How to understand that a tooth can be removed
Baby teeth begin to loosen at about 5-7 years of age.
A loose tooth can cause a lot of trouble for a child. The difficulties are mainly related to eating. With a loose tooth, it is difficult to eat solid foods, for example, raw fruits, vegetables, crackers, etc. Sooner or later, the baby tooth will fall out as it is replaced by a permanent tooth. Many people force this process, since a loose baby tooth is a source of discomfort in the oral cavity, which they want to get rid of as soon as possible. But how to pull out a tooth at home, and is it worth doing it yourself? A reasonable solution to this issue is to consult a doctor. But in practice, few people go to dentistry to remove a baby tooth. Therefore, if you decide to remove a child’s tooth yourself, then make sure it can be done.
First, examine the child's oral cavity using artificial light. Make sure there is no swelling in your mouth and your gums are a healthy pink color. Also make sure that the child does not have caries or other dental diseases, chips or cracks. If you find any, consult a doctor and give up the idea of removing them yourself.
The most important condition for removing a baby tooth is its mobility. If it wobbles slightly, then it’s too early to tear it. You can remove it when it is very loose. When you wiggle your fingers, you should be left with the impression that the tooth is being held on by one string. If the range of movements is insufficient, then persuade the child to be patient until the right moment arrives.
Content:
- Are baby teeth pulled out?
- How to remove a baby tooth yourself
- Removal technique
- If teeth are removed too early
- If you had to remove several neighboring units prematurely
- Caring for the child's psyche
Removing children's teeth is an exciting event for both the child and his parents.
All mothers and fathers want the manipulation to be absolutely painless. And it’s better if everything happens at home. But you should not focus on pulling out incisors, canines and molars at home. If there are indications for the removal of a loose baby tooth, but the child does not want or cannot loosen it on his own, he should make an appointment with pediatric dentistry.
Here, thanks to the use of modern topical anesthetics and pain-relieving sprays , surgery takes place without pain and is almost invisible to the baby. While the doctor removes a baby tooth, the little patient calmly watches his favorite cartoon.
Is it appropriate to rush to remove baby teeth?
The baby tooth falls out as it is replaced by a permanent one. When it comes out, the latter puts pressure on the base of the baby tooth, which leads to its loss. This process takes about a week. At the first stage, the ligaments that hold the tooth in the socket become thinner. In most cases, this process is painless. The range of mobility increases day by day until the tooth falls out on its own.
Dentists recommend not to rush into removing baby teeth. You should not interfere with the natural process laid down by evolution. There are four reasons why rushing to remove a baby tooth is not advisable:
- The baby tooth acts as a barrier to oral microorganisms . Thus, it protects soft tissues from bacterial infection. In addition, when removed there is a risk of microorganisms entering the bloodstream.
- Formation of the correct bite . If baby teeth are removed incorrectly, the risk of developing a malocclusion increases. When physiological processes occur in a timely manner (including the appearance of molars), the likelihood of developing a defective bite is reduced. Think about this if you are concerned about how to pull out a baby tooth at home.
- Fear of the dentist . The child will have to go to the dentist in the future. If the removal is accompanied by anxiety and fear, then in the future the child will experience anxiety before visiting the dentist.
- Overgrowth of gums. If the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, this indicates that the process needs additional time. This means that the tissues are not yet ready to replace a baby tooth with a permanent one. As soon as a baby tooth falls out, a permanent tooth immediately appears in its place. And if a baby tooth is removed too early, the gums will overgrow during this time. In this case, the permanent one will have to break through the overgrown gum.
As you can see, the rush to delete is often inappropriate. If you have any doubts about this, consult your doctor.
Indications for removal
The dentist decides whether or not to remove a tooth, adequately assessing the situation in the mouth.
Direct indications are:
- advanced caries that cannot be treated;
- lack of a crown, with roots not suitable for implantation;
- crown fracture exposing the pulp;
- the dental unit is a source of infection, as a result of which complications develop (tonsillitis, periostitis, sinusitis, osteomyelitis of the jaw, abscess and phlegmon of the cheek);
- unsuccessful treatment of periodontitis;
- unerupted or incompletely erupted teeth are the cause of frequent inflammation, damage to nearby tissues and teeth;
- severe mobility with an extreme degree of periodontal damage that cannot be treated;
- purulent periodontitis, which is not relieved by conservative methods;
- crowding of teeth.
Is it possible to remove baby teeth yourself?
