The procedure for removing the upper teeth can be carried out planned or emergency. In the first case, the indications are: significant or complete destruction of the supragingival part of the tooth and the inability to use it for prosthetics, chronic periodontitis that cannot be treated conservatively, periodontal diseases with tooth mobility of the third degree, and others.
Urgent removal of the upper tooth is required for purulent periodontitis, periostitis, acute osteomyelitis, lymphadenitis (if the tooth is the source of the disease), sinusitis, deep fracture of the crown exposing the pulp, as well as some other conditions and diseases.
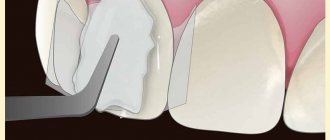
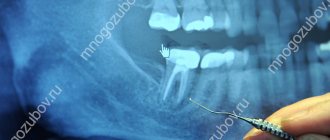
Before the operation to remove the upper tooth, an examination is carried out and, if necessary, an x-ray is taken. As a rule, the operation is done under local anesthesia. Before surgery, the dentist thoroughly cleans the teeth and mucous membranes to prevent infection of the socket.
Depending on the type of tooth, the doctor uses various devices:
- removal of the front teeth (incisors and canines) is carried out using straight forceps;
- for extraction of premolars you need bayonet-shaped and S-shaped forceps, a straight elevator;
- large molars are removed using coronal S-shaped forceps equipped with spikes.
In some cases, it is necessary to saw the tooth into pieces or cut out part of the bone tissue. This mainly applies not to the removal of front teeth, but to the extraction of molars (especially wisdom teeth).
What instruments are used to remove teeth?
Dental forceps have been and remain tools for removing teeth. For certain groups of teeth, a different type of forceps is used, since our teeth have different structures and are located differently in the dentition. For example, to remove the upper anterior tooth and the maxillary canine, there are straight forceps, and the remaining upper teeth are removed using S-shaped ones. The incisors of the lower jaw are pulled out using forceps curved at 90º with narrow cheeks (the part of the forceps that grasps the crown or root of the tooth being removed). The fangs and the two teeth following them are pulled with forceps, on the contrary, with wide cheeks. To remove large molars of the lower jaw, forceps with spikes that go between the roots are used.
Lower and upper teeth
Teeth consist of 3 parts: crown, neck and root. Their tissues are enamel, dentin, pulp. The teeth of the upper and lower jaws are mirrored. This limits the similarity between the organs of the upper and lower jaw.
The characteristic features of the lower teeth are as follows:
- The lower jaw bone around the teeth being removed is denser
- Diseases develop more often. The reason is the settling of more food debris.
- The frontal incisors are smaller and weaker than the upper ones.
The small and large molars (premolars and molars) have smaller roots than the upper ones. All of the above explains why the removal of lower teeth occurs more often and more difficult than the upper ones.
What is the typical tooth extraction process like?
When teeth are removed, local anesthesia is first administered. The doctor then removes about half a centimeter of gum tissue from the tooth. Then forceps are applied to the crown of the tooth being removed. When removing teeth in the upper jaw, the doctor presses on the forceps with his entire right hand. When removing teeth on the lower jaw, pressure is applied with the thumb of the right hand. The tooth is then dislocated to destroy the tissue that holds it in place. To remove single-rooted teeth, such as front teeth, rotational or pendulum-like movements are performed. When removing molars, pendulum-like movements are performed. The culmination of this action is the tooth extracted from the hole.
Indications and contraindications
Diagnosed factors that determine the feasibility of the procedure include:
- Exposing the area of nerve endings;
- Formation of a carious cavity dangerously close to the root canals;
- Deviations in the anatomical structure of the elements of the dentition;
- Increased abrasion of tooth enamel;
- Development of inflammatory processes in adjacent tissues;
- Mechanical damage provoking necrotic processes;
- Hypertrophy of the pulp chamber.
