Every resident of our country is familiar with these problems first-hand - the prevalence of dental pathology in two-year-old children is already close to 30%, by adolescence it reaches 98%, and in adulthood only a few have an absolutely healthy oral cavity.
These figures are all the more depressing because most diseases can be successfully prevented: modern dental science and practice know the causes and conditions of their occurrence and development, and are armed with effective methods of primary and secondary prevention.
As with most diseases, most of the risk factors for the development of dental caries, periodontal pathology and occlusion pathology are determined by people's behavior. Therefore, an important part of the preventive strategy is informing the population about the nature of diseases, teaching simple and effective methods of preventive self-help, and motivating them to develop healthy habits in the family.
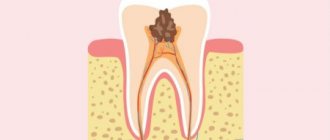
Dental caries is the most common chronic infectious disease in children and adults. The disease is caused by opportunistic microorganisms (streptococci and lactobacilli) that live in dental plaque.
The named microorganisms are normal participants in the oral biocenosis and do not cause harm to a healthy system. Every time after a meal containing carbohydrates, acidogenic microbes process food debris retained in the periodontal environment, obtaining energy through the process of glycolysis and releasing lactic, acetic and other organic acids. Acids cause partial dissolution of surface crystals of tooth enamel, consisting of calcium and phosphorus compounds - demineralization of enamel.
However, under normal conditions, demineralization is quickly replaced by remineralization: saliva, which is a supersaturated solution of the mineral components of enamel, restores tooth tissue.
Conditions predisposing to the development of caries:
- high aggressiveness of cariogenic dental plaque: determined by the properties of the strains and the number of acidogenic microorganisms in dental plaque (their numbers increase in an environment rich in carbohydrates);
- low level of enamel mineralization: determined by genetics, conditions for the formation of dental tissues (i.e., the health of both the expectant mother and the child, up to adolescence) and, in addition, is characteristic of all teeth in the first years after eruption;
- small quantity, high viscosity, low mineralization of saliva, low immune potential.
The modern model of etiotropic and pathogenetic prevention of dental caries consists of several key recommendations.
Prevention of early colonization of a child’s teeth by cariogenic microflora. The source of microorganisms is the saliva of people close to the child. It is necessary to reduce the number of cariogenic microflora of the mother (this is helped by sanitation of the oral cavity, the use of chewing gum with xylitol, rinses with antiseptics, a good level of oral hygiene) and to exclude salivary contact with the child (do not lick the pacifier, do not try the child’s food with his spoon, etc. .).
Balanced diet. To avoid encouraging the growth of cariogenic microflora, dental exposure to carbohydrates should be minimized. It is important to avoid frequent carbohydrate snacking and drinking. Teeth-safe snacks include cheese, nuts, and meat products; It is better to quench your thirst with water.
Oral hygiene. It is necessary to remove microbial plaque from all surfaces of all teeth at least twice a day. It is important to ensure mechanical removal of complex, sticky plaque with a brush and threads (floss).
The use of fluorides, calcium, phosphates. In order to prevent the dissolution of enamel and help its restoration, the periodontal environment should be enriched with macro- and microelements. An important role is played by the consumption of fluoride-containing table salt (iodized-fluorinated salt), as this ensures an increase in the concentration of fluoride in saliva. Another important source of fluoride and calcium are preventive toothpastes.
Oral hygiene
The main cause of most oral diseases is the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. We can conclude that the main preventive measure in dentistry is regular and high-quality oral hygiene. Let's look at the important rules:
|
Prevention of dental diseases
Every resident of our country is familiar with these problems first-hand - the prevalence of dental pathology in two-year-old children is already close to 30%, by adolescence it reaches 98%, and in adulthood only a few have an absolutely healthy oral cavity.
These figures are all the more depressing because most diseases can be successfully prevented: modern dental science and practice know the causes and conditions of their occurrence and development, and are armed with effective methods of primary and secondary prevention.
