Palatine tonsils - a focus of inflammation in chronic tonsillitis
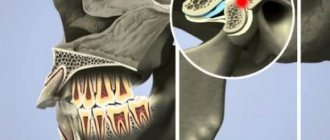
In the upper respiratory tract of a person there are a number of formations representing an accumulation of lymphoid tissue, the so-called lymphoepithelial organs - tonsils. There is a whole lymphopharyngeal ring consisting of 7 tonsils. These are unpaired pharyngeal (adenoids), lingual, laryngeal tonsils, and paired palatine and tubal tonsils. Like any organ in our body, the tonsils can be subject to inflammatory diseases.
Acute inflammation of the tonsils is a sore throat. Chronic tonsillitis refers to a long-term inflammatory process in the palatine tonsils. In most cases, tonsillitis is an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis. The palatine tonsils (tonsils) are essentially the same mucous membrane only folded into an accordion; they are dotted inside with passages - crypts, which open on the pharyngeal surface of the palatine tonsils with lacunae.
Due to the anatomical features and location of the palatine tonsils, which are located at the crossroads of the digestive and respiratory systems, they are most often, of all other lymphoepithelial formations, susceptible to the inflammatory process, which consists of degenerative processes, as a result of which, in chronic tonsillitis, the palatine tonsils are a constant source of infection and the cause of endointoxication.
Causes of traffic jams, tonsillitis
It is important to determine not only how to remove plugs from the tonsils, but also to understand the cause of their appearance. The main factor is the constant presence of a focus of inflammation. A person always has bacteria in the oral cavity, on the surface of the mucous membranes of the pharynx and tonsils. They are successfully dealt with by immune cells of lymphoid tissue.
Healthy tonsils are capable of self-cleaning - dead cells are removed from the lacunae and enter the stomach, where they are destroyed by gastric juice. But when viruses enter, a larger number of immune cells - leukocytes - are required. The mucous membrane of the palatine tonsils becomes swollen, the tissues become loose, and the lacunae become difficult to clean. Dead mucous cells, dead bacteria and leukocytes accumulate in the tonsils - this is what plugs are made of.
Active and passive drainage of tonsil lacunae allows one to develop immunity to many microorganisms. But even a single case of acute inflammation and its subsequent transformation into chronic inflammation can disrupt this process. Doctor Ovchinnikov Yu. M. emphasizes that “discharge in the lacunae can be purulent, caseous, accumulate in narrow lacunae convoluted with spurs, and form so-called fetid plugs” (Ovchinnikov Yu. M., 2000, 538)
Why do we get chronic tonsillitis?
The main causes of the development of chronic tonsillitis are inflammation of the tonsils and ongoing tonsil reactions, which can be caused by long-term exposure to an infectious factor.
In the photo - lymphopharyngeal ring
During the development of chronic tonsillitis, the overall level of the body’s immunity is of no small importance.
White pustules in the throat with fever
A purulent plaque in the throat, accompanied by symptoms of intoxication (fever, body aches, chills, headache and weakness) speaks in favor of a viral or bacterial infection.
The most common forms of sore throat are catarrhal, lacunar and follicular. The sources of infection are mainly staphylococcus, hemolytic (with scarlet fever) or fecal streptococcus, Klebsiella, etc.
The disease begins with an increase in body temperature and the appearance of pain in the oropharynx, both when swallowing and at rest.
In case of catarrhal tonsillitis
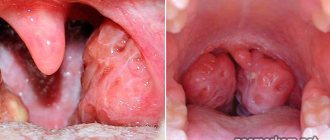
the palatine tonsils and arches are loosened, enlarged, brightly hyperemic and covered with transparent mucus. The tongue is coated with a whitish coating; swallowing and eating causes pain.
The main symptom of lacunar tonsillitis
- these are small or abundant white ulcers on the throat, or rather along the lacunae of the tonsils (in the form of threads).
The organs of the lymphatic system themselves are hypertrophied and swollen; regional lymph nodes (submandibular, anterior cervical) are enlarged and painful. Yellow ulcers with sore throat most often speak in favor of a staphylococcal infection.
Adenovirus infection and infectious mononucleosis
Both diseases are caused by viruses (in the first case, adenovirus, in the second, herpes virus type 4), which are tropic to lymphatic tissues.
Adenoviral infection begins acutely, with an increase in body temperature. Later, catarrhal symptoms such as nasal congestion and rhinitis appear.
