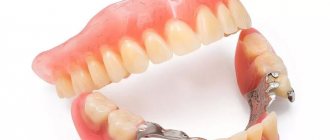
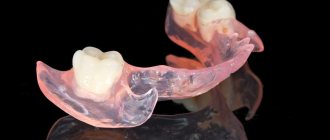
The design of the clasp prosthesis consists of the following main components:
- Metal frame-arc
- Support-retaining elements
- Artificial teeth attached to an arch
The metal arch, which runs along the palate of the upper jaw or under the tongue, is an important component of the clasp denture, as it combines two bases on which artificial teeth are installed.
Base - an element of the prosthesis, including artificial teeth and connected to the branches of the metal parts of the supporting prosthesis. With the help of locks (connecting elements), the base is installed and secured to the supporting teeth, while resting against the alveolar process.
The base is made of plastic reinforced with metal mesh.
Prosthetics using clasp
Modern dentistry allows you to use this type of removable prosthetics, such as a clasp denture, when several teeth are lost.
Most experts believe that there is no alternative to it today: the advantage lies in the comfort of wearing and the even distribution of the load when chewing between the remaining teeth and gums.
Prosthetics using a clasp makes it possible to replace any part of the teeth.
Advantages
They are distinguished by the presence of a cast metal frame in the form of a thin arc - a clasp. The plastic base and artificial teeth are fixed on this thin frame.
Dentures are installed in cases where it is impossible to use permanent structures in the form of a bridge. The thin arch in clasp dentures makes wearing them comfortable - it does not cover the palate, making it possible to feel the taste of food.
Clasp denture on the lower jaw
If a prosthesis is installed on the lower jaw, the metal arch does not allow it to fall out and does not interfere with the movement of the tongue. In addition, diction does not deteriorate during a conversation. Thanks to the clasps, the service life of dentures increases to 5 years; for plastic options, this period is 2.5 years.
It has been established that bone tissue and gum tissue atrophy over time when wearing prostheses, their shape changes and no longer coincides with the shape of the prosthesis. Discomfort, pain appears, and fixation worsens. Under clasp dentures, such atrophy occurs much more slowly - this allows you to increase the period of wearing them.
Features of clasp dentures
The first clasp dentures had the shape of an arc. Even the name of this design is literally translated as “arc”. The main advantage is that the clasp denture distributes the chewing load across all supporting teeth and hard tissues of the oral cavity. But unlike removable dentures, they do not completely cover the palate or most of the gums. This means that they do not distort the sense of taste, do not affect diction, and getting used to them takes less time.
In the form of fastening on clasp dentures, a beam, locks and clasps are used. All of them do not injure tooth tissue and do not interfere with chewing or talking. In addition, their special installation ensures an aesthetically pleasing appearance while smiling.
Clasp prosthesis is partially removable. Patients can take it off in one motion and put it on just as easily. But it is worth noting that there is no particular need to remove the clasp dentures at night, as happens with removable plastic dentures. In most cases, patients remove it only to perform hygiene procedures. Due to the special type of fastening, the clasp denture will never fall off during chewing or talking, which is considered its main advantage over other dentures.
Advantages and disadvantages
Experts highlight the following advantages of clasp-type dentures:
- uniform distribution of chewing load throughout the entire jaw;
- aesthetics, which is achieved by equipping the structure with tiny fasteners;
- comfortable wearing, which is ensured by the small size of the metal frame;
- strength and reliability (the metal arc can withstand regular and heavy loads, unlike polymer analogues).
The disadvantages of clasp structures may not appear if the preparatory work for installing the prosthesis and measurements are performed at a high level. Most of the complaints from patients are related to calculation errors by the dentist.
As for the prosthesis itself, despite its strength, sometimes there are cases of clasps breaking. Such a defect cannot be repaired; the entire structure must be replaced.
The disadvantages are also attributed to the high cost of the product, but it is quite justified. The metal arc casting process involves the use of high-tech technology that requires high precision.
This ensures the strength and reliability of the prosthesis, hence the long service life, which is fully compensated by comfortable wearing.
The structure of the clasp prosthesis
The main parts of a clasp denture are a metal frame, the fasteners listed above, an arch, and also a base on which artificial teeth are attached. The arch, clasps and base are responsible for fixation in the prosthesis. Support-retaining structures in clasp dentures are solid, individually cast from metal and then soldered, and also soldered wire. The choice is made purely individually depending on the number of missing teeth and the condition of the jaw.
In most cases, clasps are used. They are special hooks that hold the clasp denture on the supporting teeth:
There are several ways to make a clasp for clasp dentures:
- It is considered simple to bend the wire in accordance with the shape of the prosthesis model.
- A complex clasp is cast as a solid crown from a special alloy during the manufacture of the arch of the clasp prosthesis.
But the holding elements are divided not only according to the manufacturing method.
