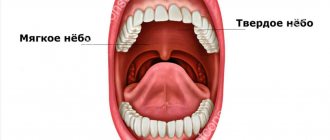
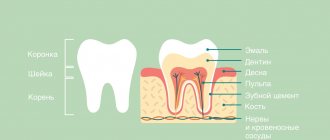
Dental problems
Dental diseases
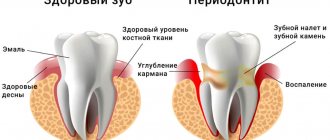
With deep caries and its complications - pulpitis, periodontitis - the pain radiates to the jaw in the area of the affected tooth.
Infectious and inflammatory processes of the soft tissues surrounding the tooth - periodontitis, abscess - cause swelling, which, by squeezing the nerve endings, provokes the appearance of painful sensations in the jaw.
With increased tooth sensitivity, eating hot, cold, spicy, sour or sweet foods and drinks, and brushing your teeth cause acute pain that spreads to the jaw.
When third premolars - wisdom teeth - emerge, complications often arise: pericoronitis, inflammation of the periosteum, one of the symptoms of which is severe pain in the jaw.
Dental treatment procedures associated with violation of tissue integrity - implantation, prosthetics, tooth extraction, installation of fillings, professional teeth cleaning and whitening - contribute to the appearance of pain in the jaw.
Bruxism
With bruxism, involuntary grinding of teeth at night significantly increases the load on the masticatory muscles, which leads to their prolonged spasm. In this case, the correct occlusion of the dentition is disrupted with the development of pain in the jaw when chewing.
Temporomandibular joint problems
If pain occurs in the jaw when opening the mouth, this is a symptom of temporomandibular joint pathology.
Pain in the projection of the jaw is often accompanied by pain in the ear, head, and face. The causes of joint dysfunction are injuries, malocclusions, incorrectly installed dentures, arthritis, arthrosis, and hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles.
Tumors of the lower jaw
Pain in the jaw area is characteristic of benign and malignant neoplasms. Benign tumors are characterized by slow growth and lack of invasion into adjacent tissues and organs.
Malignant neoplasia rapidly progresses, pain intensifies with irradiation into the eye, temporal region, ear, jaw.
Pain in the temple area
Arthritis
19015 October 28
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pain in the temple area: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition _
Pain in the temple area is one of the most common complaints that brings patients to the doctor.
In the bone structures of the skull and brain tissues, pain sensitivity is insignificant, so the main sources of pain are blood vessels, meninges and cranial nerves.
Types of pain in the temple area
According to the International Classification of Headaches 3 (2013), all headaches are divided into:
- for primary pain not associated with diseases of the brain and other structures of the head and neck;
- secondary pain associated with other diseases;
- painful cranial neuropathies, other facial and headaches.
Possible causes of pain in the temple area
Arterial hypertension
is one of the common causes of headaches in the back of the head and temples. When pressure increases, attacks of headaches occur, which may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and “spots” before the eyes.
Tension headache
– one of the common reasons for visiting a neurologist and therapist. Patients characterize it as squeezing, pressing.
Tension headaches interfere with quality of life and performance, despite the fact that they are considered benign and do not carry serious consequences.
Migraine
is the most common form of attack-like headache.
Migraine is characterized by localization of pain in the temporo-frontal-orbital region and a paroxysmal nature of the course.
If the pain is not paroxysmal, then it is not a migraine. Seizures can occur on one side of the head or on both sides, and can also change their location (right-left).
A headache attack can occur at any time of the day, more often during a night's sleep in the morning or after waking up. The pain is pulsating, bursting, with a gradual increase in intensity over several hours. Before the onset of an attack, a so-called aura is possible (harbingers of pain, they vary from person to person, but are often described as disturbances in vision, speech, or dizziness). The pain intensifies in bright light, from loud sounds and other irritants, including changes in head position. The attack can last up to several days.
Harris' periodic migraine neuralgia
- characterized by the sudden onset of pain in the eye area on one side and spreading to the temporal, frontal and zygomatic areas, and sometimes even to the neck.
Unlike migraines, there are no warning signs of pain.
The pain is burning, cutting, bursting, accompanied by redness of the eye and lacrimation on the painful side. Some patients experience a sensation of the eye “bulging out of its socket.” All these attacks are characterized by a certain seasonality or periodicity. The duration of the attack ranges from 6–8 weeks to 3 months.
Pain in the temple area may occur immediately after drinking cold water
or ice cream due to arterial spasm. In this case, the pain is aching, squeezing, sometimes throbbing.
Cold pain occurs in individuals with increased sensitivity to cold stimuli and high reactivity of the body.
