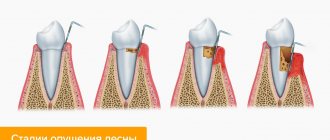
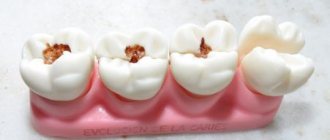
What types of caries are there?
There are several stages of the disease. They have a certain appearance and symptoms.
How to determine the stage of caries:
- In the spot stage: a white spot is observed on the surface of the enamel (focus of demineralization). The spot gradually turns brown. Enamel is the densest tissue in the human body, but due to various cariogenic factors it is gradually destroyed. Detecting the white spot is quite difficult.
- Medium caries: characterized by damage to the enamel-dentin junction in the form of a cavity, short-term sensitivity.
- Deep: extensive lesion affecting the deep layers of dentin. Pain appears from different types of irritants: mechanical, temperature, chemical.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using a visual examination and an x-ray. The image will show violations of the integrity of the enamel and dentin with uneven contours.
Why is caries dangerous for the heart and blood vessels?
When brushing your teeth, there is a risk of injury to your gums. This can happen due to a brush that is too hard, careless use of dental floss, or sensitivity of the gums themselves. One way or another, cariogenic bacteria enter the resulting wounds, which can be carried throughout the body by the bloodstream. If they get into the tissue of the heart, inflammation of its valves may develop - infective endocarditis.
Studies show that with advanced caries, the risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies increases by 70%. When bacteria enter the blood, they settle on the vascular walls next to atherosclerotic plaques. As a result, the plaque begins to actively grow and can clog the vessel, disrupting normal blood flow. The most dangerous consequences can be thrombosis, stroke, heart attack, atherosclerosis.
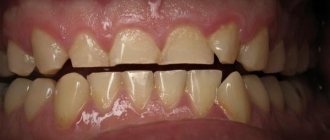
What does caries look like on teeth?
Not all patients know how to identify dental caries. To do this, you need to come to the dentist for an examination.
Black cavities of varying sizes are found on the chewing units. The pathological process develops in the natural depressions of the enamel: fissures, pits.
This disease leads to the destruction of hard tissues and cosmetic defects. There are black cavities on the front teeth, noticeable when talking or smiling:
General recommendations for treatment
Traditional preparation of the defect is carried out using a drill. If the carious cavity is located within the dentin and does not affect the pulp, then after thorough cleaning, a filling is applied. However, sometimes with a small cavity, applying a multi-layer filling (insulating pad + filling material) is impossible. This feature is taken into account when treating caries on the contact surface of premolars and molars.
Another way to treat shallow caries in dentistry is to use a composite material with adhesive properties. In this case, extensive preparation and creation of a wide cavity is not required. Another method involves polishing a carious defect with remineralization of the enamel with medicinal applications, electrophoresis with a 1% sodium fluoride solution and other approved medications.
Medium caries is treated only by deep preparation and filling. In this case, the cavity is cleaned until the affected tissue is completely removed. High-quality sanitation ensures reliable fixation of the filling and increases its service life.
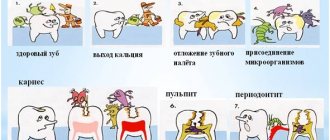
How does caries form?
The causes of caries are poor hygiene and the presence of bacteria in the oral cavity.
There are many bacteria in the human oral cavity. These bacteria feed on food debris that remains on the surface of the enamel after eating. Bacteria “love” foods high in carbohydrates: sweets, flour. During their life, bacteria produce acid, which destroys teeth.
Caries occurs in both adults and children. This disease spreads in each person at a different rate.
Factors contributing to the rapid development of caries:
- insufficient or lack of oral hygiene;
- excess carbohydrate foods: flour products, sweets, carbonated drinks;
- low buffering capacity of saliva, when acids and alkalis are not sufficiently neutralized in the oral cavity;
- insufficient fluorine and calcium content in enamel;
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- severe somatic pathologies suffered in childhood (tuberculosis, rickets);
- reduced immunity.