There are clasps:
- supporting;
- holding;
- performing these two functions at once.
The first distribute the load from the clasp denture, which occurs during talking, chewing, clenching teeth, onto the supporting teeth and partially onto the mucous membrane. In contrast, the retaining clasps of clasp dentures transfer the load to the mucous membrane, plunging into it when pressure occurs. The latter are capable of performing the functions of both the former and the latter.
All clasps consist of several parts. The clasp body of the clasp denture is located on the supporting tooth in its upper area. The clasp arm touches the side surface of the tooth. Due to the presence of an occlusal pad, the clasp prosthesis does not sink deep into the gum and does not injure it during chewing. In addition, it is able to restore the height of crowns. In addition, there is a process of the clasp or that part of it that is located in the body of the base of the clasp prosthesis.
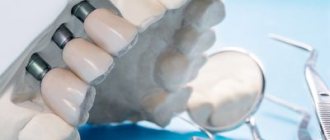
Clasp dentures with locking fastening look and attach differently. Unlike dentures with clasps, they are completely invisible to others, because fixation is carried out by micro-locks that are located in the clasp denture system.
In this case, metal-ceramic crowns are placed on the supporting teeth, in which one part of the lock is attached. Its second part is fixed in the clasp prosthesis. During dressing, the clasps are fastened and the denture is securely held in the oral cavity and does not fall off during chewing. In this case, the load from the clasp denture falls only on the supporting teeth, so you should not use this method of fixation in cases where the teeth have mobility.
Based on the fastening methods, it remains to conclude that a clasp denture is indicated only in cases where there are supporting teeth. Without them, the clasp prosthesis will not hold.
In addition to the support system, the clasp prosthesis has a base. The teeth are attached to it. Today, prosthetics are carried out using various dental manufacturing companies. Due to this, you can achieve high aesthetics and an attractive appearance. The same applies to the plastic used for the base of the clasp prosthesis. High-quality materials have a long service life and are distinguished by their perfect resemblance to living gums and natural teeth. The price of such a prosthesis will be a little more expensive, but it will have virtually no disadvantages.
You can choose a suitable clasp prosthesis from the photo, but it is better to hold it in your hands. Therefore, only a visit to the dentist will provide comprehensive information about the clasp denture.
Stages of clasp prosthetics
Preparation of prosthetics
Preparation for clasp prosthetics begins with an examination of the patient. Doctors carefully listen to the patient’s complaints and wishes, conduct a dental examination, and study the patient’s medical history. After this, after analyzing the results of the examination, dentists decide on the need for clasp prosthetics.
Treatment of dental diseases
Before the production of the prosthesis begins, teeth that cannot be preserved are removed, periodontal disease and other dental diseases are treated. If there is a pronounced inclination of the abutment tooth or if there are restorations on it, as well as with prosthetics using telescopic or locking fixation, crowns are put on the abutment teeth.
Clasp dentures have a number of advantages over bridges:
- Installation of clasp removable dentures does not require preparation of some teeth and does not limit their mobility.
- Chewing pressure is evenly distributed between the alveolar processes and the remaining teeth.
- Clasp dentures are hygienic; they can be cleaned mechanically outside the oral cavity.
To individually assess the condition of your teeth and make various solutions to your problem, you need to have a free consultation with an orthopedic dentist. A highly qualified specialist will help in any of your situations.
Making a prosthesis
All video presentations
Taking an impression
The production of a clasp prosthesis begins with taking a diagnostic impression. This impression is used to create a working model, which the dental technician is guided by when making the frame.
Production of clasps
The most critical stage of work is the production of clasps or crowns with fasteners. The clasps must accurately follow the shape of the patient’s supporting teeth and tightly cover them without damaging the enamel. In turn, the crowns with the mating parts of the locks must completely correspond to the clasp itself with the lock. Precision in the production of fasteners is a guarantee of the durability of the prosthesis and ease of use.
Casting the prosthesis frame
Having completed work on the manufacture of fasteners, the dental technician sketches the frame of the prosthesis and duplicates the working cast, that is, creates a fire-resistant master model. Then the sketch of the future clasp is transferred to a fireproof cast, and casting channels and a flask are installed on it. Gold-platinum, titanium or cobalt-chromium alloys are used to cast the frame.
Installation of artificial teeth and fitting
The finished frame is polished, support-retaining and unloading elements are attached to it, and it is tried on in the patient’s growth cavity. After this, artificial teeth matching the color are installed on the base and re-fitting is performed. On average, the production of a prosthesis takes 2 months.
Conclusion: Indications for the use of removable clasp dentures
In persons with partial absence of teeth, along with end defects, combined and included defects are often encountered. Plate and clasp removable dentures can successfully replace end defects. Clasp dentures have a number of significant advantages over removable plate dentures:
- The base part of clasp dentures is minimal.
- The arch in the prosthesis ensures uniform distribution of the load between its sides.
