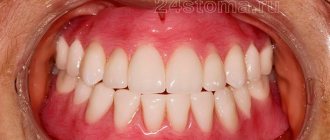
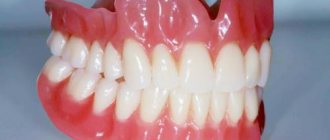
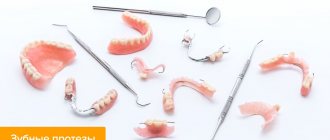
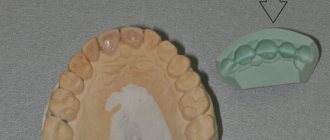
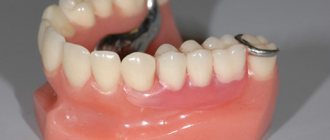
Clasp prosthetics today can be called a popular service in a dental clinic. It has been used in orthopedics for quite a long time, so specialists and patients are familiar with this type of prosthesis.
Clasp dentures are installed on all dentitions.
In translation, “bugel” is an arc, and “bugel” is something that has an arc. Structurally, clasp dentures are made with a metal or plastic arch of the required type. In addition to the arch, the prosthesis has a base that copies the gum and fixation elements (hooks, crowns, locking mechanisms).
The most common type of fixation of such a prosthesis is clasp.
What are clasp dentures and what do they look like?
These are removable structures used to restore included and terminal defects of the dentition. They are lighter and more comfortable than plate prostheses with a “sky”, and are in demand in cases where prosthetics on implants cannot be performed.
With the help of a clasp prosthesis, chewing function and aesthetics are restored both in the anterior and lateral sections of the jaw. In the smile zone, they most often use prosthetics from one to three consecutive teeth, and in the lateral sections - longer areas (3-5 missing teeth on one or both sides).
Externally, it is a simple design consisting of a metal arch and plastic imitation of gums with artificial teeth. The absence of a “sky”, characteristic of plate dentures, makes the clasp a lighter and more compact option. You get used to it faster and feel less discomfort. It does not interfere with conversation and is hardly noticeable in the mouth.
Features of the clasp
A clasp denture is a conditionally removable structure that fully restores teeth and all their functions. It is fixed in the oral cavity to the supporting crowns in several ways: clasps, crowns, locks.
The prosthesis consists of a metal frame, a plastic base with artificial crowns. The frame consists of an arch, saddles (for crowns) and support-retaining components. The size and location of the arch depend on the defect in the dentition, the jaw, the shape of the alveolar process, the individual anatomical features of the patient’s oral cavity, and the condition of the mucous membrane. On the upper jaw it has a width of 8-10 mm and is flatter. On the bottom – 4-6 mm and semi-convex shape. This form ensures convenient use and quick adaptation to the design.
Due to the presence of the arch, the prosthesis has a very small base, the patient’s palate remains open - the taste and thermal perception of food is not disturbed. The prostheses are quite lightweight, but very durable and easy to use.
A big advantage is the possibility of using it for diseases of periodontal tissue and mobility. Unlike other structures, it does not loosen, but strengthens and splints the supporting teeth. The components of the structure correctly distribute the chewing load across the jaw. For high-quality clasp prosthetics, you need at least 5 healthy teeth for support.
What does a clasp prosthesis consist of, what materials are used in its manufacture?
A modern clasp prosthesis, made from high-quality materials, looks quite aesthetically pleasing. It consists of four parts.
- Frame (clasp). Durable, thin and light. It includes: a cast arch that evenly transfers the load to the jaw in places of missing teeth, slowing down the processes of bone resorption;
- mesh for attaching artificial teeth, allowing you to create a single structure;
- fasteners (clasps, beam structures, telescopic crowns, anchor and magnetic clamps) for rigid, elastic or hinged fastening on supports (healthy teeth, implants, crowns);
- splinting elements (according to indications - claw-shaped hooks, clasps, Elbrecht splints).
Materials for making a prosthesis
- Frame, fasteners. Using classical technology, the base of the structure is made of metal using modern casting methods. Depending on individual tolerance and other criteria, alloys of noble metals, cobalt-nickel-chrome with minor impurities, as well as titanium are used.
Currently, there are more modern materials - thermoplastic polymers, which are not inferior in strength to metal, but are more elastic and comfortable. The most famous are ACETAL or Dental D from QuattroTi.
- Base. It is made using classical technology - hot polymerization from acrylic, and in modern versions, like the frame, from thermopolymers.