Answering a frequent question from patients: “Why do caries form on teeth?”, we note that the most important factor is insufficient hygiene. All dentists strongly recommend brushing your teeth regularly and using floss to clean the gaps. Without careful hygiene, bacteria will destroy teeth one by one, leading to serious complications.
Modern methods of caries treatment
Modern technologies for the treatment of caries are based on reducing the invasiveness and aggressive effects of the drill and hard attachments and brushes. Minimally invasiveness and comfort during treatment are especially important in pediatric dentistry. Popular methods:
- ICON technology. Suitable for the treatment of caries at the chalk spot stage. Rehabilitation of the defect is carried out using the unique ICON resin, which has an antibacterial and regenerating effect. The component literally fills the pores in the enamel layer and prevents the further development of the pathological process. The procedure itself lasts no more than 20 minutes.
- Ozone therapy. Triatomic gas ozone is a natural oxidizing agent with high antibacterial properties. The substance removes pathogenic microflora and cleans the tooth surface of plaque. Ozone treatment is indicated for early stages of caries, as well as for superficial demineralization of enamel on molars and the cutting surface of teeth. In the treatment of complex cases, ozone treatment is auxiliary.
- Air abrasive processing. Dental sanitation is carried out using finely dispersed abrasive particles under pressure. This method eliminates the use of a drill and does not injure dead tooth tissue.
- Laser treatment. A minimally invasive treatment method that in most cases replaces a drill. The exclusion of traditional preparation of a carious cavity is possible only in case of superficial caries. Despite the fact that sanitation occurs with a laser beam, patients require anesthesia. During the removal of affected dentin, the laser somehow reaches the pulp and causes acute pain.
- Art methodology and artistic restoration. Non-traumatic cleaning of the defective cavity is performed mechanically, followed by filling with glass ionomer material. The method was developed in underdeveloped countries where it is not possible to open full-fledged dental clinics with a wide range of services. Manual cleaning helps to accurately remove affected tissue while preserving the thickness of the healthy part of the tooth as much as possible.
All methods of caries treatment are widely used in modern clinics, but are not advanced. Most often, dentists sanitize pathological cavities and remove dental defects using a drill.
What happens if caries is not treated?
- For a long time, the disease may not bother the patient in any way. When the destruction of hard tissue has reached a significant extent, sensitivity appears during eating.
- If you do not consult a doctor at the first stage, the carious process will go further and reach the pulp (nerve). Spontaneous severe pain appears. Treatment of pulpitis will be required.
- If the patient does not seek help at this stage, the infection spreads beyond the root. Periodontitis occurs. The prognosis here is unfavorable, since such a tooth often needs to be removed to eliminate the infection.
Therefore, timely visit to the dental clinic will help to avoid acute pain and complications.
Causes and types of complications
The culprits in the development of caries and its complications are streptococcus bacteria – Streptococcus sanguis, mutans, viridans. These pathogenic microorganisms oxidize and destroy tooth enamel, and then penetrate deep into the hard tissue through the dentin canals.
In the absence of proper treatment, the infection affects the coronal part of the soft tissue, the pulp, and the first stage of complicated caries occurs - acute pulpitis.
Pulpitis
When the infection reaches the pulp, an inflammatory process begins in the neurovascular bundle of the tooth in the form of:
- acute focal;
- diffuse (general) pulpitis,
a characteristic symptom of which is severe, throbbing pain in the tooth and increased sensitivity to cold.
If you do not go to the dentist with pulpitis in the first 2-3 days, the acute stage of the complication becomes chronic and develops:
- fibrous;
- hypertrophic;
- concretory;
- or gangrenous chronic pulpitis.
With chronic pulpitis, the inflamed tissue of the neurovascular bundle degenerates and is gradually destroyed, dentin formation in the tooth stops, and it becomes dead.
Over time, decay processes reach the peri-apical tissues and ligamentous apparatus - periodontium.
Periodontitis
Between the root of the tooth and the alveolus there are periodontal tissues, they act as a shock absorber during chewing and hold the tooth in the socket.
With periodontal inflammation, periodontitis, the integrity of the tooth ligaments is disrupted, the jawbone becomes infected and damaged.