Within the framework of orthopedic practice, devitalization is used only in cases where other therapeutic treatment methods do not allow achieving a positive result. In this case, the limiting factors relevant for any surgical intervention are taken into account, which include:
- Acute form of leukemia and the presence of oncological tumors;
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- Intolerance to anesthetic drugs;
- Stomatitis, which is in an acute phase of development;
- Mental disorders, bad habits, etc.
The final decision to perform an operation is made based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis carried out in a clinical setting.
How is a complex tooth extraction performed?
Complex wisdom tooth extraction is considered to be a case when the tooth cannot be removed with the simple application of forceps. As a rule, in such situations, access to the root of the tooth being removed is first created by cutting the mucous membrane and periosteum. Complex tooth extraction with an oblique or horizontal position is carried out in parts, for which a laser or a special saw is often used. You should not be afraid of this, since cutting a hard-to-reach tooth only shortens the time of its removal. After the procedure, the doctor smoothes the sharp edges of the bone wound, washes it with hydrogen peroxide or furatsilin, the mucoperiosteal flap is placed in place and fixed with sutures.
In complex cases, tooth extraction surgery does not have a uniform technique. How the doctor will act depends on the specific case.
Indications for care after removal of the upper tooth
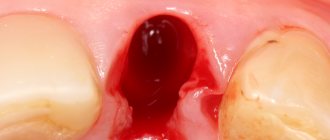
- After removing a front tooth or root tooth, the doctor places a gauze swab into the hole, the purpose of which is to create compression and block small capillaries. This is necessary to stop bleeding. You can keep the tampon in your mouth for no more than half an hour. If it remains in the hole longer, the wound may become infected.
- The blood clot (thrombus) that forms in the hole should not be touched with the tongue, toothpick, hands, or try to rinse it out of the mouth. The blood clot protects the wound from penetration of microbes and promotes its healing.
- For two to three hours after the removal of the upper teeth, you should not eat or drink, so as not to infect the socket. Within three hours, the blood clot will be completely formed, then the likelihood of food getting into the hole will be negligible.
- For several days after surgery, you should refrain from spicy foods and hot drinks.
- On the day of removal of the upper tooth, it is not recommended to perform any hygienic manipulations in the oral cavity. You can brush your teeth the next morning, but avoid the surgical area. In the future, you can return to normal dental care.
We also advise you to read the article about the removal of upper wisdom teeth
When is complex tooth extraction indicated?
Tooth extraction is considered difficult due to tumor or edema, periodontitis, periodontitis, abscess and gumboil. The presence of a cyst and a fistulous tract in the tooth also complicates the removal procedure. Impacted (unerupted) teeth are also indications for surgical tooth extraction. Complex cases include the removal of a dystopic wisdom tooth located outside the dentition; removal of 4 teeth to correct malocclusion; removal of baby teeth in children at an early age. Severe curvature of the roots and fracture of the apical part of the root are also indications for surgery. Please note that complex tooth extraction is not performed during pregnancy.
The method in which your tooth will be removed depends on the individual case. Only a specialist can determine the removal strategy. In any case, you should not be afraid of this procedure. A competent doctor will perform the removal correctly, and all you have to do is say “thank you”
Contraindications for removal
Extraction of teeth is undesirable, so dentists recommend saving every tooth. If removal is inevitable, then you need to know that this procedure is not carried out in the following cases:
- viral infections and fever;
- exacerbation of cardiovascular diseases;
- stomatitis;
- pregnancy in the last month.
Critical days in women are a relative contraindication. If the removal of the lower teeth is supposed to be done under anesthesia, the following is added to the above: pathologies of the endocrine system, epilepsy, heart failure, old age, pregnancy.
Result of prosthetics
To restore the aesthetics of the front teeth, 3 visits to the clinic were required (1- consultation with a dentist and periodontist, 2- cleaning and preparation of teeth, 3- securing a bridge). Within 7 days all work was completed. For the bridge prosthesis, the Sculpture FiberKor ceromer was used. The cost of the entire range of dental services was 40,950 rubles. The result is a great-looking smile.