A distinctive feature of the infection is damage to the outer membranes of the eyes in the form of conjunctivitis and palatine tonsils. The tonsils increase in size, become bright red, and then become covered with whitish deposits.
During infectious mononucleosis, secondary flora often joins, so viral tonsillitis becomes mixed - viral-bacterial.
First of all, the patient’s appearance attracts attention: a significantly enlarged neck due to the reaction of the anterior, posterior cervical and submandibular lymph nodes; puffiness of the face due to hypoxia (the tonsils hypertrophy so much that they reach the uvula, completely blocking the pharynx). During examination of the oral cavity, a purulent throat is visualized - abundant dirty gray or yellow plaque on the tonsils. The liver and spleen become larger than normal, wave-like and prolonged fever is recorded, and taking penicillin antibiotics can provoke the appearance of a toxic-allergic reaction in the form of a rash
The liver and spleen become larger than normal, wave-like and prolonged fever is recorded, and taking penicillin antibiotics can provoke the appearance of a toxic-allergic reaction in the form of a rash
During examination of the oral cavity, a purulent throat is visualized - abundant dirty gray or yellow plaque on the tonsils. The liver and spleen become larger than normal, undulating and prolonged fever is recorded, and taking penicillin antibiotics can provoke the appearance of a toxic-allergic reaction in the form of a rash.
Types of chronic tonsillitis
There are several classifications of chronic tonsillitis. The issue of classification of chronic tonsillitis is closely related to the clinical manifestations of this disease. The most widely used classification is that there are only two forms: compensated and decompensated.
- The compensated form is characterized by a course without complications, rare sore throats, often the only complaint can be only plugs in the throat, the protective role of the tonsils works by holding back harmful bacteria, and their further penetration, due to this, no special manifestations of the disease are observed.
- Decompensated form This form of chronic tonsillitis is characterized by frequent sore throats at least once a year, the occurrence of local complications, such as peritonsillar abscess, and diseases of other organs and systems of the body, such as glomerulonephritis, rheumatism.
Are tonsillitis always removed?
If the lumps are not associated with a sore throat, while the temperature is normal and your health is normal, then cleaning the tonsils at home will not be necessary at all. But you can stop the formation of tonsillitis by maintaining oral hygiene:
- In the morning and evening after meals, you should regularly clean the inner and outer surfaces of your teeth.
- The brush does not clean the gaps between them, so you need to use a thread.
- After lunch or every snack, you should rinse your mouth with a prepared disinfectant or just a saline solution.
Regular oral hygiene will prevent the formation of plugs on the tonsils and relieve bad breath.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
The main manifestation of chronic tonsillitis is tonsillitis; as a rule, all patients suffering from this disease at least once have had tonsillitis. Sore throat is a fairly serious disease that affects all systems of the body and carries the risk of a number of serious complications, so the choice of treatment tactics for chronic tonsillitis should be related to the frequency of tonsillitis. The main symptoms of the disease can be identified:
| Smell from the mouth | One of the most common symptoms disturbing the patient is bad breath. This symptom is due to the fact that the area of the epithelium of the palatine tonsil is quite large; during inflammation, pathological secretions accumulate in the crypts of the tonsils in the form of caseous (curdled) masses. Caseous masses are evacuated through the lacunae into the pharyngeal cavity, causing bad breath. |
| Sore throat, ear | One of the main symptoms of chronic tonsillitis is pain in the throat, often a feeling of a lump in the throat. Also, the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis can be expressed by headache, unpleasant sensations in the ear, mild pain in it, which is caused by irritation of the nerve endings in the parenchyma of the palatine tonsil and irradiation of pain along the nerve fiber to the ear. |
| Enlarged lymph nodes | You can often observe an enlargement of the lymph nodes located under the jaw, and the cervical lymph nodes also enlarge. When palpating the lymph nodes, mild pain occurs. |
Quite a large number of patients do not immediately detect the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis and delay contacting an ENT doctor, which often leads to decompensation of the disease and longer treatment in the future.
Treatment at home
To determine the diagnosis and begin treatment, contact your doctor. If you are diagnosed with acute tonsillitis, you must observe strict bed rest in the first days of the disease, then limit physical and psycho-emotional stress, which will help get rid of complications, among other things. The patient is given a personal plate, spoon, mug and, if possible, isolated. Prescribe non-irritating, soft foods, mainly plant-based, dairy, vitamin C, and plenty of warm drinks. Symptomatic therapy is also carried out: taking antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, painkillers.
