Treatment methods for bacterial tonsillitis
Modern medicine uses two methods of treating bacterial tonsillitis - surgical and conservative.
Regardless of the stage and type of disease, you should not self-medicate. Since the drugs that helped cope with the disease once, the next time they may not cope with the infection. Therefore, you should definitely consult a doctor. The doctor at the ENT clinic will conduct an examination, prescribe the necessary tests (culture of flora from the throat) and prescribe a prescription for effective medications.
Bacterial tonsillitis in adults can only be cured with complex therapy, which combines various drugs for symptomatic therapy. In addition to drugs aimed at combating pathogens, medications are also prescribed that help reduce the intensity of accompanying symptoms, for example, to reduce body temperature and eliminate headaches.
In order to reduce a fairly high temperature (above 38.50C), you need to take one of the following medications:
- Ibuprofen;
- Paracetamol and others;
In a child, hyperthermia is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Traditional methods will help cope with hyperthermia - wiping the face and body with a damp towel or alcohol solution. During treatment of bacterial tonsillitis, bed rest and a gentle diet are mandatory. In case of intoxication, it is recommended to drink a lot of fluids (herbal infusions, compotes, milk, teas).
Based on the results of an analysis of the throat flora, the pathogen is determined and an antibiotic is prescribed, the action of which is aimed at combating this particular bacterium. For severe headaches accompanying bacterial tonsillitis, painkillers are prescribed - Aspirin, Ketonal, Nimesulide, Analgin.
Painful sensations in the throat are dulled and the tonsils are simultaneously disinfected when using the following medications:
- Givalex;
- Yox;
- Theraflu;
- Hexoral;
- Inhalipt.
Lollipops that reduce inflammation - Grammidin, Neo-angin, Decathylene, Strepsils - also cope well with this task. Solutions for gargling the mucous membranes of the throat - Chlorhexidine, Furacillin solution.
The surgical treatment for bacterial tonsillitis involves surgical removal of the tonsils. It should be borne in mind that these organs are of great importance for immunity.
Forms and classification of tonsillitis in children5
It should be noted that there is fundamentally no difference between adult and child forms.
The disease is divided according to:
- By shape
- By pathogen
- According to the form of the lesion
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | According to the form they are distinguished: | a comment: | - acute tonsillitis or sore throat - chronic tonsillitis |
| classification: | According to the causative agent, tonsillitis can be: | a comment: | Bacterial: - beta-hemolytic streptococcus A and other groups - staphylococcus - pneumococcus - moxarella Viral: — Influenza and parainfluenza virus — adenovirus — coronavirus — Epstein-Barr virus — enteroviruses — Coxsackie virus — herpes virus types I and II Fungal: mold fungus Candida albicans. As noted above, tonsillitis may be a manifestation of another disease: — measles — rubella — scarlet fever — mononucleosis |
| classification: | According to the form of the lesion: | a comment: | - catarrhal - follicular - lacunar - phlegmonous - ulcerative-necrotic - mixed form |
Most often, children suffer from the viral form of tonsillitis.6
treatment of bacterial tonsillitis at the clinic of Dr. Sichinava
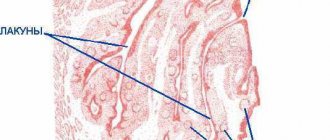
The specialized ENT clinic of Otto Sichinava uses advanced methods of treating bacterial tonsillitis without surgery. The procedure consists of washing the lacunae of the tonsils with an antiseptic solution. For this, a special gun with a thin tip (author’s development) is used, which delivers the solution directly into the lacuna.
Treating bacterial tonsillitis in children is much easier if the child does not feel pain. The advantages of this method are absolute painlessness and effectiveness. Treatment of bacterial tonsillitis consists of 10 procedures, after which the swelling and hyperemia of the tonsils decreases, and the appearance returns to physiological norms.
By seeking help from the clinic of Dr. Otto Sichinava in Moscow, you are guaranteed to be cured of pathological processes in the tonsils.
Prevention of tonsillitis in children
Regular walks in the fresh air, sports and hardening.
The children's diet must contain a large amount of fresh vegetables and fruits, herbs, and low-fat protein foods. Eating fatty, fried foods, fast food, and fast carbohydrates is not recommended for children.
Parents need to carefully monitor their child’s personal hygiene: regularly wash their hands and brush their teeth.
At home, it is recommended to maintain optimal humidity (50-60%) and air temperature (no more than 21 degrees) and carry out daily wet cleaning with room ventilation.
Diagnosis of tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is a serious disease that requires timely diagnosis and individually selected treatment.
