All people have a unique appearance and unique facial features. Some of us sometimes experience gaps between our teeth. Sometimes this defect may be subtle. But in other cases, such imperfection leads to serious physical as well as psychological consequences, and the issue of correcting this disorder is very relevant for a person.
Classification of dental gaps
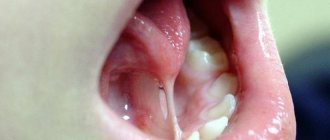
Diastemas
– these are gaps of any size between the front central incisors. Tremae are spaces between any other teeth in the upper or lower jaw. Gaps between the lower front incisors are uncommon, but gaps between the upper central teeth can be seen several times more often. In many cases, the presence of a diastema of this kind provokes serious psychological discomfort, interfering with the harmonious socialization of patients.
Depending on what type of teeth are – baby or permanent – a distinction is made between false and true gaps between them. False dental gaps are observed in children - such defects go away on their own along with the change of teeth. True gaps form between permanent teeth and can only be removed with specialized help from a dentist. Doctors advise starting to correct such defects immediately after they occur, since then it will require much less time and effort.
What is diastema
The dentition is not always continuous. Often they contain enlarged spaces - trema between the teeth (from the Greek trema - hole). Such chips can be from 1 to 10 millimeters in size. In dentistry, the space between the front teeth in the center of the upper dentition is designated by the separate term “diastema.” Moreover, diastema of the upper teeth is more common than the lower ones.
Experts divide diastemas into false and true. If a gap appears in a child as a result of early loss of baby teeth, this is a false diastema, which will disappear on its own over time. However, parents often ask doctors why the distance between children's teeth increases with age. Because the jaw grows and there is more space on it, and the size of the teeth increases slightly. As a result, the chips become more noticeable. In this regard, true diastemas, that is, gaps between teeth in adults, must be corrected by resorting to the qualified help of an orthodontist.
Gap between teeth: what should be done?
If you have a very small diastema, then a visit to the dental clinic can wait. However, even a small gap should be regularly monitored by a doctor, since tooth gaps tend to grow over time. However, if the diastema is significant, it is better to visit the dentist as soon as possible. This defect can contribute to the development of caries, malocclusion, gum disease, etc. Various methods have been developed for correcting diastemas. Typically, the doctor carries out treatment on an individual basis and selects a method that will be most effective for a particular patient. The technique is chosen based on the reasons for the appearance of a gap between the teeth, the size and degree of development of the dental gap, and the wishes of the person himself.
Tooth extraction
- Removal of a tooth.
- Wisdom tooth removal.
- Resection of the root apex.
- Removal of an impacted (unerupted) tooth.
- Removal of bony protrusions (exostoses).
- Removal of the gingival hood.
- Plastic surgery of the frenulum and gums.
- Price list.
Dental clinics providing comprehensive dental care cannot exist without dental surgery.
All surgical interventions are performed with anesthesia.
Medicine currently has a wide range of painkillers, used individually depending on the age and condition of the patient (children, pregnant women, hypertension, allergies, etc.). The correct selection of anesthetics and other medications is the key to the overall well-being of the patient. Surgical dentistry involves interventions on the teeth, jaws, oral mucosa and gums. A dental surgeon must master all the skills from simple tooth extraction to complex operations to restore the volume of the jaw bones for dental implantation. The section of surgical dentistry includes: tooth extraction, resection of the root apex, removal of impacted (unerupted) teeth, removal of bony protrusions (exostoses), plastic surgery of the frenulum and gums, removal of the gingival hood (“creeping” of gum tissue over the erupting wisdom tooth), bone grafting and sinus lifting for dental implantation, splinting of teeth and jaws for jaw fractures, removal of benign tumors on the gums, mucous membrane, tongue, etc.
In this section we will describe the main surgical procedures performed in a dental clinic.