- Teeth. Plastic, composites.
The choice in favor of one or another material is determined by the individual sensitivity, wishes and financial capabilities of the patient.
Types of clasps
Clasp-type structures are equipped with the following types of clasps, depending on the case:
- Supporting. Pressure distribution with such clasps is carried out on the mucous membrane and on dental supports.
- Retaining hooks. When the clasps settle, all the pressure falls on the mucous membrane
- Support-retaining clasps. Combines characteristics of both types
By shape and method of girth:
- With one or two arms, with one link, double, in the form of a ring
- Flat, tape
- Round or semicircular shape
By production:
- Molded (no elasticity)
- Bent (according to blanks)
Pros and cons of clasp prosthetics
This type of replacement structure is the pinnacle of removable prosthetics. On the one hand, it can be used to restore a large number of lost teeth. On the other hand, even in difficult cases (for example, two teeth are missing in front, three on the right, and five on the left), this is still a light and comfortable prosthetic system.
The following are responsible for comfort during clasp prosthetics:
- a very thin arch that presses tightly against the palate when worn;
- reliable fasteners providing rigid fixation.
Thanks to this, the prosthesis does not play during conversation, chewing and is practically not felt by the patient. This is a truly reliable type of prosthetics.
The main advantages of clasp dentures
- Functionality. A rigid type of fixation with support not only on the gums, but also on the teeth, completely restores chewing function.
- Strength. The presence of a metal frame makes it possible to install prosthetic teeth even with severe violations of the integrity of the dentition.
- Hygiene. Depending on the type of fixation, clasp dentures are removable and conditionally removable. Some are easy to clean at home, while others can be cleaned during hygienic cleaning at the dental clinic.
- Durability. Durable modern materials and uniform load distribution make the prosthesis reliable, allowing it to be used for 5–10 years.
- Aesthetics. Correct selection of the shade of the polymer base and dental crowns makes the artificial part indistinguishable from the patient’s own teeth. Options with attachments, telescopic crowns and thermopolymers are invisible in the smile area.
- Bioinertness. Thanks to titanium, as well as modern thermoplastics, replacing lost teeth does not harm the body. The materials are hypoallergenic and do not interact physically or chemically with the oral environment. This means that the taste sensations are completely preserved.
- Convenience. The minimal size of the prosthesis (thin arch and only one layer of polymer) allows you to not feel it when wearing it, does not affect diction, does not cause discomfort or a gag reflex, so the prosthesis can be worn around the clock.
- Splinting. This type of prosthetics can be used even with loose gums and loose supporting teeth. Adding special splints to the frame will help keep the supporting teeth in the desired position, prolonging their life.
- Maintainability. In most cases, a prosthesis can be repaired if it breaks. Only some types of fasteners cannot be restored.
The production technology has been worked out to the smallest detail, and is optimal in terms of price and time. This is also an important advantage.
Disadvantages of clasp dentures
- High price. If we compare the clasp with a conventional plate prosthesis, the difference in price attracts attention. It is formed taking into account complex manufacturing technology and the use of expensive materials. This cannot be considered a real disadvantage, because better quality means additional comfort and aesthetics, as well as 2-3 times longer service life.
- Grinding teeth for crowns. In some cases, it may be necessary to prepare healthy tissue and remove the dental nerve to form a support.
- Not used for edentulous patients. In case of complete absence of teeth, our dentist will offer more cost-effective prosthetics using All-on-4 implants.
Cheaper options have additional disadvantages, including the effect of galvanization and allergies to metal, discomfort for 1–2 weeks during the adaptation period, less aesthetics of fasteners, as well as bone resorption, which can only be avoided by prosthetics on implants.
Clasp denture with clasps –
Clasp denture with clasp fixation is one of the most popular types of removable dentures among patients (Fig. 1-11). Clasps are the branches from the metal frame of the prosthesis that clasp the remaining supporting teeth from different sides, thereby ensuring reliable fixation of the prosthesis in the oral cavity. But clasps perform not only a holding function, but also a supporting one.
This means that they ensure the distribution of the chewing load in such a way that it is transferred from the prosthesis not only to the gums, but also to the supporting teeth. As a result, approximately 1/3 of the chewing load of the clasp is transferred from the prosthesis to the supporting teeth, and the remaining 2/3 of the load is distributed from the base of the prosthesis to the gums. But with dentures made of plastic or nylon, the entire chewing load goes only to the gums - which is why pain occurs when chewing food.