As with most diseases, most of the risk factors for the development of dental caries, periodontal pathology and occlusion pathology are determined by people's behavior. Therefore, an important part of the preventive strategy is informing the population about the nature of diseases, teaching simple and effective methods of preventive self-help, and motivating them to develop healthy habits in the family.
Dental caries is the most common chronic infectious disease in children and adults. The disease is caused by opportunistic microorganisms (streptococci and lactobacilli) that live in dental plaque.
The named microorganisms are normal participants in the oral biocenosis and do not cause harm to a healthy system. Every time after a meal containing carbohydrates, acidogenic microbes process food debris retained in the periodontal environment, obtaining energy through the process of glycolysis and releasing lactic, acetic and other organic acids. Acids cause partial dissolution of surface crystals of tooth enamel, consisting of calcium and phosphorus compounds - demineralization of enamel.
However, under normal conditions, demineralization is quickly replaced by remineralization: saliva, which is a supersaturated solution of the mineral components of enamel, restores tooth tissue.
Conditions predisposing to the development of caries:
— high aggressiveness of cariogenic dental plaque: determined by the properties of the strains and the number of acidogenic microorganisms in dental plaque (their numbers increase in an environment rich in carbohydrates);
- low level of enamel mineralization: determined by genetics, conditions for the formation of dental tissues (i.e., the health of both the expectant mother and the child, up to adolescence) and, in addition, is characteristic of all teeth in the first years after eruption;
- small amount, high viscosity, low mineralization of saliva, low immune potential.
The modern model of etiotropic and pathogenetic prevention of dental caries consists of several key recommendations.
Prevention of early colonization of a child’s teeth by cariogenic microflora. The source of microorganisms is the saliva of people close to the child. It is necessary to reduce the number of cariogenic microflora of the mother (this is helped by sanitation of the oral cavity, the use of chewing gum with xylitol, rinses with antiseptics, a good level of oral hygiene) and to exclude salivary contact with the child (do not lick the pacifier, do not try the child’s food with his spoon, etc. .).
Balanced diet. To avoid encouraging the growth of cariogenic microflora, dental exposure to carbohydrates should be minimized. It is important to avoid frequent carbohydrate snacking and drinking. Teeth-safe snacks include cheese, nuts, and meat products; It is better to quench your thirst with water.
Oral hygiene. It is necessary to remove microbial plaque from all surfaces of all teeth at least twice a day. It is important to ensure mechanical removal of complex, sticky plaque with a brush and threads (floss).
The use of fluorides, calcium, phosphates. In order to prevent the dissolution of enamel and help its restoration, the periodontal environment should be enriched with macro- and microelements. An important role is played by the consumption of fluoride-containing table salt (iodized-fluorinated salt), as this ensures an increase in the concentration of fluoride in saliva. Another important source of fluoride and calcium are preventive toothpastes.
Periodontal diseases.
A healthy periodontium - a multicomponent complex of tissues surrounding the tooth - ensures complex processes of restructuring the root tissues of temporary and permanent teeth, prevents tooth dislocation during biting and chewing food and in other situations, distributes the load and prevents the tooth from being driven into the bone, and also serves as protection for the internal environment body from the aggressive environment of the oral cavity.
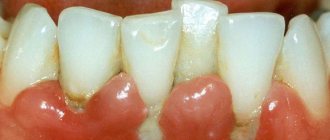
In the depths of a thick layer of dental deposits, i.e. With poor oral hygiene, anaerobic periodontopathogenic microorganisms actively develop - Neisseria, Bacteroides, Prevotella, Actinobacillus and others.
Feeding mainly on proteins, releasing proteolytic enzymes and toxic metabolic products, they attack the epithelium and cause an inflammatory reaction of the gums (swelling, bleeding, pain), i.e. gingivitis. With high aggressiveness of the microflora and/or in the absence of proper protection and tissue regeneration, microorganisms destroy not only epithelial, but also connective tissue (ligaments, bone), move along the tooth root, depriving it of its connection with the bone, as a result of which the teeth become increasingly mobile - those. periodontitis develops.