Removal of a tooth
There are many factors involved in tooth extraction. Teeth with root cysts often need to be removed. Unerupted wisdom teeth that interfere with orthodontic treatment are removed. One of the reasons for tooth extraction is the impossibility of saving it through therapeutic treatment or excessive mobility in moderate and severe forms of periodontitis. In the latter case, when the tooth is mobile and its root is exposed by half or more, removal does not present any difficulties. When the coronal part is destroyed, the tooth extraction technique becomes more complicated. The inability of an instrument to fix a badly damaged or missing coronal part of a tooth often forces the surgeon to remove it in fragments by sawing the roots. The walls of previously pulpless teeth are fragile and can crumble if they are not grasped correctly with a surgical instrument. Removing front teeth is easier compared to removing side teeth. Incisors and canines are single-rooted teeth, premolars and molars have 2-3 roots. The roots of molars are located along different axes and require a certain range of motion when removed. Of all the teeth, the canines have the longest root.
To remove the specified tooth, it is necessary to conduct a computed tomography scan of the thinned area of the bone to exclude a fracture of the lower jaw
Tooth extraction of any degree of complexity should be carried out under full pain relief. In a modern clinic, the pain of any dental procedure is eliminated.
Tooth extraction is always preceded by an examination. It is necessary to determine the mobility of the tooth and the degree of its destruction. X-ray diagnostics is mandatory, where the condition and location of the roots, the degree of their exposure, the presence of granulomas and cysts are studied. Patients are given recommendations: eat 2-3 hours before removal, if they are excessively nervous, take medicine to relieve tension, etc. Children, pregnant women and the elderly require an individual approach. Patients with previous heart attacks, hemophilia (inability to clot blood), epilepsy, hypertension, allergic diseases, with a pacemaker, etc. require a special approach and preparation, and sometimes even hospital conditions.
When removing teeth with granulomas and cysts, the dental surgeon knows that in addition to removing the tooth, he needs to perform a thorough curettage (cleaning) of the area in the area of the granuloma. When removing the roots of damaged teeth, it is necessary to preserve the interroot bone septa as much as possible. This area of the jaw bone is very important for restoration (regeneration) of the height of the bone of the jaw process, when subsequently installing implants of sufficient length. The outer (labial) wall of the jaw bone is thinner than the palatine; uncoordinated movements of the doctor when removing a tooth can lead to its breakage, which will subsequently create aesthetic problems in the area of the anterior teeth of the upper jaw.
- high blood pressure - it is necessary to consult a cardiologist (therapist) and adapt the patient’s blood pressure on the day of tooth extraction;
- pregnancy - tooth extraction is recommended in the second period of pregnancy (except for the last month). Gynecologist's recommendations;
- hemophilia (incoagulability of blood) - inpatient tooth extraction under the supervision of a hematologist;
- suffered a heart attack - it is not recommended to use anesthetics containing adrenaline when removing a tooth and removing it in the next 2-3 months;
- the presence of infections (flu, herpes, acute respiratory infections, etc.) - delay tooth extraction until the acute period has passed, if it is necessary to provide assistance, take preventive measures for staff and the institution;
- epilepsy – tooth extraction depending on the underlying pathology, the presence of a neurologist, resuscitator;
- the presence of specific infections (hepatitis, AIDS, tuberculosis, etc.) - during tooth extraction, during and after special training of specialists, instruments, premises.
At the clinic “Dentistry of Professor Abakarov”:
- professors, doctors of medical sciences, candidates of medical sciences, associate professors
- specialist doctors
- modern technologies for diagnosing and treating diseases
- latest achievements in world dentistry
Removal of a wisdom tooth at the clinic “Dentistry of Professor Abakarov” on Paveletskaya. When should a wisdom tooth be removed?
It is believed that wisdom teeth are quickly destroyed due to insufficient load. They take a long time to erupt and cause the patient a lot of problems:
- Form a gingival hood;
- They grow to the side, injuring the surface of the cheek or tongue;
- Interfere with existing teeth;
- They put pressure on the teeth in front and distort the bite.
Sometimes it is enough for the doctor to adjust the gum tissue to relieve inflammation and save the tooth, but in some cases the tooth is removed to eliminate the source of constant discomfort of inflammation. Removal of wisdom teeth on Paveletskaya is carried out by qualified specialists who are ready to conduct a preliminary examination and offer an informed decision. If treatment and reconstruction of a tooth is justified, the doctor will do everything to preserve it. Without reasonable indications, a wisdom tooth should not be removed.
