Sanitation of the oral cavity is a rather important event, which, unfortunately, is underestimated by many. Although this procedure helps to promptly identify problems with teeth and gums and effectively eliminate them in the early stages. Sanitation can be planned (preventive), or prescribed in connection with other events. A certificate of oral hygiene may be needed in many situations. For example, it is necessary for pregnant women or people who are preparing for surgery.
What is oral sanitation and what procedures does it consist of?
Sanitation of the oral cavity is a set of measures aimed at treating diseases of this area (teeth, gums, tongue, mucous membranes) or preventing their occurrence, as well as eliminating various pathologies (congenital or acquired).
The complex of these measures includes the following procedures:
- treatment of caries (including complicated ones that have progressed to pulpitis or periodontitis). This is the most frequent therapeutic intervention, since almost 90% of the population suffers from dental caries, and also because it is with minor destruction of the enamel that large and intractable problems begin - diseases of the dental roots, infectious lesions of hard and soft tissues, destructive lesions leading to loss of functional units,
- treatment of periodontitis. This is a disease that affects various structures around the tooth root. The danger is that during inflammation, the infection can spread not only to neighboring teeth, but also to the bone, and even to other organs of the head - eyes, ears, sinuses,
- treatment of tooth enamel destruction (including hypoplasia). The enamel covering the crown performs a protective function, so any violation of its integrity threatens damage to softer and unprotected tissues. Depending on the diagnosis and the degree of development of the pathology, the doctor builds a treatment strategy - from the use of remineralizing pastes to installing crowns on the affected teeth.
- treatment of inflammatory processes of soft tissues of the oral cavity. These can be diseases of the gums, tongue, oral mucosa, palate and larynx. Therapy tactics are built depending on the diagnosis and individual factors of the patient’s condition (heredity, pregnancy, the presence of other diseases that provoke inflammation in the oral cavity, bad habits, etc.),
- elimination of tooth deformation (both congenital and acquired) and filling defects. Depending on the clinical picture, defects are corrected using fillings or prosthetics,
- cleaning and curettage of gum pockets. Gum pockets are called the separation of the edge of the gum from the wall of the tooth. In such depressions, as a rule, plaque accumulates, which then hardens, turning into tartar. All sorts of pathogenic microbes love to live there. Removing these deposits prevents the spread of infection and the development of many diseases,
- removal of teeth that have completely lost their functionality. The doctor resorts to this method when restoring the unit is no longer possible for some reason,
- correction of bite. This stage is very important for maintaining dental health, since malocclusion causes inconvenience not only in aesthetic terms. With various defects in the dentition, digestion and speech are affected, the process of salivation is disrupted, and there is a risk of developing caries or other infectious diseases,
- prosthetics. Replacing missing teeth is needed not only to restore the aesthetics of a smile. A complete set of teeth allows you to chew food better, improve diction, maintain the strength of the jaw bone,
- professional teeth cleaning. This set of preventive procedures includes not only the removal of plaque and tartar, but also the treatment of crowns with special restorative and protective preparations, bleaching, fluoridation, silvering (mainly for children) and other hygienic procedures.
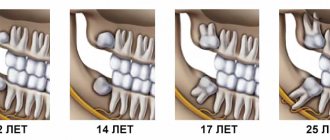
Stages of a full range of events
A full range of treatment and preventive measures consists of the following stages:
- examination by a dentist;
- identifying a problem and making diagnostic assumptions about the need to solve it;
- taking an x-ray of the problem area;
- ultrasonic cleaning, removal of plaque and tartar;
- drawing up a plan for further therapy (if necessary);
- referral for consultations to highly specialized specialists, for example, surgeons or orthodontists (if occlusion disorders and other specific problems are detected);
- carrying out health procedures;
- coating of teeth with a special gel polish, which contains calcium and fluoride;
- providing an opinion from a specialist;
- drawing up an individual additional schedule of visits (if necessary).
Indications for sanitation
- upcoming surgical treatment (even with minor interventions, such as abortion, replacement of the eye lens, removal of adenoids, etc.). This is done in order to avoid complications after surgery, because an infection from the oral cavity can enter the blood,
- entering kindergarten or school. Upon admission to an educational institution, a health card is created for each student, which indicates chronic and other diseases, and also monitors what treatment the child receives,
- before pregnancy. When planning to become a mother, women should take care of their health, since pregnancy is a serious test for the body, and the presence of infectious diseases can become a serious test for the fetus. Therefore, it is important to take preventive measures in advance,
- upcoming orthopedic (prosthetics, implantation) or orthodontic (bite correction) treatment,
- work in hazardous industries (especially those related to the chemical industry). Harsh working conditions weaken the body, so workers in hazardous professions must undergo a medical examination, and if any pathologies are detected, immediately receive medical care.
