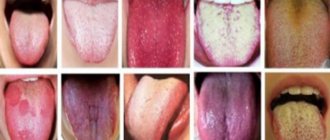
Black hairy tongue syndrome is an unexpected and even frightening term. Such a strange name is not always clear to others. AiF.ru asked experts what this syndrome is.
“A hairy tongue is a manifestation of systemic diseases in the oral cavity. The name itself is associative. Of course, the tongue is not covered with hair. In fact, these thread-like papillae on the surface of the tongue acquire a tint that makes them look like hairs,” says dentist, chief physician of the dental clinic Ilya Antonov .
He notes that in addition to external changes, other symptoms may appear. Among them, the specialist names:
- foreign body sensation;
- the appearance of a feeling of dryness;
- slight burning sensation (not always).
Article on the topic
Summer misfortune. Why do ENT diseases occur in the warm season?
Causes
The exact causes of the pathology are not fully understood. The disease is not an independent disease; it appears against the background of other diseases. Most often, this phenomenon occurs in men over 40 years of age, but is sometimes observed in women. This disease is very rare in children.
The pathology is most often observed in people with gastrointestinal dysfunction, ulcers and gastritis. The development of the disease is greatly facilitated by poor oral hygiene, smoking habits and excessive coffee consumption.
The main causes of the development of the disease are considered:
- long-term use of medications, especially antibiotics;
- fungal infections;
- dehydration;
- chemotherapy;
- metabolic disease;
- weakened immune system;
- Regular rinsing of the mouth with solutions containing astringents.
The risk group also includes people with dental defects and the absence of a large number of teeth, since in this case they are forced to eat only soft food, which does not have the proper abrasive effect on the surface of the tongue.
Associated symptoms
If there really is a hair in the oral cavity, then the person feels:
- The presence of a foreign object that makes swallowing difficult;
- Constant desire to expel it by expectoration.
You should know! It’s another matter if we are talking about more than just a single sensation of a hair on the tongue.
When a symptom accompanies a number of signs , and there is actually no hair in the oral cavity, then this indicates the development of serious diseases .
Along with this unpleasant feeling, the following symptoms may occur :
- Irritation of the nasopharynx , accompanied by painful swallowing;
- Sore throat and urge to cough ;
- Unpleasant dryness , causing a desire to wet the throat;
- Difficulty breathing and hoarseness of voice ;
- Fever, swelling and lethargy;
- Feeling of nausea and vomiting ;
- Nervous obsessive states ;
- Changing the color of the tongue.
The presence of at least one of the listed signs is a reason to visit a doctor .
Remember! Timely detection of pathology will help protect health from possible serious consequences.
Symptoms
Pathology is immediately detected during a visual examination by a dentist. In the initial stages of the disease, the presence of a foreign object in the mouth is felt, other unpleasant signs gradually appear, then the upper part of the tongue noticeably turns black. In advanced cases, the affected area occupies two-thirds of the tongue. The disease is accompanied by unpleasant odor from the mouth, changes in taste sensations, a metallic taste appears in the mouth, a feeling of tickling and soreness on the surface of the tongue, as well as causeless nausea. In rare cases, there is a burning sensation and severe itching.
Can hair grow on the tongue?
For your information! It goes without saying that nature does not provide for the presence of hairs on the tongue.
A rather rare disease of the oral cavity is glossophytia , in which the receptors of the tongue lengthen and become keratinized and blackened.
As a result, we can say that the tongue has become “hairy” and the feelings in the mouth are exactly like that.
This happens due to lack of hygiene, poor diet and excessive smoking..
Although the deformation of the receptors is in no way associated with the growth of hair on the tongue, however, this does not relieve the unfortunate patients from painful and unpleasant symptoms.
Treatment
It is necessary to contact a dentist or maxillofacial surgeon with such a problem. To obtain a complete clinical picture, it is necessary to undergo examination by a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist and neurologist. Since the pathology develops against the background of other diseases, a comprehensive treatment regimen is used.
Only treatment of concomitant diseases, professional cleaning and treatment of the oral cavity, taking multivitamin complexes, antifungal medications and, if necessary, sedatives will help eliminate this unpleasant defect. Removal of heavily overgrown papillae can be carried out by cryodestruction (exposure to the pathological focus with liquid nitrogen). It is also necessary to adjust your diet, enriching it with foods with fiber, vitamins and minerals.
The prognosis for black hairy tongue is usually favorable. Elimination of causative factors, as well as appropriate comprehensive treatment of the disease, leads to complete restoration of the surface of the tongue.
How to get rid of it?
Don’t be shy and think that the problem of “hair in the mouth” is not worth going to the doctor about.