Rinsing
Special attention should be paid to local therapy. Gargling with antiseptic solutions (Hexoral ® gargling solution) is useful for tonsillitis. The drug Hexoral ® has broad antibacterial activity, including against gram-positive microbes, is also active against the pathogenic genus of fungi Candida, and has an effect in the treatment of infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Proteus. The antimicrobial effect of the drug is associated with the suppression of metabolism in bacteria, their oxidative reactions, without which the latter cannot exist (thiamine antagonist). At a concentration of 100 mg/ml, the drug inhibits the growth of most bacterial strains. The development of resistance to Hexoral ® is not observed. The active substance hexethidine has a mild analgesic effect on the mucous membrane of the pharynx and tonsils, can linger on it for a long time and is practically not absorbed. Therefore, it does not have a systemic effect. When using the drug Hexoral ®, regression of inflammatory changes in the pharynx may be observed5. It is recommended to use 15 ml of undiluted solution 2 times a day after meals, unless otherwise prescribed by a doctor. Before use, consult a specialist.
Rinsing is an effective method and an important component of the fight against tonsillitis, which can be successfully used in home treatment. Rinsing with a salt solution, irrigating the oropharynx with sprays with sea water, a decoction of chamomile, sage, chlorhexidine and other antiseptics help well. Rinsing with solutions at body temperature (36-37 degrees) reduces inflammation, mechanically cleanses the mucous membrane of the oropharynx from viruses, bacteria, pus, helps relieve swelling, and as a result, reduce sore throat. Rinsing is completely safe for children, pregnant women and nursing mothers.
Washing the lacunae of the tonsils with antiseptics is used for many types of both acute and chronic tonsillitis. The most common method of washing the lacunae of the tonsils is according to N.V. Belogolov. and Ermolaev V.G1. This effective procedure is performed by an otolaryngologist. Under the control of pharyngoscopy, the doctor sequentially inserts a thin cannula through each lacuna into the crypt of the tonsil, and with a syringe filled with an antiseptic, under pressure washes out everything unnecessary from the lacuna. As a rule, 2-3 crypts of the upper part of the tonsil are washed. All tonsil crypts are usually connected to each other, so the entire tonsil is washed and drained. After this, the treated mucous membrane is lubricated with Lugol’s solution, iodine, and 5% collargol. The positive effect of the procedure is achieved by mechanically flushing the lacunae from pus and restoring their drainage function. Treatment is carried out in a course of 10-15 washes, which are prescribed every other day.
How to identify chronic tonsillitis
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis does not present any particular difficulties for an experienced otolaryngologist. The patient's medical history and complaints are of utmost importance in diagnosis; as a rule, the history includes previous sore throats and complaints of frequent pain and discomfort in the throat.
Examination of the throat for chronic tonsillitis
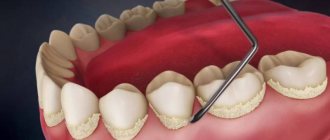
During mesopharyngoscopy (examination of the pharynx) for chronic tonsillitis, the following signs are present: hyperemia and roller-like thickening of the edges of the palatine arches; cicatricial adhesions between the tonsils and palatine arches; loosened or scarred and hardened tonsils; caseous-purulent plugs or liquid pus in the lacunae of the tonsils.
Getting rid of traffic jams using improvised means
If you decide to clear your throat with tools yourself, you need to know how to clear tonsils from blockages at home and not harm your health. It is safest to use sterile cotton swabs. Otherwise, an infection may occur during the procedure.
Attention! You should not try to get rid of the plugs by pressing on the tonsils with a hard spatula. A lump of pus is easily pressed inside with unpredictable consequences. In addition, the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils is easily injured, which will further aggravate the situation.
In addition, it should be taken into account that the instrument in the oral cavity becomes slippery. During the procedure, pharyngeal spasm and swallowing of the instrument may occur. Therefore, you need to be careful.
How to remove tonsil plugs yourself - step by step steps:
- In good lighting, examine the tonsils, identifying the location of tonsillitis. To see them better, move your tongue forward and make the sound ah-h-h.
- Dip the head of a cotton swab into the disinfectant solution of Chlorhexidine or Cholorophyllipt.
- Gently pressing on the tissue adjacent to the plug, lift the lump and remove it from the tonsils. Important! For the next manipulation, take a new stick.
- After the procedure, rinse your mouth with a disinfectant solution.