Periodontitis is the leading cause of tooth loss in adulthood.
In most cases, periodontal health can be ensured by daily thorough mechanical removal of dental plaque using a brush, paste and dental floss. The appearance of the first, reversible signs of pathology (bleeding when brushing teeth) is by no means a reason to switch to a gentle regime, but, on the contrary, a signal about the need to develop effective methods of cleaning teeth and periodontal space. The dentist can provide significant assistance to the periodontist not only by hygienic training, but also by eliminating local conditions in the oral cavity that reduce the protective capabilities of the periodontium and or complicate the removal of dental plaque: we are talking about carious tooth decay, poor dental restorations and dentures, bite pathology, unfavorable features architectonics of soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Thus, modern dentistry considers most cases of oral pathology as a consequence of an unhealthy lifestyle. Every doctor should remember the fundamental possibilities for preventing dental diseases and create in patients a sense of responsibility for maintaining health, leaving the choice of individual preventive recommendations and training in specific self-help technologies to the dentist.
HEALTHY TEETH IS THE KEY TO HEALTH
Oral health plays an important role in maintaining the health of the entire body.
The most common dental diseases are dental caries and periodontal disease. They do not pose a threat to life, but their treatment requires large economic costs. The disease most often begins in childhood, progresses steadily and eventually leads to irreversible dental damage, pain and discomfort. If the process is not stopped, the tooth gradually collapses.
The main cause of these diseases is dental plaque - a specific formation on the surface of the tooth caused by the accumulation and growth of microorganisms. Plaque is attached to the surface of the tooth and cannot be washed off with water.
Plaque bacteria convert sugar and food debris in the mouth into acids, which dissolve tooth enamel, resulting in the formation of a cavity. In addition, toxic substances released by bacteria cause gum inflammation (gingivitis) and bleeding. The inflammatory process can spread to the jaw bones and the ligament that holds the teeth in the tooth socket; they lose their stability and become mobile.
Primary prevention of dental diseases is based on the combined use of the following 3 methods: oral hygiene, use of fluoride, rational nutrition.
You need to brush your teeth 2 times a day: in the morning (after breakfast) and in the evening, since during sleep the protective properties of saliva decrease. Preference should be given to toothbrushes made of artificial bristles (nylon) of medium or soft hardness, which are much more hygienic than brushes made of natural bristles.
Before brushing your teeth, you need to wash your hands to avoid introducing infection into your mouth, rinse your mouth with water, rinse your toothbrush thoroughly, and squeeze out a pea-sized drop of toothpaste onto it.
Rules for brushing teeth:
- brush your teeth with your jaws open;
- first brush the teeth of the upper jaw, placing the brush at an angle of 45 degrees to the surface of the tooth. On each section consisting of 2-3 teeth, 10 movements are made in the direction from the gum to the cutting edge of the tooth;
- start cleaning from the back surface of the teeth (when cleaning the back surface of the front teeth, the brush is placed perpendicular to the cutting edges, and movements are made forward); then clean the chewing surface of the molars;
- brush the teeth of the lower jaw in the same order;
- complete the cleaning with a massage of the gums - with the teeth closed, the brush performs circular movements, grabbing the teeth and gums.
Fluorides are chemical compounds that, in specially selected dosages, reduce the risk of caries. They help strengthen the enamel (by retaining calcium ions in the hard tissues of the tooth), increasing its resistance to acids; prevent the attachment of microorganisms to the surface of the tooth and inhibit their reproduction, preventing the appearance of plaque.
Fluorine compounds enter the body with water and food (seaweed, sea fish, tea, Darida mineral water), but their quantity is small. To replenish reserves of fluoride compounds, it is necessary to eat fluoridated salt and fluoride-containing medications. It is also necessary to brush your teeth with a fluoride-containing toothpaste (the fluoride content should be indicated on the toothpaste packaging and be 500-1500 PPT).