In most cases, children cope with this problem themselves when the tooth is sufficiently loose. In this case, there is no need to use excessive force to remove it.
It takes up to 6 days from the moment of loosening to falling out. A loose tooth brings discomfort to the child, preventing him from eating solid food. Therefore, when the tooth is already loose enough, children (or parents) remove it on their own. In other cases, “independent activity” in this matter is inappropriate.
When NOT to do this
There are a number of circumstances under which you should not pull out a child’s tooth at home. Let's look at typical cases when this procedure cannot be done at home:
- Psychological unpreparedness . Children are afraid to take such a step. This should not be treated with disdain. What seems like a trifle to adults is a tragedy to a child. These are emotions and strong experiences from which it is better to protect the child. If you notice that the child does not give in to persuasion, then you should not insist on your own. Moreover, such a procedure cannot be carried out by force.
- Acute and chronic pathologies . If the child has any acute or chronic diseases, then the procedure should be postponed or abandoned altogether. In the presence of other diseases, the removal of a baby tooth sometimes results in the development of serious complications. Only a competent doctor will be able to assess the risks and perform the procedure without complications for the child’s health.
- Hemophilia . This is a rare hereditary disease in which blood clotting is impaired. People with hemophilia are at risk of losing too much blood even from minor injuries. For this reason, a banal tearing procedure leads to large blood losses.
- Increased body temperature . The procedure is undesirable at elevated body temperatures. Even if the cause of such a symptom has not been established, the procedure should be postponed until the temperature returns to normal.
- Infectious pathologies of the oral cavity . We are talking about pathologies such as gingivitis, stomatitis and others. The danger of unauthorized removal in case of an infectious lesion of the oral cavity is the risk of introducing infection into the bloodstream.
- Inflammatory pathologies of the oral cavity . You should postpone tooth extraction if there is swelling or redness of the gums, cheeks and mucous membranes.
- Affected teeth . If the tooth that is to be removed is affected by caries, then this should only be done in a dental setting. Also, self-removal should be avoided if there are cracks or chips in the enamel.
- Painful tooth . This problem should be dealt with by a dentist. Self-removal in this case often leads to complications.
You should also refuse to remove it yourself in cases where you are not confident in your own abilities. If you have never pulled out a baby tooth before, then you should not experiment. During the removal process, something can go wrong and this will lead to undesirable consequences. In this case, it is better to entrust even a very loose baby tooth to a professional who will do this without harming the baby’s health.
Experts' opinion
According to research conducted by Irina Vladimirovna Klimova, Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Department of Pediatric Dentistry at Novosibirsk State Medical University, the Asepta treatment and prophylactic line of products has a pronounced hygienic, anti-inflammatory, and hemostatic effect in periodontal diseases in children and adolescents.
The use of an integrated approach and consistency in the selection of drugs from this line of products has demonstrated an improvement in clinical indicators and confirmed high efficiency in the treatment of periodontal pathology in children of different ages. The proposed treatment regimen using the Asepta therapeutic and prophylactic series of products can be recommended to pediatric dentists in the complex treatment of inflammatory diseases of periodontal tissue in children and adolescents.
How to pull a tooth at home without pain
Proper preparation should be made before beginning the removal procedure. Let's look at the important preparatory steps before this procedure:
- Assess your capabilities . Proceed with the procedure only if you are confident in your abilities. If in doubt, consult a doctor. This also applies to the child. If he has a strong fear of this procedure, then it is better to take him to the doctor.
- Examine the oral cavity . Carefully examine the oral cavity for swelling, redness, as well as carious lesions and other dental diseases. If you find any, consult a doctor and do not do anything on your own.
- Check tooth mobility . Be sure to check how flexible the tooth is. If the amplitude of loosening is insignificant, then postpone the procedure until later. We remind you once again that the tooth should wobble as if it were being held on by a string.
- Prepare your tools . Later we will talk about how you can pull out a tooth at home, and what tools and things you will need for this. Prepare them in advance so that the necessary items are on hand. Prepare a small container for your child to spit into during (or after) the procedure. You should also have an antiseptic on hand.
- Have a conversation with your child . Talk to your child about this first. Tell him that the procedure is painless, so there is nothing to be afraid of. Remember that if the child twitches or acts up during the procedure, there is a high risk of incorrect tooth extraction.
- Feed the baby . After removal, it is not recommended to eat for 2-3 hours. Therefore, it is advisable to feed the child before the removal procedure.
Now let’s look at five ways to pull out a child’s loose tooth.
