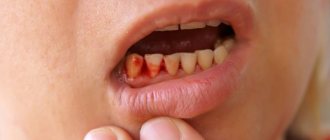
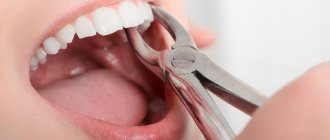
Causes of bleeding Classification How to stop?
Dentist's help Prevention Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure that cannot be performed without damaging tissues and blood vessels. This causes bleeding from the tooth socket. The blood forms a clot that protects the wound from bacteria. Usually, it stops coming out of the wound after a few minutes, but there are cases when bleeding continues for several hours or even days.
Local reasons
- Vascular rupture during traumatic surgery;
- breaking off the root septum or alveoli (socket);
- inflammation in the area of the tooth that was removed;
- the effect of adrenaline (after the narrowing of blood vessels, the second phase begins - their expansion);
- melting of blood clots clogging blood vessels under the influence of purulent secretions;
- local hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels). Occurs from hot food, drinks, rinses or compresses.
Under no circumstances should you apply heat to the wound after extraction!
Thus, the occurrence of bleeding can be provoked not only by a doctor’s error, but also by the patient’s actions.
Efficiency. Professionalism. Mercy
At yesterday's first aid courses, conducted by the Tyumen Emergency Medical Service, there were at least ten people. The courses are free. Everyone listened with interest to emergency doctor Andrei Rogotnev.
Useful tips based on practical experience
It is immediately worth noting that there is a lot of information on first aid on the Internet. The courses conducted by emergency doctors in Tyumen are valuable because the training is based on practical experience. Let's give a simple example. How long do you think it is possible to clamp an artery on the thigh or shoulder? Many will answer that no more than 1.5 hours. In fact, this recommendation has long been outdated, because after an hour and a half of compression, the blood below the tourniquet will clot in all vessels, and the limb will then have to be amputated. We are not at war, and we not only need to save a person’s life, but also try to save an injured arm or leg. However, first things first.
We find out where the blood is coming from - from a vein or from an artery
Before giving useful tips and recommendations for stopping bleeding, Andrei Rogotnev reminded that bleeding can be venous and arterial. We did not consider ordinary cuts, since they are not life-threatening. In venous bleeding, the blood comes from a vein; in arterial bleeding, the blood comes from an artery. It's generally simple. It is much more difficult for people far from anatomy and medicine to distinguish one bleeding from another. Meanwhile, it is important to understand this before you start saving a person. In fact, everything is simple here: blood from the artery flows like a fountain, but not in a continuous flow, but pulsates in time with the heartbeat, since blood from the heart enters all organs through the arteries. The blood flows back through the veins, so during venous bleeding there is no such pressure, the blood flows in a continuous stream, like water from a tap.
In case of arterial bleeding, you have no more than 3-8 minutes left
With arterial bleeding, the probability of death is greatest; with venous bleeding, death is unlikely; damage to large veins in the neck is dangerous. In case of bleeding from large arteries, those around you have no more than 3-8 minutes left. In such a short period of time, the ambulance will not have time to get there. Therefore, we drive away all fears, put plastic bags or rubber gloves on our hands if they happen to be nearby (so that in case something happens we don’t catch dangerous viruses), and look for points on the body to press the arteries with fingers. There are more than 10 such points on the body at which pulsation is felt on each side of the vertical axis of the body. We need to remember only three main ones: the carotid, brachial and inguinal arteries.
How to clamp the carotid artery
The carotid artery in the neck is to the right and left of the trachea. The pulse is clearly felt in this place. We feel and pinch this artery below the wound with our fingers. We compress the artery until the blood stops gushing out. If this happens, you did everything right. Do not under any circumstances reduce the pressure or remove your hand; the artery will be more difficult to find later.
And only after you have managed to stop the bleeding, Andrei Rogotnev advises you to do everything else: scream, call for help, ask passers-by to call an ambulance. If it is not possible to squeeze the artery with your fingers, you can secure a bandage (tourniquet, belt or piece of fabric) through the arm opposite to the wound. Thus, the artery will be compressed only on the side where the wound is. The most correct option is to compress the carotid artery until the ambulance arrives.
