Suspect No. 1 – herpes
- Cause. When pimples appear on the lips, the cause may be the activation of the herpes virus, which occurs under the influence of external factors, for example, hypothermia.
- Emergence. Before the rash appears, swelling and pain occur, then severe itching appears, after which vesicular pimples on the lip “ripen.”
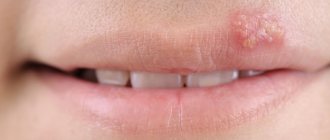
- Localization. Most often, herpes is localized along the edges of the lips or in their corners.
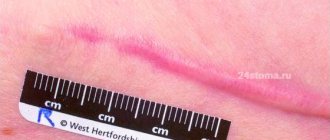
- Appearance. With herpes on the lip, pimples resemble vague blisters with liquid. They do not have a specific shape, they are more like spots.
- Quantity. Multiple rashes.
- Feel. Patients with herpes experience burning and itching.
If pimples on the lip turn out to be a manifestation of herpes, doctors prescribe antiviral drugs. This disease should not be left to chance, because after the bubbles burst, the virus spreads along with the leaked liquid, and a new rash appears.
Pimples on the forehead or chin in women: causes
Why do acne form on the chin in women? The reasons here may also be hidden in hormonal background. The fact is that increased concentrations of androgens can occur not only in adolescents. Clinical studies show that 30% of women with acne have laboratory confirmed absolute hyperandrogenism, i.e. increased production of androgens of ovarian or adrenal origin.
Acne in middle-aged women is most often localized in the chin and cheeks; sometimes women also experience acne on the forehead:
We have already said above that in women, in the period from 2 to 7 days after ovulation, current symptoms of acne may arise or intensify. This is due to peak concentrations of luteinizing hormone, which promotes the transformation of androstenedione into testosterone, and the latter, thanks to enzymes, is already converted into dihydrotestosterone. Therefore, taking into account all the above-mentioned causes of acne in women, a remedy for acne on the face, such as oral contraceptives or antiandrogens, can be used as part of complex therapy.
Another cause of acne in women may be the use of oral contraceptives based on pure progesterone. This is due to the fact that sebocytes (these are the cells of the sebaceous glands that produce fatty secretions) have receptors not only for androgens, but also for progesterone. However, the largest group of adult acne patients (both women and men) do not have an increase in androgen production, but they still have overactive sebaceous glands. What this is connected with - read below.
Other causes of acne in adults -
As we said above, the sebaceous glands have receptors for androgens. The fact is that hyperactivity of the sebaceous glands can occur even with normal concentrations of androgens (if these receptors, due to genetics, have increased sensitivity to androgens). The receptors become more sensitive to androgens due to increased activity of the following enzymes: 17-β GSD, 3-β GSD, and 5 α-reductase. The first 2 enzymes convert dehydroepiandrosterone and androstenedione into free testosterone, and 5 α-reductase further converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (24stoma.ru).
In general, it is precisely due to the increased activity of these enzymes that in men and women there is an increase in the concentration of dihydrotestosterone (even if the level of androgens is normal). It is dihydrotestosterone that is the main and direct hormonal stimulator of the activity of the sebaceous glands. Studies have shown that in patients with acne and pimples, the synthesis of dihydrotestosterone in the sebaceous glands is increased from 2 to 30 times - compared to patients without acne symptoms. And, by the way, one of the markers of increased activity of these enzymes is the presence of androgenic alopecia in the patient (which occurs not only in men).
Suspect No. 2 – acne
- Cause. Acne is a multifactorial disease. The main links in its pathogenesis are hyperkeratosis, excessive sebum production, colonization of propionibacteria, and inflammation. For example, if a small whitehead appears on the lip, a blockage of the sebaceous gland could occur, leading to the formation of a closed comedon.
- Emergence. Acne usually appears suddenly.
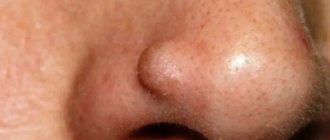
- Localization. With acne, pimples rarely appear on the lip, since there are few sebaceous glands in this area. Most of them are in the so-called seborrheic zone - the nose, forehead, chin, this is where acne occurs most often.