Clasp denture with clasps: photo
As you already understood, clasps are in most cases made of metal, and that is why this type of clasp prosthesis has one big disadvantage. The fact is that metal clasps will be clearly visible if they fall into the smile line (Fig. 10). Of course, in some situations, the dental technician can place the clasps on the denture in such a way that they do not fall into the smile line, but, unfortunately, this is not always possible for every patient.
Some way out of this situation may be to replace the retaining metal clasps that fall into the smile line with nylon ones. These clasps can be given any color (white or pink), and they are almost invisible when you smile. But it is also impossible to make all the clasps of the prosthesis only from nylon, because... nylon has high elasticity, which means the prosthesis will be less secure in the oral cavity.
Clasp prosthesis with clasps: video 1-2
Indications and contraindications for installation
The choice in favor of clasp dentures is made in the presence of dentition defects, both single (1-3 teeth - Quadrotti’s “butterfly”), and multiple – included and terminal bilateral.
Contraindications:
- metal allergy;
- complete absence of teeth;
- atrophic processes in the jaw;
- inflammatory diseases of the gums and periodontium;
- low height of supporting teeth, insufficient for prosthetics.
Many contraindications apply to classic metal prostheses. The use of technologically more advanced thermoplastic options expands the range of indications for installation.
Advantages and disadvantages
With high-quality prosthetics, taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient, the clasp has many advantages:
- Excellent functional properties;
- Full restoration of functions;
- Strong fixation;
- Possibility of treatment in the absence of varying numbers of teeth;
- Possibility of prosthetics for diseases of periodontal tissues, mobility;
- Protection of periodontal tissue from unwanted load;
- Splinting;
- Elimination of horizontal pressure and proper distribution of chewing load;
- Support-retaining fixation elements prevent subsidence of the prosthesis;
- During use, prevention of alveolar ridge atrophy occurs;
- Possibility of prosthetics for location anomalies (tilting, rotation of teeth);
- Excellent fixation and stabilization;
- There is no need to prepare the abutment teeth;
- With the help of a prosthesis (onlays, splinting), you can change the height of the bite;
- Good aesthetics and appearance of the structure;
- The clasp takes up little space in the oral cavity;
- Tactile, taste or temperature sensitivity is not impaired;
- Quick habituation process;
- Simple hygienic care;
- Long service life;
- The prosthesis can be adjusted;
- The strong position of the clasp gives self-confidence to each patient, the use of the design is psychologically comfortable.
The disadvantage of the clasp is the complex manufacturing technology, which requires the skills of a doctor, special equipment, and materials from a dental technician.
Manufacturing and installation process, stages of work
Preparation
The creation of a clasp prosthesis begins with the planning stage. The patient's oral cavity undergoes a thorough examination. Orthopantomography and CT scanning of the jaw will help to examine all its anatomical features and ongoing processes.
It is important to know:
- Causes of tooth loss. This will help protect the supporting crowns from caries, as well as periodontal and periodontal diseases.
- The degree of their mobility. If necessary, the frame is supplemented with hooks, tires and other fasteners.
- Presence of jaw atrophy. In advanced cases, clasp prosthetics is not recommended. Only implantation can help.
If any diseases are revealed during the examination, sanitation of the oral cavity is required before prosthetics. Professional hygienic cleaning is also recommended, which will reveal the natural color of the patient’s tooth enamel in order to correctly select acrylic, thermopolymers or composite materials.
Impressions
To work, it is necessary to obtain two-layer anatomical impressions, with the help of which working models are made and the degree of fit, load distribution, compression level and other important parameters of the functionality of the prosthesis are subsequently controlled. The impression is taken using an individual tray.
Working model
Using super plaster, two working models are created based on the impression. One of them is used in the process of planning and modeling the frame, as well as installing dental crowns - up to the complete production of a partial denture. And the second is needed to check the cast metal frame.
Subsequently, using the plaster model as a basis, an identical one is made in a dental laboratory, but from refractory ceramics. With its help, wax modeling of the frame is carried out, taking into account all clasps, branches, retention meshes, fastening processes, occlusal pads and other elements, and subsequent metal casting is also performed.
Frame formation
Making a refractory ceramic model on top of the primary one with a wax model of the frame allows you to create space for pouring metal in exact accordance with the frame drawings. Subsequently, in an induction furnace or using other technology and equipment, the metal is heated to the required temperature and poured into the mold.