It is better to be known as a hypochondriac than to subsequently treat a chronic disease.
However, real hair can be removed fairly quickly by simply rinsing or swallowing hard bread .
But if there really is no hair , then you should definitely turn to professionals. First of all, you need to visit a therapist's office.
If the doctor does not determine the cause of the sensation, he will refer you to other specialists - otolaryngologist, oncologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, surgeon.
Stay up to date! Then you will need to undergo an examination, including:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- Hormone test;
- X-ray of the spine.
If the test results are normal, then the cause of the symptom should be sought in the office of a neurologist or psychotherapist.
When the patient already exhibits obvious obsessive movements, he is referred to a psychiatrist .
For each specific case, a specific approach is required :
- If the sensation of hair in the mouth is associated with endocrine diseases, then hormonal correction will be required;
- If spinal diseases are detected, massage or physical therapy classes will be prescribed;
- If the cause of the sensation of hair in the mouth is nervous strain and stress, the doctor will prescribe medication;
- When diagnosing glossophytia, cleaning of the oral cavity through cryo-procedures will be required.
Prevention
As such, there is no prevention of black villous tongue. Even with good oral hygiene, you can encounter a similar phenomenon, but with timely treatment of diseases that lead to the development of such a complication, you can minimize the likelihood of the disease occurring.
The following rules must also be observed:
- thoroughly brush your teeth, gums and tongue with a soft brush;
- It is necessary to drink enough water, because if there is a lack of hydration in the oral cavity, it begins to develop; bacteria;
- reduce coffee consumption and quit smoking and alcoholic beverages.
The disease recurs quite rarely. During an exacerbation, the patient is advised to follow a gentle diet; food should be warm and soft in consistency.
How to treat?
“Treatment includes several main areas - examination and determination of the level of hygiene, followed by professional cleaning with special solutions and brushes. A smear is also taken from the surface of the tongue to determine the pathological composition of plaque in the laboratory and select effective drugs,” says Ilya Antonov. He notes that such a syndrome can be false and becomes a consequence of severe systemic diseases, such as leukoplakia and Addison's disease.
“To exclude these diagnoses, the dentist refers the patient for additional studies. In any case, you should not hope that the situation can be dealt with using home remedies. Therefore, you should consult a doctor,” says Ilya Antonov.
Otorhinolaryngologist Zaitsev, in turn, notes that one must pay attention to the controllability or uncontrollability of the situation. “A controlled state is when it is enough to give up some foods or the same medications for the situation to gradually level out. An uncontrollable situation is when a person goes on a diet, and a strict one, but the situation does not change. In this case, it is necessary to consult a doctor and not delay,” says Vladimir Zaitsev. After all, the situation, as doctors emphasize, can be quite serious, and there is no point in wasting time, as this will directly affect the outcome of treatment.
Why does there be a feeling of a foreign body in the throat?
Acute infections
The sensation of a foreign body is provoked by swelling, inflammation, accumulation of sputum, and plaque formation. It is detected in infectious diseases such as:
- ARVI.
The manifestation is insignificant, disturbing at the initial stage of the disease, complemented by weakness, weakness, moderate redness of the throat, general hyperthermia, and muscle pain. - Measles.
The symptom occurs with the onset of the first wave of fever and is more pronounced in children. The pharynx is hyperemic, the posterior wall of the pharynx is granular. The face is swollen. After 3-5 days, the condition improves and characteristic rashes form on the skin. - Diphtheria.
Accompanied by the formation of fibrinous plaque first, then a dense smooth coating. With widespread damage to the oropharynx, involvement of the larynx and trachea, breathing disorders and the development of diphtheria croup are possible. - Scarlet fever.
The throat is bright red, painful, sometimes there is involvement of the tonsils and enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes. A little later, the tongue and lips also become bright red, a pinpoint rash appears on the face and upper body, spreading to the limbs.
Inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs
In acute inflammation, the symptom does not have a clear localization, occurs suddenly, quickly reaches a significant degree of severity, and disappears after a few days. Chronic inflammatory processes are accompanied by periodic moderate or slight sensation of a foreign body, which is more disturbing during periods of exacerbation.
- Tonsillitis.
The tonsils are hyperemic, enlarged in volume, covered with superficial films, multiple small yellowish-white foci or loose plaque. Sore throat, general hyperthermia, and symptoms of intoxication are observed. With chronic tonsillitis in the acute phase, all symptoms are smoothed out. - Pharyngitis.