Resection of the root apex.
Resection of the root apex is a tooth-preserving operation. The cyst located (attached) at the apex of the root is a sac with dense fibrous walls filled with serous-purulent contents. The cause of the appearance of granulomas and cysts is poor-quality filling of the canals. When the canal is loosely and incompletely filled, inflammation develops at the apex of the tooth root, leading to bone resorption and the appearance of a granuloma, and then a cyst.
In some cases, the appearance of granulomas and cysts is asymptomatic, and the patient learns about their presence from the doctor after X-ray diagnosis. When the disease worsens, pain appears when biting, swelling and redness of the gums in the area of the root of the corresponding tooth. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, the swelling increases and periostitis (flux) may begin. In these cases, tooth extraction cannot be avoided.
Small cysts (granulomas) can be treated therapeutically, provided that their size does not exceed 1-1.5 cm in diameter. In other cases, surgery is indicated. If the root part of the tooth is 1/3 or more covered by a cyst, then the tooth with the cyst is removed. If the cyst is located at the apex of the root, then it is removed by cutting off the apical part within 3-5 mm. Excessive root excision is unacceptable, because this impairs the stability of the tooth in the jawbone.
A prerequisite before resection of the root apex is treatment (filling) or retreatment of the tooth canal.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia and is completely painless. The duration of the manipulation depends on the location of the tooth. It is easy to operate on the front teeth, but the side teeth require more effort and time. On average, the operation takes 30-50 minutes. To create access to the root apex, a small incision is made on the gum in the area of the diseased tooth, through which access to the cyst itself is formed. The mucous membrane in the area of the incision is peeled off to expose the bone tissue, after which the surgeon makes small holes in the bone using a drill. The cyst is removed, the root apex is cut off with a drill, and the incision line is sutured. Anti-inflammatory therapy, rinsing with an antiseptic solution are prescribed, and recommendations are given for the prevention of complications.
The ability to save a tooth by resecting the tip of a tooth with a cyst is a serious argument for the patient. In the case of the removal of such teeth, it becomes necessary to grind adjacent teeth to make a metal-ceramic bridge prosthesis or implant a tooth and then cover it with a crown. Replenishing a missing tooth using these methods takes a long time and involves significant material costs.
Removal of an impacted (unerupted) tooth
Removing an unerupted tooth is a common problem. This is especially true for the third molars, i.e. wisdom teeth Such teeth can become a serious problem for neighboring teeth, affecting their position, changing the bite, and causing inflammation of the gums (gingivitis). These teeth definitely need to be removed.
Recommended removal of wisdom teeth in the lower jaw for orthodontic reasons
Computer tomogram for dental implantation on the lower jaw on the left and diagnosis of an impacted wisdom tooth on the right.
Removing impacted teeth requires some preparation. It is imperative to analyze the radiograph. It may have to be done in several projections to clarify the location of the tooth in the jawbone. And in some cases, computed tomography is indicated. It is necessary to determine the relationship of the impacted tooth with the maxillary sinus, mandibular or trigeminal nerve, with the nasal sinus, depending on the location of the tooth. Removing impacted teeth is easier on the upper jaw than on the lower jaw, because the latter has harder and denser bone.
| Impacted wisdom tooth of the upper jaw on the right | Impacted teeth of the lower jaw on the left |
After the examination, the patient is given anesthesia and dissection of the gum area above the tooth. Next, access is created in the bone tissue using a drill. If the tooth cannot be removed entirely, then it is removed in fragments, in parts. It is extremely important to remove absolutely all bone particles. After the procedure, the gums are treated with an antiseptic and sutured. The postoperative period may be accompanied by slight swelling, pain, and sometimes fever. Therefore, it is extremely important to carry out all prescribed anti-inflammatory therapy, follow the regimen and all preventive measures. If the surgical protocol is followed and all recommendations are followed, the sutures are usually removed after 8-10 days.