- a history of serious illness (such as diabetes, tuberculosis, rheumatological systemic diseases, etc.). Such complex diagnoses, as a rule, disrupt the functionality of many body systems, and teeth are most often the first to be affected.
- the presence of chronic or genetically determined oral diseases,
- passing the draft commission (for conscript or contract service),
- upcoming long-term business trip to places with limited medical care (for example, third world countries), expeditions, extreme hikes.
Myth or reality?
There is an opinion that during pregnancy, the teeth of the expectant mother can rapidly deteriorate, because the developing baby “takes calcium” from the mother’s tooth enamel. This is, of course, a myth, since the calcium necessary for the development of the child comes from the mother's gastrointestinal tract. In general, pregnancy is a period of changes in a woman’s entire body, when all its systems are subject to special stress, including the oral cavity. Most often, expectant mothers complain of increased tooth sensitivity, the appearance of many carious cavities, and bleeding gums. Untimely treatment in such a situation can overshadow both the pregnancy itself and the postpartum recovery period.
How is sanitation carried out?
This event is usually divided into three types:
- individual (is the initiative of the patient himself),
- periodic (if the patient falls into one of the groups for which undergoing sanitation is a necessity, for example, before surgery or pregnancy),
- planned (when the procedure is included in the occupational safety plan or is a prerequisite for employment).
Sanitation of foci of chronic infection
The presence of a focus of chronic infection in the body does not allow a person to be considered absolutely healthy until it is completely sanitized, regardless of whether this focus manifests itself in any way or not.
Most often, these foci are carious teeth, chronic tonsillitis and cholecystitis. However, the paranasal sinuses (chronic sinusitis, frontal sinusitis), ears (chronic otitis media, tubootitis) or even the nasal cavity (all forms of chronic rhinitis) can also act as foci of chronic infection. Even if these lesions do not manifest themselves in any way, they can cause a wide variety of, often very serious, diseases. If clinical manifestations are present, they are most often symptoms of general intoxication. Most often they are not very pronounced and have an unstable and intermittent character. Low-grade fever without a clearly defined cause, loss of appetite, sleep disturbances, increased fatigue, decreased performance - these are the most common complaints found in carriers of chronic infection. Various disturbances of cardiac activity are very often observed - rhythm disturbances, interruptions, extrasystoles, decreased aerobic endurance. Sometimes tonsillogenic toxic changes in the myocardium and coronary vessels are also observed, leading to ischemic pain and even heart failure.
It must also be remembered that foci of chronic infection are often combined and even connected with each other. The combination of various foci enhances their adverse effects on the body, suppresses the immune system and worsens the general condition. It should be noted that foci of chronic infection located in the palatine tonsils are especially dangerous. They are the cause of such serious complications as rheumatism and rheumatic endocarditis and endovasculitis, which subsequently lead to damage to the valvular apparatus of the heart and cardiac muscle with subsequent disability.
Intoxication from chronic foci of infection also has a noticeable negative effect on the musculoskeletal system, in particular the joints.
There are also persistent headaches, neurotic and mental disorders caused by the presence of foci of chronic infection in the body.
The long-term presence of foci of chronic infection in the body inevitably leads to the negative impact of infectious intoxication, functional, and subsequently organic changes in organs, especially if they are not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner.
All of the above illustrates the urgent need to sanitize foci of chronic infection. We can say that such foci are a time bomb that inevitably affects the entire body, and there is a dangerous possibility of its “detonation” in the form of various, sometimes life-threatening, complications. In our clinic in Kupchino, qualified specialists will conduct a full course of sanitation of such foci of chronic infection as tonsils or carious teeth. After consultation, the doctor will prescribe the necessary examination and draw up an individual plan for the sanitation of infectious foci, and specialists will perform their part of the task of ridding your body of the constant unpleasant presence of microorganisms and the dangerous pathogenic process they cause.
Stages of reorganization
Stage 1: diagnostic.
At this stage, the dentist examines the oral cavity and identifies defects that need to be eliminated. In some situations, the doctor may prescribe an additional examination - tests, x-rays or ultrasound diagnostics to identify hidden problems.
Stage 2: therapeutic.
This stage is always individual. Its duration, intensity and cost depend on the identified pathologies and the choice of method for their elimination. If the condition of the oral cavity is neglected, then sanitization begins with the removal of damaged teeth, “stumps” and restoration of the gums. Next, the doctor follows the individual clinical picture,
Stage 3: preventive.