Symptoms of acute periodontitis:
- acute pain when biting or touching a tooth with the tongue;
- pain is transmitted along the trigeminal nerve - to the temple and jaw;
- general malaise, deterioration of health;
- increase in body temperature to 37-38 degrees.
The acute phase with severe pain lasts from 2 to 14 days, after which the disease takes on a chronic form.
With chronic fibrous or granulating periodontitis, a fistula, that is, a through hole, can form in the gum. Patients also complain of a feeling of the diseased tooth moving out of its row and attacks of aching pain.
Granuloma
An advanced form of chronic periodontitis, granulomatous, leads to the formation of a capsule with exudate (pus) at the apex of the tooth - granulomas.
The gums of the diseased tooth become inflamed, patients complain of a feeling of bulging bone and persistent, severe pain.
A granuloma that is not eliminated in time can cause the formation of gumboil or a cyst at the root of the tooth.
Multiple caries
Another common type of complication is multiple (acute, blooming) caries, in which the infection simultaneously affects the coronal part of eight or more teeth.
In record time, caries destroys the enamel-dentin junction, penetrates the pulp and leads to tooth loss. The infection affects the cement on the roots of adjacent teeth, and the patient feels as if the entire dental arch hurts. Most often, multiple caries is detected in people with diabetes and preschool children.
What to do if caries appears on teeth
First of all, you need to immediately contact your dentist. When a tooth is destroyed due to caries, treatment cannot be delayed. Otherwise, the complications described above arise. It is worth noting that no available means at home will relieve the patient of this problem. Only a dentist can cure this disease.
You should also pay attention to your oral hygiene:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day.
- Use floss and mouth rinses.
- Visit your dentist for a checkup every six months.
- Come for professional hygiene every 6 months.
Dentists will help you select individual hygiene products (brushes, pastes, threads, rinses) at your appointment. The doctor will also determine why dental caries appears in your particular case and give the necessary recommendations.
How is periodontitis treated?
The approach to treating periodontitis may vary depending on its type, severity, patient history and other factors.
The chronic form of the disease is treated according to the following scheme:
- The area of the diseased tooth is numbed with anesthetics.
- First, the affected tissue and old fillings are removed from the root canal, the tooth is depulped, and, if necessary, the root canal is expanded using dental drills or a microscopic incision.
- At the second stage, the root canal is cleaned and washed with antiseptic solutions. An antibacterial drug is placed into the canal cavity, which relieves the inflammatory process and fights infection.
- The tooth is covered with a temporary filling, and antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
- The patient is sent home, where he must strictly follow all the dentist’s recommendations. The next appointment is usually scheduled after three or four days.
- At the second stage of treatment, a control photograph is taken. If the inflammation is stopped, the dentist removes the temporary filling and medicine from the root canals, rinses the cavities with an antiseptic, and fills the canals with a special composite material. It contains substances that help restore dental tissues and destroy pathogenic microorganisms. This filling of the canals is temporary and is needed in order to completely stop the inflammation and reduce the risk of re-developing periodontitis in the future. It is done for several months, and the tooth is again covered with a temporary filling.
- A few months later, the patient comes for a follow-up appointment with the dentist, where a tooth photograph is taken again to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. If the inflammation has completely stopped, the final stage of treatment begins - replacing temporary fillings with permanent ones and restoring the dental crown with a permanent light-curing filling. After this, the process of treating chronic periodontitis is considered complete.
- Unfortunately, it is not always possible to carry out conservative treatment of this disease. In advanced forms, the dentist is forced to resort to surgical treatment, when part of the root or the entire tooth is removed.
Treatment of periodontitis is long, complex and expensive, and the disease itself is a source of chronic infection, negatively affects the entire body, and weakens the immune system. It is easier and safer to contact the dentist on time and treat early caries. The consequences of an advanced disease are dangerous for the body.
How is caries treated?
The treatment is carried out in professional dentistry by a general practitioner and is absolutely painless. This treatment is carried out in one visit, and several teeth can be treated in one visit.
