, the formation of blisters on the palate may be signs of the following pathologies:
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- heart and kidney diseases;
- hypovitaminosis;
- cancer;
- immunodeficiency;
- respiratory diseases;
- chicken pox;
- reaction to chemotherapy;
- syphilis;
- Saturnisms.
Thus, the presence of blisters on the palate is a sign of dangerous pathologies or poisoning, therefore, in order to completely cure them, it is necessary to establish a correct diagnosis and eliminate the root cause of their appearance.
Treatment Options
The mass of treatment options for a blister in the mouth does not mean that you can easily and simply eliminate both the symptom itself and the disease that caused it. You can only temporarily alleviate the condition on your own, but treatment should be carried out comprehensively and under the supervision of a doctor.
Microorganisms from the oral cavity easily enter the gastrointestinal tract and can provoke inflammatory processes in all organs. The palate is easily injured, which complicates treatment. But you can help yourself for a while.
Pharmacy products
Ointments and sprays available in pharmacies can relieve pain, itching and burning. There are many drugs containing antibiotics that will prevent the spread of inflammation and speed up the healing process.
- Rinse your mouth with a solution containing an antibiotic.
- Using a cotton swab or turunda, take the required amount of ointment (Solcoseryl, Tetracycline, zinc, Vishnevsky ointment, Levomikol).
- Apply to the skin around the blister and the blister itself, being careful not to disturb its integrity.
- Let the ointment absorb and dry. At this time, it is better for the patient to keep his mouth open and his head thrown back so that saliva does not wash away the medicine. A cork, a matchbox, or a spool of thread inserted into the mouth between the teeth will help with this, if there is no special device.
- Repeat the procedure every 4 – 5 hours in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations.
Often such blisters are treated with hydrogen peroxide, iodine, and a weak solution of manganese. For any infections of the oral cavity, including those with a blister on the roof of the mouth, irrigating the affected areas with chlorhexidine and rinsing with Iodinol will help.
Drug treatment
The existence of a huge number of treatment methods does not mean that it is possible to quickly and easily eliminate both the blister itself and the pathology that caused it.
You can alleviate your condition a little on your own, and then only for a while.
The main treatment should be comprehensive and should be prescribed by a doctor. Medicines (sprays and ointments) purchased at the pharmacy help relieve pain, burning and itching. This especially applies to drugs that contain an antibiotic:
- rinse your mouth with an antibiotic solution;
- Apply the required amount of ointment (Vishnevsky, Tetracycline or Levomikol) to a cotton swab;
- Carefully treat the blister and the skin around it with ointment;
- wait until the product is absorbed and dry (leave your mouth open and tilt your head back slightly);
- The blister should be treated every 5 hours, after consulting with your doctor;
- can be treated with iodine, hydrogen peroxide or potassium permanganate (a very weak solution);
- Irrigating the mouth with Chlorhexidine and rinsing with Iodinol will help get rid of the infection;
- pharmaceutical tablets (for resorption): Gramidin, Septolette, etc. help get rid of infection in the oral cavity.
However, they should be used very carefully so as not to damage the palate. If blisters appear (without headache, cough or fever), you must urgently contact a specialist to diagnose and determine the exact cause of the disease.
Professional treatment includes:
- rinsing with antiseptics;
- use of anti-inflammatory drugs;
- anesthesia;
- antibacterial therapy;
- use of antiviral and antifungal drugs;
- treatment with antihistamines (for allergies).
In addition to prescribed medications, the patient must follow certain medical recommendations.
Treatment with folk remedies
The use of folk remedies to treat blisters on the roof of the mouth perfectly complements medication treatment. Let's look at the most effective of them:
- Soda solution: 1 tsp. dissolve soda in 1 tbsp. water (warm). This remedy relieves inflammation and has an antimicrobial effect.
- A decoction of oak bark will help remove the infection and also relieve redness: 1 tbsp. l. bark pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, put on fire and simmer over low heat for about half an hour, then cool. Rinse your mouth with the resulting decoction 5-6 times a day.