When examining the pharynx, swelling and diffuse hyperemia are revealed. The general condition remains normal, sometimes there is weakness and an increase in temperature to low-grade levels. In the chronic form, one part of the pharynx is predominantly affected: the oropharynx, nasopharynx or hypopharynx. - Laryngitis.
The patient complains of scratching, soreness, and tickling in the lower parts of the throat. The voice becomes hoarse; in severe cases, the patient speaks in a whisper. There is a paroxysmal dry cough. The symptom is more noticeable in phlegmonous and infiltrative forms. Chronic laryngitis is manifested by coughing, the need to periodically clear the throat, and rapid voice fatigue.
Laryngeal sore throat is accompanied by the same symptoms as acute laryngitis, but is characterized by a more severe course. The pain in the throat is so severe that patients refuse to eat and take a forced position.
Purulent processes
Abscesses in the throat area occur with sore throat, and less often result from rhinitis, pharyngitis, or sinusitis. Sometimes they develop with otitis media, mastoiditis, mumps, and are formed against the background of acute infections or carious teeth. The sensation of a foreign body has a clearer localization than in inflammatory pathologies, appears on the side or in the central part of the throat, and is accompanied by significant hyperthermia and severe intoxication. Detected under the following conditions:
- Peritonsillar abscess.
It manifests itself as sharp, rapidly intensifying pain when swallowing. The pain becomes tearing and radiates to the ear and lower jaw. There is a tilt of the head towards the affected area and a putrid odor from the mouth. Possible trismus. - Retropharyngeal abscess.
It is accompanied by extremely intense pain, forcing patients to refuse food. When the abscess is located in the upper part of the pharynx, nasal breathing disturbances and nasal sounds are observed; in the middle and lower parts - difficulty breathing and hoarseness. - Epiglottitis.
Signs of a purulent process are combined with breathing problems. The patient complains of pain in the lower part of the throat. Hoarseness and muffled voice, wheezing, cyanotic lips and nasolabial triangle, and tachycardia are detected.
Ludwig's angina is one of the most common purulent processes. The sensation of a foreign body appears when the pharynx is involved, accompanied by severe fever, swelling of the neck, breathing problems, loss of voice, and drooling.
Sensation of a foreign body in the throat
Traumatic injuries
The sensation of a foreign body in the throat may indicate the presence of a foreign object or injury caused by the object as it passes through the throat. The cause of the symptom is fish bones, crackers, fruit and berry seeds. Children sometimes swallow inedible objects with sharp edges, such as building blocks. With thermal and chemical burns, discomfort in the throat occurs due to swelling and damage to the mucous membrane.
Tumors
The symptom is included in the typical clinical picture observed with benign neoplasms of the pharynx and is combined with a sore throat, nasal voice, and difficulty in nasal breathing. Slowly builds up over a long period of time. It is detected with papillomas, fibromas, and hairy pharyngeal polyps. It is noted for angiomas, neuromas, and pharyngeal cysts. With benign neoplasia of the larynx, complaints of the sensation of a foreign object are less common, and voice changes prevail.
In patients with pharyngeal cancer, the sensation of a foreign body is the first symptom of the disease. Later, pain, choking, difficulty swallowing, and sensitivity disorders occur. Manifestations quickly progress, complemented by general signs of the oncological process - weight loss, weakness, intoxication. The symptom is also characteristic of laryngeal cancer, affecting the upper parts of the organ.
Allergy
The symptom is observed in allergic reactions accompanied by swelling of the throat. It appears suddenly. The patient is bothered by sneezing, nasal congestion, lacrimation, sore throat, itchy skin. In the spring-summer period, allergies are provoked by contact with plant pollen, throughout the year - with wool, dandruff, feathers of animals and birds, house dust, and food products. The most striking picture is observed with Quincke's edema.
Thyroid pathologies
The thyroid gland is located near the upper part of the trachea, its enlargement causes irritation of the receptors, causing the sensation of a foreign body. The symptom is detected in the following pathologies:
- Iodine deficiency conditions
: diffuse euthyroid goiter, nodular goiter. - Mainly hyperthyroid conditions
: diffuse toxic goiter, thyroiditis (subacute, autoimmune, others). - Benign and malignant tumors
: adenomas, cysts, lymphomas, thyroid cancer.
Digestive system diseases
Foreign body sensation is sometimes accompanied by GERD. Patients complain that they want to drink water or cough to get rid of a foreign object. The symptom is provoked by constant irritation of the receptors with acidic contents thrown into the upper parts of the digestive tract during reflux. A distinctive feature is the increase in discomfort when lying down. With dyskinesia of the esophagus, the symptom appears due to a violation of the passage of the food bolus due to a disorder in the motility of the organ.