The accumulated saliva must be spat out and then rinsed. Another important point is that you cannot put pressure on the cork itself. Otherwise, you can drive the lump deep into the tonsil, which will lead to the formation of an abscess.
Complications of chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis has serious complications; they are divided into two groups: local and general. All complications, as a rule, occur during an exacerbation of the process occurring in the form of a sore throat and represent the consequences of untimely treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
With chronic tonsillitis, in the upper respiratory tract of a person, more precisely in the palatine tonsils, there is a focus of chronic inflammation; the problem of focal infection is very acute in modern medicine. Currently, there are about fifty different metatonsillar diseases, which are the result of chronic inflammation in the palatine tonsils. Let's take a closer look at what this can most often threaten.
Peritonsillar abscess
This is the most common local complication. The fact is that between the palatine tonsil and the muscles of the pharynx to which it is attached there is fiber, the so-called paratonsillar fiber. With severe inflammation, the infection can enter this tissue through the hematogenous route, causing its infiltration and purulent melting, and an abscess is formed. Peritonsillar abscess is a very serious disease that requires immediate surgical treatment, usually in a hospital setting, since there is a threat of the purulent process spreading through the cellular spaces of the neck into the mediastinum, which can be fatal.
Diseases of the heart, joints and kidneys
An important role in the inflammatory process in chronic tonsillitis is played by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, which often parasitizes the palatine tonsils. The fact is that immune complexes that form in the body as a response to the aggression of this antigen can also attack healthy tissue in the joints, heart and kidneys, which, if not treated in a timely manner, can even lead to disability.
Weakness and decreased ability to work
The parenchyma of the palatine tonsils is densely penetrated by blood and lymphatic vessels, and in the thickness of the organ there are many nerve endings that connect to important autonomic centers. In chronic tonsillitis, inflammatory products enter the circulatory and lymphatic systems, and constant endotoxification occurs. All these factors plus pathological impulses from irritated nerve endings lead to decreased tone, bad mood, and apathy.
Regular colds
With chronic tonsillitis, the body spends a lot of effort to contain inflammation in the tonsils, the immune system is under constant stress, which leads to its significant weakening. Added to this is the not always correct work-rest regime, nutrition, and environmental conditions, as a result of which a person with chronic tonsillitis may literally not “get out” of a cold.
Inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system
The palatine tonsils are anatomically located in the pharynx, close to such organs as the trachea, larynx, and paranasal sinuses. With chronic tonsillitis, microbial contamination of the entire area of the respiratory mucosa occurs, which contributes to the development of diseases such as sinusitis, bronchitis, and laryngitis.
Stomach and intestinal problems
The palatine tonsils are located at the crossroads of the digestive and respiratory systems. Due to certain anatomical features, they represent a rather large conglomerate of the mucous membrane. In chronic tonsillitis, this entire area of the mucosa is involved in the inflammatory process and secretes a pathological secretion in the form of a liquid fraction and caseous masses. This pathological content is evacuated into the pharynx through lacunae and then swallowed with saliva, which often causes disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Why do white lumps form on the tonsils?
The tonsils - the palatine tonsils - are very important for human health. They create a barrier to prevent harmful bacteria from entering the body through the blood. These organs of the immune system protect a person from infections, bacteria, viruses that enter by airborne droplets. Sometimes you can find white lumps on the tonsils. They can be soft or have a dense stone-like structure.
White lumps form in the throat in the recesses of the tonsil tissue - lacunae. They can be deep inside without expressing themselves. When they are visible on the surface, this is a clear signal of the development of the inflammatory process. The lumps can be yellowish, grayish or even red. Their systematic appearance indicates chronic tonsillitis. The disease is accompanied by:
- soreness;
- unpleasant odor;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- cough;
- pain when swallowing;
- temperature rise.
White lumps in the throat may appear when you sneeze, cough or cough up. Purulent (caseous) plugs reach several centimeters in size. They often have an unpleasant, stinking odor. Its reason is that white growths in the throat are formed when mixing:
- microorganisms;
- waste products of bacteria;
- dead cells;
- leukocytes;
- leftover food.
The exact origin of white lumps in the throat is not known to medicine. There are factors that can trigger their occurrence. It could be:
- drinking cold food and drinks;
- overwork;
- stress;
- bad ecology;
- smoking;
- hazardous production;
- drafts;
- decreased immunity;
- frequent colds;
- streptococcal infection;
- recurring sore throats;
- thrush;
- staphylococcal infection;
- diphtheria.