Method No. 1 - gradual loosening
This is the simplest and most effective way that the child himself can cope with. You don't need any improvised means for this. Gradually loosen the tooth until it falls out.
In this case, it is important to ensure that the child’s hands are clean. So before you start loosening, wash your hands with soap and water.
Method number 2 - solid food to help
Another simple way to quickly pull out a tooth at home without pain. Give your child solid food - juicy apples, dried apples or crackers. Within the first minutes, the child will feel the tooth falling out. The important thing here is not to swallow it.
Method number 3 - removal with thread
An old-fashioned method that has not lost popularity to this day. Wrap the loose tooth with floss and tie the other end to the doorknob. Then sharply pull the door, after which it will “fly out”.
If pulling a tooth with a doorknob sounds archaic to you, you can do this procedure without a door. To do this, simply pull the thread sharply. The important thing here is to pull the thread upward. If you pull to the side, you risk damaging your gums.
Method No. 4 - removal using medical gauze
Pre-moisten the gauze in an antiseptic solution. Then grab the tooth with gauze and slowly rock it. If you see that the tooth is loosening well, then it is better to pull it out in one sharp movement. In this case, removal will be painless.
Method No. 5 – tooth extraction at the dentist
The surest way not to harm your child is to see a dentist. The doctor will examine the oral cavity and take into account all the circumstances. This is the most reliable way from the point of view of the child’s health.
Recommendations after surgery
- Do not eat or drink water for 6-7 hours after surgery;
- reduce physical activity, avoid visiting saunas and swimming pools for 4-5 weeks to prevent the development of bleeding;
- take analgesics to relieve pain in the early period;
- regularly take antibiotics prescribed for a course of 7 days;
- rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution after eating;
- follow a gentle diet, avoid solid and irritating foods;
- stop smoking - nicotine provokes bleeding.
Following the doctor's recommendations reduces wound healing time and prevents the development of complications.
Stopping bleeding after removal
After a baby tooth is removed, there may be some bleeding. It can be stopped by applying turunda from a bandage to the wound. This stops the bleeding within 1-3 minutes.
If the bleeding does not stop within 30 minutes or more, you should consult a doctor. Medical help should also be sought in cases where complications occur. For example, these are swelling and redness of the gums, suppuration, infection, as well as remaining fragments of teeth in the gums.
Main stages
Regardless of the indications, the tooth is removed in several stages:
- examination by a doctor, diagnostic procedures, medical history;
- anesthesia of nearby areas (carried out by injection into the gum of the anesthetic Ultracaine, Ubestezin, or others)
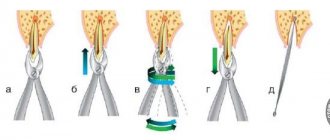
- ligamentotomy (detachment of the tooth itself from the gum);
- application of forceps, their gradual movement to the area under the gum and further fixation;
- tooth dislocation;
- direct removal of the element from the hole;
- inspection and treatment of the hole using antiseptics and other medications;
- suturing (carried out only if there is a large wound surface).
Usually, tooth extraction goes without problems, but in rare cases, some complications of the procedure itself are possible. This may be a root fracture, bleeding, soft tissue injury and other pathologies that are promptly corrected by a doctor.
If we are talking about removing a wisdom tooth that has not yet erupted but is growing incorrectly, then in this case an incision in the gum is necessary to extract it. In such a situation, the wound is quite deep and the gums take a little longer to heal after tooth extraction.
How to keep teeth healthy for adults
Changing teeth occurs only once in a lifetime. Permanent teeth require special care, since once they fall out there will be no new ones. To ensure your teeth last as long as possible, doctors at the Center for Israeli Dentistry recommend adhering to the following rules:
- Visit your dentist twice a year for a checkup.
- Get timely treatment for caries and other dental diseases.
- Brush your teeth twice a day.
- Limit the consumption of sweets - the main factor in the growth of pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity.
And remember that gum and dental diseases are easier to treat in the early stages. Therefore, at the first symptoms, immediately seek help from a doctor.
In what cases is simultaneous implantation indicated?
The main indication for simultaneous dental implantation is the loss of one or more teeth, provided that an important condition is met, namely, maintaining the required volume and strength of the jaw bone.