In middle-aged and older patients, X-ray diagnostics may accidentally reveal an impacted tooth that has been in the jaw bone for decades in a passive state. In this case, there is no need to discuss the issue of its removal if it does not cause disturbances or does not interfere with any interventions.
Removal of bony protrusions (exostoses).
In dentistry, exostoses are the bone protrusions (spikes) that remain on the jawbone under the mucous membrane after tooth extraction. They do not cause any inconvenience to the patient. The problem arises with an orthopedic dentist when making a removable denture on a toothless jaw. Before taking an impression, the orthopedist always studies the relief of the bony process of the jaw where the prosthesis will be located. It is enough to run your finger along the edge of the jaw to assess its condition. If there are bony protrusions (spikes), it is necessary to delay the manufacture of the prosthesis, recommending that the dental surgeon remove the spines and smooth the jaw bone. This is done under anesthesia using a surgical carbide cutter. This manipulation (revision of the bone ridge) should always be performed by surgeons when removing teeth from patients who are to have a removable denture made. Otherwise, in the area of the bone spike, the gums will always be injured by the prosthesis, which will rub, stain and hurt. The patient will not be able to wear the prosthesis. Repeated visits to the orthopedist to adjust the prosthesis will not be effective and will ultimately lead to poor fixation in the mouth. A dental surgeon’s knowledge of the design features of a removable denture and the appropriate preparation of the maxillary process will eliminate intermediate procedures and visits to the dental clinic and reduce the rehabilitation time for a patient with complete absence of teeth.
Removal of the gingival hood.
Basically, this manipulation is carried out when the eruption of wisdom teeth is difficult. In the area of all other teeth, as the gum tissue erupts, it gradually becomes thinner and dissolves, without causing significant distress to the patient. When wisdom teeth erupt, the gum located above it is a continuation of the mucous membrane located behind the last tooth (wisdom tooth).
Conservative methods of treatment and prevention are not always effective. Rinsing the distance between the erupting tooth and the overhanging gum with disinfectant solutions removes food debris and microbial flora, and rinsing relieves discomfort and pain for a short period of time. The effect of using ointments and medications is equivalent. If there is an antagonist tooth on the opposite jaw in the projection of the hood, it is additionally injured when the teeth are closed and is in a stable inflamed state.
Excision of the hood does not always solve the problem. In all cases, the patient undergoes an X-ray examination. It is possible that the abnormal location of the wisdom tooth blocks its further eruption and excision of the hood will not give any result. The question should be raised about tooth extraction or excision of the hood and sections of bone blocking the coronal part of the erupting tooth.
The procedure for removing the hood is not complicated. After anesthesia, the dental surgeon exposes the chewing surface of the erupting tooth by excision of the overhanging gum tissue with a laser, electrocoagulator or scalpel. If necessary, several stitches are applied. For small volumes you can do without them. There is no need to prescribe general drug therapy. Sufficient local use of medicinal ointments and disinfectant rinsing solutions.
Initially, it is necessary to determine the exact area of the gum to be excised. If it is not removed sufficiently, a relapse may occur and the need for additional gum excision may occur.
Plastic surgery of the frenulum and gums.
Frenules are special folds of the oral mucosa with the help of which the tongue and lips are attached to the jaw. From a physiological point of view, all three frenulums should be located exactly in the center of the dentition and face and have a certain length. If there is an off-central position or excessive height in one of them, then surgical plastic surgery is necessary.
With untimely frenuloplasty, complications may develop, such as the formation of a diastema (the gap between the central incisors), exposure of the necks of the teeth, and the development of periodontitis. Wide and short frenulums impede hygiene, contribute to the accumulation of plaque, can interfere with the movement of the tongue and lips and change pronunciation (phonetics). The manipulation is carried out under local anesthesia (and a large amount of anesthetic is not required) and takes 10 - 15 minutes.
The postoperative period usually passes without complications, except that after the effect of painkillers wears off, the patient may experience minor pain and discomfort. It is necessary to strictly follow all recommendations, exclude hard and hot foods from the diet, and rinse with prescribed antiseptic solutions. There is no need for special drug therapy for frenuloplasty. Complete healing occurs within 2-3 weeks.