“Sausage” headache
(in English-speaking authors -
hot dogs headache
) occurs when eating foods containing food additives such as sodium nitrate. During a chemical reaction in the body, nitrate is converted into nitrite, which has a vasomotor effect (controlling the process of contraction and relaxation of the muscular lining of the walls of blood vessels, and, consequently, the lumen of blood vessels), and sensitive people may feel pain in the frontotemporal region.
A similar effect sometimes occurs when eating Chinese dishes (“Chinese restaurant headache”), where monosodium glutamate is often used.
Giant cell arteritis
is the most common systemic vasculitis in the world, affecting large vessels. The favorite localization of this disease is the temporal artery. Most often, the pain is intense, accompanied by limited function of the corresponding temporomandibular joint, blurred vision with its gradual decrease, and a hardened artery in the temple area is detected.
Without treatment, it can lead to permanent blindness of the eye on the affected side.
With inflammatory diseases of the ear,
pain in the temporal and parotid region is possible, which is accompanied by fever, redness, swelling in the ear area, and purulent discharge from the ear.
Meningitis
develops when an infectious agent enters the membranes of the brain, followed by an inflammatory process.
The headache is sudden, sharp, diffuse, predominant in the frontotemporal areas, sometimes accompanied by vomiting.
Neuralgia of the auriculotemporal nerve
often occurs after an inflammatory process or traumatic lesion of the parotid gland. It is characterized by burning, throbbing pain in the area of the external auditory canal, temple, temporomandibular joint, radiating to the lower jaw. The pain is accompanied by increased salivation and redness of the skin over the affected area. Attacks are triggered by eating and smoking.
Neuralgia of the ear ganglion
manifests itself as attacks of burning pain in the temporal region lasting from several minutes to an hour. May be accompanied by ear congestion and increased salivation.
For altitude sickness
There is a change in arterial tone due to reduced oxygen pressure and changes in barometric pressure. Headache is accompanied by shortness of breath, palpitations, and blurred vision.
The severity of symptoms depends on the speed of ascent to altitude.
The pain is relieved by applying cold to the temples and drinking cool water.
Traumatic lesion of the temporal region
may be the cause of pain. This includes a wide group of pathologies: fracture of the temporal bone, dislocation of the temporomandibular joint, soft tissue contusion.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
occurs for various reasons, for example, as a result of a rupture of a cerebral aneurysm, a person feels like a strong blow to the head, hot liquid pouring into the head, strong contraction, and then bursting. The pain may initially be localized in the corresponding part of the head - in the temporal region when an aneurysm of the internal carotid artery ruptures.
Damage to the temporomandibular joint
(both inflammatory - arthritis, and non-inflammatory - arthrosis, malocclusion) may be accompanied by pain in the parotid and temporal region. When moving the lower jaw, crunching and clicking may occur in the joint; the pain intensifies when chewing and during conversation.
Which doctors should I contact if I have pain in my temples?
If you experience intense and recurring pain in your temples, you should consult a specialist.
If pain persists after taking painkillers or other symptomatic treatment previously prescribed by your doctor (for example, to lower blood pressure), and there are no signs of injury, you should contact or. Depending on the accompanying symptoms, you may need to consult a neurologist, rheumatologist, otolaryngologist, or ophthalmologist. In case of previous injury, it is necessary to contact a traumatologist or to exclude severe injury.
Diagnostics and examinations for pain in the temples
The list of examinations is prescribed by the doctor depending on the indications. An approximate list of studies that may be prescribed:
- computed tomography of the head;
Causes of jaw pain not related to dental disorders
Neuralgia
When the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for the sensitivity of the face and oral cavity, is damaged, the pain is strong, sharp, reminiscent of the pain of pulpitis. Often patients with trigeminal neuralgia undergo unnecessary dental treatment with depulpation or tooth extraction, but the pain syndrome persists.
Sialolithiasis
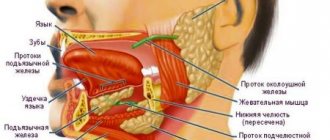
Salivary stone disease is characterized by the formation of stones in the ducts of the large salivary glands. Since the salivary glands are located in the mouth, pain during their inflammation also affects other nearby organs of the oral cavity, in particular the jaw.
Sinusitis
When the mucous membrane of the maxillary cavity becomes inflamed, increasing swelling and accumulation of exudate cause pain spreading to the upper jaw area from the side of the affected sinus.
Otitis
Sometimes the symptoms of otitis media are similar to toothache. With inflammation of the middle ear, pain often radiates to the jaw. The pain is sharp, shooting, aggravated by chewing and swallowing.
Submandibular lymphadenopathy
Enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes is observed in diseases of the tonsils, acute respiratory viral infections, stomatitis, and oncological tumors. Pain under the jaw is often accompanied by limited range of motion - it is difficult for the patient to bend and turn his head, or open his mouth wide.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Irradiation of pain into the lower jaw can be observed during an attack of angina and myocardial infarction. A characteristic symptom of coronary heart disease is burning, pressing pain behind the sternum. But with an atypical course of a heart attack, retrosternal pain may be completely absent, only reflected pain comes to the fore: in the left arm, in the neck, in the face, in the jaw.
Head and jaw hurt
According to doctors, pain in the head and jaw can occur simultaneously. Similar symptoms are caused by dental pathologies. Sometimes the problem can be caused by pathologies of the visual organs, blood vessels and ENT organs. The article will describe the reasons for this phenomenon.
- Malocclusion
Pain in the jaw and head can be caused by impaired jaw closure and the functioning of the masticatory muscles. Bite pathologies can lead to scoliosis.
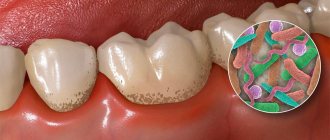
- Caries in an advanced stage
Pain caused by inflammatory dental diseases (caries, pulpitis, granuloma) is felt in the jaw and the area of the affected unit. Initially, discomfort occurs due to temperature or mechanical influence. At an advanced stage, sharp pain occurs independently and radiates to adjacent areas.
- Edentia or damaged elements
With partial edentia, neighboring teeth and nearby muscles are subject to intense stress. The patient has to adapt and chew food on the healthy part of the jaw.
- Availability of orthodontic and orthopedic products
Pain may occur after placement of bite correction devices. This is a normal condition when the dentition gets used to a new position. Unpleasant sensations arise due to the pressure of the structure on the teeth. The discomfort goes away within a few weeks.
There should be no pain or discomfort during prosthetics. This indicates the low quality of treatment.
- Strong galvanic currents
The occurrence of galvanosis is due to the movement of galvanic currents in the mouth and their intense influence. The anomaly is typical for patients with metal prostheses in the mouth. The reaction occurs due to an allergy to metal alloys and non-compliance with production technology.
- Bruxism
An involuntary phenomenon at night. Manifested by excessive clenching of the jaw. People learn about pathology from their relatives. Patients experience fatigue and tension headaches in the morning. Teeth are brittle and have worn out enamel.
- Dental treatment
Patients note such negative phenomena immediately after treatment. Discomfort occurs after therapeutic manipulations and surgical interventions. This is due to stress, prolonged stay in a position with an open mouth, and the traumatic nature of the doctor’s actions.
- Erupting wisdom tooth
The third molar, as it passes through the jawbone, exerts pressure and irritates the nerve endings. The pain is blurred and spreads to the entire jaw, radiating to the temples and head.
It is worth going to the dentist and getting an x-ray. Third molars may be impacted or dystopic. Such elements provoke crowding of the jaw row, malocclusion, pericoronitis, accompanied by pain and discomfort.
- Complications after surgery
Surgical procedures are accompanied by pain, swelling and other manifestations. Gradually the unpleasant sensations subside. If acute pain remains 3-4 days after treatment, this indicates complications. Alveolitis develops - inflammation in the diseased socket. In the absence of timely treatment, there is a risk of developing flux, abscess and osteomyelitis.
Doctors are sure that pain in the head or jaw is sometimes mistaken for toothache.
- Subluxations and dislocations
Develop due to arthritis or joint disease. The problem can be caused by excessive opening of the mouth and displacement of the articular head of the lower jaw. Soreness is felt in the head, temples and cheeks.
- Trigeminal neuralgia
When the trigeminal nerve is damaged or inflamed, acute pain is felt like a migraine. The patient experiences discomfort in the jaw.
- Diseases of the ENT organs
Sinusitis, tonsillitis and other ENT diseases are disguised as dental problems. Otitis media provokes intense pain in the head and jaw. Identical symptoms are characterized by sinusitis and sinusitis. This is due to the close location of organs and the spread of pathogens through the bloodstream.
- Cluster headache
Characterized by pain in the upper jaw area. Acute pain is mistakenly mistaken for manifestations of pulp inflammation or periodontitis.
- Viral, infectious diseases, hypothermia
Hypothermia or ARVI can provoke a migraine. Associated symptoms characteristic of infectious diseases occur: hyperthermia, rhinitis, cough.
- Angina pectoris
Discomfort in the heart can shoot into the arm or shoulder on the left side of the body. Occasionally, pain is felt in the head or lower jaw.
Only a doctor can determine the cause of a headache and choose the right treatment. If symptoms occur, you should contact your dentist.
Diagnostics
When there is pain in the jaw, the patient first seeks advice from a dentist.
A dental examination includes the following steps.
- Clarifying patient complaints and collecting anamnesis. Since the main complaint is pain in the jaw, the time of its appearance (at night, during the day), the nature of the pain (sharp, dull, pulsating, aching), and duration (constant, paroxysmal) are specified.
- Examination of the oral cavity with assessment of the condition of the mucous membrane, tongue, gums, determination of the type of bite.