Dental treatment at Dial-Dent means precise planning of the number and duration of visits, as well as drawing up an estimate for treatment, indicating the cost of each stage of work, and appointments at the appointed time. This approach makes treatment convenient for patients with busy work schedules, as it allows them to clearly plan their time and finances. A special feature of Family Dentistry is the solution of complex cases using the most advanced technologies in dentistry, the availability of the necessary diagnostic equipment and various specialists in one clinic.
See other examples of treatment, implantation and dental prosthetics at Dial-Dent here.
Make an appointment for a consultation by phone +7-499-110-18-04 or through the form on the website. You can ask questions about dental treatment and prosthetics to the chief doctor of the clinic, Sergei Vladimirovich Tsukor, at
Dentist consultation
The orthopedic dentist conducted an examination, found out the reasons why the front tooth was removed, listened to the patient’s wishes, and assessed the condition of the adjacent teeth and the entire oral cavity. Since the front tooth was removed because it was loose, a panoramic photo of the teeth was taken to assess the condition of the roots and do everything to prevent further tooth loss.
Tooth loss may be associated with periodontal conditions or the presence of certain diseases, such as diabetes. The patient consulted a periodontist at Dial-Dent about tooth loss and received the necessary recommendations.
Preparation and planning of prosthetics
The option for urgent tooth restoration, which the patient saw on the website, is to install a fixed bridge prosthesis secured with a composite material to the adjacent teeth (more details about this work here). The disadvantage of this design is the lack of physiological pressure on the jaw bone during chewing load, as well as additional load on the supporting teeth. However, the undoubted advantage of this method is the speed of restoration of aesthetics, so this method is suitable as temporary prosthetics.
A large amount of dark plaque is visible on the teeth, which spoils the appearance of the teeth and does not allow one to determine their natural color. The patient underwent professional teeth cleaning with Air Flow (hygienist E.P. Smirnova), which significantly changed the appearance of the teeth, making them lighter by removing old plaque. Professional cleaning also improved the condition of the gums, as accumulated hard plaque and tartar in the cervical area of the teeth led to bleeding gums and bad breath.
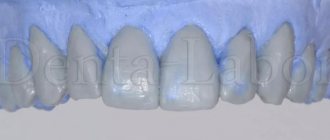
After brushing the teeth, a diagnostic model was created. To secure the bridge, the orthopedic dentist tried to minimally grind the adjacent teeth in order to keep them alive. In this case, the prosthesis must hold securely. The turning depth was determined together with the dental technician using a diagnostic model.
After careful calculations, grinding is carried out on living teeth. After grinding the supporting teeth, a model was made for the manufacture of a bridge prosthesis on inlays in the Dial-Dent dental laboratory.
As a result of careful preparation and calculations, the teeth remained alive and the strength of the structure was ensured. Two models side by side show how the idea came to life.
The color of the denture was carefully selected.
The presence of our own dental laboratory significantly reduces the production time of dentures and increases their convenience, since in difficult cases the dental technician, together with the prosthetist and the patient, participates in the planning of denture structures.
A bridge prosthesis is a ceramic tooth with an imitation of a gum area, and lateral protrusions - inlays in the supporting teeth, thanks to which it is fixed.
The denture is made on a model, which ensures high precision and comfort.
The bridge is fixed on the inside of the teeth.
This option for restoring a lost front tooth allowed the patient to quickly return to work, maintaining the appearance of the teeth in an aesthetic condition. The prosthesis is firmly attached enough that you can eat almost any food without fear (it is not recommended to chew nuts and crackers).
The patient is consulted about possible methods of restoring the front tooth.
In the absence of one tooth, one of the best methods is dental implantation, which is carried out at the Family Dentistry by an experienced implant surgeon V.P. Alaverdov. using the most reliable implant systems. It is recommended to install a completely ceramic dental crown on an implant. All-ceramic crowns have enhanced aesthetic characteristics, which is very important for prosthetic teeth in the anterior region. A plan for dental implantation and implant prosthetics was drawn up, the required number of visits and their duration were outlined, so that the patient could plan his visits to the clinic in accordance with the work schedule.