To prevent dental diseases, it is important to follow certain nutritional rules, which provide a complete set of foods while limiting the consumption of carbohydrates. A rational diet involves 3-4 full meals a day. In the intervals between main meals, you should not eat foods high in sugar, especially candies and flour products (cookies, crackers, cakes), the remains of which remain on the teeth for a long time. The constant presence of sugar in the oral cavity stimulates the production of acid by plaque microorganisms, which gradually destroys enamel. The longer sweets are in the mouth, the sadder the outcome can be. Sugary carbonated drinks (Fanta, Cola and others), and intake of carbohydrates more than 5 times a day (including snacks) increase the risk of dental caries by 40%.
Dental and gum diseases are prevented by consuming milk, cottage cheese, cheese, fish, fresh vegetables and fruits, thoroughly chewing food, regular dental care and additional use of calcium and fluoride supplements.
It is very important to visit the dentist at least 2 times a year: the doctor will give recommendations on oral hygiene, promptly identify any problems that have arisen, and provide the necessary treatment.
Currently, oral hygiene products are presented quite widely: various types of toothbrushes and pastes, powders, elixirs, dental floss, toothpicks, gels, lozenges, chewing gum, dragees, hygiene tablets.
Toothbrushes. Preference should be given to toothbrushes with artificial bristles. This is explained by the fact that the synthetic fiber used for the working part of the brush can be of a given rigidity, elasticity, its ends are rounded and do not injure the mucous membrane of the gums. They are less susceptible to microbial contamination than brushes with natural bristles.
You should purchase those toothbrushes that have a certificate of hygienic registration in the Republic of Belarus. The toothbrush must be sold in a sealed package, which must indicate its name, the degree of stiffness of the bristles and information about the manufacturer.
A new toothbrush should be rinsed well with warm running water. You should not treat it with boiling water, as this will damage the artificial bristles.
The size of the toothbrush must be selected individually for each person: the working part should not exceed the size of 2-3 diameters of the crowns of the teeth, which will allow you to clean hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity. For adults, the most suitable brush head is 22-28 mm long, for children - about 20 mm. The tufts of bristles should be spaced quite sparingly. The shape of the toothbrush does not affect the cleaning efficiency, so when choosing any brush design, you can be guided by individual preferences. The toothbrush should be changed every 2-2.5 months, stored cleanly, in a glass, with the working part facing up.
A children's brush should be soft, with a small, short head. This brush can be used to clean even hard-to-reach tooth surfaces. The attractive shape and bright color of the toothbrush will help children make brushing their teeth fun and attractive.
Toothpastes are the main and most common means of oral care. There are a number of requirements for toothpastes: they must be neutral, have cleansing and polishing properties, have a pleasant smell, taste and appearance, have a cooling and disinfecting effect, be harmless and have a therapeutic and prophylactic effect. Today, the role of fluoride in the prevention of dental diseases has been scientifically substantiated and proven, so preference should be given to fluoride-containing toothpastes. When choosing a fluoride toothpaste, make sure the packaging is sealed and the contents have not expired.
Pastes usually consist of an abrasive filler, a binder, surfactants, an antiseptic and a fragrance. In addition, therapeutic and prophylactic additives can be added to the paste. Depending on whether such additives are introduced or not, pastes are divided into therapeutic and preventive and hygienic.
Hygienic toothpastes have only a cleansing and refreshing effect and are currently rarely used.
Therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes, in addition to known components, contain biologically active additives: vitamins, extracts and infusions of medicinal plants, salts, trace elements, enzymes. Such pastes are intended both for everyday oral care for preventive purposes, and for targeted prevention of dental caries and periodontal diseases.
Depending on the biologically active substances included in the formulation, therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes are divided into 5 groups:
- anti-carious;
— pastes containing herbal preparations;
- salt toothpastes;
— pastes containing various biologically active additives;
- toothpastes containing enzymes.
Anti-carious toothpastes strengthen the mineral tissues of the teeth and prevent the formation of plaque, which is achieved by introducing fluorine, phosphorus and calcium compounds into the toothpastes.