White spots in a child's throat
Children's bodies are more prone to diseases associated with the mouth and throat. The child may be seriously ill for a long time. He becomes capricious, gets tired quickly, and cries. White lumps appear on the tonsils and the temperature rises. Children are characterized by frequent occurrence of:
- tonsillitis;
- tonsillitis;
- laryngitis;
- pharyngitis.
Child illnesses are difficult trials for parents. If they are associated with throat diseases, you must have an inhalation nebulizer at home. This will help quickly eliminate white lumps and cure a sore throat. To protect your baby from unpleasant diseases, we recommend:
- hardening procedures;
- walks in any weather;
- taking vitamins;
- reduction of loads;
- quality food;
- healthy sleep;
- active physical activity;
- reducing contact with household chemical products.
White spots on the throat of an adult
It's hard to explain, but white lumps are more common in men. They often become signs of chronic tonsillitis. They require regular visits - twice a year - to an ENT doctor. Special rinses help avoid serious complications. The appearance of white growths in the mouth of women during pregnancy is considered dangerous. This can affect the baby’s health and requires immediate attention to specialists.
Surgical treatment of chronic tonsillitis
The whole variety of methods for treating chronic tonsillitis is divided into two large groups: surgical methods and conservative ones. Let us dwell in detail on surgical treatment. A radical surgical method is tonsillectomy - removal of the organ along with the capsule should not be confused with tonsillotomy, which is often done in childhood.
Video: tonsillectomy - removal of tonsils
With tonsillotomy, unlike tonsillectomy, not the entire organ is removed, but only a fragment of the hypertrophied parenchyma of the pharyngeal surface of the tonsil. It is necessary to resort to tonsillectomy in extreme cases; for this there must be compelling indications, such as a complicated advanced form of the disease, despite the fact that all possible methods of conservative treatment have been exhausted. Despite these “canons” that have been established for many years, removal of tonsils is often resorted to due to the lack of availability of conservative treatment, and sometimes due to the banal lack of a competent specialist dealing with this issue.
The function of the palatine tonsils is extremely important - it is an element of the pharynx, after the removal of these organs, areas of the pharynx that were covered by these formations begin to be subject to irritation by air and food masses, is this good or bad? Apparently this is bad, since nature, as a result of a long process of evolution, did not give us a single extra organ.
Preparation of an ozonized solution for a session of deep vacuum ultrasonic sanitation of the palatine tonsils
Often, tonsils are removed from patients who have not even had a history of sore throat, and whose only complaint was caseous plugs in the throat and bad breath. The long-term result of operations to remove palatine tonsils is often severe sore throat and the development of atrophic pharyngitis, which is difficult to treat.
Conservative methods of treating chronic tonsillitis include various methods of washing the tonsils. Comprehensive information about this manipulation is presented in the article washing the tonsils.
How to remove plugs by rinsing
First, you can use an easy and safe way to remove tonsillitis by rinsing. For this, various disinfectant solutions are used:
- Prepare a solution of Hydrogen Peroxide 3% at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. per 100 ml of warm boiled water. Oxygen bubbles released during rinsing wash away deposits on the tonsils. The procedure is carried out 3 times a day. After completing the procedure, the oral cavity is washed with plain water.
- A solution of Chlorophyllipt and Chlorhexidine is used in its pure form 5-6 times a day.
- A soda-salt solution is prepared in a proportion of 1 tsp. table salt and sodium bicarbonate per 1 glass of water. Add 5 drops of iodine to the resulting mixture. Rinsing can be done 6-8 times a day.
- Furacilin solution is prepared in the proportion of 2 crushed tablets per glass of hot water. Rinsing is done 8 times a day, holding the warm solution in the mouth for 5 minutes.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis without surgery
Despite the wide market of medical services, there are not so many effective conservative methods of treating chronic tonsillitis. The fact is that in modern otorhinolaryngology it is customary to divide the mucous membrane into fragments, there are doctors who deal only with diseases of the nose - rhinologists, there are specialists who deal only with the treatment of the throat. In fact, the entire area of the mucous membrane lining the upper respiratory tract is one organ.