- Spring view. A slight swelling of red color; if a purulent pimple has formed on the lip, then a white head can be seen inside, the acne takes a cone-shaped shape.
- Quantity. Most often they pop out one at a time. In severe cases of acne, they may merge.
- Feel. Papules and pustules may be painful, especially when palpated.
After opening, the acne fades, so many people think that this is a great way to get rid of them, but this approach can lead to aggravation of the problem, an even greater spread of the rash.
Pimples on the lips: causes
Acne on the lip may appear for the following reasons:
- herpes virus;
- blockage of the sebaceous glands;
- stress, psycho-emotional disorders;
- allergic reaction;
- disruptions in the functioning of the facial nerves;
- improper hygiene;
- endocrine disorders;
- eating large amounts of sweets and fatty foods.
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of the appearance of a pimple on your lip, so before you run to the pharmacy for the ointment that you prescribed for yourself, it is better to first visit a specialist and entrust him with drawing up a treatment plan.
How to deal with acne?
Treatment for acne depends on the severity of the disease. It is prescribed exclusively by a specialist. For mild to moderate acne, external therapy is primarily used18. For severe acne, emphasis is placed on systemic treatment18.
Clindovit® is a topical antibiotic that can be prescribed for acne vulgaris6. The main active ingredient in its composition is the antibiotic lincosamide clindamycin6. It fights a wide range of propionibacteria strains6. After contact with the skin, clindamycin quickly accumulates in comedones, exhibiting antimicrobial activity6. Clindovit® gel helps reduce free fatty acids on the skin6.
The drug must be applied twice a day (morning and evening) to previously cleansed and dry skin. The first results from treatment with a topical antibiotic usually become noticeable after 6-8 weeks. It is recommended to combine the use of the drug with the use of benzoyl peroxide or azelaic acid (Azelik® gel)18,28.
Key Factors in Acne Formation –
You probably already realized that overproduction of sebaceous gland secretions is one of the main reasons why acne appears on the face. But this factor is far from the only one. This also includes the process of follicular hyperkeratosis, and in addition, the bacteria Propionibacterium acne (P.acne), which live both on the surface of the skin and subsequently in the ducts of the sebaceous glands, are also important.
- Hyperproduction of sebaceous gland secretions – it is caused by increased production of androgens, as well as increased sensitivity of sebaceous gland receptors to androgens. We have already described this process above, but as it turned out, what is important here is not only that there is an increase in the secretion production of the sebaceous glands. A very important point is the change in the chemical composition of the secretion of the sebaceous glands (sebum). In particular, against the background of increased secretion, there is a decrease in the content of linoleic acid in the sebum.
The function of the latter is to regulate the processes of differentiation and desquamation of follicular and epidermal keratinocytes. The stratum corneum of the epidermis of the skin consists of epidermal keratinocytes, and follicular keratinocytes line the lumen of the hair follicle. A decrease in the content of linoleic acid in sebum causes follicular hyperkeratosis, which is one of the most important factors in the development of acne and pimples (we will talk about follicular hyperkeratosis below).Simultaneously with the decrease in the concentration of linoleic acid, the content of unsaturated fatty acids in the sebum increases (from 5 to 20%). Such acids are comedogenic and also contribute to the development of follicular hyperkeratosis and the onset of inflammation. And lastly, an increase in sebum secretion also leads to the fact that follicular keratinocytes begin to release an inflammatory mediator called IL-1α (interleukin-1α). This mediator also promotes follicular hyperkeratosis and the development of inflammation.
- Follicular hyperkeratosis - the lumen of the hair follicle is covered with layers of follicular keratinocytes of varying degrees of differentiation.
