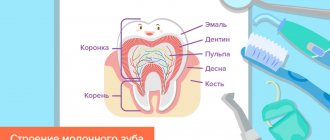
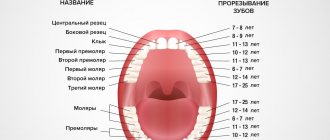
The order of eruption of baby teeth.
The first teeth that a child begins to erupt at the age of 5 - 8 months on the lower jaw are the deciduous incisors. Next, the central primary incisors on the upper jaw begin to appear. At the age of 9 - 13 months, the lateral incisors on the upper and lower jaws erupt. At the age of 13 - 19 months, the first chewing teeth (first primary molars) are cut on the upper and lower jaws. A gap is formed between the lateral incisors and molars, during which the primary canine begins to erupt at 16 months. The last to begin to emerge is the second chewing tooth (second primary molar), first on the lower jaw, then on the upper jaw. By age 3, a full set of baby teeth should have formed.
Features of the period and symptoms of the eruption of the first teeth.
DATES OF TEETHING ARE INDIVIDUAL FOR EACH BABY AND DEPEND ON A NUMBER OF FACTORS: NUTRITION, HEREDITY, ETC. THIS IS WHY YOU SHOULD NOT WORRY MUCH IF THE LONG AWAITED APPEARANCE OF YOUR FIRST TEETH IS DELAYED.
PHOTO: Gums of a child at 6 months. Before the first baby teeth erupt, the gums in the area of the future teeth turn slightly white due to tooth pressure.
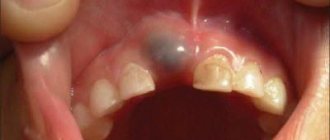
It's hard to miss when children's first teeth appear. As the tooth erupts, it “tightens” the mucous membrane (the tooth can be felt with your finger under the mucous membrane) and, having “broken through” it, ends up in the oral cavity. In some children, a bluish “bump” or “ball” with transparent contents forms on the mucous membrane above the erupting tooth. This is a small eruption cyst that usually breaks out on its own WITHOUT outside help (despite the menacing name), although sometimes the intervention of a pediatric dentist is required.
The first teeth that appear may be located asymmetrically and “not evenly” - this is the norm. Such dental disorder has the right to exist until the eruption of 16 teeth: baby teeth are independently ordered as they erupt, aligning each other. This is facilitated by the intake of solid food, pressure of the tongue and lip muscles.
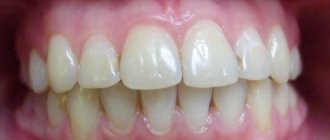
In a normal primary occlusion, gaps form between the primary incisors and canines (on average 1 mm), which is normal and a sign that the permanent wider incisors will have enough space in the dentition during the period of physiological change of teeth. The absence of these spaces indicates a lack of space for permanent teeth.
In most cases, teething does not cause the child any discomfort, although sometimes the process of teething can be accompanied by “itching” of the gums and lead to sleep disturbances in the child, causing a lot of trouble for the child and his parents.
Signs of formation of permanent teeth
The most characteristic symptom of the formation of adult teeth in childhood is the growth of jaw size. The gaps between the first teeth are small; if the jaw grows, this means that it creates conditions for new dental units. Adult teeth are larger than temporary teeth, so they require a lot of space. The distance between baby teeth increases. They lose stability and fall out. With any deviations, the teeth will break through with pain, bend, and ruin the bite. In order for a child’s teeth to grow correctly, parents need to control this process.
Pay attention to the distance between your child's teeth
Permanent teeth can erupt at 6-7 years of age without any symptoms, but most often the child behaves restlessly, is capricious, gets irritated over trifles, and eats poorly. Often the formation of permanent teeth has the same signs as during the eruption of milk teeth. If other diseases occur during teething, they can distort the symptoms.
- How to make teething easier for babies
Permanent teeth erupt at 6 or 7 years of age
Increased secretion of saliva is a very common symptom, although it is no longer as abundant as in infancy, but the difference can be noticed. At the age of 6, children can already be taught to wipe their mouth with a napkin, otherwise irritation will appear on the face, since saliva contains many microbes that aggressively affect delicate skin.
If your child is drooling, have a supply of clean tissues ready.
During the period of growth of permanent teeth, the gums and mucous membranes become inflamed again. If you notice redness in the mouth, it is better to show the child to a dentist, who can accurately distinguish the beginning of teething from a banal viral infection.
Take your child to the dentist if you notice redness in your child's mouth
Over time, swelling is observed on the gums - this is an adult tooth making its way to replace the temporary one. The germination process is painful; parents can alleviate the child’s condition with anesthetics.
Pain is replaced by itching. The child pulls any things to his mouth to soothe his gums.
The child may suck or chew fingers or other objects
A natural symptom will be deterioration in sleep quality. If he is bothered by toothache, the baby will not be able to fall asleep for a long time, often wakes up at night, cries, and tosses and turns.
If your baby is having difficulty sleeping and crying, this could be a symptom of teething.
Some children develop a fever, cough, and upset stool.
Fever and cough may appear
The listed signs may appear periodically and do not necessarily have to be present in all children.
Typical problems.
PHOTO: a child’s teeth at 3 years old. Gaps between baby front teeth at age 3 are normal. On the front upper teeth there is caries in the cervical area of the teeth.