Sequence of treatment stages:
- Examination of the oral cavity. Carrying out diagnostics: a targeted diagnostic image of one tooth or computed tomography of the jaws (if multiple caries is detected during the examination). This is done in order to make an accurate diagnosis and see the volume of destroyed tissue.
- Local anesthesia: selected individually according to health conditions. Only after the desired area of the oral cavity has become numb does the doctor proceed to the next manipulations.
- Placement of isolation: the doctor places a rubber dam on the desired area - this is a latex plate that isolates the tooth from the rest of the oral cavity. The rubber dam creates comfortable conditions for the doctor, the patient, and also allows you to create dry, sterile conditions for placing a filling. This is necessary for the filling to serve for a long time and with high quality.
- Preparation of enamel, dentin: necrectomy. The doctor uses a drill to drill out the destroyed tissue.
- Treating the cavity with antiseptic solutions, applying an adhesive - a special solution that, like glue, reliably bonds hard tissue to the filling.
- Filling with light-curing materials. The anatomical shape of the tooth is restored, and the color is carefully selected.
- Polishing and grinding so that the filling does not feel different from your own teeth. Also, using special guidelines, the doctor checks whether the filling is too high or does not interfere with the normal closure of the jaws. Excess is removed, sharp edges are sanded.
- The doctor gives recommendations after treatment. If a tooth has been severely damaged by caries, then in addition to a filling, an orthopedic onlay or crown may be required. This is due to the fact that the filling is not as strong as enamel. Over time, cracks and chips are possible. Orthopedic structures will help protect the treated tooth from these complications.
After these stages, the tooth is completely free of caries. Next, you will need to maintain regular hygiene, come for preventive examinations and professional cleaning.
How is pulpitis treated?
Pulpitis can be treated biologically or surgically. The first is applicable if the disease is in its early stages. The dentist strives to preserve the pulp by eliminating only the inflammation. If possible, pulpitis of primary teeth is treated using a biological method, when it is especially important to preserve the tooth root. Treatment is carried out in several stages. First, the dentist prepares the carious cavity, opening it as wide as possible. Then he treats it with an antiseptic, puts a swab with an antibacterial agent and covers the tooth with a bandage. During the next appointment, if the patient has no complaints, the cavity is treated with medication, filled with a special composition that stimulates dentin production, and a temporary filling is placed for a period of 5 to 7 days. During the third appointment, the dental crown is filled.
When the biological method of treating pulpitis is ineffective, surgical treatment is used. In this case, the inflamed neurovascular bundle is removed completely or partially. Without a nerve, a tooth becomes unviable and its service life is reduced.
Surgical treatment is performed with local anesthesia. First, the carious cavity is prepared, the pulp is removed, the affected area is treated with an antiseptic, medication is injected, and first the root canals are filled, and then the dental crown. As with the biological method, surgical treatment is carried out over several visits to the dentist.
If pulpitis is not treated, it will progress and can lead to very serious complications:
- flux - inflammatory process in the periosteum;
- periodontitis - inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth;
- pulp necrosis - death of its cells;
- sepsis is a blood infection that can develop when an infection enters the bloodstream.
You can avoid such complications if you do not delay your visit to the dentist and begin treatment for the disease at the first symptoms.
Granuloma
Granuloma is advanced periodontitis. Symptoms of the process:
- A purulent sac in the periapical area, which is visible on x-ray.
- The process does not give a clearly defined clinical picture for a long time.
- If the process worsens, then unbearable pain is observed.
Treatment consists of delayed filling of the root canal with a temporary calcium-based filling material. This material in the canal used for filling is periodically renewed, usually after six months the granuloma resolves. If not, then a resection of the apex of the tooth root is performed, along with the granuloma.
Alternative medicine in the fight against caries
Caries can be eliminated at home only at the initial stage of destructive changes in the enamel. Non-traditional recipes can stop the progression of tooth decay, especially if treatment is currently difficult or impossible according to indications. Popular rinse recipes:
- Sage decoction. 1 tbsp. raw materials, pour 200 ml of boiling water, infuse until a bright amber-brown hue is obtained, filter and rinse your mouth throughout the day. The plant kills pathogenic microflora and is effective against stomatitis and periodontal disease. You can make lotions with a decoction of sage by applying a gauze pad to the affected area.