- Aloe compresses: remove the skin from 1 leaf of the plant and knead thoroughly, wrap the pulp in gauze and apply to the blister for 20 minutes.
- A decoction of calendula helps relieve itching from a blister on the roof of your mouth and is also an excellent antiseptic. Use for rinsing.
- Goldenseal infusion: 2 tsp. plants pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 2 hours and use for rinsing.
- Decoctions of rose hips, propolis and chamomile provide an excellent anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, they are all absolutely safe.
To treat blisters, you should stop the underlying pathology, and not hope that the disease will go away on its own. If treatment is not started in time, the situation will only get worse.
What should you not do?
There is no need to open the blisters on the roof of your mouth, try to remove them or cauterize them. Self-diagnosis leads to many complications; in advanced forms, the disease is much less treatable.
Taking antibiotics and hormonal drugs without a doctor’s prescription will blur the picture of the disease, which will make it difficult for professionals to diagnose, so when taking them, you need to clearly remember the dosage.
There is no need to self-medicate; if a blister appears on the roof of your mouth, it is best to immediately consult a doctor.
When to see a doctor
The appearance of a blister on the roof of the mouth is often a symptom of a dangerous pathology in the body and always requires contacting a specialist. Many possible reasons causing its appearance necessitate testing to establish the correct diagnosis.
First of all, you should contact a general practitioner (pediatrician), who, after a thorough examination, will refer you to a dermatologist, ENT specialist or oncologist.
If blisters appear not only on the palate, but also on other areas of the mucous membrane or skin, you should consult a dermatovenerologist. If your throat is affected (swelling and pain), then you have a sore throat and should be treated by an ENT specialist.
What not to do with blisters
The first thing that should not be done is to ignore the symptoms, since possible infections or cancer can cost the patient his life. Blisters on the palate always pose a danger in the form of infection entering the body and the development of a palate abscess.
What is prohibited to do during treatment:
- warm the throat so as not to increase suppuration;
- remove rashes yourself;
- If ulcers appear, the mouth should not be disinfected with alcohol-containing products.
How to make calendula decoction at home, watch this video:
Remember that you should not self-medicate, because very often it is possible to cure the underlying disease only with the help of antibiotics prescribed by a doctor.
How to avoid their reappearance
It is necessary to perform preventive procedures:
- carry out oral hygiene daily;
- regular visits to the dentist (once every six months);
- support immunity with vitamins;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Healthy food;
- Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly;
- quit smoking;
- avoid spicy and too hot foods so as not to injure the mucous membranes.
It is important to follow all the doctor’s instructions and not interrupt treatment, otherwise you will not be able to avoid the recurrence of blisters.
A small number of rashes can be easily eliminated, and if the disease starts, the unpleasant consequences will not take long to appear. Strengthen your body and you will quickly defeat all bacteria and viruses.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
A consultation with a dermatologist or infectious disease specialist is absolutely necessary; you can ask for help either in a regular clinic or in private dermatological clinics:
- immediate help is necessary if the swelling spreads quickly - this threatens the patient’s life;
- An ambulance should be called if a child is sick, he has shortness of breath, he cannot eat or drink for several hours;
- If there is a thick plaque in the mouth, high temperature and blisters, it is also better to call a doctor at home, it could be an airborne infection.
Attention. Rapid deterioration of the condition, suspicion of anaphylactic shock, increased swelling or other life-threatening conditions - all this should prompt you to call an ambulance.
In all other cases, you can make an appointment with a dermatologist as usual.
Prevention and care
If you have an allergic reaction or inflammation on the roof of your mouth, you must disinfect your mouth as often as possible.
After each meal, rinse your mouth thoroughly.
The most common preventive measures will help you avoid infection:
- do not take other people’s personal hygiene items;
- brush your teeth and rinse your mouth at least twice a day;
- do not drink too hot drinks;
- take care of the mucous membranes and prevent them from being injured.
A blister on the roof of your mouth can be a consequence of an injury, burn, or a symptom of an illness, including a dangerous one. If bubbles appear on the roof of your mouth, you should definitely seek help from a hospital to diagnose the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment.