Chronic tonsillitis: symptoms and treatment at home
Chronic tonsillitis is an inflammatory process localized in the palatine tonsils, which has taken on a sluggish, protracted form. The form of the disease is characterized by periodic relapses (recurrence at certain intervals in the presence of predisposing factors for acute episodes of the disease).
Considering that we are talking about an important organ that plays a decisive role in the chain of formation of the immune and physiological types of defense of the body, the importance of diagnosis and effective mechanisms for treating pathology among doctors is beyond doubt. This is an article prepared by our specialists based on materials from the work of practicing otolaryngologists.
What it is?
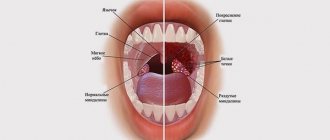
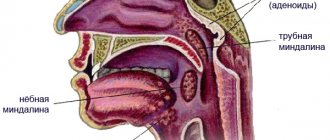
Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term inflammation of the pharyngeal and palatine tonsils (from the Latin tonsollitae - tonsil glands). Develops after a sore throat and other infectious diseases accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx (scarlet fever, measles, diphtheria), or without a previous acute illness.
Causes
Factors that contribute to the development of chronic tonsillitis in adults and children:
- allergic rhinitis;
- deviated nasal septum;
- decreased local and general immunity;
- frequent runny nose;
- inflammatory diseases that develop in other ENT organs;
- caries;
- the presence of foci of chronic infection in the human body;
- allergic mood of the body.
Chronic tonsillitis is an infection-dependent inflammatory process that develops as a result of the pathogenic activity of microorganisms. Normally, the tonsils in the body exist to trap infectious agents and prevent them from penetrating deeper into the respiratory tract. If there is a decrease in local or general defenses of the body, then pathogenic microorganisms that linger on the tonsils begin to actively develop and multiply, provoking the progression of the disease.
Do I need to see a doctor?
If, with the help of a mirror, a hole was discovered in the tonsil, and there is pus inside, this is a serious reason to consult a doctor, since in this way only a small part of the inflammatory process can be seen.
Moreover, it is categorically impossible to remove these accumulations of pus on your own - even the slightest damage to the lymphoid tissue can provoke the spread of infection throughout the body, including blood poisoning.
Cases where there are holes in the tonsils, but they are without pus, should not be ignored by doctors either. The presence of such a deformation indicates the absence of a natural barrier to infections and is a favorable environment for the free proliferation of pathogenic microbes.
First, you can seek help from a general practitioner, who, if necessary, will refer the patient to specialized specialists - an otolaryngologist or an ENT surgeon.
Symptoms
Chronic tonsillitis in adults occurs with periods of remission and periods of exacerbation. With the development of an exacerbation, signs of tonsillitis (acute tonsillitis) develop:
- a sharp increase in body temperature to febrile levels (39-40 degrees);
- intense sore throat;
- regional lymph nodes enlarge;
- purulent plaque appears on the tonsils;
- There may also be purulent follicles on the mucous membrane of the tonsils.
During the period of remission, the patient may have the following symptoms of chronic tonsillitis:
- discomfort in the throat;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- slight pain in the morning;
- bad breath;
- plugs on the tonsils;
- small accumulations of pus in the lacunae.
Also, in addition to the signs of tonsillitis itself, there may be symptoms of concomitant diseases - chronic pharyngitis, rhinitis, sinusitis.
With the development of the decompensated form, the following symptoms appear:
- increased fatigue;
- general malaise;
- headache;
- prolonged low-grade fever (temperature stays around 37 degrees).
In addition, signs of complications may appear. The most common complication in the decompensated form of chronic tonsillitis is a peritonsillar abscess.
It begins as a sore throat, but later the patient cannot swallow or open his mouth at all. There is pronounced swelling of the pharyngeal tissue. The patient requires urgent medical care and hospitalization. Exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis can be triggered by hypothermia, an acute respiratory viral infection, or drinking cold drinks or food.
Step-by-step procedure for removing pus from tonsils
The procedure for getting rid of purulent plaque is simple; its difficulty lies in carrying out the manipulation yourself in compliance with all sanitary standards.
How to deal with ulcers at home:
- Use a hard object to press on the area near the plug; a white liquid will appear on its surface.
- The object must be surgical tweezers, a pencil, a teaspoon handle.
- The manipulation is carried out near a mirror in a illuminated place. A person's hands must be completely free.
- It is necessary to disinfect the item by wiping it with alcohol.
- Tweezers or a spatula should be wrapped in a piece of sterile bandage, after moistening it in Furacilin or another antibacterial agent.
- The object is brought to the throat carefully, because the abscess is removed with the slightest pressure.
After the manipulation, it is necessary to clean the tonsils from any remaining pus, so the throat is gargled with chamomile decoction, saline solution, and Furacilin. If you use hydrogen peroxide, then after the procedure you will also have to wash off this medication.
Diagnostics
During the examination, the doctor palpates the lymph nodes and examines the tonsils directly. But experts do not limit themselves to this, given how many complications can be caused by this disease. The contents of the lacunae are also sampled and sent for analysis. Taking material for laboratory testing is carried out by pressing on the tonsil, from which pus is released. If the pus has a mucous structure and an unpleasant odor, then most likely there is a chronic form of tonsillitis. But even this analysis cannot show the complete clinical picture and accurately determine the diagnosis.
To make an accurate diagnosis, doctors pay attention to the general condition of the body and the presence of deviations from the norm. Such deviations are primarily considered to be thickened edges of the palatine arches and hyperthermia. Experts also determine cicatricial adhesions between the palatine arches and tonsils.
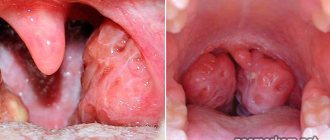
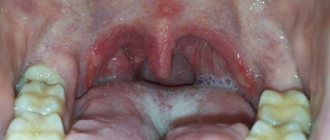
Tonsils, in the chronic form of tonsillitis, have a loose appearance and a scar-altered surface. In the lacunae of the tonsils there are purulent plugs or purulent discharge.
Possible complications
Cellulitis of the neck
Purulent formations are dangerous because they spread through the circulatory and lymphatic systems, which leads to diseases of the kidneys, heart or joints. Treatment cannot be put off for a long time; if the disease is neglected, the following complications are possible:
- Peritonsillar abscess. If pus gets into the tissue, the neck begins to swell and the pain intensifies. Treatment requires surgery, which involves suctioning out the pus.
- Mediastinitis. Pus enters the neck, thereby causing swelling of the tonsils, which makes breathing difficult. This complication can be fatal.
- Cellulitis of the neck and general blood sepsis.
- Septic arthritis.
Do not delay treatment; at the slightest symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Consequences
When tonsillitis becomes chronic, the body's immune response decreases, which can affect the functioning of internal organs. In severe cases, when symptoms of intoxication appear, some complications develop.
Prolonged infections lead to complications associated with cardiac dysfunction and kidney disease. Often, advanced tonsillitis is accompanied by rheumatism and tonsillocardial syndrome. Serious damage to health is caused by toxins that are released during sore throats.
Infectious mononucleosis
This disease is also typical mainly for children, it is often confused with manifestations of a cold or acute respiratory infection, but it is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, which is transmitted by airborne droplets and goes straight to the mucous membrane, where it begins to affect the nasopharynx, tonsils and lymph nodes, resulting in purulent tonsils and plaque appear on them, as in the photo. Hence, difficulty breathing, hoarseness of voice, and snoring in sleep. The main goal of the virus in this disease is to damage lymphocytes, which are one of the main cells of the immune system.
Infectious mononucleosis looks like this
As you can see, there are a lot of options why you might have pus in your tonsils. This is fraught with intoxication of the body, which will affect the digestive tract, liver, spleen, kidneys, cardiovascular system, and blood composition. To prevent this from happening, it is important to undergo treatment on time, and we suggest we talk about it further.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis
When treating a compensated form and in the absence of complications, chronic tonsillitis is treated conservatively at home using effective drugs. If the patient has signs of decompensation of chronic tonsillitis and complications develop, then surgical intervention may be required.
First of all, measures are taken to strengthen the body's defenses - proper nutrition, reduction of bad habits. If there are concomitant diseases, which are also sources of constant infection, they need to be cured:
- mandatory sanitation of the oral cavity - treatment of inflammatory diseases (caries, stomatitis);
- treatment of sinusitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis.
How to treat chronic tonsillitis: list of drugs
For the conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis in adults, the following drugs are used:
- Antibiotics for tonsillitis. This group of drugs is prescribed only in the presence of an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis; antibiotic therapy is recommended based on tank data. sowing. It is not worth prescribing drugs blindly, as this can cause a lack of effect and loss of time, not to mention side effects and worsening of the condition. Depending on the severity of the inflammatory process in sore throat, the doctor may prescribe a short course of the safest and easiest remedies, since with long courses of strong drugs it is necessary to supplement the treatment with a course of probiotics. In the latent course of chronic tonsillitis, treatment with antimicrobial drugs is not indicated, since this additionally disrupts the microflora of the oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract, and also provokes immune suppression.
- Painkillers. For severe pain, the most optimal is Ibuprofen or Nurofen; they are used as symptomatic therapy and for minor pain their use is not advisable (see the full list and prices of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the article Injections for back pain).
- Probiotics. When prescribing aggressive forms of broad-spectrum antibiotics and in the presence of concomitant gastrointestinal pathologies (reflux, colitis, gastritis), before taking antibiotics, it is necessary to take probiotics that are resistant to the action of the former - “Normoflorin”, “Gastrofarm”, “Primadofilus”, “Narine”, "Rela Life", "Acipol".
- Antihistamines. To reduce swelling of the mucous membrane, tonsils, and swelling of the posterior pharyngeal wall, you need to take desensitizing medications; they will also contribute to better absorption of other medications. From this group of drugs, it is better to use the latest generation of drugs, since they have a prolonged effect and do not have a sedative effect, they are safer and stronger. Among the antihistamines, the best are Fexofast, Fexadin, Telfast, Zodak, Letizen, Zirtec, Parlazin, Cetrin.
- Antiseptic local treatment. An important condition for effective treatment is gargling; for this you can use various solutions, either ready-made sprays or dilute special solutions yourself. It is most convenient to use Miramistin (250 rubles), which is sold with a 0.01% solution spray, Octenisept (230-370 rubles), which is diluted with water 1/5, as well as Dioxidin (1% solution 200 rubles 10 ampoules), 1 amp. diluted in 100 ml of warm water (see list of all throat sprays). Aromatherapy can also have a positive effect if you gargle or inhale with essential oils - lavender, tea tree, eucalyptus, cedar.
- Antiseptic local treatment. An important condition for effective therapy is gargling. For these purposes, you can use both ready-made sprays and self-prepared solutions. It is most convenient to use Miramistin 0.01% solution, Octenisept, Dioxylin, which are diluted with warm water. Aromatherapy also has a positive effect if you gargle and inhale with essential oils - cedar, eucalyptus, tea tree, lavender.
- Immunostimulating therapy. Among the drugs that can be used to stimulate local immunity in the oral cavity, perhaps only Imudon is indicated for use, the course of therapy is 10 days (absorbable tablets 4 times a day). Among the products of natural origin, you can use Propolis, Pantocrine, ginseng, and chamomile to boost immunity.
- Emollients. Inflammation in the throat and taking certain medications may cause dry mouth, sore throat, and sore throat; in such cases, it is effective to use sea buckthorn, peach, and apricot oils, provided there is no individual intolerance to them. In order to soften the nasopharynx well, you can instill one of the oils into the nose in the morning and evening, a few drops at a time, during the procedure you should throw your head back. Another method of softening the throat is 3% hydrogen peroxide, which is used to gargle for as long as possible, after which the mouth is rinsed with warm water.
Purulent plugs in chronic tonsillitis
Preventive measures
To avoid the formation of pus on the tonsils during a sore throat, you must regularly gargle, take antibiotics prescribed by your doctor, stay in bed and drink a lot. Proper nutrition and regular oral care are also recommended. As a preventive measure, it is necessary to periodically gargle with herbal decoctions and a solution of soda and iodine.
If there is pus on the tonsils, you should not warm your throat or apply warm compresses. Due to such procedures, active proliferation of bacteria occurs. Moreover, the blood vessels dilate, causing opportunistic microflora to enter the mucous membrane. For this reason, if plugs appear in the tonsils, you need to visit a doctor and follow his recommendations.
Physiotherapeutic methods
Physiotherapeutic treatment of chronic tonsillitis can be effective during remission - laser therapy is recognized as very effective due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect due to its direct effect on the tonsils. Short-wave UV radiation of the throat and oral cavity is also used.
There are methods of ultrasonic treatment of the tonsils, which act on the source of the disease itself, destroying the structure of the resulting cheesy mass. Using ultrasound, you can also irrigate the tonsils with antiseptic solutions.
An effective remedy is inhalation of wet steam. But there is one contraindication here - high temperature, so the temperature must first be lowered, and only then inhalation. Inhalations can be used using various medicinal herbs - chamomile, calendula, etc., chlorhexidine solution, or you can simply breathe over potatoes. You should not take deep breaths when inhaling, because in the case of tonsillitis, only the inflamed tonsils need to be affected.
Treating tonsillitis at home
Let's look at some of the most interesting recipes for treating tonsillitis at home, which include honey and its derivatives:
- For oral administration, prepare half and half onion juice and honey. Mix thoroughly and drink 1 teaspoon 3 times a day;
- Mix chamomile flowers and oak bark in proportions 3:2. Pour four tablespoons of the mixture into 1 liter of hot water and boil over low heat for 10 minutes. Before turning off, add a tablespoon of linden flowers. Let cool, strain, add a teaspoon of honey to the solution. Mix thoroughly and gargle while warm.
- To lubricate the tonsils, prepare a mixture consisting of 1/3 freshly squeezed aloe leaf juice and 2/3 natural honey. The mixture is carefully mixed and stored in the refrigerator. Before use, the medicinal composition must be warmed to 38-40 degrees Celsius. Using a wooden or plastic spatula, the composition is carefully applied to the sore tonsils 1-2 times a day, at least 2 hours before meals. Repeat treatment daily for two weeks. Then the procedure is done every other day.
Surgical treatment
Such treatment is mainly carried out when decompensated chronic tonsillitis is detected and in the absence of a positive effect from repeated conservative treatment.
A tonsillectomy can be complete or partial. A total tonsillectomy involves total excision of the affected tonsils. Partial tonsillectomy can reduce the size of enlarged tonsils, but this operation is now rarely performed due to the high risk of relapse of the disease. Rare types of surgical treatment include galvanocaustics and diathermocoagulation.
New types of treatment for tonsillitis include laser lacunotomy, an operation to remove the tonsils is performed using a surgical laser. It is possible to carry out such treatment using surgical ultrasound.
Cryodestruction – freezing the tonsils with liquid nitrogen – is gaining popularity. Its use is justified with a slight increase in the size of the tonsils.
Tonsillectomy (removal of tonsils)
Prevention
Prevention of exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis:
- Compliance with the rules of hygiene of home and work premises.
- Elimination of dust and air pollution.
- General hygiene measures.
- Hardening.
- Balanced diet.
- Sanitation measures: identification and treatment of diseases of the gums and teeth, sinusitis, otitis media, nasal breathing disorders.
It should be noted that even the implementation of all of the above measures does not at all guarantee the exclusion of relapses.
Respiratory diphtheria
This is a serious infection, which, in addition to the formation of large gray or white ulcers on the throat and swollen tonsils, as in the photo, is characterized by fever, inflammation of the lymph nodes, difficulty not only in eating and swallowing, but even in breathing.
This is what respiratory diphtheria looks like
It may be helpful for you to know that the best way to prevent diphtheria is through vaccination,1 which was first invented in the 1920s. This is what has made it possible to sharply reduce the number of children and adults with this disease. To this day, the vaccine is given at the age of 2.4 and 6 months (if there are no contraindications), then it is recommended to repeat it at the age of 18 months and when the child reaches 6 years. Further, after 16 years, it can be repeated every 10 years of life. Today, vaccines of this type make it possible to stop several infectious agents at once: diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus.
What do you think about mandatory vaccinations? Do you think that they should be done for children or will all this only bring harm? We are waiting for answers in the comments>>>