How to compress the brachial artery
We do the same with the brachial artery. The shoulder is the part of the arm from the elbow to the shoulder joint. Press your thumb against the inside of your shoulder to the bone and you will feel a pulsation. This is where you need to pinch the artery, clasping your hand with your thumb and forefinger until you find something to tighten it with. Motorists have a tourniquet in their first aid kit; in all other cases, you can use any available means - a shoe lace, a belt, a charger wire, etc.
How to clamp an abdominal artery
Bleeding from the abdominal artery (internal bleeding) can be stopped by pressing your fist on the abdomen in the navel area. You need to apply pressure towards the spine until the bleeding stops or decreases. Signs of internal bleeding: the person is pale and has a rapid heartbeat.
How to clamp the femoral artery
To stop arterial bleeding when the lower limb is damaged, you need to squeeze the inguinal fold between the thigh and lower abdomen with your fist. Here is another point of pressure on the artery.
The points for applying a tourniquet for injured limbs are the middle of the thigh or shoulder
If a limb is damaged, the artery should be pressed with a tourniquet above the wound. The points for applying the tourniquet are the middle of the thigh and shoulder. There is no point in applying a tourniquet to the lower leg or forearm (from the hand to the elbow), since here the arteries pass between two bones and stopping the bleeding is not guaranteed; significant force will need to be applied, which can damage the tissue.
If you are somewhere far from a populated area - in the forest or on the road - you should clamp the artery with a tourniquet for no more than 15 minutes. No more, otherwise a person risks losing an arm or leg. After 15 minutes, the tourniquet must be loosened without removing the last two rounds (turns of the tourniquet). We rest for the same amount of time as we walked, then tighten the tourniquet again and walk or drive further - to where we will receive medical assistance.
How hard should you squeeze the tourniquet?
Many people have a question: with what force should the artery be clamped with a tourniquet? We tighten the tourniquet until the bleeding stops, then fix it. It's better to try it yourself. The force should be minimal, as when squeezing with a tonometer cuff.
What to use instead of a tourniquet
Instead of a tourniquet, you can use fabric (scarf, shirt sleeve, trouser leg) or lace or bandage, with which you can make a “twist”. We wrap the bandage around the limb twice, tie a knot, but do not press it tightly to the hand, leaving a distance the size of a finger. Then insert a key, a pen or any stick and begin twisting until the bleeding stops.
Well, that’s actually all you need to know about stopping arterial bleeding. The main thing is not to faint at the sight of blood. Of course, you need to be mentally prepared for such situations in advance.
It is much easier to stop bleeding from a vein when the limbs are injured
With venous bleeding everything is much simpler. As soon as we understand that blood is running from the vein, we clamp the wound with a tight bandage, just as ordinary wounds are bandaged. The bleeding must stop.
If the tension of the tourniquet is weak, the blood flow from the vein will only increase
There are situations when people cannot understand whether blood is flowing from a vein or from an artery. At the same time they are trying to help. It should be remembered that when a tourniquet is applied, the bleeding should stop. If the tourniquet is loosely secured, the blood flow from the vein will only increase.
Yuri Shestak, Medical Information Agency NEDUGAMNET
Common reasons
The most common of them is a sharp rise in blood pressure as a result of a hypertensive crisis, excessive physical activity, and thermal procedures (bath, sauna, hot bath).
In second place are diseases that affect blood clotting: hemophilia, leukemia, hemorrhagic diseases.
Profuse bleeding occurs with unrecognized vascular tumors (hemangiomas). Therefore, it is important to conduct an X-ray examination, which shows such changes.
Taking anticoagulants can also provoke socket bleeding after removal.
Why might my nose bleed?
Nosebleeds are classified into “anterior” and “posterior.” In the first case, the cause is damage to small blood vessels, this type is usually easy to stop. The second case is considered more dangerous; bleeding occurs due to injury to large vessels located deeper in the nose, so it cannot be dealt with at home. If the blood is “spouting”, this is a reason to urgently call an ambulance.
Causes of nosebleeds include:
- nasal injuries;
- thinning of the mucous membrane;
- inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity;
- fragility of blood vessels, heart and blood diseases;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications (anticoagulants, NSAIDs, vasoconstrictor drops for the common cold).
