In what cases may the bone fail to take root?
The bone may not take root in cases where it becomes infected, including when the patient violated the schedule for taking antibiotics or did not follow the doctor’s orders.
Much attention is paid to food intake: the patient can simply, out of forgetfulness, bite into something hard, and his stitches will come apart, and the material and bone graft will become infected through the open wound.
The above accounts for 90 percent of cases
when the bone may not take root.
Are there any contraindications to bone grafting?
Of course, there are contraindications to bone grafting. These include
:
- various chronic diseases, incl. diabetes mellitus with high sugar levels,
- the period when the patient takes a number of drugs, including chemotherapy,
- in the period after chemotherapy, when the bone cannot be “touched” at all.
Features of hygiene after bone grafting
After bone grafting it is recommended
:
- use of special surgical toothbrushes,
- the use of toothpaste should be limited, and even better, use special toothpastes for post-surgical interventions,
The main thing when carrying out hygiene is NOT TO INJURY
area of bone grafting! You should try to eliminate contact with this area or reduce it to a minimum.
When can you do without bone grafting?
You can always do without bone grafting when you can install an implant of the required diameter and required length into the remaining bone.
And, in fact, you shouldn’t do bone grafting just to assert yourself. Some doctors suffer from this, trying to prove to themselves or someone else how they can do bone grafting.
But, as they say, the best bone grafting is the one we don’t do: if the patient can be rehabilitated without bone grafting, then it’s better to do just that. Since volume can be added with soft tissues, connective tissue can be transplanted - a graft, or drugs can be added to replace the volume of soft tissues - and achieve an excellent result!
Materials used
The material used to make the bone plate can be natural or synthetic. They are similar in their ability to replenish bone tissue and have comparable engraftment rates. Synthetic materials are powder or shavings and are currently used by dentists in all developed countries of the world.
But better than synthetic is material of animal origin (xenograft) or your own bone material. Synthetic takes root well, but materials from animals or your own (autogenous material) have a lower risk of rejection, a lower degree of resorption, and the body accepts them better. To produce materials of animal origin, biomaterial from cows and bulls is used, which goes through several degrees of purification and sterilization. In fact, in terms of purity, this material corresponds to synthetic, but depending on the manufacturer, it can give better results than synthetics. Natural material is taken from the donor area, usually the chin or bone tissue near the wisdom teeth. The only difficulty in using your own bone material is that its collection requires additional intervention (in fact, harvesting an autograft is an operation not much different from removing a wisdom tooth and in some cases even simpler). Another type is xenotransplantation.
There is no specific standard, so the material is selected by the doctor together with the patients. The final cost of bone grafting may depend on the material chosen. The use of artificial biocompatible osteoplastic material or sampling from the patient himself is considered more justified and popular. If necessary, you can select material from extraoral areas without damaging the gum tissue.
If bone grafting is carried out correctly and in full, then subsequently the installed implant will hold securely, regardless of the complexity of installation and healing.
What implants are used after bone grafting?
Are there “special implants” that are recommended in cases of bone grafting? Both with bone grafting and without bone grafting, it is necessary to use implants only from good, proven manufacturers, those that have a good clinical base. For example – Straumann, Nobel, Ankylos, Xive, Astra Tech.
There are a number of other implant systems that give good results. But at the German Implant Center we use only the best implant systems, only premium ones.
Non-carious lesion of tooth tissue
One of the reasons for the appearance of bone tissue atrophy is damage for various reasons. This disease takes second place in visits to the dentist after caries. It can affect one tooth or several and manifest with various symptoms.
Non-carious lesions of tooth tissue can be congenital or acquired. One of the phenomena of damage may be erosion. The enamel is damaged, which leads to darkening, increased sensitivity and aesthetic problems. The disease can last a long time and lead to tooth loss. Sometimes the cause of the development of pathology is a diet with a high content of acids and salts. Marinades and orange juice provoke the development of the disease. At the initial stage, the disease is not diagnosed, because the loss of enamel shine is not very noticeable. But over time, the patient begins to complain of pain. Prevention of erosion is an important component to prevent the development of damage to dental hard tissues and atrophy.
Another common cause of dental damage is increased tooth sensitivity. Under the influence of temperature, severe pain occurs, which quickly subsides. The disease can bother one tooth or affect several. If left untreated, there is a risk of surgery or removal. To replenish missing minerals in tooth tissues, vitamin and mineral complexes are taken.
How is implantation performed during bone grafting?
Implantation during bone grafting can be carried out either simultaneously with bone grafting, or delayed - when the implants are installed in the new “grown” bone.
As an experienced implant surgeon, in my practice, in 80-90 percent of cases I perform bone grafting at the same time
with implantation.