When their cell layers are renewed, a constant process of exfoliation of their surface layer occurs. A low concentration of linoleic acid in sebum leads to: 1) hyperproliferation of follicular keratinocytes, i.e. to a sharp increase in the number of their layers and their thickness, 2) to a disruption in the desquamation of keratinocytes into the lumen of the hair follicle. Follicular hyperkeratosis, together with an increase in sebum production, leads to the formation of fatty plugs (comedones) in the lumen of the follicles, obstruction of the follicles and the onset of the inflammatory process. Moreover, at the first stage, inflammation is not associated with a sharp increase in the number of P. acne bacteria in the lumen of the follicle and its damage, but is associated with the production of interleukin-1α by follicular keratinocytes, as well as with an increase in the concentration of free fatty acids. - The presence and activity of the bacteria "P. acnes" - the bacterium Propionibacterium acnes (and to a lesser extent Staphylococcus epidermidis) - are the main microorganisms that are involved in the formation of acne.
These bacteria are representatives of the normal opportunistic skin flora, which is also present on the skin of people without acne symptoms. For a long time, the importance of these bacteria was underestimated; for example, it was believed that they were only responsible for the development of local inflammation in the hair follicle. However, this bacterium also affects the formation of comedones (blackheads) themselves. In particular, the increase in the content of free unsaturated fatty acids in sebum occurs precisely thanks to the enzymes (lipases) of these bacteria. These enzymes break down di- and tri-glycerides contained in the secretions of the sebaceous glands into free fatty acids. And as we said above, free fatty acids are comedogenic and contribute to follicular hyperkeratosis and the development of inflammation. In addition, the listed bacteria secrete enzymes, which subsequently lead to rupture of the walls of the hair follicle - as a result of which the entire contents of the follicle are poured into the surrounding tissue, which leads to a pronounced local inflammatory reaction.
What factors can aggravate the appearance of acne -
- use of comedogenic cosmetics,
- insufficient cleansing of the skin from water- and fat-soluble contaminants,
- medications (prednisolone, steroid hormones, drugs with lithium, anticonvulsants, iodides and bromides),
- active sweating.
Phototherapy and lasers for acne treatment
Phototherapy and lasers are used to treat acne - either endogenous porphyrins contained in P. acnes, or sources of exogenous porphyrins are additionally applied to the skin before the procedure. Porphyrins have the property of absorbing light in the blue regions of the spectrum (wavelength 415 nm), which leads to the formation of unstable oxygen and, as a result, to the destruction of pathogenic bacteria P.acnes. The FDA recommends Lumenis devices (for example, the IPL module of the M-22 device), which use high-intensity light from the blue part of the spectrum, for the treatment of papulopustular acne, i.e. acne.
Light from the red part of the spectrum can also be useful because... Compared to blue light, it has a stronger anti-inflammatory effect (although it has a lesser effect on porphyrins). Therefore, a combination of light from the blue and red parts of the spectrum will be even more useful. Facial procedures are carried out 2 times a week for 15 minutes. According to the dermatology textbook Fitzpatrick's Dermatology, after a 4-week course of therapy in 80% of patients, the number of acne decreased by 60%. But in the absence of supporting procedures, their number returns to the original level - within 3-6 months.
Photodynamic therapy is even more effective in treating acne. It consists of applying exogenous porphyrins to the skin 1 hour before the procedure (aminolevulinic acid/ALA), after which exposure to a high-power light source occurs. The latter can be pulsed dye lasers, intense pulsed light or a broadband light source in the red part of the spectrum. ALA is metabolized in the sebaceous glands and hair follicle to porphyrins, which when exposed to light lead to the release of unstable oxygen, which damages the sebaceous glands. Several photodynamic therapy treatments can provide improvement for up to 5 months.
Pulsed KTP laser (wavelength 532 nm) - also leads to a reduction in the number of acne by about 40%. Use this laser 2 times a week for 2 weeks (a total of 4 treatments are required). In addition, some of the non-ablative infrared lasers at 1450 nm and 1320 nm wavelengths may also be useful for treating acne. they cause thermal damage to the sebaceous glands. However, any of these lasers requires a course of several treatments (and the improvement lasts up to about 6 months).