Classification of bleeding
Bleeding is divided into primary, which begins immediately after surgery, and secondary, when bleeding begins after some time.
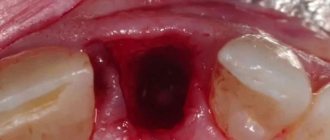
The intensity of bleeding is determined depending on how much the hole bleeds after removal:
1st degree
– blood flows
for 20-30 minutes
, saturates the tampons and colors the saliva.
2nd degree
– bleeding continues for more than 40 minutes, blood and saliva mix intensively.
3rd degree
– the bleeding does not stop for more than an hour, the patient spits blood.
With prolonged bleeding, the patient's general condition worsens. Weakness, dizziness appear, and the skin turns pale. Blood pressure drops, the heart begins to beat less frequently. In case of bleeding, dentists advise not to delay a visit to the doctor so that he can take measures to stop the bleeding and prevent the condition from worsening.
What to do if your nose bleeds?
When bleeding begins, it is important to try not to be nervous, as nervousness causes our heart to beat faster, which leads to more blood loss.
The algorithm for stopping bleeding is as follows:
- Sit up straight, tilt your head forward.
- You should be comfortable: loosen your belt and collar, open the window if necessary.
- Apply a cold, wet towel or ice to your nose and place a warm heating pad on your feet. This will help narrow the blood vessels in your nose and widen them in your legs, which will reduce bleeding.
- Pinch the bleeding vessel: squeeze the wings of the nose with your fingers for 3-5 minutes, the bleeding should stop. Also for this purpose, you can insert a gauze swab pre-moistened in hydrogen peroxide into the nostril.
If you have completed all of the above points and the blood continues to flow, call an ambulance immediately, because even a small loss of blood can lead to fainting.
What should you remember when you have a nosebleed?
- Do not lie down or let your legs be higher than your head - this will increase bleeding;
- Do not throw your head back: a large amount of blood entering the stomach can cause vomiting, in addition, blood can flow into the windpipe and make breathing difficult.
- Once the bleeding has stopped, avoid eating or drinking caffeinated drinks to avoid increased blood pressure and further bleeding.
Preventing nosebleeds
Remember, frequent nosebleeds are a reason to consult a doctor. The specialist will identify the cause of the problem and prescribe treatment, which may include the use of hemostatic agents, as well as medications that improve blood circulation.
To prevent rebleeding, a specialist may recommend:
- Taking medications and vitamins to strengthen blood vessels.
- Proper diet. Adding foods rich in vitamin K and C to the menu. Vitamin K is responsible for blood clotting; parsley, spinach, basil, bananas, avocados, broccoli, bran, etc. are rich in it. Vitamin C strengthens the walls of blood vessels, it is found in large quantities in rose hips, sweet peppers, currants, citrus fruits, etc.
- Activity and moderate physical activity: light exercise in the morning, daily walks in the fresh air, visiting the pool, etc.
Be healthy!
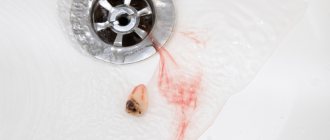
How to stop bleeding from a socket after tooth extraction
After the tooth is removed, the dental surgeon cleans the wound and applies a sterile swab. The patient is asked to tightly clamp the tampon with his teeth and hold it for about half an hour. If the tampon quickly becomes saturated with blood, it should be changed.
If the bleeding does not stop after 20-30 minutes
, the dry swab is replaced with one moistened with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
A cold compress can be used to constrict blood vessels. Ice is applied to the cheek, after wrapping it in a towel so as not to freeze the skin. Keep the compress for 10-15 minutes
, then take a break and repeat the procedure.
After surgery, the dentist recommends painkillers. You should follow these recommendations to avoid accidentally taking a product containing aspirin, which thins the blood and can cause bleeding.
If after all the manipulations there is still bleeding from the tooth socket, you need to contact a dental clinic.
Treatment
For treatment of this condition to be effective, the causes of the disease must be determined. It is very important to promptly identify and treat the main disorders - liver pathologies or oncological lesions.
Additional therapy methods include:
- injection of vitamin K;
- drugs to improve clotting;
- transfusion of frozen blood plasma;
- Other medications include hydroxyurea and oprelvekin, which help eliminate platelet problems.