Blend-a-med Complete and Blend-a-med Mineral Action toothpastes help reliably protect teeth from caries thanks to active fluoride in the Fluoristat system, which provides teeth with the same amount of free fluoride as other dental products in 1 minute of brushing. pasta in 10 minutes. They effectively remove bacterial plaque, reduce the formation of tartar, improve the condition of the gums, effectively remove dark plaque and restore the natural whiteness of teeth, keeping your breath fresh for a long time.
"Dentavit Q10" contains coenzyme Q10, which has a healing effect on the gums, and active fluoride reliably protects teeth from caries.
Toothpastes “Lacalut sensitive” and “Colgate sensitive” are used for increased sensitivity of tooth enamel to external irritants, pain reaction to cold, hot, sour, sweet.
Pastes containing herbal preparations as additives improve metabolic processes, stimulate tissue regeneration, help reduce bleeding gums, and have excellent deodorizing properties. "Lacalut" phytoformula contains extracts of green tea, St. John's wort, and sage. Designed to strengthen gums, prevent their bleeding, and prevent the development of periodontal disease.
Salt toothpastes contain various salts and mineral components that improve blood circulation, stimulate metabolic processes in the periodontium and oral mucosa, cause an increased outflow of tissue fluid from the inflamed gums, and have some analgesic effect. Salts help dissolve mucus and prevent the formation of soft plaque.
Toothpastes containing various biologically active additives (vitamin B5, boroglycerin) have anti-inflammatory and regenerative effects, which allows them to be used in the treatment of gingivitis, periodontitis and diseases of the oral mucosa.
Enzyme-containing toothpastes are hygiene products with a high cleansing effect. They dissolve soft plaque, food debris, and nicotine plaque, thereby improving the condition of the oral cavity. Such pastes are recommended for oral hygiene in the treatment of periodontal diseases and oral mucosa in the acute phase.
Relatively recently, non-abrasive cleansers and gel-like transparent toothpastes have appeared in the range of oral care products. Gel toothpastes are especially effective for restoring enamel.
A dentist should select a toothpaste for a child, taking into account the age and condition of the hard tissues of the teeth. It is advisable for preschool children to use low-foaming toothpastes, and for school-age children to use foaming ones. Children's toothpastes "Vitosha F", "Putzi", "Drakosha" contain calcium or fluoride compounds, which strengthen tooth enamel. The fluoride content in children's toothpastes is 2-3 times less than in toothpastes intended for adults, which is safe for the baby, even if some amount of the paste is accidentally swallowed by him while brushing his teeth.
Dental floss is widely used to remove plaque on the contact surfaces of teeth. However, in pediatric practice it is advisable to use them either during professional oral hygiene or in children of senior school age. Toothpicks are also used for the same purposes.
In recent years, a number of studies have been conducted to study the effect of regular use of chewing gum on the incidence of tissues and organs of the oral cavity. Chewing gum has been proven to reduce the amount of plaque on teeth; If you add therapeutic and prophylactic additives to the gum, it can also have a preventive effect. The use of chewing gum stimulates the rate of salivation by 3-10 times, neutralizes the effect of acid in the oral cavity, promotes the penetration of saliva into hard-to-reach interdental spaces, and helps remove food debris. It must be remembered that chewing gum is an additional remedy, but does not replace regular teeth brushing.
The main purpose of dental elixirs is to deodorize the oral cavity. Used for rinsing after brushing teeth or after eating. The introduction of therapeutic and prophylactic additives into elixirs allows them to be used as an additional prophylactic agent. Thus, the “Special” tooth elixir contains sodium fluoride and vitamin B.
Thus, the use of individually selected oral hygiene products in combination with regular dental care makes oral hygiene one of the cost-effective mass methods of preventing dental diseases.