It is recommended to perform one-stage implantation with preliminary tooth extraction when:
- Traumatization, when part of the tooth is damaged and it is not subject to conservative treatment. As a rule, if you consult a dentist in a timely manner after an injury, the bone tissue does not have time to undergo pathological changes and simultaneous implantation is possible with non-traumatic and painless removal of the injured tooth;
- Advanced stages of caries, in which the inflammatory and destructive process does not affect bone tissue. If conservative methods of caries treatment cannot help the patient (most of the tooth crown is destroyed), then it is best to carefully remove the tooth and perform a one-stage implantation;
- The need to restore the dentition as quickly as possible. Single-stage implantation is considered the operation of choice for patients whose professional or social activities require constant contact with people, and therefore require an appropriate appearance. The efficiency of the procedure is the main advantage of one-stage implantation among other methods of dental restoration;
Tooth extraction followed by implant installation is possible only if several important conditions are met. In addition to the absence of atrophic processes in bone tissue, complete sanitation of the oral cavity and the absence of symptoms of inflammatory gum diseases and other dental pathologies are necessary. Therefore, in addition to delicate and low-traumatic tooth extraction before implantation, it is also important to comprehensively prepare the patient for the intervention in order to obtain the desired result from implantation and minimize possible risks.
Factors determining the choice of tooth extraction technique:
- condition of the tooth (degree and nature of destruction of hard dental tissues);
- features of the anatomical structure and position of the tooth, taking into account its group affiliation;
- features of the anatomical structure of the dentoalveolar segment in the area of the tooth being removed;
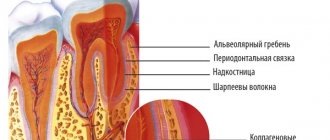
- The condition of the marginal periodontium is the degree of tooth mobility.
The operation of tooth extraction is the most common in the outpatient practice of a dental surgeon. Like any surgical intervention, tooth extraction surgery may be accompanied by complications that arise during the operation:
- Fracture of the tooth or root being removed. It can be associated both with significant tooth destruction and with structural features of the root or surrounding bone tissue.
- Fracture, dislocation and removal of an adjacent tooth occur as a result of using forceps with wider cheeks than the crown of the tooth being removed, or when elevators are used incorrectly, when the elevator rests on the adjacent tooth.
- Damage to the crown of the antagonist tooth occurs when the forceps slip off the tooth being removed.
- Pushing the root into the soft tissue is possible when removing the third lower molar in case of insufficient fixation with the fingers of the left hand.
- Fracture of the mandible is rare. The development of this complication is facilitated by pathological processes in the body of the lower jaw, which reduce its strength (odontogenic osteomyelitis, benign and malignant tumors.)
- Fracture of a section of the alveolar process. May be as a result of a pathological process in the periodontium.
- A fracture of the tubercle of the upper jaw can occur when the upper 8th tooth is removed.
- Dislocation of the lower jaw can occur when the mouth is opened wide and strong pressure is applied to the lower jaw with forceps or an elevator.
- Damage to soft tissue as a result of instrument slipping.
- Perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus can be a result of individual structural features of the upper jaw or due to previous pathological processes in the area of the apex of the tooth root.
- Aspiration of teeth and small instruments. This is facilitated by a decrease in the gag reflex after anesthesia and the position of the patient in a chair with his head thrown back.
Early postoperative complications may also occur. This type of complications includes:
- bleeding, which may be the result of a mechanical injury or a consequence of arterial hypertension or diseases accompanied by dysfunction of the body’s coagulation system;
- alveolar (socket) pain that appears after the cessation of anesthesia in the area of the extracted tooth. This is a natural response to tissue injury;
- alveolitis – a purulent infectious-inflammatory process in the periodontium of an extracted tooth;
- osteomyelitis;
- neuritis of the inferior alveolar nerve.
How long does it take for a wound to heal?
Normally, the wound surface heals in 4-5 weeks. In older patients, healing is delayed due to decreased tissue repair and reduced blood circulation.
The rate of healing depends on the extent of the procedure and the roots. In the case of complex removal of a molar with 3-4 roots, the process of tissue regeneration is delayed up to 20-25 days.
Restoration of gum tissue goes through the following stages:
- in the first days, the wound is closed by a blood clot (thrombus), formed as a result of stopping the bleeding;
- 3-4 days after removal, the thrombus resolves, and new tissue appears on the surface of the wound in the form of a thin film;
- bone tissue forms on the sides of the socket already at 3 weeks;
- after 3-6 months, the hole heals and has no differences with the jaw bone.
The speed of wound healing after removal depends on the characteristics of the body and the age of the patient. If necessary, the doctor corrects the tissue regeneration process with medications and physiotherapeutic methods.