The patient's diet should include foods high in calcium, folic acid, vikasol, and amino acids.
These include dairy products: cheese, cottage cheese, kefir. Fish and meat will also help eliminate the symptoms of pathology. It is equally important to eat leafy vegetables - green onions, spinach, cabbage.
What does a dentist do?
First of all, the doctor will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis. In accordance with it, the dentist will carry out treatment.
First aid is to stop blood loss. To do this, local anesthesia is performed, blood clots are removed, the wound is dried and the place where the blood is coming from is determined.
Methods to stop alveolar bleeding depend on its cause and location:
- if there is a rupture of the gums or mucous membrane, they are sutured;
- a ligature (a special thread for ligating blood vessels) is applied to the bleeding vessel;
- If there is bleeding from the alveoli (socket), a tampon of iodoform gauze is placed on it. It is left in the wound for several days.
Tamponation is used as a prophylactic measure if there is a risk of bleeding. The tampon is left in the hole for several days. Then they take it out and see how well the wound has healed.
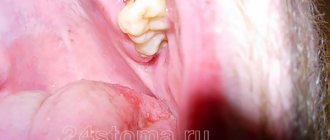
Removing wisdom teeth is potentially dangerous. Such operations are often difficult. Sometimes you have to cut the gum, saw the roots or the tooth itself and remove it piece by piece. Bleeding after such complex operations occurs more often than after ordinary ones.
Measures taken when a hole bleeds after wisdom tooth removal are the same as after regular removal. If there is a history of blood diseases, preparations are made for such an operation in advance. A blood test is carried out, in some cases calcium chloride injections and vitamin C
and
K.
_
If the cause of alveolar bleeding is systemic diseases, general hemostatic agents are used (calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, aminocaproic acid, dicinone, vikasol).
For hypertension, antihypertensive therapy is prescribed. After the pressure normalizes, the bleeding usually stops.
When to seek medical help as soon as possible
Here are some signs of a Bleeding Cuts or Wounds wound that should be seen by a doctor. In some cases, your life may depend on it. Don't hesitate.
- The cut looks deep, bleeds a lot, and you can't stop the bleeding within 10 minutes. There are no options: either urgently go to the emergency room or call an ambulance.
- The wound can be described as “gaping.” The cut is deep and wide enough or has jagged edges.
- A deep cut is located on the face. Even if it is safe, if stitches are not applied in time, it may leave an unaesthetic scar.
- You have been bitten by an animal or person. If you are bitten by a pet and the scratch is minor, most likely there will be no trouble. But if we are talking about a bite from an unfamiliar animal, it is better to see a doctor. Rabies, once symptoms appear, is incurable by Rabies and 100% fatal. But if you get vaccinated in time, death can be avoided.
- You got a scratch or cut on the street, dirt got into the wound with it, and you don't have a tetanus shot. Or there is a vaccination, but more than 10 years have passed since the vaccination. Tetanus pathogens enter the wound along with dirt. The prognosis is more favorable than with rabies: in the absence of timely treatment, up to 80% of patients die, and not all 100%. But whether you will be lucky is another question.
- The wound was caused by a nail. Especially rusty Deep Cut First Aid. Such puncture wounds are the most dangerous in terms of tetanus.
- Signs of infection appeared. Reddened hot skin, swelling, purulent discharge from the wound, increased temperature, red stripes under the skin in the area of the cut - all this indicates an infection. There is a chance that the body will cope on its own. If not, you are at risk of blood poisoning. It's lethal, if anything.
However, no matter what the cut is - dangerous or safe - first aid begins with the same step. You must stop the bleeding. Well, or at least try to do it.
What is the main danger of capillary bleeding?
First aid for capillary bleeding should not be called an unnecessary procedure. Compared to arterial and venous bleeding, capillary bleeding is not so dangerous, and in most cases the body copes with it on its own. But there are situations that are life-threatening:
- the skin is extensively damaged;
- the ambient temperature is increased;
- blood clotting is impaired;
- There is blood poisoning, oncology, hepatitis, arterial hypertension and other severe pathologies.