One of the newest acne treatment devices is the Isolaz device (from Solta Medical). The nozzle of the device is made in the form of a photo-pneumatic device, which creates negative pressure that sucks out the fatty secretion from the mouths of the hair follicles. Immediately after this, broadband pulsed light (wavelength from 400 to 1200 nm) is turned on, which acts on the P. acnes porphyrins, destroying these bacteria, and also has an anti-inflammatory effect.
What do phototherapy and lasers do?
Regular use in courses not only improves the course of acne, thereby reducing the number of inflammatory elements. The use of phototherapy (IPL) and lasers in courses often avoids the need for oral medications (antibiotics, isotretinoin), as well as the numerous side effects associated with them. But the cost of such treatment is high. We hope that our article on the topic: How to remove acne on your face was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher medical education of the author of the article, 2. Textbook on dermatology “Fitzpatrick's Dermatology” (8th edition), 3. “Modern methods of treatment and rehabilitation of patients with acne vulgaris” (Barinova), 4. “Acne from the position of evidence-based medicine” (Anisimova), 5. “Cellular mechanisms of barrier protective functions of the skin and their disorders in skin diseases” (Medelets).
Prevention
In order not to wonder why acne appears on the chin, you need to take preventive measures in a timely manner. It is based on proper nutrition and care. It is also worth considering the following tips:
- when a red lump appears, do not squeeze, apply ice, apply a targeted ointment;
- do not increase the number of washes - the dermis needs its sebum to maintain hydration and elasticity;
- You need to play sports in breathable light clothing, and take a shower after training;
- It is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air, and to ventilate the premises.
Proper nutrition for acne
Fine:
- Foods rich in dietary fiber and pectin (buckwheat, pearl barley, bran, broccoli, spinach, Brussels sprouts and others).
- Foods high in zinc: liver, beef, seafood.
- Cooking food by steaming and in a slow cooker. This way, more nutrients are retained and a minimum of fat is used.
- Foods rich in vitamin A (fish oil, carrots, corn), B (cheese, cabbage, wheat cereal), E (vegetable oils, green peas, wheat germ, parsley).
Badly:
- roast;
- salty;
- spicy;
- fat;
- sweet;
- monotonous.
The recommendations are obvious and very simple. Therefore, when they ask why there is acne on the chin, doctors first of all find out the diet.
Caring for problem skin
It is recommended to wash with cool water. It is better to use special lotions, foams, micellar, but not soap with a high alkali content. Once a week you can make cleansing masks based on clay, use a scrub or light peeling.
Creams with hyaluronic acid, collagen and urea are suitable for moisturizing. Nutrition is provided by products containing panthenol, vitamins and microelements.
The most effective remedies for acne on the face -
How to remove acne from the face quickly and without complications? The most difficult thing here is to choose the right combination of drugs and draw up a treatment regimen taking into account the specific clinical situation. Below you can see that the approach to treating acne on the face may differ - depending on the predominance of different types of inflammatory elements (papules or pustules), as well as on the severity of the disease. The most effective remedies for acne on the face:
- antibiotics,
- products with benzoyl peroxide,
- topical retinoids,
- oral contraceptives in women,
- phototherapy (IPL), photodynamic therapy and lasers,
- comedones extraction method.
Only a dermatologist or a dermatologist-cosmetologist can professionally treat acne on the face. Unfortunately, in most cases, patients seek consultation with a specialist late, and this leads to complications - the appearance of persistent age spots, as well as superficial atrophic scars. Below you can see a treatment plan for acne, which is based on recommendations from the most famous English-language textbook for dermatologists around the world, Fitzpatrick's Dermatology.
How to get rid of acne on your face (according to Fitzpatrick's Dermatology):
Below we will look at all the types of drugs that are indicated in this scheme, and now you will know for sure which ointment for acne on the face will be the best in your case. Please note that azelaic and salicylic acids are not the main remedy for acne on the face, and can only be used as “second-tier” drugs. You can find out more about them at the link above. At the same link you can learn about the use of oral contraceptives in women.