Lip and tongue frenuloplasty are not the most difficult operations, but they should be approached responsibly, observing the diagnosis, surgical protocol and postoperative rehabilitation. Our specialists have more than 200 successfully performed operations of this type, which once again guarantees the safety and quality of the service.
Gum plastic surgery (gingivoplasty) is performed in cases where there are problems such as uneven gum contour, strong gum growth on a tooth, or, on the contrary, exposure of tooth roots. With the help of gingivoplasty, excess gum tissue is either removed or missing ones are built up. This type of surgery is performed both on your own teeth and in the area of implants.
Increased volume (hypertraffed) gums are surgically brought to the correct dental relief and smile contour
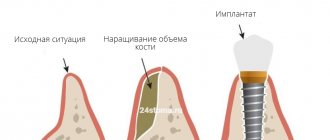
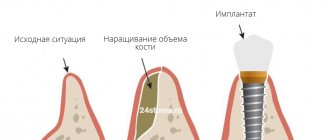
The need for gum plastic surgery during implantation in the area of missing teeth occurs in the anterior and anterolateral areas of the dentition for aesthetic reasons. An area of the jawbone where teeth were removed long ago, or where their removal was difficult, may have a significant change in contour. To change such “gum gaps,” the volume and height of the gums are increased to create the aesthetics of crowns. This is necessary to achieve a correct and beautiful gum line and crown margin, especially in the smile area. In severe cases, it is impossible to restore the gum relief without increasing the volume of the jaw bone. In case of significant “failures”, in order to avoid additional jaw operations, it is possible to manufacture a metal-ceramic prosthesis with modeling of additional volumes with pink ceramic mass (gingival).
Gingivoplasty is a simple procedure and is performed under local anesthesia. The duration of the operation may vary and it depends on the volume of intervention and the number of teeth. Before surgery, dental plaque removal and pocket hygiene are required. During the operation, excess tissue is either removed or a flap of the mucous membrane of another area is transplanted. Typically, a donor piece of tissue is taken from the palate. The flap is cut out and fixed with surgical sutures in the required place. Subsequently, the donor site is sutured. In the case of a favorable course of the postoperative period, after 15-20 days, the site of gum plastic surgery does not differ from the rest of the oral mucosa.
In difficult cases, it is necessary to make diagnostic models, macro photographs, and the necessary measurements. A virtual relief of the future gum line should be created in relation to the edge of the crowns (or cervical areas of the implant). It is important to demonstrate the upcoming operation and the results obtained, including prosthetics, on the monitor to the patient. Those. outline the protocol of all stages, execution options and prognosis of overall treatment.
Most often, gingivoplasty is part of a complex treatment stage using expensive technologies (ceramic veneers, metal-free ceramics, dental implantation, etc.). To obtain the final result, continuity, mutual understanding and coordinated work of all specialists (orthopedic dentist, dental surgeon, dental technician) are important. These are the working principles of the doctors at the ABADENT clinic.
Take advantage of the best price
Call now
+7
Leave a request for a call back
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
Use of artistic restoration
Some patients are advised to undergo aesthetic artistic dental restoration to eliminate diastema. This is a therapeutic intervention during which composite microprostheses (veneers) are installed on the two central incisors, between which there is a gap. The doctor uses a filling material that matches the patient’s natural enamel shade and builds up additional volume of hard tissue on the two central front teeth. To undergo this procedure, you only need to visit the clinic once.
When restoring a tooth, the doctor restores its shape and function. The presence of colored deposits and cracks in the enamel, and other signs of destruction of dental tissue does not play any role, since most of the visible dental tissue is removed. Then its natural shape, color and functional properties are formed using composite materials (build-up method). If the root of a tooth is damaged, it is treated first, and restoration is carried out only at the next stage. If no pathologies associated with the tooth root are detected, then in 5-6 hours a qualified doctor is able to restore at least 4-5 teeth. However, if the dentist first works with the root of the tooth, then further manipulations are carried out after at least two days.
An important advantage of artistic restoration is its complete painlessness. Another important advantage of this method is its safety, therefore it has a minimal list of contraindications. Dental restoration can be performed on women even during pregnancy.