Dental diseases
Patients with certain tongue pathologies complain of a feeling of a foreign body in the throat: black hairy tongue, papillomatous form of rhomboid glossitis. In the first case, there is a significant increase in taste buds in the posterior and middle thirds of the tongue, coloring the affected area in black and dark brown shades. With rhomboid glossitis, pale pink growths appear on the tongue.
The symptom accompanies benign and exophytic malignant tumors of the oral cavity if they are located on the root of the tongue or in the palate. In addition, the sensation of a foreign body occurs with the stylopharyngeal variant of stylohyoid syndrome.
Neurosis of the pharynx
Initially, the sensation of a coma (foreign body) in the throat was described as a typical symptom of hysteria. Currently, along with hysteria, the causes of pharyngeal neurosis include astheno-neurotic syndrome and severe stress. Pathology can also be observed in cervical osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia, spondylolisthesis, and certain diseases of the nervous system (neoplastic tumors, stroke, multiple sclerosis).
Throat examination
Language structure
To understand what is happening and why the papillae of the tongue hypertrophy, let us consider its structure. It is a muscular organ that is covered with a mucous membrane. The body of the tongue is covered with papillae of four types:
- leaf-shaped, they are located on the lateral surface of the tongue and contain taste buds and glands that produce a secretion resembling viscous saliva;
- grooved, they are located at the root of the tongue, the largest and fewest papillae of the tongue, contain taste buds;
- mushroom-shaped, they are randomly located over the entire surface of the tongue, also containing taste buds;
- thread-like, the most numerous, located on the back of the tongue, their function is to retain food and touch, they do not contain taste buds.
Thus, the anatomy of the tongue lacks hair follicles from which hair grows. Therefore, the name “hairy tongue” is conditional. The overgrown filiform papillae are very reminiscent of hair.
How to remove a hair
If the sensation of a foreign object in the throat is associated with infectious inflammation, the patient is prescribed medication, but what to do if there is a real hair stuck in the throat?
Most often, hair penetrates the mucous membrane of the throat during haircuts or after interacting with dogs or cats. If you find a small hair, try taking a large sip of water or saliva . Together with the liquid, the hair will pass through the esophagus and penetrate the stomach, after which the body will sink on its own.
If the hair is long, but you can’t reach it with your fingers, take a big sip of water. But it happens that swallowing and fluids do not help the patient. In this situation, inspect your throat in the mirror using a flashlight. Perhaps the foreign object is not stuck in the throat, but in the larynx area. In such a situation, hair removal can only be done with the help of a doctor.
If going to the hospital is not possible at the moment, ask your household for help. Using disinfected tweezers, carefully pick up the hair. In this case, movements must be precise and careful, since any action can injure the mucous membrane.
For reference! To temporarily eliminate the gag reflex, treat your throat with any antiseptic.
After removing hair from the larynx, gargle with herbal decoction . Healing plants will help eliminate irritation and normalize the functioning of the respiratory system. If the patient is particularly sensitive to medicinal herbs, replace them with furatsilin solution or water with soda.
You can learn how to gargle with baking soda here.
Rinsing will reduce the risk of infection and eliminate irritation of the mucous membrane.
What to do for treatment and elimination?
It is worth noting! The first thing you need to do is contact an otolaryngologist.
An ENT doctor examines the pharynx to confirm or rule out chronic tonsillitis (long-term inflammation of the palate and tonsil glands).
Caseous masses accumulate in the palatine tonsils, causing constant inflammation.
The doctor prescribes conservative therapy according to indications or, if necessary, surgical intervention is recommended.
Modern clinics have special diagnostic equipment, flexible endoscopes, which allow them to study in detail the condition of the nose, nasopharynx, and throat and identify the root causes of inflammation and eliminate them.
As you know, the cause of the sensation of a hairball in the throat can be a problem in the digestive tract.
This requires consultation and assistance from a gastroenterologist. Gastroscopy (EGD) is prescribed.
This method is used to visually examine the condition of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum using a flexible endoscope.
A small-diameter device is inserted into the patient through the mouth or nose.
For your information! The specialist excludes or confirms the pathology of the gastroesophageal sphincter (examination of the valve-orifice, orbicularis muscle of the lower esophagus).
Gastroesophageal reflux - esophagitis (GERD) is manifested by a burning sensation, a sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
Patients often complain of voice changes.
Immediate drug therapy is necessary ;
Ignoring the problem entails serious consequences, including mental disorders. Non-existent hair in the larynx may cause changes in the volume of the thyroid gland .
According to statistics, women over 35 years of age face this problem more often.