I will explain why I perform plastic surgery with implantation at the same time, and what is the advantage of this approach. Bone grafting itself requires a long healing period, from 4 to 9 months. And if we maintain this period and then do implantation, then we have to wait another 4 months. That is, the time frame in this case increases significantly.
And if I do implantation along with bone grafting, then the implant takes root along with the bone. A good implant has an excellent osteogenerating surface, and when fused, an excellent result
.
This reduces the patient’s rehabilitation time. And most importantly, the patient DOES NOT NEED
second surgery. We understand that a large number of surgical interventions do not improve trophism, mucous membranes, or bone tissue.
Everything we do at the German Implant Center, from tooth extraction to implantation, is carried out as atraumatically as possible for the patient.
How many implants are placed during a total restoration?
We specialize very broadly in total implant rehabilitation. In the upper jaw, 6-8 implants are recommended according to our protocol; in the lower jaw, 6 implants are sufficient for total rehabilitation.
Often, implantation occurs simultaneously with the installation of temporary teeth, that is, the patient leaves the clinic “with teeth”, and not on the second or third day, but on the same day when implantation is done:
Preliminary implantation planning is carried out using CBCT, the implants are placed in the required positions.
After this, a surgical template is made, according to which the implants are installed. And based on the same computed tomography (CBCT) and images, a temporary structure is made that will be attached to the implants installed for the patient.
And it turns out the so-called “full case” is when the patient comes, if necessary, if circumstances require it, teeth are removed (or they have already been removed/lost earlier), implants are placed on the patient and an orthopedic structure is fixed - his new teeth.
Dentine
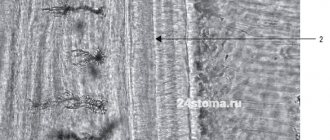
The bone substance of the tooth is its main part. Dentin performs an important function as it protects the pulp from external irritants. Having a loose structure, the bone substance of the tooth ranks second in strength in the body after enamel. The composition of this tissue is 2/3 inorganic substances, 1/5 collagen and 10% water. If you look at dentin under a microscope, you can see that it is a substance that is unevenly covered with calcareous deposits. A huge number of dentinal tubules filled with nerve endings of the pulp pass through it. There are 3 types of bone substance of the tooth: 1. Primary dentin, the formation of which begins even before the first eruption of the tooth. 2. Secondary or physiological, it is formed after the appearance of the tooth. It is characterized by a chaotic arrangement of dentinal tubes and fibers, and their smaller number. 3. Tertiary or, as it is also called, replacement, it is formed as a result of tissue irritation. It is characterized by an uneven appearance with slight mineralization. Dentinal tubules are most often absent in this type. The formation of dentin is individual and depends on numerous factors. This process can be influenced, for example, by tooth wear or other defects, as a result of which dentin replacement occurs at different rates of intensity.
On which jaw does tooth bone resorption occur faster?
How quickly does a deficiency of bone and bone tissue occur in the absence of a tooth?
In fact, tooth bone tissue decreases faster in the upper jaw, since the upper jaw is softer and more porous. In the lower jaw, the bone also disappears quite quickly, since the vestibular plate near the teeth is quite thin. Six months after tooth loss, quite severe atrophy of bone tissue occurs, and the atrophy progresses. And therefore, in order to avoid atrophy, it is advisable to do implantation simultaneously immediately after tooth extraction.
This format is the regular, daily work of the specialists of the German Implantology Center. For example, a patient comes with a crack in the root of a tooth - the tooth must be removed. We can go with two options:
Option 1.
We can remove the tooth and 3 months later implant the tooth into the patient.
But during these three months, shrinkage of the bone tissue still occurs, since - I said earlier - the vestibular bone plate is very thin. And in this case, the patient undergoes 2 surgical interventions
: the first is tooth extraction, the second surgical intervention is the installation of a dental implant.
Option 2.
In our practice, we recommend and practice the second option. This is a one-step implantation, when the patient has a tooth removed, an implant is installed, and in order to avoid collapse of the bone tissue in the places where the roots of the tooth used to be, these places are filled with a bone graft. Due to graft filling, we do not have tissue “collapse”; the contour of both the gums and the jaw bone tissue is preserved. Which, in turn, is very difficult to achieve with delayed, delayed implantation.
Who can undergo bone grafting?
Who are potential patients for bone grafting, and what are the age restrictions for it?
This is a bit of a tricky question :). The oldest patient I have performed bone grafting on is a 75-year-old patient, a wonderful, purposeful woman. She had bilateral terminal defects on her lower jaw. She really wanted implantation and refused a removable structure.
I performed bone grafting on this woman at the same time as implantation. And literally 6 months later she was fitted with prosthetics. And everything went great.
In the case of the patient’s age, the main thing is that he has no contraindications. Perhaps there are age restrictions, but they are not so pronounced, because, although trophism deteriorates with age, regenerative abilities decrease, but the main thing is the presence of contraindications. You need to look at the tests, and if the patient is healthy at 75 years old, then why not?