- The prosthesis contains supporting clasps, which allow partial transfer of the load through the tissues of the supporting teeth.
- Compared to other complete removable dentures, clasp dentures can be slightly adjusted.
- The oral mucosa and gingival papillae are partially released.
- Reliable fixation of the prosthesis speeds up adaptation.
Indications and contraindications
Installation of beam prostheses is indicated for:
- existing extensive defects: loss of several teeth (4–5);
- defects in the lateral part of the dentition, combined with minor defects in the terminal and anterior parts;
- the presence of defects in the end and side sections of the row;
- the need to splint abutment teeth by connecting them into one structure with a beam and artificial crowns;
- treatment of periodontal diseases with complications in the form of partial tooth loss.
Contraindications include:
– insufficient height of the supporting teeth, which does not allow reliable fixation of artificial crowns;
– a small gap between the toothless alveolar processes or the process and the antagonist tooth;
– fragile fixation in the absence of 1-2 teeth: support-retaining clasps are required to strengthen the structure.
Caring for a clasp denture
As already mentioned, the clasp prosthesis does not need to be removed at night. You can wash it in the morning after sleeping and in the evening after eating using a toothbrush. There are many products for caring for dentures, including rinses. The doctor can explain to you how they work and help you choose based on the materials of the clasp prosthesis.
Clasp dentures are not suitable for everyone. The condition of the teeth is important, as well as the general reaction to the materials from which the prosthesis is made. However, here too experts have found a way out, using a special type of plastic that does not cause allergies. The cost of such a clasp prosthesis will be a couple of thousand rubles more than a simple one, but you will be able to use it with great pleasure.
No patient can choose a denture option on their own. Only the dentist will determine the condition of the jaw and supporting teeth, and also select the type of clasp denture.
All you have to do is make an appointment with a dentist at our center and receive all the comprehensive information from him. Once you understand what a clasp prosthesis is, we are confident that you will give us a positive review, like many others.
Care, repair and service life
It is recommended to carry out hygiene procedures at least 2 times a day
The process of caring for a clasp-type prosthesis is simple, but requires regular attention.
Throughout the day, bacteria accumulate in the oral cavity, which leads to the development of inflammation of the mucous membrane and the formation of an unpleasant odor.
At night, salivation decreases, as a result of which plaque appears on the teeth and structures.
Timely cleaning of the mouth using special means: toothpaste and brush, dental floss, mouthwash balm will help get rid of complications.
It is recommended to carry out hygiene procedures at least 2 times a day, and after each meal you need to rinse your mouth with water.
To prevent the surfaces of the prosthesis from wearing out prematurely, it is better to purchase pastes with a mild action (not aggressive). Once every six months, you should contact a specialist for professional cleaning of the oral cavity, especially for coffee lovers, because the drink changes the color of artificial teeth (turn yellow).
During wear, the prosthesis may break. The reasons are different, but they are all provoked by a sharp mechanical impact on the structure. The possibility of repair depends on the severity of the product failure.
The main types of breakdowns include:
- broken metal fasteners;
- formation of a crack anywhere in the structure;
- detachment of artificial teeth;
- damage to the lock part;
- fracture of the prosthesis into two parts.
The service life of the prosthesis with proper care is 5-10 years.
Orthopedic dentistry (dental prosthetics). Certification tests with answers - option 100
content .. 98 99 100 101 ..Question No. 1
To form a circular valve, the prosthesis must overlap the valve zone by: 1) 2-6 mm; 2) 1-2 mm; (+) 3) 3-4 mm; 4) 0.5-1 mm; 5) up to 7 mm
Question No. 2
Elastic pads must meet the following requirements: 1) firmly connect to the rigid base 2) have low hygroscopicity 3) do not cause allergies 4) be pleasant to the taste 5) 1+2+3 (+) 6) 1+3+4
Question No. 3
surgical preparation of the prosthetic bed for prosthetics with complete removable dentures includes: 1) mandatory removal of the palatine torus 2) deepening of the vestibule and floor of the mouth 3) removal of cords and scars, movement of frenulum 4) elimination of exostoses 5) correct 2) 3), 4) (+ )
Question No. 4
To carry out the stage “Determination of the central relationship of the jaws in the complete absence of teeth,” the clinic receives: 1) Models with wax bases and occlusal ridges (+)
2) Wax bases with occlusal ridges 3) Models with wax bases and occlusal ridges fixed in the occludator 4) Models with wax bases and occlusal ridges fixed in the articulator 5) Models with wax bases and artificial teeth Question No. 5 The arc of the clasp
denture
is located relative to mucous membrane: 1) never touching (+) 2) always lightly touching 3) always tightly fitting 4) lightly touching when chewing 5) tightly touching when chewing
Question No. 6
For complete removable prosthetics, the most favorable are 1) dense mucous membrane (+) 1) thin mucous membrane 2) loose, pliable mucous membrane 3) mobile mucous membrane
Question No. 7
With complete loss of teeth in the lower jaw, bone tissue atrophy in the anterior section is more pronounced: 1) on the vestibular surface 2) on the crest of the alveolar part 3) lingual surface of the alveolar process (+) 4) palatal surface of the alveolar part
Question No. 8
The stage of checking the design of the prosthesis begins with: 1) determining the height of the lower part of the face 2) introducing the finished prosthesis into the oral cavity 3) fitting and applying the prosthesis 4) introducing wax bases into the oral cavity 5) assessing the quality of the construction on a plaster model in an occluder (+)
Question No. 9
with a one-sided slightly overhanging slope of the alveolar process, the vestibular edge of the complete removable denture should end: 1) on the passively mobile mucous membrane (neutral zone) (+) 2) actively mobile mucous membrane 3) fixed mucous membrane 4) does not matter
Question No. 10
If the fixation of a complete removable denture is not good enough due to the elongated boundaries of the base, it is necessary: 1) Take an impression and make a new denture 2) Correct the edges of the denture (+) 3) Clarify the boundaries of the denture with self-hardening plastic 4) Take an impression using the denture and reline in the laboratory 5) Reline with elastic base plastic
Question No. 11
The impression mass must have the properties 1) be harmless 2) not shrink before casting the model 3) give an accurate impression of the prosthetic bed 4) be easily inserted and removed from the patient’s mouth 5) true, 3.4 (+)
Question No. 12
Classification according to Lekholm and Zarb (1985) reflects the main phenotypes of the architectonics of the body and alveolar processes of the jaws and includes: 1) 1 class of bone quality 2) 2 classes of bone quality 3) 3 classes of bone quality 4) 4 classes of bone quality 5) 5 classes bone quality (5 degrees of atrophy) (+)
Question No. 13
Splinting of teeth 18, 17, 16, 15, 14, 13, 12, 11 corresponds to stabilization: 1) parasagittal 2) sagittal 3) frontal 4) along the arc 5) fronto-sagittal (+)
Question No. 14
When making artificial crowns, plaster models are fixed in: 1) occluder 2) articulator 3) esthesiometer 4) gnathodynamometer 5) correct 1) and 2) (+)
Question No. 15
with complete loss of teeth, the heads of the lower jaw move: 1) forward 2) posteriorly 3) downward 4) posteriorly and upward (+)
Question No. 16
A late local complication of injury to the maxillofacial area is: 1) ARVZ 2) asphyxia 3) traumatic osteomyelitis (+) 4) periodontitis 5) lower macrognathia
Question No. 17
To identify allergies to acrylic plastics, use: 1) exposure-provocative test 2) chemical silvering test 3) leukopenic test 4) correct 1) and 2) 5) correct 1), 2) and 3) (+)
Question No. 18
“Marbling” of the plastic base of the prosthesis appears when: 1) the expiration date of the monomer 2) the expiration of the polymer expiration date 3) violation of the polymerization temperature regime 4) non-compliance with the plastic preparation technology (+) 5) rapid cooling of the cuvette after polymerization
Question No. 19
Nonspecific factors that contribute to the development of an allergic reaction when using metal prostheses include: 1) corrosion processes 2) changes in the pH of saliva to the acidic side 3) abrasion processes 4) thermal effect 5) 1), 2) and 3 are correct (+)
Question No. 20
Types of occlusal curves: 1) sagittal (+) 2) transversal 3) horizontal
Question No. 21
the use of low-quality complete dentures can: 1) disrupt phonetics 2) cause marginal periodontitis 3) cause TMJ dysfunction 4) cause prosthetic stomatitis 5) true 1), 3), 4) (+)
Question No. 22
Pain on palpation anterior to the tragus of the ear indicates: 1) spasm of the lateral pterygoid muscle; 2) about spasm of the temporal muscle; 3) about arthritis; (+) 4) about temporal arteritis.
Question No. 23
in the complete absence of teeth, the progenic type of placement of artificial teeth is characterized by: 1) the type of plaster casting of the wax base into a ditch 2) the cross placement of the lateral teeth 3) the type of apparatus used for fixing the models 4) reducing the number of artificial teeth in the upper jaw prosthesis to 12 5) true 2.4 (+)
Question No. 24
Which direction of the clasp line is preferable in the upper jaw? 1) transversal 2) sagittal 3) diagonal (+)
Question No. 25
As a material for relining a removable denture, you can use: 1) thermoplastic mass 2) silicone corrective impression mass 3) elastic plastic (+) 4) zincoxyeugenol material 5) self-hardening plastic acrylic oxide
Question No. 26
When planning the holding arm of a clasp ...... is the main criterion 1) the design features of the clasp 2) the features of the material from which the clasp is made 3) the method of manufacturing the clasp (cast, bent) 4) the amount of possible maximum bending of the end of the clasp when passing through the equator of the tooth (+) 5 ) aesthetic advantages or disadvantages of the clasp
Question No. 27
To carry out the stage of “determining the central relationship of the jaws,” the clinic receives: 1) models with wax bases and occlusal ridges 2) wax bases with occlusal ridges 3) models with wax bases and occlusal ridges fixed in the occludator (+)
4) models with wax bases and occlusal ridges fixed in the articulator
Question No. 28
When treating bilateral end defects with supported prostheses, when the toothless part of the alveolar ridge on the lower jaw slopes to the distal side, it is recommended to use 1) support-retaining clasps 2) multi-link clasps ( +) 3) continuous clasps 4) load crushers 5) anti-tipping devices
Question No. 29
The main method of examining a patient in an orthopedic dentistry clinic is 1) clinical (+) 2) x-ray 3) biometric 4) rheographic 5) measurement of diagnostic models
Question No. 30
Treatment of wounded people with jaw fractures: 1) surgical 2) orthopedic 3) therapeutic 4) complex (+) 5) physiotherapeutic
Question No. 31
The grinding method is used for: 1) I form of the Popov-Godon phenomenon 2) II form of the Popov-Godon phenomenon 3) I and II forms of the Popov-Godon phenomenon (+) 4) increased abrasion of hard dental tissues
Question No. 32
The chewing test of S. E. Gelman shows: 1) the degree of grinding of 5 g of nuts after 50 chewing movements 2) the time required to complete 50 chewing movements 3) the degree of grinding of 5 g of almonds after chewing for 50 seconds (+)
4) degree of grinding of 0.8 g of nut after chewing until the swallowing reflex appears 5) time of chewing food
Question No. 33
When casting a plaster model and filling the cast with very liquid supergypsum leads to 1) an increase in plaster shrinkage (+) 2) a decrease in gypsum shrinkage 3 )to the formation of voids and pores in the gypsum model 4)to an increase in the surface roughness of the gypsum model
Question No. 34
Central occlusion and forced secondary occlusion (“habitual occlusion”) are distinguished 1) by the position of the articular heads in the fossae 2) when comparing the central relationship of the jaws with the relationship of the jaws with multiple closures of the teeth 3) take both signs into account (+)
Question No. 35
With repeated prosthetics, the adaptation time 1) lengthens 2) shortens (+)
Question No. 36
The sprues must extend from the main feeder at an angle of 1) 5-10o 2) 10-20o 3) 20-30o 4) 30-40o (+) 5) 40-50o
Question No. 37
The length of the main sprue should be 1) 5-10 mm 2) 10-15 mm (+) 3) 15-20 mm 4) 20-25 mm
Question No. 38
For the manufacture of a solid-cast frame of a supported prosthesis, the following is widely used: 1) stainless steel; 2) gold alloy; 3)chrome-nickel alloy; 4) chromium-cobalt alloy; (+) 5) silver-palladium alloy.
Question No. 39
What taper of the side walls of the cap is acceptable in a telescopic system? 1) 5 degrees (+) 2) 10 degrees 3) 15 degrees 4) 20 degrees
Question No. 40
The relationship of the jaws in the absence of teeth changes to: 1) orthognathic; 2) prognathic; 3) progenic; (+) 4) deep; 5) no changes.
Question No. 41
Occlusion is: 1) all possible closures of the dentition of the upper and lower jaws (+) 2) the position of the lower jaw relative to the upper in a state of relative physiological rest 3) all possible positions of the lower jaw relative to the upper 4) the ratio of toothless jaws 5) type of bite
Question No. 42
The guideline for placing the central incisors on the upper jaw is the location of: 1) the wings of the nose 2) the frenulum of the upper lip (+) 3) the line of the aesthetic center 4) the nasolabial folds.
Question No. 43
The depth of damage to the hard tissues of teeth in the II degree of increased abrasion reaches: 1) up to 1/3 of the length of the crown 2) from 2/3 of the length of the crown to the neck of the tooth 3) from 1/3 to 2/3 of the length of the crown (+) 4) from 1 /3 to 1/2 crown length 5) to 1/4 crown length
Question No. 44
To identify supercontacts in the posterior contact position, the lower jaw is shifted: 1) distally (+) 2) into the right lateral occlusion 3) into the left lateral occlusion 4) into the anterior occlusion 5) by opening the mouth within 1-2 cm
Question No. 45
To obtain a functional impression in case of complete loss of teeth, an impression tray is used: 1) standard made of metal, smooth 2) standard made of plastic, perforated 3) individual made of elastic plastic 4) individual made of hard plastic (+) 5) standard made of plastic with refined edges wax
Question No. 46
Type II of the toothless lower jaw according to Keller is characterized by: 1) the alveolar processes are atrophied slightly and evenly; 2) pronounced atrophy of the alveolar processes in the lateral sections with relative preservation in the anterior section; 3) pronounced atrophy of the alveolar process in the anterior part; 4) the alveolar processes are atrophied evenly, the places of muscle attachment are located almost at the level of the alveolar ridge. (+)
5) there is no correct answer.