Session of deep vacuum ultrasonic sanitation of palatine tonsils with ozonated solution
We are forced to obtain oxygen from the air, and the air is not sterile; the respiratory organs, like no other system of our body, experience a colossal biological load and are constantly in contact with microbes. The anatomical structure of the upper respiratory tract is the product of a long period of evolution. The upper respiratory tract is a complex mechanism created by nature with one purpose: to be a protective barrier. Moreover, many ENT diseases (adenoids, vasomotor rhinitis, sinusitis, chronic pharyngitis), which are classified as different and treated in different ways, are essentially one disease in different stages of development, so to speak, a “machine” in different stages of breakdown.
Video: treatment of chronic tonsillitis
So, the essence of many inflammatory ENT diseases, including chronic tonsillitis, is a degenerative process in the mucous membrane, caused by the microbes that we breathe, as a result of the weakening of the protective properties of the mucous membrane. It follows from this that when doing treatment you need to influence the entire area of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, you just need to take into account some anatomical features - such as the structure of the palatine tonsils, and taking these features into account, locally enhance the therapeutic effect. Since the palatine tonsils are essentially the same mucous membrane only folded into an accordion, washing the tonsils should be an integral part of the treatment process.
Conducting a photodynamic therapy session on the pharynx area for chronic tonsillitis
The lack of effective methods for treating chronic tonsillitis is also due to the fact that there are a number of dogmas in modern medicine. One of them is that the most common way to fight germs today is with antibiotics. Antibiotics, unfortunately, do not penetrate well into the upper layers of the degenerative mucous membrane; moreover, they do not restore it. With chronic inflammation, the regeneration of the mucous membrane is disrupted and microerosions form on it. Figuratively speaking, the mucous membrane becomes like a “sieve,” which is the most important basis for the inflammatory process.
Stimulation of reflexogenic zones in chronic tonsillitis
Taking into account the above, the main task of treating chronic tonsillitis is to influence all parts of the pathogenesis of the disease, therefore the following methods are used in our clinic:
| Cleansing tonsils with ozonized solution | In our clinic, we wash the palatine tonsils using the tonsillor apparatus with an ozonated solution, which is by far the most effective way to cleanse the entire thickness of the tonsils from pathological contents. |
| Sanitation of mucous membranes with mineral salts | In our clinic, we irrigate the entire mucous membrane with a solution of individually selected mineral salts, which sanitize the mucous membrane and restore it, which cannot be achieved with modern antibiotics. We also activate mucosal regeneration using photodynamic therapy. Lymph stasis plays an important role in the pathogenesis of inflammation, including chronic tonsillitis. Activation of lymph flow in the area of inflammation plays an important role: this is how the “soldiers” of our immunity - lymphocytes - move along with lymph. |
| Stimulation of reflexogenic zones | With the help of injections into the reflexogenic zone of the neck, ozone causes a spasm of the subcutaneous lymphatic vessels, which activates the lymph flow in the pharynx, leading to rapid stabilization of the immune system. The integrated approach we use affects all parts of the pathogenesis of chronic tonsillitis, which allows it to be treated conservatively, avoiding surgical treatment. |
Prevention of the formation of purulent plugs
Purulent plugs are almost always the result of a sluggish inflammatory disease - chronic tonsillitis. Therefore, the main measure to prevent their formation is attention to your health and timely treatment of the underlying disease. It is important to influence all stages of the development of the disease. Prevention consists of following the following doctor’s recommendations:
- Personal hygiene: mandatory brushing of teeth twice a day, timely sanitation of the oral cavity, if possible, rinsing the mouth after eating, especially sweets.
- Timely and complete treatment of tonsillitis according to the doctor’s recommendations: properly selected antibacterial therapy will help prevent chronic inflammation. Regular and frequent gargling will help clear the tonsils, reducing the likelihood of plugs forming in the loose tissues.
- Drinking regimen: drinking plenty of fluids during exacerbations helps cleanse the palatine tonsils of contents and promote rapid recovery.
- Timely treatment of concomitant pathologies, rehabilitation of foci of infection: treatment of caries and inflammation of the gums, correction of the nasal septum when it is bent, treatment of sinusitis, etc.
- Preventing hypothermia. It helps to reduce defenses and activate opportunistic microorganisms in the tonsils.
Sometimes the only option to remove tonsil plugs is to remove them, so it is important to consult a specialist to make the right decision.
Be sure to contact a specialist regarding the removal of purulent plugs from the tonsils in adults for professional, qualified help. The information contained in this material is not a call for self-medication; it is presented for informational and informational purposes. The authors adhere to a scientific point of view and are not responsible for the quality of services provided by third parties.