What does bone destruction lead to?
Atrophy is not only an aesthetic problem; with this pathology, changes occur in the body and difficulties arise in other organs. Restoring the dentition becomes a complex task and requires bone tissue augmentation during dental implantation.
In the absence of teeth, food is crushed poorly, which over time leads to a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
The loss of a large number of teeth leads to impaired diction and causes the appearance of deep wrinkles on the cheeks.
How to do without bone grafting
Is it possible to do without bone grafting and sinus lift?
Yes, in some cases you can do without bone grafting. But you need to understand that if the patient does not have bone tissue, and we install an implant, the crown will hang over the gum, and something from food will constantly get clogged there. That is, it is aesthetically unsightly, and all the food will be stuffed there, the patient will always have a “pocket of food supplies” from yesterday and the day before yesterday.
Option with a smaller diameter implant
You can place an implant of a smaller diameter, and at the same time we can carry out soft tissue regeneration - replant the mucous membrane (this can be connective tissue from the palate, from the tubercle of the upper jaw). And thus we achieve replenishment of the volume of soft tissues. Due to this, aesthetics are visually improved and hygiene problems are eliminated.
Whenever it is possible to avoid various surgical procedures, but not at the expense of quality, then they should be avoided.
That is, surgery for the sake of surgery - it is not needed
.
Bone atrophy - what is it?
Bone atrophy is the process of a gradual decrease in the hard tissue of the jaw bone, while the size of the alveolar ridge is significantly reduced, pronounced nasolabial folds appear, the jaw decreases in size, and a “drooping” of the face occurs. Bone resorption (loss) occurs most often after surgical removal of the root, but a person can be born with this pathology.
Clinical case: a person’s tooth and root were removed a long time ago, and an implant and prosthesis were not installed in their place. Over the course of a year, bone tissue atrophies by approximately 25%.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Protecting the jaw from atrophy
Atrophy of the dental bone tissue is treated surgically, but this can be avoided if the destruction of hard tissue is prevented.
To do this, it is necessary to restore lost teeth in a timely manner and prevent the loss of existing ones. Implants are much better than other methods, because they have a root and create a load on hard tissues. Removable dentures do not provide full load on the lower jaw, and over time, atrophy of the hard tissues of the teeth will occur. Treatment is similar for significant loss of jaw bone. If hard tissues subside gradually, then correction of the prostheses will be required without treating atrophy.
When treating atrophy, the choice of treatment method depends on the wishes of the patient. What does he want to achieve? Complete restoration of bone tissue and its function or create external beauty?
To prevent atrophy and other oral diseases, you should visit the dentist twice a year.
First letter "d"
Second letter "e"
Third letter "n"
The last letter of the letter is "n"
Answer to the question “Bone tissue of the tooth”, 6 letters: dentin
Alternative crossword questions for the word dentin
Type of bone tissue
Bone tissue of teeth
Main tooth mass
Hard tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth
Definition of the word dentin in dictionaries
Explanatory dictionary of the Russian language. D.N. Ushakov
The meaning of the word in the dictionary Explanatory Dictionary of the Russian Language. D.N. Ushakov (de), dentin, pl. no, m. (from Lat. dentes - teeth) (med.). Bone substance of the tooth.
Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The meaning of the word in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia dictionary (from Latin dens, genitive dentis ≈ tooth), a type of bone tissue that makes up the main mass of the tooth and is also found in placoid scales. Unlike other types of bone, the ground substance of D. does not contain cavities with cells, but is penetrated by tubules, ...
New explanatory dictionary of the Russian language, T. F. Efremova.
The meaning of the word in the dictionary New explanatory dictionary of the Russian language, T. F. Efremova. m. Hard tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth of vertebrates and humans.
Wikipedia
The meaning of the word in the Wikipedia dictionary Dentin (dentinum, LNH; - tooth) is the hard tissue of the tooth, constituting its main part. The coronal part is covered with enamel, the root part of the dentin is covered with cement. Consists of 72% inorganic substances and 28% organic substances. Consists mainly of hydroxyapatite...
Explanatory dictionary of the Russian language. S.I.Ozhegov, N.Yu.Shvedova.
The meaning of the word in the dictionary Explanatory Dictionary of the Russian Language. S.I.Ozhegov, N.Yu.Shvedova. [de], -a, m. (special). Bone tissue of the tooth.
Encyclopedic Dictionary, 1998
The meaning of the word in the dictionary Encyclopedic Dictionary, 1998 DENTIN (from Latin dens, genitive dentis - tooth) a type of bone tissue that makes up the main mass of teeth; In the crown area, dentin is covered with enamel, in the root area - with cement. Also found in the scales of cartilaginous fish.