After cooling, the surface is processed to remove mold residues and polished until an ideal fit to the working model is achieved, and then in the oral cavity during fitting.
Basic requirements for this:
- compliance with original drawings;
- absence of defects (sagging, cavities);
- ideal fit on the support and prosthetic bed;
- no problems when closing the dentition.
Formation of the base and installation of dental crowns
Artificial teeth are installed on a finished metal frame using a wax roller, and then the base of the clasp denture is modeled, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s gums (size of interdental papillae, periodontal ridges).
Then, after checking the correctness of the created design by trying it on with the patient, the prosthesis is plastered and the wax is replaced with acrylic. The finished result must be aesthetic and correspond to the drawing conceived at the very beginning.
Checking the prosthesis for fit and installation
The finished prosthesis is tried on a model, and then the fit in the oral cavity is assessed. The result is considered ideal if the prosthesis is as similar as possible to the tissue in the patient’s oral cavity. It must be perfectly polished, match the color scheme of natural tooth enamel and periodontal tissues, fit accurately onto the support and prosthetic bed, and ensure ideal occlusion. After the final fitting, the finished product is polished and then secured in the patient’s mouth.
Consultation
The dentist at our clinic will definitely instruct the patient on how to care for the clasp denture in order to maximize its service life. Will answer any question and remind you of the need for professional hygienic cleaning of dentures. This will save artificial teeth for many years.
Stages of prosthesis manufacturing
Making clasps is a long, step-by-step process. The device is created for each patient using casts of his jaws.
The stages of prosthesis manufacturing are divided into clinical and laboratory.
The clinical stage involves
- Examination of the patient. The condition of the oral cavity and dentition is analyzed, the type of occlusion is determined, support units are selected, and a schedule for eliminating the defect, if any, is drawn up. Installation of a prosthesis is carried out only after complete recovery of detected oral diseases.
- Preparation of supporting units for prosthetics;
- Taking impressions of jaws to make diagnostic and auxiliary models. Correction and identification of deficiencies is done during a trial fitting. Deficiencies are corrected in the laboratory;
- Final placement of the structure, checking balance.
After receiving the impressions, the specialist begins manufacturing the device. The stages of manufacturing a clasp prosthesis in laboratory conditions are as follows:
- A diagnostic version of the model is created from marble plaster. The specific structure of the patient’s oral cavity must be taken into account.
- The type of bite is modeled by correctly placing the jaws relative to each other. The pressure on the units that are planned to be used as reference is measured.
- The diagram of the future design is presented on the layout. The same model simulates the process of grinding teeth-supports.
- A model of the system frame is being developed, as well as its casting.
- Artificial chewing parts are placed on wax balls, and a row of restored teeth is formed from them.
- The resulting structure is placed in a plaster mold and melted. The wax is removed and an acrylic mass is poured in its place.
- All parts are combined into one structure. Grinding and polishing is carried out. The finished product is sent to an orthopedic dentist to be fixed in the patient’s mouth.
The process of adaptation to the prosthesis occurs without discomfort. The unusual sensations after the installation of the structure pass quite quickly.
How clasp dentures are attached, their types, methods of fixation
Artificial structures are fixed using four main methods:
- adhesion. This is the name for the process of adhesion of two surfaces. In a clasp, it is acrylic or thermoplastic on one side, and the mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed on the other. This effect is enhanced by the presence of oral fluid;
- adhesion. One of the types of adhesion, when there is stronger adhesion between the molecules of the liquid and the surface during prosthetics than the intermolecular adhesion force of the oral fluid;
- anatomical retention. A number of structural features of the jaws make it possible to fix and hold the prosthetic structure in the oral cavity. These are the alveolar parts, maxillary cusps, interdental spaces, perigingival zone of the crowns;
- artificial fixation. It is carried out using manually created fastening elements. Among them, the following retainers are distinguished: Straight, located on the supporting teeth. Their task is to prevent the prosthesis from moving vertically.
- Indirect, located on the periphery of the structure. Also called kipmaiders. Prevents the structure from falling off. These include continuous clasps, occlusal overlays, and special extensions.
Let's consider all the options for artificial fixation in more detail.
On clasps
These are support-retaining clamps that have been used in prosthetics since 1926. Since their introduction, they have significantly expanded the possibilities of replacing lost teeth.