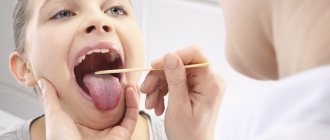
Self-medication can cause irreparable harm to children's health, therefore, if there is any suspicion of pathology of the upper respiratory tract, the patient should be shown to an experienced doctor. At the initial appointment, the ENT doctor will collect an anamnesis (medical history), clarify the symptoms of the disease, the duration of their presence, and any history of previous acute inflammatory processes. Then the specialist proceeds to examining the pharynx (pharyngoscopy) and palpating the lymph nodes. During the examination, the doctor uses a special instrument – a pharyngoscope, which allows a detailed examination of the condition of the child’s tonsils. If you suspect the presence of diseases concomitant with tonsillitis, you may need to consult a dentist, rheumatologist, pediatric cardiologist and other specialist doctors. To confirm the diagnosis and exclude possible complications, the small patient is sent to undergo a series of laboratory and instrumental studies:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- general urine analysis;
- biochemical examination of a smear from the tonsils;
- radiography of the nasal sinuses;
- ECG of the heart.
The results of the research will allow the specialist to identify the true cause of the disease, determine the characteristics of the course of the disease and the presence of concomitant disorders in the child’s body.
Specific features of bacterial sore throat
It is often difficult for parents to distinguish bacterial tonsillitis from other types of acute tonsillitis. Because of this, the patient’s condition often worsens.
- A sore throat caused by bacteria can be recognized by the following clinical picture:
- The lymph nodes in the neck and lower jaw become inflamed. On palpation they are sharply painful.
- There is no mucus or redness on the back of the throat.
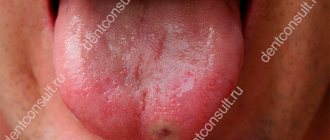
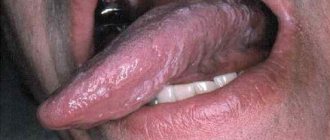
- Pus accumulates on the tonsils in the form of white or gray-green dots, but it does not extend beyond them. With a viral sore throat, pus spreads over the entire surface of the throat and surface of the mouth.
Sore throat caused by bacteria differs from other types of acute tonsillitis in that the runny nose and cough are mild, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and indigestion are absent.
What is "angina"?
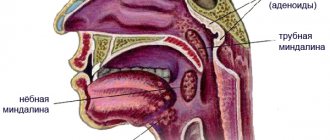
Immunity is the body’s ability to recognize “strangers” and fight them. “Strangers” are cancer cells and infectious agents. In the body there are groups of cells that perform certain common and similar functions; these cells are called tissue. Examples of tissues are bone, muscle, nervous, glandular. There are cells responsible for the production of immunity and form the so-called lymphoid tissue. Lymphoid tissue is present in the intestines (both small and large), in the bone marrow, and the thymus gland is entirely composed of it. It is not difficult to see lymphoid tissue. To do this, you need to go to the mirror and open your mouth wide. In the depths of the oral cavity, behind the arches that limit the entrance to the pharynx, there are semicircular formations - tonsils.
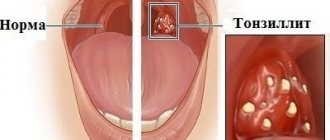
Tonsils consist of lymphoid tissue, are one of the main organs of the lymphoid system, participate in the development of immunity and very often become inflamed. Why often? Yes, because all substances that enter our body - both air and food - come into contact, first of all, with the tonsils. Here, in the oral cavity, to the esophagus and stomach, to the larynx and lungs - the tonsils are the vanguard of the immune system. It is not surprising that this squad has a great time and often gets it.
Inflammation of the tonsils is called tonsillitis (tonsilla in Latin). The most common cause of tonsillitis is the well-known acute respiratory viral infections, the common symptoms of which, in addition to fever, cough and runny nose, are a “red” throat and pain when swallowing.
The number of microorganisms that can cause an inflammatory process in the tonsils is in the dozens. It is not surprising that tonsillitis is a common symptom of many infectious diseases.
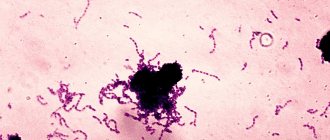
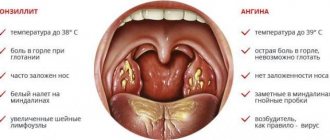
At the same time, there are two microorganisms - streptococcus and staphylococcus, which affect the tonsils especially often and in a special way. The disease begins very quickly, with a high temperature, sharp pain in the throat, and pustules (plaques) appear on the surface of the tonsils. This is a sore throat. The frequency with which these two microbes cause it is approximately as follows: 80% - streptococcus, 10% - staphylococcus and 10% - staphylococcus + streptococcus.