The help of a therapist or endocrinologist is needed to promptly block the development of thyroid pathology:
- general increase, changes in the tissues themselves - diffuse changes in the thyroid gland;
- formation of benign nodes in the tissues of the thyroid gland;
- the most dangerous are malignant neoplasms.
Important! Only a doctor can diagnose the causes and prescribe treatment after an ultrasound and special tests for hormones.
What to do if there is real hair there, how to get it?
First aid methods at home are simple. Especially if a person is in the country, outside the city, on the road or on vacation (there is no opportunity to immediately contact a specialist).
It is difficult to remove a hair or a stuck thread on your own; you will need an assistant .
- First, you need to carefully examine the oral cavity to find the “source” of irritation. To do this, it is better to use a table lamp or flashlight so that the cavity can be clearly seen even in the depths of the throat.
- Secondly, the easiest way is to simply swallow saliva several times so that a hair or foreign body enters the digestive tract.
- Thirdly, you can grab the hair with your fingers and pull it out .
Need to know! If this does not help, the hair is really stuck, you must perform the following procedures:
- Rinse your mouth or throat (depending on where the hair is located) with plenty of water . Use plain water, without any additives, so as not to cause a gag reflex. The water should be at room temperature.
- “Push” the hair into the esophagus . You need to drink a cup of tea or eat some rough food (crust of bread, cracker). Often any fermented milk product (kefir, fermented baked milk) is used. The foreign body is enveloped and moves unhindered into the digestive tract.
Forced removal of a foreign body from the throat:
- for this manipulation, you need to thoroughly sterilize the tweezers (wipe with alcohol or immerse in boiling water for 1-2 minutes);
- the pharynx and vestibule of the larynx are treated with an antiseptic (preferably from a spray bottle, can be lubricated with a special solution);
- additional lighting is used , directed specifically to the larynx:
- carefully remove the object with tweezers , without touching the mucous membrane, so as not to cause vomiting;
- Upon completion of the procedure, you should gargle with saline, soda solution , dissolved furatsilin or chamomile decoction for disinfection.
Remember! To forcefully remove a foreign body from the larynx or throat, it is better to consult an ENT doctor.
Thanks to professional skills and abilities, special equipment, the problem will be solved quickly and painlessly. The price of this procedure is insignificant even in paid clinics.
Preventive measures
To minimize the likelihood of coming face to face with such an unpleasant problem, it is important to ensure competent and high-quality prevention. To do this, experts in the field of hygiene and dentistry strongly recommend adhering to the following rules:
- daily brushing of the tongue: twice a day you need to brush not only your teeth, but also your tongue, because no less bacteria accumulate on it than on the surface of the enamel. To do this, you can use the rear ribbed surface of the brush, if it has one, or, for example, purchase a special device in the form of a tongue scraper,
Cleaning your tongue daily will help avoid the problem. - use of rinses: an excellent option can be a pharmaceutical product that not only fights bacteria, but also helps reduce inflammatory processes, helps remove food debris not only from the surface of the organ, but also under the tongue,
- systematic visits to the dentist: it is advisable to undergo preventive examinations at least once every six months. Regular visits to the dentist’s office will allow you to quickly detect the problem in its very beginning, and therefore quickly eliminate it,
- floss and irrigator: to maintain general oral hygiene, do not forget about such important devices as dental floss and irrigator - a portable device that removes plaque and dental deposits through a jet of water and air supplied under high pressure.
Any dental problem can be solved if you respond in time to suspicious changes in the condition of the teeth and oral cavity. The appearance of any neoplasms on the mucous membrane, the occurrence of pain and the formation of plaque on the tongue - all this is a serious cause for concern and an obvious signal that you need to see a doctor.
- Borovsky E.V. Therapeutic dentistry, 2003.
Definition - what a “hairy” tongue actually is
If the tongue is noticeably blackened and processes resembling small hairs appear on its surface, we can talk about chronic hyperplasia of the filiform papillae. The development of this pathology is accompanied by severe deformation of the structure of the surface of the tongue. It all starts with the hardening of mucosal cells, which ultimately leads to an increase in the length of the taste buds.
"Hair" can reach a length of up to 2 cm
On a note! The disease occurs in both adult patients and children. At the same time, males are more likely to encounter it in adulthood.
Black hairs “grow” from the root of the tongue, gradually increasing in diameter, usually up to 2 mm. The length of one such process can reach 2 cm or more1. In this case, the surface of the papillae becomes hard, and over time acquires a brown or even black color - the saturation of the shade can say a lot about the degree of neglect of the problem. Typically, the pathology proceeds slowly, and pronounced manifestations make themselves felt only in the active stage of development of the disease.