There may be a slight rise in body temperature and anxiety in children when their first teeth are cut. This is due to minor inflammation and itching of the gums in the area where teeth are about to erupt. To relieve discomfort, it is recommended to treat the oral cavity with special napkins for oral hygiene, containing special antiseptic and tanning substances.
The most common problem faced by parents aged 12 - 18 months is “bottle” caries, the main cause of which is poor oral hygiene in the child and night feedings. As a result of poor hygiene, a large amount of soft plaque forms on the teeth. Plaque contains a large number of bacteria that produce acid, which “corrodes” the enamel, leading to the formation of caries.
Night feedings at the age of 12 - 18 months create the most favorable conditions for the development of caries, because... At night, saliva production is reduced - the acid of bacteria living in dental plaque is not neutralized.
BREAST-fed children are LESS likely to develop dental caries than bottle-fed children. Breast milk helps saturate the surface of teeth with calcium and phosphate ions. Breast milk contains a large number of immunological protective factors. At the same time, it has been noted that long-term night feeding (both breast and bottle feeding) leads to the development of dental caries, especially in the area of the upper front milk teeth.
PHOTO: A one and a half year old child’s teeth. The front incisors and first molars have erupted. The fang (3rd tooth) is emerging. Often at this age the first injuries occur: the child fell and hit his front upper tooth - the tooth broke.
Against the background of poor hygiene and a weakened immune system, inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane and stomatitis may develop. Stomatitis in young children is severe, accompanied by general malaise, loss of appetite and increased body temperature.
IT IS VERY IMPORTANT TO START TEACHING YOUR CHILD TO THE NECESSITY OF INDIVIDUAL ORAL HYGIENE FROM THE MOMENT OF THE APPEARANCE OF THE FIRST TEETH. GOOD ORAL HYGIENE IN A CHILD IS THE KEY TO HEALTHY TEETH FROM EARLY CHILDHOOD.
Symptoms and first signs of wisdom tooth growth
Seal
The structure of third molars or “eights” is no different from other teeth. Their peculiarity is different. Wisdom teeth erupt much later than others - on average, this occurs at 18-26 years of age. Since the dental system has already been formed by this time, there is not much free space left. The third molar is forced to “conquer” space from its neighbors.
The result is unpleasant sensations and even severe pain. In addition, teething can cause inflammation, against which complications such as abscess, phlegmon, etc. develop. To avoid undesirable consequences, you should know the symptoms and consult a dentist at the first signs of wisdom tooth growth.
Khashchenko Stanislav Sergeevich is a dental surgeon at the Dentoclass clinic.
How does eruption occur and what signs indicate its beginning?
An interesting feature of the “eight” is that it erupts immediately - without preliminary preparation of the gums with a baby tooth. For this reason, the process is much like the growth of teeth in young children. The formed tooth is, as it were, pushed outward, overcoming the resistance of bone and soft tissues. At the same time, the gums swell and become more sensitive. Then a small wound is formed at the site of tooth growth, after which the upper part of the crown appears.
The most common signs of third molar eruption are:
- mild, but constant aching pain caused by the fact that the “eight” makes its way through bone and soft tissue;
- redness and swelling of the gums are normal to a small extent, but severe swelling indicates the development of inflammation;
- discomfort or severe pain when swallowing, as well as when trying to open your mouth wide;
- enlarged lymph nodes under the jaw due to an increasing inflammatory process;
- the formation of a hood of soft tissue covering the partially erupted figure eight.
Note! Due to the location of the “eights”, access to them is difficult. This negatively affects the quality of hygiene. As a result, food particles accumulate under the hood, which serve as a breeding ground for the development of pathogens. This is how pericoronitis begins - the most common complication that occurs when wisdom teeth erupt. If this process is ignored, the inflammation progresses and in the future, hospital treatment may be required to stop it.
Pericoronitis is the most common complication of wisdom tooth eruption.
What can and cannot be done during the eruption of wisdom teeth?
The best thing you can do when you have suspicions about the growth of the “eight” is to consult a dentist. The doctor will perform an examination, recommend anti-inflammatory and painkillers, prescribe an x-ray or an orthopantomogram to assess the position of the tooth in the image and make sure that the latter is growing correctly and is not pressing on the root of the “seven”. Also, if indicated, the dental surgeon can remove the hood. The procedure is performed using local anesthesia and significantly alleviates the patient's condition.
A visit to the clinic is the best solution. But sometimes it happens that the patient for some reason is forced to postpone visiting the doctor. In this case, it is very important to know what you can and cannot do. So:
| Can: | It is forbidden: |
|
|
In conclusion, it should be noted that in case of severe pain, increased body temperature or general deterioration in health, you should immediately visit the dentist. These conditions indicate the development of serious inflammation that can cause significant harm to the patient's health.
Still have questions? Sign up for a consultation at our clinic or call:
8 8
Liked? Tell your friends!
Treatment.
Providing QUALITY dental care to children from the moment the first tooth appears and up to 3 years of age is LIMITED to physiological reasons: mild excitability, restlessness, fear of unknown manipulations in the oral cavity. An attempt to cure teeth by talking to a child or holding him by force in his arms ends with POOR-QUALITY treatment, as a result of which various local complications can develop.
REMEMBER: FORCED TREATMENT WITH CHILDREN RESTRAINT CAUSES IRREPAIRABLE PSYCHOLOGICAL TRAUMA TO THE CHILD!
Like