Question No. 47
The glandular zone of compliance of the mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed, according to Lund, is located in the area of: 1) sagittal suture, has a slight submucosal layer, low compliance (+)
2) the alveolar process, has a slight submucosal layer, low compliance 3) the distal third of the hard palate, has a pronounced submucosal layer, has the greatest degree of compliance 4) transverse folds, has a submucosal layer, has an average degree of compliance 5) the middle third of the hard palate, the submucosal layer is insignificant , high degree of compliance
Question No. 48
Incorrectly adjusted interocclusal contacts of a lamellar prosthesis can lead to 1) injury to the mucous membrane in the center of the alveolar process (+)
2) trauma to the mucous membrane along the edge of the prosthesis 3) to bedsores in the area of bone protrusions 4) to hypertrophic growth of the mucous membrane
Question No. 49
Etiological factors of increased abrasion associated with functional overload of the teeth: 1) nutritional deficiency 2) bruxism (+) 3) impact hygiene products 4) chemical exposure 5) 1) and 4) are correct 6) there are no correct answers
Question No. 50
The angle of the sagittal incisal path is 1) 11 degrees 2) 17 degrees 3) 30-33 degrees 4) 40-50 degrees (+) 5) 100-110 degrees
Question No. 51
The purpose of the root protection of a pin tooth is 1) without root protection it is impossible to connect the pin with the root part 2) to exclude trauma to the gingival margin 3) protects the tooth root from destruction and promotes fixation (+) 4) reduces functional overload, being a shock-absorbing link in the pin-tooth root system
Question No. 52
the clinical picture of a toothless mouth is characterized by: 1) atrophy of the alveolar parts of the jaws and loss of fixed height of the lower part of the face (+)
2) topography and size of dentition defects 3) condition of the mucous membrane covering the prosthetic bed
Question No. 53
The obligatory symptom of a fracture of the base of the skull is: 1) liquorrhea (+) 2) nosebleeds 3) pathological mobility of the lower jaw 4) pathological mobility of the upper jaw 5) bleeding from the external auditory canal
Question No. 54
Diseases leading to defects of the maxillofacial area: 1) osteomyelitis 2) actinomycosis 3) tuberculosis 4) periodontitis 5) correct 1), 2) and 3) (+)
Question No. 55
an increase in the interalveolar distance when determining the central ratio of the jaws in edentulous patients is accompanied by the following symptoms: 1) knocking of the teeth during eating and speaking 2) rapid fatigue of the masticatory muscles 3) deepening of the nasolabial folds 4) when the lower jaw is in functional rest, there is no clearance between the dentitions 2-4 mm (+)
Question No. 56
when placing teeth in a complete removable denture on the lower jaw, they are guided by: 1) the middle of the ridge of the alveolar part (+) 2) Pound's triangle 3) mylohyoid lines 4) the angle of intersection of the interalveolar height with the occlusal plane
Question No. 57
For cement fixation of a bridge on implants, the following cements are used: 1) Silicate; 2) Silico-phosphate; 3)Double curing; (+) 4) With silver; 5) Water dentin
Question No. 58
If the tooth being prepared is excessively shortened, 1) a decrease in the aesthetic standard of the prosthesis, 2) a decrease in the functional value of the prosthesis, 3) a decrease in fixation and frequent de-cementation of the prosthesis (+) 4) a decrease in diction 5) all of the above can be observed
Question No. 59
Type I atrophy of the alveolar process of edentulous jaws according to Oksman: 1) uneven, moderate 2) uniform, insignificant (+) 3) uniform, moderately expressed 4) uniform, strongly expressed 5) uneven, moderately expressed
Question No. 60
The curves described by the teeth during transversal movements of the lower jaw are: 1) Gothic angle (+) 2) incisal path 3) Bennett movement 4) Bennett angle
Question No. 61
The rapid occurrence of restriction of mouth opening after injury indicates in favor of: 1) dislocation of the articular disc; 3) dislocation of the lower jaw; 3) traumatic arthritis; (+) 4) spasm of the masticatory muscles.
Question No. 62
Typical complaints for toxic stomatitis caused by metal prostheses: 1) burning of the tongue to causalgia 2) hypersalivation 3) disturbance of nervous status 4) correct 1) and 2) 5) correct 1), 2) and 3) (+)
Question No. 63
The name occlusal plane corresponds to the definition: 1) a plane passing through the cutting edge of the central incisors and the distal cusps of the second molars separately for each of the jaws (+)
2) a plane passing through the tragus of the ear and the lower edge of the wing of the nose 3) curvature of the occlusal plane in the transversal direction 4) a plane passing through the tragus of the ear and the lower edge of the orbit 5) curvature of the occlusal plane in the sagittal direction.