For the purpose of prevention, the doctor necessarily recommends that the patient undergo professional teeth cleaning, during which all deposits are removed, and then he applies strengthening or protective preparations to the enamel, and carries out whitening if necessary. Sometimes this stage precedes treatment and even diagnosis. This is done to make it easier to identify problems, because carious lesions and other foci of infection may be hidden under a layer of plaque. And professional hygiene reduces the risk of re-infection with caries during treatment.
Remember! You can skip the therapeutic stage if you pay due attention to oral hygiene every day, follow your doctor’s recommendations and give up bad habits. Preventing caries allows you to avoid more serious health problems and save money.
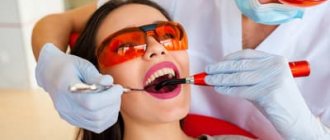
Removing dental plaque
The main goal of this event is to eliminate pathogenic microflora, which is present in large quantities on the teeth and gums in soft and hard plaque and tartar. By the way, once the deposits are removed, the bad breath will go away, and the enamel will acquire a natural shine and tint.
On a note!
Bacterial deposits on teeth and gums appear in all patients without exception throughout life, even in those who regularly perform hygiene procedures.
After all, the process of their accumulation is facilitated by the conditions that exist in the oral cavity: constant humidity and warmth, microparticles of food, consumption of sweets and carbohydrates. Unfortunately, people cannot remove such deposits on their own. But the dentist will do this easily and simply with the help of professional hygiene, an ultrasonic scaler and an Air Flow device. After this procedure, in agreement with the patient, the doctor can strengthen the enamel with fluorine compounds and remineralize it, which will increase its resistance to bacterial attack and improve its structure. The procedures will help restore the integrity of the enamel structure, eliminate the slightest cracks and even caries at the stain stage. They are especially useful if you are considering whitening or braces.
The photo shows professional cleaning of dental plaque.
“Even before treating tooth decay, I recommend that my patients first visit a hygienist and have a professional hygiene done if necessary. This will make it easier to diagnose all foci of carious destruction. Otherwise, they may go unnoticed under a layer of bacterial deposits. In addition, the procedure will make subsequent treatment better and more successful. After all, it significantly reduces the risk of re-infecting a diseased tooth,” explains Antonina Yuryevna Malysheva, a dentist whose experience in dentistry is 11 years.
Sanitation during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a very important period not only for the woman herself, but also for her fetus, so it is better to prepare for such an event in advance. Sanitation of the mouth at the stage of pregnancy planning is a must, because during gestation all calcium and other active substances will be sent to the development and growth of the small organism. Therefore, mom needs to take care of the health of her teeth in advance.
Sanitation of the oral cavity allows not only to treat caries, but also to strengthen tooth enamel, because it bears the main burden. The acid-base balance of saliva changes, the body as a whole undergoes hormonal and metabolic changes, and with vomit during toxicosis, gastric juice gets onto the enamel, which corrodes the enamel. That is why it is important to strengthen your teeth and get rid of all pathologies that increase the risk of developing serious diseases, such as pulpitis or periodontitis.
Important! If conception occurred unplanned, then the woman also needs to undergo sanitation, but here it is important to consult a doctor. Firstly, because in the first trimester there are restrictions on the use of various medications (and some of the drugs used in dental treatment still enter the body with saliva). Secondly, in many women, toxicosis and the gag reflex intensify, which makes it impossible to carry out manipulations in the mouth.
What to expect after anesthesia
Temporary agitation of the child, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting are possible. The anesthesiologist will give detailed recommendations in the post-anesthesia observation room. You need to start drinking and feeding your baby no earlier than 1.5-2 hours after the end of treatment.
What cannot be a consequence of anesthesia?
Anesthesia does not cause diarrhea, fever, cramps, abdominal pain, runny nose, cough, or allergic reactions. If these symptoms occur in your child, you should consult with our pediatrician or anesthesiologist, as always in such situations.
Sanitation before implantation
Installation of a dental implant is a complex surgical procedure involving the implantation of a foreign body into the jawbone. If there is some source of infection in the oral cavity (an area of carious lesions, inflammation in soft tissues, ulcers on the mucous membranes or tartar), then with a high probability this infection will penetrate into the open wound. This can lead not only to implant rejection, but also to more serious consequences - inflammation of bone tissue and even sepsis.
Therefore, before proceeding directly to installing the implant, the orthopedist directs the patient to sanitize the oral cavity in order to minimize risks.