Once again the symptoms of a sore throat:
- acute onset, fever;
- general intoxication (weakness, chills, sweating, loss of appetite, headache);
- inflammation of the tonsils - increase in size, redness, plaque, pain in the pharynx, sharply increasing when swallowing;
- enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes - anterior cervical (down from the ear), near the angle and under the lower jaw.
In all organs and tissues, in addition to blood vessels (veins and arteries), there are lymphatic vessels that collect a special interstitial fluid - lymph. No part of the human body can even approximately compare with the tonsils in terms of the number of lymphatic vessels. It is not surprising that the purulent inflammatory process is immediately accompanied by a pronounced reaction of those lymph nodes that collect the lymph flowing from the tonsils.
The word “angina” itself owes its origin to ancient Greek doctors (ango - to choke, squeeze). The ancient Greeks had no idea about viruses and bacteria; by the word “angina” they understood all diseases accompanied by inflammation of the tissues of the pharynx and accompanied by impaired swallowing and breathing. Modern doctors treat viral and bacterial infections differently. Each specific disease accompanied by tonsillitis has its own specific methods of therapy.
That is why it is absolutely illiterate to call a sore throat any disease in which there is redness of the throat and pain when swallowing.
SOLISH is an acute infectious (contagious!) disease. It is the damage to the tonsils that determines the severity of the disease in angina.
Sore throat is a certain complex of symptoms, and we described this complex above. And redness in the throat, and pain, and plaque on the surface of the tonsils, and the reaction of the lymph nodes, i.e., all the symptoms typical of sore throat, can occur with diphtheria. The same symptoms can occur with a not at all rare viral disease - infectious mononucleosis. But in addition to the symptoms described, diphtheria affects the heart, kidneys, and nervous system; for infectious mononucleosis - all lymph nodes, liver, spleen. Sore throat is treated with antibiotics, diphtheria with anti-diphtheria serum; for infectious mononucleosis, neither antibiotics nor serum are effective.
The significance of the information provided is to once again emphasize: tonsillitis is not a bunch of all sorts of different diseases, tonsillitis is a specific disease that has specific symptoms and is caused by a specific microbe (usually streptococcus).
It is very important to note that angina is an acute disease. It cannot last for months, you cannot have it every month. People get infected with tonsillitis - from a person with tonsillitis or from a carrier of streptococcus. You can't get a sore throat just by getting your feet wet. You must first get your feet wet, and then find a person from whom you can get infected (of course, it is easier to get infected after hypothermia).
Sore throat, like any acute streptococcal infection, has two important features:
- tonsillitis can be treated very successfully and fairly quickly with the correct and timely administration of antibiotics;
- A sore throat that is not treated at all or that is treated incorrectly very often gives complications, since it is streptococcus that affects the heart, joints and kidneys.
Once again, please note: almost 100% of all rheumatic diseases and glomerulonephritis are a consequence of “ordinary” sore throat!
Pus plugs in the tonsils
“Congestion in the tonsils” is a separate problem, mostly hygienic, causing bad breath, sometimes also a feeling of pressure or a foreign body.
What is tonsillitis? It is a cast of food that has fallen into a lacuna (a kind of pocket) of the tonsil, tonsil epithelium and bacteria (most often fusobacterium nucelatum, the main bacterium of dental plaque). But this is not pus, since there are no dead leukocytes and bacteria underdigested by leukocytes.
The conditions for the formation of “plugs” are usually dry mucous membranes of the tonsils, which occurs when nasal breathing is impaired and/or air with low humidity.
Often, if you solve the problem with nasal breathing and the humidity of the inhaled air, then the “traffic jams” disappear by themselves.
What's the moral? If there are “traffic jams”, but no sore throat, then you should pay attention to the state of nasal breathing. And only if the problem persists even with a well-breathing nose, should you look for a solution in the palatine tonsils themselves.
Description of the disease
Tonsillitis is an inflammatory disease common in childhood, in which the source of inflammation is localized in the palatine tonsils.
Most often the disease occurs in children 5-10 years old, but it can also develop at an older/younger age. Tonsillitis is infectious in nature, that is, it occurs when bacteria, viruses and (less often) fungi enter the child’s body. There are two forms of tonsillitis - acute and chronic. Acute tonsillitis is nothing more than a common sore throat. The pathology is characterized by a rapid course and pronounced symptoms. The chronic form of tonsillitis has an asymptomatic clinical picture and occurs with frequently recurring inflammation of the tonsils or as a result of untreated tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis brings significant discomfort to the child - the patient suffers from severe sore throat, high body temperature, and the inability to eat and drink normally. In addition, in the absence of treatment, a number of complications can occur in the organs and systems of the body: sepsis, rheumatic diseases, myocarditis, pyelonephritis, vasculitis, etc.