Question No. 64
According to Rumpel’s classification, removable lamellar dentures according to the method of transmitting chewing pressure are classified as: 1) physiological 2) semi-physiological 3) non-physiological (+) 4) combined 5) supported
Question No. 65
in a patient with complete loss of teeth, type IV of the upper and lower jaws is determined according to Oksman. When checking the wax models, the contact of the front teeth and the gap between the lateral teeth are noted. What is the likely cause of teeth misalignment? 1) significant compression and displacement of the mobile mucous membrane when taking a functional impression 2) compression of the mucous membrane by the wax base when determining the central relationship of the jaws 3) displacement of the upper wax base forward 4) lack of tight contact of the occlusal ridges in the lateral sections when determining the central relationship of the jaws (+)
Question No. 66
Stability of the prosthesis during chewing movements: 1) retention 2) stabilization (+) 3) adaptation 4) polymerization
Question No. 67
When studying the electrical excitability of intact teeth, the most sensitive points are noted 1) for the frontal teeth - in the middle of the cutting edge, for premolars - at the top of the buccal cusp, for molars - at the top of the anterior buccal cusp (+)
2) for frontal teeth - on the oral concavity of the crown between the cusp and the incisal edge, for premolars - at the top of the oral cusp, for molars - at the top of the anterior oral cusp 3) for frontal and lateral teeth in the area of the neck of the tooth
Question No. 68
When casting a plaster model and filling the cast with very liquid supergypsum leads to 1) an increase in gypsum shrinkage (+) 2) a decrease in gypsum shrinkage 3) the formation of voids and pores in the plaster model 4) an increase in the surface roughness of the gypsum model
Question No. 69
In lateral occlusions on the working side there may be contacts: 1) group buccal cusps of chewing teeth 2) canines and lateral incisors 3) incisors and buccal cusps of premolars 4) incisors 5) buccal cusps of chewing teeth or canines (+)
Question No. 70
The location of the shoulders of the intraosseous implant in relation to the cortical plate: 1) the shoulders are located at the level of the cortical plate; 2) above the cortical plate; 3) below the cortical plate by 2-3 mm; (+) 4) above the cortical plate by 2-3 mm; 5) depending on the condition of the bone.
Question No. 71
Nonspecific factors of allergization of the body when using removable lamellar dentures include: 1) disturbance of heat exchange (increase in temperature under the denture) 2) mechanical trauma 3) discrepancy between the prosthesis and the prosthetic bed 4) true 1) and 2) 5) true 1), 2) and 3 ) (+)
Question No. 72
the most favorable type of atrophy of the lower jaw for prosthetics is: 1) slight uniform loss of the alveolar part (+) 2) pronounced uniform loss of the alveolar part 3) pronounced loss in the anterior section 4) uneven pronounced loss
Question No. 73
When checking the design of a complete removable lamellar denture, there is a lack of tight fissero-tubercular contact during movements of the lower jaw, the reason is: 1) overestimation of the height of the lower part of the face 2) fixation of anterior occlusion 3) fixation of lateral occlusion 4) crushing of the bite ridge 5) displacement of the bite ridge ( +)
Question No. 74
When making a cantilever bridge, the negatives are 1) the need for depulpation of abutment teeth 2) preparation of a large number of abutment teeth 3) unsatisfactory aesthetic quality 4) the presence of a tilting moment on the abutment teeth (+) 5) grinding of a large number of tissues of abutment teeth
Question No. 75
the height of the lower part of the face with a central relationship of the jaws compared with the height with relative physiological rest: 1) equal 2) more 3) less (+)
Question No. 76
Indications for the manufacture of a pin tooth are: 1) fracture of the angle of the cutting edge of the tooth 2) destruction of the tooth root by 1/2 3) carious cavity of class I according to Black 4) destruction of the tooth crown at the gum level (+) 5) tooth mobility of the second degree
Question No. 77
Titanium density: 1)10.2 g/cm3; 2) 2.7 g/cm3; 3)4.8 g/cm3; (+) 4) 8.9 g/cm3; 5) 5.5 g/cm3.