Stages of manipulation
Removal of the tooth wall is part of a multi-stage restoration of an artificial crown. Treatment protocols may differ significantly depending on the clinical picture.
The simplest restoration procedure is the placement of a composite filling. Removal is a radical measure, which is taken only in cases where the problem cannot be solved using restoration methods.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis for making a decision about tooth extraction includes interviewing the patient, an initial examination of the oral cavity, probing, and palpation to assess the mobility of the damaged tooth. To assess the condition of the roots, an x-ray and an orthopantomogram are prescribed.
Based on the clinical picture, a treatment protocol is drawn up.
Preparation
Before starting the procedures, the patient’s oral cavity is treated with an antiseptic solution. If plaque accumulates, ultrasonic professional cleaning may be prescribed. Local anesthesia is administered using the infiltration method.
Recovery techniques
If removal of the tooth wall is indicated, the procedure is carried out at the preparation stage using one of the restoration methods.
If the subgingival part is in satisfactory condition, then the tooth can be restored using fillings, installation of onlays, inlays, and crowns. For filling, a light-polymerizing composite material is used, which, after exposure to light, acquires the required shade.
Before installing microprostheses, an impression is taken to make the missing part of the tooth. It is fixed into a previously prepared cavity using special glue.
When a tooth is completely replaced with an artificial crown, an impression is taken to make the latter, then an artificial tooth is made. For fixation, a special cement composition is used.
The installation of a pin is prescribed when the entire clinical crown is destroyed, if the tooth root is in satisfactory condition for subsequent use. The stump pin insert is made of metal and includes a stump from which the pins come. The latter are installed in the root canals. This technology is the most reliable way to restore a severely damaged tooth crown.
Root removal is carried out in the presence of inflammation or the development of an infectious process in one of the roots of the tooth. It is removed in order to prevent subsequent destruction of healthy roots. During the procedure, the doctor removes the flap at the site of damage and cuts a hole in the alveolar wall to extract the destroyed root.
Removal of a tooth
If the crown is strong enough, forceps are used for removal. If their use is not allowed, the tooth is removed using an elevator. During all restoration activities, it may be necessary to eliminate foci of inflammation.
The antiseptic chlorohexidine is used to treat the wound. If tissue detachment was performed, a suture is applied after the operation is completed. Instead of detaching the flap and suturing the wound, modern dental practice uses a laser technique.
Rehabilitation
After filling, you should refrain from eating and drinking for two hours.
After operations with tissue detachment, the following recommendations must be followed:
- remove the tampon with the drug at the specified time;
- limit food intake for two to three hours;
- in the first two to three days after the procedure, avoid hard, viscous, cold, hot foods and drinks;
- reduce the chewing load on the side with the operated tooth;
- carefully monitor oral hygiene, avoid contact of the toothbrush with the operated area.
To prevent infection and inflammation, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with decoctions of herbs that have antiseptic properties (for example, chamomile, calendula, sage).
To relieve pain in the first days, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics, histamines and painkillers.
Rehabilitation after the most complex dental operations does not exceed two weeks. To speed up wound healing, it is recommended to follow the doctor's instructions. As practice shows, most complications arise due to violations.
In case of any complications, you must immediately inform your doctor about them.
Surgical plastic surgery
For many patients, the determining factor in choosing a method for eliminating diastema is the cost of therapy. Be sure to consider your financial resources when you and your doctor select a method for correcting a dental gap. Choose the method that suits you best, but do not skimp on your health, as otherwise you may not achieve what you want and spend even more money on eliminating the negative consequences of unsuccessful treatment.
A tooth gap can also be removed using surgical plastic surgery. This technique involves installing dental crowns. Dentists correct the defect by placing ceramic veneers or crowns on the front teeth. This intervention allows you to achieve an excellent aesthetic effect that lasts for many years. Some disadvantage of this technique is its rather high price.
If for one reason or another you cannot use this technique, the doctor can fill the front teeth for corrective purposes, as a result of which the gap will be eliminated. Pay attention to the above method if the diastema occurs a second time or the installation of staples does not bring the desired result.