General overview
The status of the operation is determined by concomitant factors identified during the preliminary diagnosis of the condition of the dentofacial apparatus. Complex tooth extraction is a formulation used in the following situations:
- Separation of root sections, characterized by a curved multidirectional position of the processes;
- Finding a problematic unit in a structure affected by pathological processes;
- The absence of the entire crown, which precludes fixation of the element using forceps;
- The presence of a filling material capable of deformation;
- Identification of impacted and dystopic elements;
- Difficult wisdom tooth removal.
The listed conditions are characterized by conditions under which the use of a standard protocol does not provide the required result. In addition, it is important to take into account the features of the anatomical structure of the jaw, determined by the specific development, as well as congenital anomalies.
Destruction of bone structures
The supporting alveolar bone contains a spongy substance that absorbs the chewing load. If at least one tooth is missing, this load changes. Remodeling begins in the bone: its structure, shape, and volume change. In order for it to remain dense and not deform, it needs a constant load that will stimulate it. With edentia, the bone becomes less dense. The alveolar process (or the alveolar part in edentulous lower dentition) becomes narrower. The next stage of destruction is when the bone gradually loses height. Without prosthetics, it decreases by 4 mm in just a year. The width is also reduced - by 25% of the original per year. This process does not stop: if implantation is not performed, destruction will continue. Installing a bridge can only partially solve this problem. This design transmits the chewing load, which is absorbed by the surface layer of bone tissue. The deeper layers remain without constant stimulation. Because of this, blood supply deteriorates and the volume of bone tissue decreases.
When even one tooth is lost, the alveolar bone is rebuilt and resorbed. In place of the hole, a narrow ridge is formed, running along its center. The formation of this ridge complicates prosthetics. When using a removable denture, it rests on the ridge and injures the overlying gum tissue.
Another consequence of bone loss is an increased risk of injury. It especially increases for the lower jaw. With a significant decrease in the volume of bone tissue, there is a possibility of a fracture in this area, even with minor injuries.
It is not only the alveolar bone that suffers from the lack of chewing load. Over time, destruction begins to occur in the main jaw bone. This process occurs faster in the posterior parts of the lower jaw, where destruction of up to 80% of the bone tissue volume is possible in the socket area.
You have questions?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7
Bone resorption changes the characteristics of the dental system:
- oblique ridges are formed on the jaw in the sublingual area. May be accompanied by the formation of a local bedsore;
- changing the shape of the chin. In its anterior part there are two tubercles, which can protrude forward during the destruction of bone tissue;
- the muscles are attached near the top of the ridge, which can provoke pain and discomfort;
- thinning of the mucous membrane, causing discomfort even when eating or performing hygiene procedures;
- formation of functional bedsores.
Healing time
The dentists of our clinic understand each patient very well. Any procedure associated with surgery is stressful for a person. And in the period after graduation, you will certainly want to have a snack, relieve stress with hot tea, smoke, and perhaps even drink something stronger. We ask: read the leaflet carefully and try to follow all the recommendations. As the tissues recover, the pain will disappear, and after 12-14 days the hole will be completely filled with epithelium. Take care of yourself, follow the doctors' recommendations and you will reduce the time spent on treatment!
Easy removal
If the above features are not present, then the removal of the figure eight is carried out in the usual way. The total time of the procedure is about half an hour, but the tooth itself is removed quickly - in about 10 minutes. The rest of the time is spent on preparing and suturing the wound (if necessary).
The standard algorithm is:
- The dentist questions the patient about existing diseases, drug allergies and general health.
- Based on the data obtained, an anesthetic and sedative agent are selected.
- An anesthetic injection is given, and after it begins to act, the doctor begins to remove the eighth tooth.
- The tooth is loosened using forceps and removed from the jaw in one motion.
- Medicine or plasma membrane is placed in the socket to prevent inflammation and promote healing.
- If necessary, stitches are applied. This is usually required when removing the bottom eights.
Simple removal very rarely causes complications and is quite easily tolerated.