Question No. 78
an increase in the interalveolar distance when determining the central ratio of the jaws in edentulous patients is accompanied by the following symptoms: 1) shortening of the upper lip 2) deepening of the nasolabial folds 3) knocking of the teeth during eating and speaking, and rapid fatigue of the masticatory muscles (+)
Question No. 79
Functional changes in the temporomandibular joint after complete loss of teeth: 1) atrophy of the articular tubercle 2) flattening of the articular fossa 3) fiberization of the intra-articular disc 4) thinning of the intra-articular disc 5) displacement of the articular head of the lower jaw posteriorly and upward (+)
Question No. 80
To diagnose TMJ disease, the following methods are used: 1) analysis of functional occlusion 2) x-ray examination 3) electromyographic study 4) correct 1), 2) and 3) (+)
Question No. 81
The retention depth…… for the Ney clasp No. 1 is optimal 1)0.25 (+) 2)0.5 3)0.75
Question No. 82
The following have the least pain sensitivity: 1) oral surface of the gums (+) 2) vestibular surface of the gums 3) soft palate 4) root of the tongue 5) floor of the mouth
Question No. 83
Name the main disadvantage of a bent clasp: 1) high strength 2) high rigidity 3) high elasticity 4) high ductility 5) ease of manufacture 6) complexity of manufacture (+)
Question No. 84
When making a metal-ceramic prosthesis, the anterior teeth are 1) prepared with a circular shoulder 2) prepared with a vestibular shoulder (+) 3) prepared with proximal shoulders 4) without a shoulder
Question No. 85
Factors contributing to the emergence and development of arthrosis: 1) congenital shortening of the lower jaw branch 2) underdevelopment of the articular head on one side 3) violation of functional occlusion 4) macrotrauma of the maxillofacial area 5) 1), 2) and 3 are correct (+) 6 )there are no correct answers
Question No. 86
During an X-ray examination, the following is noted: bone tissue dystrophy, characterized by a decrease in the number of bone crossbars per unit of bone volume, thinning and complete resorption of some of these elements 1) osteolysis 2) bone tissue atrophy 3) osteoporosis (+) 4) osteonecrosis
Question No. 87
with complete loss of teeth, the heads of the lower jaw move: 1) forward 2) posteriorly 3) downward 4) posteriorly and upward (+)
Question No. 88
The endurance limit of premolar periodontium to pressure, i.e. threshold loads, the increase of which leads to pain 1) 25-30 kg (+) 2) 35-40 kg 3) 45-50 kg 4) 55-60 kg 5) 65-70 kg 6) 75-80 kg
Question No. 89
For the orthopedic stage of treatment of patients with increased tooth wear, the following is used: 1) a plate with a vestibular arch 2) a plate with an inclined plane 3) a plastic aligner (+) 4) a Porta splint 5) a plate with an orthodontic screw
Question No. 90
Chips or cracks of the ceramic coating in the cervical area of the supporting crown are caused by 1) incorrect modeling of the frame of the intermediate part of the prosthesis 2) openwork intermediate part of the prosthesis 3) incorrect occlusal contacts in the finished prosthesis 4) overheating of the metal when palletizing the finished prosthesis (+) 5) too smooth surface prosthesis frame
Question No. 91
to obtain a functional impression in case of complete loss of teeth, the following is used: 1) standard tray 2) individual tray (+)
Question No. 92
When the jaws are positioned in a central relationship, the articular heads are... 1) in the upper, non-stressed position in the corresponding fossae (+) 2) in the lower non-stressed position in the corresponding fossae 3) in the anterior non-stressed position in the corresponding fossae 4) in the posterior non-stressed position in the corresponding fossae pits 5) in an average relaxed position in the corresponding pits
Question No. 93
At what index of destruction of the occlusal surface of the tooth is it recommended to use pin core structures? 1) 0.2 – 0.3 2) 0.3 – 0.6 (+) 3) 0.6 – 0.8 4) more than 0.8
Question No. 94
Indications for the manufacture of a composite bridge: 1) mobility of the supporting teeth 2) terminal defect of the dentition 3) greater convergence of teeth limiting the defect (+) 4) large extent of the defect of the dentition 5) low clinical crowns of the supporting teeth
Question No. 95
According to the classification of cavities in the crowns of teeth according to G. Black, the fifth class includes: 1) on the proximal surfaces of the anterior teeth 2) in the cervical zone of all teeth (+) 3) in the natural fissures of the chewing teeth 4) on the proximal surfaces and corners of the anterior teeth on the proximal surfaces
Question No. 96
Cold sensitivity in the direction from the anterior to the posterior parts of the oral cavity: 1) does not change 2) increases 3) decreases (+) 4) first increases, then decreases 5) changes in waves
Question No. 97
when selecting artificial teeth, the orthopedic dentist must take into account: 1) skin color 2) face shape 3) patient’s gender 4) patient’s age (+) 5) type of nervous system 6) shape of the alveolar arch
Question No. 98
unfavorable factors that complicate prosthetics with complete edentia are: 1) sharp and uneven atrophy of the alveolar process. 2) narrow thin ridge of the alveolar process 3) sharp bony protrusions (exostoses and sharp mylohyoid lines 4) in the presence of “mobility” of the ridge 5) correct1,2,3,4 (+)
Question No. 99
If the tooth being prepared is excessively shortened, 1) a decrease in the aesthetic standard of the prosthesis may be observed, 2) a decrease in the functional value of the prosthesis, 3) a decrease in fixation and frequent de-cementation of the prosthesis (+) 4) a decrease in diction 5) all of the above.
content .. 98 99 100 101 ..