The structure of clasps is very diverse. They usually consist of two pointed arms and an occlusal pad, but different variations are possible depending on the purpose and purpose of fixation (two pads and an extended arm, multi-link splinting options, etc.).
Classification of clamps is carried out according to:
- principle of creation (bent, cast);
- material (plastic, metal);
- cross-sectional shape (round, ribbon, semicircular);
- rigidity of fixation (rigid, elastic, hinged);
- functionality (retaining, supporting, combined);
- degree of coverage of the dental crown (2-arms, 1-arms, flip-flop, double, multi-link);
- location of the shoulder (dental, alveolar, combined).
There are several requirements for clasps. They should not:
- harm aesthetics;
- injure periodontal tissues;
- interfere with the closure of the dentition;
- influence the physicochemical constancy of the environment.
They must also be able to be reactivated.
On locks (attachments)
Commonly used mechanical fasteners. Used for stabilization and retention. They consist of two parts - patrix and matrix. Functions – transmit the load through the axes of the teeth-supports into the periodontal tissue, participate in the redistribution of chewing pressure.
Pros - they fix and stabilize better than clasps. Higher hygiene and aesthetics, mechanical reliability and convenience. They allow you to create bridges of high quality and aesthetics when prosthetizing included defects in the smile area.
They are actively used in cases where increased demands are placed on dentures in terms of aesthetics, if there are secondary deformations of the dentition, atypical position and high crowns of supporting teeth.
On telescopic crowns
A fixation system consisting of two crowns - external (tooth-shaped) and internal (looks like a cap that is placed on prepared supporting tissues). Based on the manufacturing method, telescopic crowns are divided into stamped (simpler) and cast (high-quality), and based on the overlapping supports - closed, open and combined.
Plus - more reliable redistribution of load along the axis of the supports during operation. The downside is the need for significant preparation of the supporting teeth.
Beam system
The prosthesis is secured with this type of fixation by connecting its fixed and removable parts. The first is placed on the tops of crowns or prepared tissues of supporting teeth and has the form of a beam with a rounded cross-section. The second, removable, is located inside the prosthetic frame and is tightly fixed to the beam.
Pros – actively used for periodontal diseases. Recommended in the presence of partial edentia, single supporting symmetrical teeth, as well as a long-term defect in the lateral part of the jaw.
On anchors
This is a special type of fixation that works on the principle of a clothing button. The anchor consists of two fastening elements – a male and a matrix. Most often, the first is placed on the supporting tooth, and the second on the structure.
Pros: miniature size. Due to this, the anchors can be placed in areas of the base inaccessible to other clamps. Disadvantages - rapid wear during use (when removing/putting on).
Clasp denture for the upper jaw –
The clasp denture for the upper jaw will also have a metal arch, which can occupy an anterior, middle or posterior position on the hard palate, or be “ring-shaped”. In the latter case, the arc will be located along the perimeter of the hard palate, leaving its central part open. The position of the arch is of great importance for comfortable chewing, diction, and preservation of taste sensations. But the choice will depend not on your preferences, but on the clinical situation in the oral cavity.
For example, from – 1) the number and location of missing teeth, 2) the relief of the palate, more precisely, the severity of the torus and the height of the vault of the palate, 3) the severity of the patient’s gag reflex. In terms of comfort, the best option is the rear position of the arch, i.e. in the projection of the chewing group of teeth (not reaching 4-5 mm to the border of the hard and soft palate). In this case, the arc will not interfere with the tongue, diction will not suffer, the usual comfort when chewing food will remain, and the expression of taste sensations will not suffer.
Options for clasp dentures for the upper jaw –
Important differences between clasp dentures and other types of dentures:
But above we have not yet listed all the advantages - why patients love clasp dentures. The fact is that a clasp denture (better than all other types of removable dentures) will allow you to chew food painlessly and efficiently. This possibility is achieved through special systems for attaching the prosthesis to the supporting teeth - these can be support-retaining clasps, or special micro-locks (attachments), or so-called “telescopic crowns”.
The fact is that conventional dentures made of acrylic plastic transfer chewing pressure - not to the remaining teeth, but to the gums under the plastic base of the denture. This leads to pain when chewing, as well as accelerated atrophy of the bone tissue under the denture. A clasp prosthesis, due to clasps, attachments or telescopic crowns, is able to transfer most of the chewing pressure - precisely to the supporting teeth, and not to the tissue under the base of the prosthesis.