- Examination of the surfaces of all teeth using a probe and mirrors, identifying the integrity of the dentition, detecting defects in the hard tissues of the teeth.
- The percussion method is used to determine caries complications.
- Thermodiagnostics is used to identify pain reactions.
What patients may complain about with diseases of the temporomandibular joint or TMJ
Clicking, crunching near the ear, namely in the projection of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), pain in the jaw, jamming of the jaw when opening the mouth - all these are symptoms of muscular-articular dysfunction.
To find out the cause of this dysfunction, you first need to know how the joint works.
- Joint capsule
- Articular head or condyle
- Articular disc
- Articular tubercle
Where does everything come from?
Clicking is characteristic of dislocations of the articular disc, which can be anterior, posterior and lateral. The picture below shows from left to right: normal disc position, posterior dislocation, anterior dislocation. Dislocation occurs with or without reduction, i.e. with and without reduction. So, with a dislocation with reduction, you can hear two clicks: the first at the moment of opening the mouth, the second at the moment of closing.
What are the dangers of clicking in a joint? The danger lies in premature wear of the joint elements, which will lead to the development of arthritis, arthrosis and the final stage - ankylosis (complete immobility of the joint).
As for the crunching sound in the joint when the jaw moves, this sound is more characteristic of arthrosis of the TMJ. It occurs as a result of friction of deformed surfaces. The outcome of arthrosis is ankylosis or complete immobility of the joint.
Pain syndrome may often accompany TMJ arthritis, and in the projection of the joint, i.e. in front of the ear tragus there is swelling, skin hyperemia, general malaise, increased body temperature, etc. Arthritis pain is acute. Purulent inflammation in a joint can result in complete destruction of all its elements.
Also, acute pain can accompany neuralgia, anterior dislocation of the articular disc, in which the posterior condylar fusion ruptures and compression of the articular disc occurs. Dull, aching pain can occur with arthrosis, chronic arthritis and TMJ pain dysfunction syndrome (TMD).
With the development of BSD, in addition to pain in the joint area, headaches, pain and noise in the ears, and muscle tension in the occipital region are also possible.
Patients complain of difficulty opening the mouth (jaw contracture) mainly with arthrosis and sometimes with BSD. The process of jaw jamming is a different problem, and should not be confused with jaw contracture. The mechanism of wedging refers to the dislocation of the articular disc, which was discussed above. Without going into details, this can be explained this way: the articular head, under certain circumstances, does not return to its original position, because cannot overcome, for example, the posterior pole of the disc if it was in a state of dislocation. Or we are talking about dislocation of the lower jaw, when the articular head, when opening the mouth very wide, moves forward from the articular tubercle.
Distinctive features
Complaints in diseases of the TMJ should be distinguished from many other pathological processes in this area. So next to the TMJ there are: the auditory canal, the parotid salivary gland, the masticatory muscle, lymph nodes, and the corresponding pathological processes: otitis media, sialadenitis, myositis, lymphadenitis. In addition, pain can be due to neuralgia and inflammatory diseases in the skin and subcutaneous tissue (for example, with a boil). Separately, it is necessary to consider tumors of the parotid-masticatory region, benign and malignant.
As for the pathology of the oral cavity, in the form of difficult eruption of wisdom teeth or complicated dental caries, the main problem they create is limited opening of the mouth (contracture), which occurs as a result of the transfer of inflammation to the masticatory muscles. The pain in this case may also be similar, because impulses from the teeth spread along the branches of the trigeminal nerve, and the pain can radiate to the ear and temple.
Which doctor can help?
The dentist deals with this problem. The area of activity may be as follows: orthopedics, orthodontics or surgery; The main thing is that the doctor specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of TMJ pathology. Currently, such specialists are usually called gnathologists.
What if my dentist finds it difficult to make a diagnosis?
And this can happen. It is necessary to consult with related specialists: ENT doctor, neurologist, maxillofacial surgeon. If these specialists rule out their pathology, then there is only one option left. What's next? See previous paragraph.
What examination is necessary to diagnose TMJ pathology?
Unfortunately, based on complaints alone, a diagnosis cannot be made and, accordingly, treatment cannot be prescribed. An examination and sometimes additional studies are required: X-ray examination, computed tomography, electromyography, recording of movements of the lower jaw, etc.
Establishing the causes of the disease can be helped by collecting anamnesis: previous injury, any treatment (especially dental), the presence of diseases of internal organs and body systems, etc.
What can you do yourself?
If TMJ is still suspected, then the only thing you can do to help yourself is to create rest for the joint. That is, exclude solid foods, exclude chewing gum, do not open your mouth wide and do not yawn. If there is severe pain, when it is not possible to visit a doctor and there are no contraindications, use analgesics.
For complete treatment of TMJ diseases, see specialized literature.