To have a beautiful snow-white smile, follow these rules: - Eat more raw fruits, nuts, and seeds instead of sweets. — Chew hard, raw vegetables, such as carrots and celery, thoroughly. — Instead of nectars or fizzy drinks with high sugar content, drink unsweetened drinks, natural juices and partially skimmed milk. — Eat milk, cheese and green vegetables containing calcium, which strengthens the hard tissues of teeth. — Use fluoride toothpastes that strengthen tooth enamel. — Brush your teeth twice a day, follow the correct brushing technique, floss and use toothpicks at least once a day. — Rinse your mouth with water or toothpaste after each meal. — Visit the dentist twice a year. — Lead a healthy lifestyle.
Eating habits
The condition of our teeth largely depends on what we eat. It is recommended to minimize the intake of fast carbohydrates (various sweets, flour, carbonated sweet water, etc.). It is necessary to saturate the diet with fermented milk products, fresh fruits and vegetables. It is important that the body does not experience a deficiency of vitamins or microelements.
Important! Food that is too cold or hot is extremely harmful to teeth; this can lead to increased sensitivity of the enamel.
BIBLIOGRAPHICAL LIST
Ch. editor - S.E. Shorin (e-mail: [email protected] ) Technical editing and layout - VA. Sysykina
License LR No. 065167 dated May 12, 1997. Signed for publication on January 16, 2001. Format 60x88 1/16 Offset paper No. 1. Typeface Petersbyrg. Offset printing. Pech. l. 21.75. Circulation 2000 copies. Order 4146 I.G. “Medical Book” 101000, Moscow, PO Box 68 Publishing House NGMD 603002. Nizhny Novgorod, st. Chkalova, 6 Printed at the VINITI Production and Publishing Plant, 140010, Lyubertsy, Moscow region. Oktyabrsky Prospekt, 403. Tel.: 554-21-8G
Preventive dental procedures
At your dentist’s appointment, you can perform several preventive procedures that will protect your teeth from various diseases:
|
CHAPTER 14. MAIN DIRECTIONS FOR PREVENTION OF DENTAL ANOMALIES AND DEFORMATIONS
14.1. Prevention of dental anomalies during fetal development
14.2. Prevention of dental anomalies associated with artificial feeding
14.3. Prevention of dental anomalies and deformations associated with bad habits
14.4. Prevention of dental anomalies and deformations associated with impaired nasal breathing
14.5. Prevention of eumaxillary anomalies and deformations associated with the destruction and absence of teeth
14.6. Hygienic education during orthodontic treatment
Recommendations from experts
The most important preventative measure is regular visits to the dentist.
. Experts strongly recommend dental examinations at least twice a year. This will allow timely detection of possible pathological processes, such as caries and other dental diseases. In the early stages, they can be easily stopped without the likelihood of relapse and complications.
Important! You should immediately visit a dentist if you experience enamel sensitivity, bleeding gums, toothache or discomfort while eating. These symptoms may indicate developing pathological processes.
Compliance with the above measures guarantees the preservation of oral health for many years.
Dental care for preschoolers (3-7 years old)
At this age, it is necessary to help the child brush his teeth; you need to control this process, checking the quality of brushing and the amount of toothpaste used. It is important to brush your teeth in the morning and evening (evening brushing should be done especially carefully). Recommended manufacturers of pastes and brushes: Curaprox, Rox, Splat. To check the quality of cleaning, you can use tablets or liquid to determine plaque "Curaprox", "Paro".
At this age, as a preventive measure for caries, on the recommendation of a doctor, you can use a paste with a fluoride concentration of 500 ppm to 1000 ppm. The dentist may recommend prophylaxis with Tuss Mousse gel (not suitable for children with cow protein intolerance) or coating the teeth with special varnishes containing fluoride, as well as remineralizing gels, for example, Rox.
Attention , poor dental care, snacking, drinking sugary drinks, eating disorders, a large proportion of food containing carbohydrates in the diet provoke the occurrence of caries!
In preschool age, it is recommended to visit the dentist 2-3 times a year. During this same period, it is advisable to see an orthodontist, especially if there are doubts about the correct development of teeth (the child sucks fingers or tongue, places the jaw incorrectly, teeth grow crooked, etc.).