Orthodontic correction methods
Orthodontic methods for correcting diastemas are rightfully considered the safest, most effective and gentle (they allow you to preserve a maximum of healthy dental tissues). However, their main drawback is the long duration of treatment. Malocclusions are eliminated step by step - for this, braces are used. Orthopedic treatment is primarily indicated for children and adolescents whose permanent teeth have recently replaced their deciduous predecessors. Braces are special orthodontic structures that are attached to the teeth from the inside (invisibility braces) or the outside. How long do you need to wear braces? This is determined by the doctor individually, but usually treatment continues until the bite is completely corrected (from 6 to 24 months). It is best to install braces when the jaw is actively growing.
Your dentist may also recommend mouth guards, which are small transparent covers for your teeth. Aligners contain information about the normal shape and size of teeth. These devices are made in such a way that they move individual teeth in the required direction, restoring their correct position. The result of this is that the teeth move closer to each other and the diastema is eliminated. Aligners have a transparent base, so they are even less noticeable on the surface of the teeth than braces.
The advantage of mouth guards is that they can be removed while eating. Moreover, since they are filled inside with a whitening compound, using this method, you will not only eliminate the gap between the front incisors, but also lighten the tooth enamel. This will also add beauty to your smile and eliminate the need for additional whitening procedures.
Orthodontists are indispensable if a person, in addition to diastema, is diagnosed with any other malocclusion. Metal braces are considered affordable and reliable for most patients.
How to remove gaps between teeth?
Modern dentistry offers the following options:
- Veneers. They are dental onlays attached to the front surface of the patient's teeth. Their main purpose is to correct the aesthetics of the dentition without the need for orthodontic treatment. Veneers are made in Moscow strictly individually in a dental laboratory. At the first stage, the patient’s tooth is ground down (a thin layer of enamel is removed), and an impression is made of it, which serves as a sample for creating a veneer. Making a veneer takes from 7 to 14 days, during which time the patient wears temporary veneer structures. After the permanent veneers are made, fitting is carried out, their compliance with aesthetic standards and the wishes of the patient is checked, if everything is good, the specialist fixes the veneer. The advantages of this option include the ability to correct even wide gaps between teeth in the shortest possible time.
- Bracket systems. The safest, high-quality method, loyal to dental tissues, but also the longest. To correct the bite, braces are used. If the patient is a child whose baby teeth have only recently been replaced by permanent teeth, braces are the best option. Modern braces are almost invisible, so they do not cause discomfort in everyday life. In addition, you can always order lingual braces, which are attached to the inside of the dentition, which means they are absolutely invisible. The time for wearing braces is determined by the dentist individually in each case - the timing depends on the structure of the teeth, the age of the patient, the size of the gap and other factors. Usually we are talking about a time range from six months to two years.
- Artistic composite restoration. This is the most preferred method when it comes to eliminating gaps between fangs, incisors, and slight curvature. Composites are photopolymer elastic materials that are applied layer by layer and harden under a photopolymerizer (special lamp). The advantages of artistic dental restoration include the speed of achieving results (restoration takes up to half an hour to two hours), the absence of painful sensations for the patient, and the absence of the need to grind down tooth enamel.
The above are not all the ways to get rid of gaps between teeth. Perhaps your dentist, having assessed the condition of your oral cavity, will offer you a more effective and/or profitable alternative - this could be a plastic transparent mouthguard (easily removed, allowing you to combine the adjustment of the position of your teeth with their whitening), corrective fillings or crowns.
All problems can be solved
An even dentition, white teeth of regular shape adorn any person and serve as an integral part of an ideal smile. Thanks to this, everyone can feel attractive, because in the modern world almost any dental defect can be successfully corrected. Thanks to this, many patients are able to return to normal life. Therefore, if you are concerned about the presence of a diastema, this imperfection can be corrected quite quickly and painlessly in dentistry near the Krasnye Vorota, Baumanskaya, Novokuznetskaya and Tretyakovskaya metro stations. Do not be indifferent to your health and psychological state, and confidently contact dental specialists to solve your problems.