- Infusion of calamus roots. A steep tincture of calamus root helps relieve pain and slow down the development of superficial or medium caries. To prepare, you will need to pour 1 tbsp. crushed raw materials, 200 ml of vodka, alcohol solution of propolis. For greater effect, you can add 10 drops of tea tree ether. The resulting composition is placed in a dark place for 5-7 days. Before rinsing 1 tsp. alcohol infusion is combined with 100 ml of warm water.
- Mint based recipe. Fresh mint leaves are pounded in a mortar, poured with hot water (not boiling water!), and left for 30 minutes. Then add 1 tbsp. apple or wine vinegar and leave for 3 days. Mint essence prevents further destruction of dental tissue, removes plaque, softens tartar.
You can rinse your mouth with a solution of soda, sea salt, or an aqueous or alcoholic decoction of propolis. Camphor or fir oil, zinc-salicylic paste can be applied to the carious cavity.
The danger of decompensated form
Acute caries is dangerous for many reasons. The advanced form of the disease often leads to the following problems:
- development of pulpitis and periodontitis;
- development of periodontitis;
- tooth splitting;
- tooth loss.
In addition, the decompensated form is a signal of a disruption in the functioning of the entire organism. Untreated caries is often a consequence of decreased saliva production and a decrease in its bactericidal properties, which affects the general condition of the oral cavity as a whole. In pregnant women, this can affect the general physical condition of the expectant mother and the health of the fetus.
Features of multiple caries
This disease has a rather rapid course, unlike other types of caries: in a short period of time, the lesion covers almost the entire dentition. It is the speed of spread that is one of the main features of “blooming” caries. This course of the disease is due to the rather thin enamel of children's teeth and the special structure of dentin, which has low-mineralized zones that reach the pulp. Thus, the carious process penetrates through hard tissues (enamel, dentin) and quickly spreads to the pulp.
You can lose a tooth with multiple complicated caries in just a couple of months! In general, the disease affects from 6 to 20 teeth, and each of them may have several carious lesions. In this case, the transition from the initial stage to the deep stage occurs many times faster than in the chronic course of the process. Sometimes only “stumps” remain from the chewing units. By the age of 3-4 years, a child may be left with almost no teeth at all.
Prevention of decompensated form of the disease
Everyone can prevent the development of acute caries. Even with a hereditary predisposition, dental problems arise due to poor oral hygiene and poor nutrition.
Prevention of the decompensated form of the disease is quite simple. To carry it out you need:
- brush your teeth morning and evening;
- use toothpaste with fluoride;
- clean interdental spaces with dental floss;
- do not consume too cold or hot food or drinks;
- limit the amount of soft and sweet foods, since after eating them, plaque forms on the teeth, which contributes to the demineralization of the enamel;
- Visit the dentist 1-4 times a year.
Planned sanitation of the oral cavity makes it possible to identify caries at the earliest stages and prevent it from developing into an acute form. Regular visits to the doctor allow you to timely detect weaknesses in the care of your teeth and gums, make adjustments and stop their diseases. Therefore, visiting a dental clinic to check the condition of your teeth should become a rule for everyone who cares about their health.
Prevention of multiple caries in children
Children love foods that are far from healthy. Soda, chips, products with all kinds of dyes and a huge sugar content - it’s not for nothing that dentists have noted a significant increase in caries in children. Here are the measures they advise parents to take for preventive purposes:
- Monitor your child’s diet, reducing the consumption of sweets as much as possible.
- The diet must include foods rich in calcium: nuts, legumes, milk, cottage cheese.
- Children should be taught dental hygiene from an early age. Buy your child a beautiful toothbrush, a special toothpaste, turn brushing your teeth into a game, and encourage interest in this process.
- Regularly visit the dentist with your child - this way, visits to the doctor will become familiar to him, and he will not be afraid.
The sooner multiple caries is detected, the faster, more effective, and most importantly, the more painless the treatment will be. In addition, remember that treatment in the initial stage of the disease will cost much less than in its advanced form.