Special clasp-type prosthetic structures
Clasp prosthesis Quadrotti
Produced using the unique patented Quattro Ti technology since 1986. The prosthesis is based on a thermopolymer (nylon-based plastic). There is no metal. Thanks to this, the prosthesis has many advantages:
- hypoallergenic;
- highest aesthetics;
- chemical inertness;
- short adaptation period;
- complete biocompatibility;
- no gum irritation;
- installation without tooth preparation.
Attention. Due to the flexibility of the design, its significant advantage is that it can be used by those who engage in boxing, wrestling and other traumatic sports, as well as those who work in harmful and dangerous industries.
Comfort of wearing is ensured by high adhesion to the surface of the prosthetic bed, elastic material, and soft clasps. Due to the lack of possibility of relining, such prostheses must be changed once every 3–3.5 years.
Quattro Ti manufacturing features
The Quadrotti prosthesis is made in a dental laboratory individually for each patient using the thermocasting method. For these purposes, special equipment and raw materials are used, from which the future prosthesis is formed based on the impression and model of the jaw.
The manufacturing technology is worked out to the smallest detail, so butterfly prostheses and larger thermoplastic structures wear well. Their invisibility on the teeth is ensured by the presence of several shades of raw materials.
White plastic is used inside and for hooks (clasps), and red plastic is used to make the gingival part. It practically blends with the color of the oral mucosa, so the structure on the teeth is not only not felt, but also invisible.
Care for Quattro Ti prostheses should be more gentle. They need to be cleaned with a soft brush and a special paste designed for elastic plastics. Periodic disinfection with a special disinfectant solution is recommended. For details, please contact your dentist at our clinic.
Splinting clasp dentures
In case of increased instability of the supporting teeth and the presence of a defect in the dentition, it is recommended to install dentures, the design of which contains special elements (processes, clasps). With their help, the prosthesis tightly covers the crowns of the teeth, which avoids further loosening.
The indication for wearing a splinting prosthesis is not only degree II-III tooth mobility, but also a pathological deep bite along with increased abrasion of the tooth surface.
Its distinctive feature is the presence of individual hooks on the teeth or an entire arch running along the inner surface of the dentition.
The advantage of this design is the uniform distribution of the load throughout the jaw, rather than concentrating it on just the supporting teeth. It is also worth additionally noting such an important plus as light weight.
Splinting clasp prosthesis –
It should be noted that the clasp denture (in addition to restoring chewing efficiency) can be given other functions in parallel. For example, we are talking about splinting mobile teeth in case of periodontitis. A splinting clasp prosthesis will have a thin metal arch on the inside (curved to the shape of the teeth), which will tightly wrap around the necks of the teeth (Fig. 20-21).
This arch helps reduce the mobility of the front teeth and stabilize them. However, there is an alternative opinion that the removal of such a splinting prosthesis from the oral cavity, as well as the process of fixing it on the teeth, is accompanied by too much pressure from the metal arch on the weakened front teeth, which, on the contrary, can lead to loosening of the teeth.
Splinting clasp prosthesis: photo
Prosthetics for complete absence of teeth and for one tooth
In case of complete absence of teeth, clasp dentures are installed in one case - when supported by implants. This is a more advanced prosthetics principle from a functional point of view. It allows you to avoid resorption of the jaw bone tissue, evenly distributing the load on the bone.
Clasp prosthetics for one tooth before the advent of thermopolymer products were considered illogical, since they required grinding down adjacent and often completely healthy crowns. Metal-based dentures made it possible to replace a lost tooth only as part of complex structures - with lateral end defects and included defects of the anterior teeth.
Thanks to Quadrotti technology, there is currently no need to prepare adjacent healthy teeth for a prosthesis. And a single included defect in the dentition is successfully replaced with an elastic thermopolymer “butterfly”.
Components of the clasp
The simplest holding clasp consists of 3 parts - the shoulder, the body, and the appendage.
A more complex version, the support-retaining one, consists of a shoulder, an occlusal pad, a body and a process. This composition is typical for the classic type of support-retaining clasp called Akker.
The arm of the clasp is the part that holds it on the tooth.
The body of the clasp connects all the elements together.
The process or connecting rod is an element that coppers the prosthesis and the clasp itself. And the size of the process depends on the type of prosthetics.
And the foot or occlusal pad is a kind of transmitter of chewing force on the tooth at the level of occlusion.
Denture for front teeth
Prosthetic treatment of dental defects in the smile area requires special attention. A prosthesis requires a high level of aesthetics and functionality.