The most dangerous is bleeding as a result of damage to the blood vessels of internal organs. Prolonged bleeding provokes a decrease in blood pressure, oxygen starvation, and disruption of the cardiovascular system. If the blood loss is severe, the person dies without treatment. Hemorrhage in the brain affects important centers and also leads to a fatal outcome. Pleural bleeding disrupts breathing and puts pressure on the lung. In most cases, it is important to react in time to manifestations of capillary bleeding and provide first aid in a timely manner.
Walk, lie down and wet yourself
— What should be done to maintain the health of the veins and not lead to thrombosis?
— Thrombosis of the lower extremities has a huge number of causes and triggers, starting from cancer and cardiovascular diseases, ending with smoking, high cholesterol, obesity and even hypothermia.
There are factors that we cannot change. For example, gender: men are approximately twice as likely to suffer from deep vein thrombosis. On the other hand, women are three to four times more likely to have chronic venous diseases (varicose veins, post-thrombotic disease, phlebopathy). This is primarily due to hormonal levels and reproductive function - the hormone estrogen can reduce the tone of the venous wall.
In addition, women have periods in life when intra-abdominal pressure is elevated for nine months. The more pregnancies and births, the higher the risk of chronic diseases and venous thrombosis.
Phlebologist Alexey Petrikov.
Altapress.ru.
There is also a hereditary factor, which is perhaps one of the main ones. A feature of connective tissue, mutations, unfortunately, are passed on from parents to children. If blood relatives experienced episodes of thrombosis at a young age, then the likelihood of development in their descendants is high. In this case, it is necessary to engage in prevention as early as possible.
However, many risk factors are modifiable. Firstly, an active lifestyle is necessary. Any movement prevents blood stagnation and forces the venous system to be in good shape. 70-80% of the blood from the lower extremities is “pumped” by the calf muscles - this is the so-called “muscular-venous pump”.
A contrast shower is useful. Yes, the same one that was practiced in Soviet kindergartens. You just need to do it correctly: in a circular motion from bottom to top, alternating cool and warm water as tolerated.
It is quite possible to combat physical inactivity and excess body weight to reduce the risks of thrombosis. And also monitor intra-abdominal pressure: constipation and irritable bowel syndrome often lead to vein pathology.
Diet. Losing weight.
CC0
Of course, it’s worth mentioning high heels. A heel height of five to seven centimeters is considered physiological. You cannot constantly walk at a “height” of 10–15 cm. The ankle joint is also an additional blood pump; in a deformed, unnatural state it does not work.
Next, inflammation occurs, the venous valve is damaged, the pressure in the veins increases, and there is practically no muscular frame to restrain it, so the veins expand and unsightly varicose nodes appear, which are visible to the naked eye.
By the way, only humans suffer from varicose veins and no one else in nature. If you feel heaviness and swelling after a working day, you can throw your legs on the back of the sofa and lie there for 30-40 minutes: the blood will flow towards the heart by gravity. If a person is lying down, then in this position the pressure in the venous bed tends to zero. For comparison, in a standing position it is 90-100 mm of water column.
Women's legs.
fishki.net.
— That is, by running, we increase the risk of varicose veins, and while lying down, we increase the risk of thrombosis.
- That's not entirely true. Brief and short-term body positioning does not particularly affect these situations. The development of both chronic venous diseases and acute conditions is influenced by a complex of risk factors that act continuously or for a long time. An additional provoking factor can often be significant in terms of the development of thrombosis or thromboembolism. Of course, we need a golden mean.
At the same time, you need to understand that if you detect any of the symptoms that we talked about at the beginning, you need to contact a specialist. Often patients come to us with trophic ulcers who require surgery. Many are afraid of it and are treated with folk remedies, aggravating the situation.
Who is Alexey Petrikov
Doctor of Medical Sciences in the following specialties: surgery, hematology and blood transfusion.
Doctor of the highest qualification category in the following specialties: surgery and cardiovascular surgery. Professor of the Department of Faculty Surgery with a course of additional professional education at Altai State Medical University, Associate Professor of the Higher Attestation Commission. Author of more than 200 published scientific works, three monographs, seven teaching aids, one patent for an invention.
Member of the Executive Council of the Association of Phlebologists of Russia, member of the Russian Society of Surgeons, member of the Association of Cardiovascular Surgeons of Russia. Russian expert in the field of vascular pathology of various locations. Co-author of national clinical guidelines on acute and chronic venous diseases.