Before surgery
To eliminate the risk of infection during surgical interventions, it is important to undergo sanitation with a dentist before the operation, which is part of the preparatory process. During sanitation, the dentist must examine the patient’s oral cavity to exclude the presence of an inflammatory process in the periodontal tissues and carious lesions. A certificate from a dentist is required before scheduled non-oral surgery, such as ophthalmological, cosmetic, gastroenterological and other operations. This procedure is necessary to prevent infection of other organs. If emergency intervention is required, the patient will not be referred to a dentist.
Sanitation in pediatric dentistry
“Putting things in order” in a child’s mouth is an important detail not only in the prevention of caries. Timely sanitation allows you to quickly identify pathologies in the formation of the jaw or bite, correct them and thereby provide the child with healthy and properly functioning teeth.
As a rule, oral cavity sanitation is carried out in kindergartens and schools. Its technology is no different from that of an adult: after an examination, the doctor identifies problem areas, treats caries and carries out professional teeth cleaning. If a child has teeth that cannot be restored, they are removed.
Interesting! According to a sociological study in schools in Moscow and the Moscow region, almost half of parents of children of primary and secondary school age (48%) take their child to the dentist only when a problem arises, and 4.6% do not take their child to the doctor even if a pathology is detected. A fifth of respondents (21%) believe that it is enough to bring the child for examination once a year. And only 24% of respondents bring their children for preventive care twice a year.
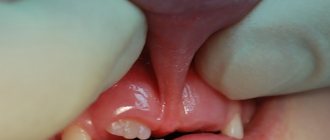
Removal of decayed teeth
Sick, decayed teeth that are not viable are a threat to the health of the entire body. Their porous, heterogeneous surface becomes a source of contamination, infection, bad breath, and problems with the stomach and intestines.
The photo shows a tooth extraction
Sometimes the patient thinks that it is better to keep these, because they are their own, family. But no professional doctor will carry out, for example, implantation or prosthetics without this stage. Preserving such teeth means risking your reputation and the health of the patient. For example, during implantation, bacteria from an infected tooth can migrate into the wound and cause inflammation of the periodontal tissues and implant rejection.
Removing wax plugs
What is wax plug, how does it manifest itself, and what to do if it is present? In the skin lining the external auditory canal there are special glands that secrete a peculiar sticky and thick yellowish-brown content - the so-called sulfur. The formation of this secretion has a protective significance - sulfur prevents dust, dirt and small foreign objects such as grains of sand and other things from entering deep into the ear canal and onto the eardrum. When opening the mouth and moving the jaws during chewing and speaking, the walls of the external auditory canal vibrate, which causes wax to be pushed out and self-cleaning occurs. But in some cases, for example, with excessive formation of sulfur, or with excessive tortuosity and narrowness of the external auditory canal, the sulfur is not completely pushed out, and complete cleansing does not occur. In this case, the remaining sulfur gradually dries out, thickens and sticks together into a dense lump, clogging the external auditory canal. This lump is called sulfur plug.
The formed sulfur plug usually does not appear in any way until the passage is completely closed by it. But as soon as the plug touches the walls of the ear canal (which happens, for example, when it swells from water), symptoms of blockage of the external auditory canal arise - a feeling of ear fullness, decreased hearing, and sometimes painful sensations in the area of the external auditory canal. All this leads to disruption of the functions of the hearing organ, so the wax plug requires mandatory removal. This manipulation is performed only by an ENT doctor. You cannot try to remove the plug yourself - this can lead to complications in the form of injury to the eardrum, even rupture.
The wax plug is removed by an ENT doctor on an outpatient basis by washing the external auditory canal using a special technique. Removal of wax plug is possible in the ENT office of our clinic in Kupchino; the procedure is very simple and takes very little time. Qualified specialists at our clinic will quickly, easily and painlessly perform this procedure for both adult patients and children.
You can make an appointment with an ENT specialist and to remove wax plugs either during a personal visit to the clinic, through the form on our website or by phone.
Home | come back
In what cases is dental treatment performed under anesthesia in adults?
The problem of ordinary fear of the dentist does not require such a radical measure as anesthesia, but can be easily solved with the help of sedation. This is a gentle alternative to general anesthesia, in which the person is half asleep, physically and emotionally relaxed, and also does not retain memories of what happened. By the way, the vast majority of clinics, when offering dental treatment under anesthesia, still mean sedation. However, real “general anesthesia” with loss of consciousness is very often used in modern dental practice.
Meanwhile, the main dental interventions for which general anesthesia may be a better choice than local anesthesia are only complex maxillofacial operations, as well as a number of indications that are worth knowing about:
- allergy to local anesthetics;
- low pain threshold;
- large volume of required treatment;
- developed gag reflex;
- increased fear of dental treatment.