Of course, the ideal option for such a lack of teeth would be implantation. However, if for objective reasons it cannot be carried out, then the choice often falls on clasp dentures.
Prostheses based on attachments and telescopic crowns have proven themselves well when installed on the front teeth. They are light, almost invisible, and attach well to the supporting teeth. If desired, you can also choose a Quadrotti prosthesis, the advantages of which we have already mentioned.
Clasp prosthesis for the lower jaw –
In Fig. 1-3 you can see what a clasp denture for the lower jaw might look like. The metal arch of such a prosthesis will always be located on the inner surface of the alveolar process of the lower jaw (slightly below the lingual surface of the lower anterior teeth). Unlike clasp dentures for the upper jaw, the design of which can have a huge number of options, the design of clasp dentures for the lower jaw is always the same.
Service life and how to care
On average, the service life of a clasp prosthesis is 2–3 times longer than that of a conventional plate prosthesis. This is achieved through more advanced production technology and high-quality raw materials.
With good care - daily at home and regular professional hygienic cleaning in dentistry - your new teeth will last from 5 to 7 years. On implants – up to 10 years due to the absence of resorption, play and displacement during chewing.
Caring for clasp dentures
Every day, twice a day at least, and ideally after every meal, you need to brush your teeth. If the denture is removable, remove it and wash it with soap or toothpaste, thoroughly cleaning the surfaces with a brush. Rinse with boiled or purified water.
Once a day, disinfection should be carried out by dipping the prosthesis in a disinfectant solution for 5–10 minutes. For its preparation, special water-soluble tablets are used. Once a week you can soak it for a longer period in a bio-solution for better cleaning.
Using this method, all biological debris, including pieces of food and plaque, are removed from the prosthetic surface. After disinfection, the product is washed with boiled water and is ready for storage in a case or use. Dentists strongly do not recommend leaving the prosthesis in storage for a long time, especially if it has a splinting effect.
You should make an appointment for professional cleaning at least twice a year. In this case, the denture workshop cleans the polymer and metal parts, as well as calibrates them to fit the patient’s jaw.
Careful care, timely repairs and relining extend the life of the product, allowing you to avoid its breakage due to the gingival contour changing over time and the associated improper load distribution.
Types of clasp dentures –
As we said above, any version of a removable clasp denture will have a metal frame. Most often, it is traditionally made from cobalt-chromium alloy (CCH), but it is also possible to use titanium, as well as alloys with precious metals. A titanium frame prosthesis is the most modern option. The use of titanium makes it possible to reduce the weight of the prosthesis by 2 times (compared to if the frame is made of CCS), and the lower weight will ensure not only comfort, but also quick adaptation to the prosthesis.
The base of the prosthesis (it is pink) can be traditionally made of acrylic plastic, or from slightly elastic materials “Acry-free” or nylon. But the most important differences in clasp dentures concern their method of fixation on the supporting teeth. There are 3 possible fixation systems for this type of prosthesis, each of which we will discuss in detail in this article.
- clasp denture with clasps,
- clasp prosthesis on attachments (micro-locks),
- clasp prosthesis on telescopic crowns.
Price
The price of clasp prosthetics depends on the degree of complexity of the clinical case - the number of defects, their location, selected materials and manufacturing technology. Prices for prosthetics start from 50 thousand rubles.
The final cost of treatment is also influenced by the preparation and depulpation of supporting teeth for a crown, concomitant treatment of caries, gum and periodontal diseases, and bleaching for the optimal choice of shade of polymers.
You can find out how much a clasp prosthesis will cost in your particular case and ask any questions you have by consulting with an orthopedist in our clinic. Call to make an appointment at a time convenient for you. We'll be happy to help!
Clasp prosthesis: price in Moscow and regions
Clasp denture is the most popular type of denture for partial absence of teeth. You can read more about reviews of this type of prosthetics in the article: “Reviews of clasp prosthesis.” Now let's figure out how much a clasp prosthesis costs in clinics for 2022 (in economy class and mid-price clinics).
- Clasp prosthesis with clasps - the cost of a simple clasp prosthesis with clasp fixation in Moscow will be from 40,000 rubles, and in Russian regions the price will be from 35,000 rubles. The cost of a complex clasp prosthesis with clasp fixation (in the presence of a complex branched system of clasps), as well as a splinting clasp prosthesis in Moscow will be from 45,000 to 50,000 rubles.
- Clasp prosthesis on telescopic crowns - the cost of such a prosthesis starts from 75,000 rubles, and on average can be about 90,000 rubles. Typically, the required number of telescopic crowns is already included in this price, but some clinics may not include the cost of manufacturing metal caps in the cost of the prosthesis. This needs to be clarified during the consultation.
- Clasp prosthesis with attachments (micro-locks) - a prosthesis using inexpensive economy-class micro-locks will cost in Moscow - from 70,000 rubles, and for the regions from 65,000 rubles.
However, if prosthetics are performed using expensive micro-locks such as Bredent, the cost will be approximately another 20,000 rubles higher. It should be taken into account that the above prices already include the cost of the prosthesis itself, the cost of micro-locks, but does not include the cost of metal-ceramic crowns and preparation of teeth for prosthetics. The price for a one-sided clasp prosthesis will be about 50,000 rubles. This type of prosthesis is made for a unilateral defect in the dentition. This includes the cost of the prosthesis and micro-lock, but does not include metal-ceramic crowns.
Clasp dentures on a titanium frame –
All the above prices are typical for clasp dentures, the metal frame of which is made of cobalt-chromium alloy (CHS). We have already said that titanium is 2 times lighter than KHS, and also up to 5 times stronger. In addition, titanium has much greater tissue biocompatibility and a much lower risk of allergic reactions to metals. But prostheses with a titanium frame are much more expensive.
The cost of the simplest clasp prosthesis with clasp fixation (no more than 2 clasps) will be at least 50,000 rubles. In turn, the price for clasp prostheses made of titanium, which have a complex design, can range from 60,000 to 110,000 rubles. We hope that our article was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Personal experience as a dentist, 2. “Orthopedic dentistry. Textbook" (Trezubov V.N.), 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. "Removable dentures: a textbook" (Mironova M.L.), 5. "Teeth restoration with clasp dentures (Fadeev R.A.) .
Conclusion: Indications for the use of removable clasp dentures
In persons with partial absence of teeth, along with end defects, combined and included defects are often encountered. Plate and clasp removable dentures can successfully replace end defects. Clasp dentures have a number of significant advantages over removable plate dentures:
- The base part of clasp dentures is minimal.
- The arch in the prosthesis ensures uniform distribution of the load between its sides.
- The prosthesis contains supporting clasps, which allow partial transfer of the load through the tissues of the supporting teeth.
- Compared to other complete removable dentures, clasp dentures can be slightly adjusted.
- The oral mucosa and gingival papillae are partially released.
- Reliable fixation of the prosthesis speeds up adaptation.
Clasp dentures have a number of advantages over bridges:
- Installation of clasp removable dentures does not require preparation of some teeth and does not limit their mobility.
- Chewing pressure is evenly distributed between the alveolar processes and the remaining teeth.
- Clasp dentures are hygienic; they can be cleaned mechanically outside the oral cavity.
To individually assess the condition of your teeth and make various solutions to your problem, you need to have a free consultation with an orthopedic dentist. A highly qualified specialist will help in any of your situations.
Materials used in the manufacture of clasp dentures
Currently, clasp dentures are made on fire-resistant models. In the case where soldering is necessary, laser or hydrogen soldering is chosen. Thanks to this, local heating is ensured, which does not allow changes in the properties of the alloys used and is usually used to securely fasten the fixing elements.
If it is necessary to make prostheses with removal from the model or one-sided ones of short length, preference is given to special types of modeling plastic, which makes it possible to almost completely eliminate deformation of the entire structure during the work.
In full accordance with the materials from which clasp dentures are made, the cost of the finished product, indicators of strength, convenience and period of use are added up.
Today, the following materials are chosen for such structures:
1. Metal-free or quadrotti prosthesis. The arc in them is made from durable types of pressed plastic and ceramics. An ideal option for those patients who have an allergic reaction to metals.
The disadvantages are:
- fragility of the structure;
- short period of use;
- high risk of various types of damage to the prosthesis.
2. Clasps, the arc of which is made of chromium-cobalt alloys. They are distinguished by high reliability indicators due to the solid metal frame. The arch of the prosthesis with locking fixation includes metal-ceramic crowns.
3. A worthy alternative to designs with chromium-cobalt alloys can be gold-platinum alloys, the most expensive, but not causing allergic reactions. They are used to make arches and caps for metal-ceramic crowns.
As you can see, you can choose prostheses in full accordance with the wishes of the patient.