Children's teeth appear in a certain sequence and in pairs (for example, two central incisors or two canines). But often the timing of teething in children shifts upward: many parents begin to worry and get nervous, but this is not worth doing, since the deviation from the norm is explained by the individual characteristics of the body, the uncharacteristic course of pregnancy, or various injuries received during childbirth.
Anatomy of permanent teeth
Each molar consists of certain parts:
- crown. This is the part of the tooth that protrudes from the top;
- the root, it goes deep into the alveoli. At the same time, it is attached thanks to special connective tissue bundles. There can be different numbers of roots (1-5 pieces). This moment affects the number of nerves and channels;
- neck. This part is located between the root and the crown.
Tooth tissues are distinguished by their heterogeneity. The enamel is on top and is known for its durability. Once the tooth has erupted, it is covered with a transparent thin layer. This is the cuticle, which eventually changes to the pellicle. The latter is a film that is created from what saliva produces.
Beneath the enamel is dentin, the tissue of the tooth. Dentin is similar to bone when you study how it is built. However, it is more durable because there is a high level of mineralization. In the area where the root is located, the dental tissue is covered with cement. The latter is rich in mineral compounds and is also associated with periodontium. Collagen fibers are used for this.
As for the part of the tooth that is inside, this is the crown and root canal. They are filled with pulp. This is loose connective tissue; it contains nerve endings and blood vessels.
Formation of periodontium and roots
This stage of development begins after the eruption of permanent teeth and usually lasts for 3.5-5 years. It includes the development processes of surrounding tissues, as well as the root system. At the same time, the crown of permanent teeth at this stage is almost completely formed and is ready for active mineralization after eruption.
The period of development of the root part and periodontal tissues is divided into the following stages:
- active growth of the tooth root in length;
- development and strengthening of the root apex;
- uncovered root tip;
- formation and strengthening of periodontium;
- completion of periodontal and root development.
Differences between baby teeth and permanent teeth
Permanent and temporary teeth are built in the same way, but still have certain differences between themselves:
- The enamel on baby teeth is whiter. And the enamel on permanent teeth has a yellowish tint;
- the best indicators of density and mineralization are noted behind the molars;
- the pulp of a baby tooth is large in size, and the dense tissues and their walls are thinner;
- permanent teeth are larger in size, here the length is greater than the width;
- The root of baby teeth is short and thin compared to permanent teeth. When the root of temporary teeth is formed, they expand in width. Therefore, the permanent bud has free space to grow.
Let's sum it up
Changing baby teeth to molars can leave an imprint on the rest of a person’s life. Therefore, it is very important to follow a few simple recommendations:
- Visit your dentist regularly for dental checkups.
- Get your child into the habit of good oral hygiene from a very early age.
- Use pastes with a high fluoride content and soft brushes.
- Do not attempt to perform the removal yourself at home.
- Use only mineral and vitamin complexes recommended by your doctor.
- Monitor your child’s complaints, control the time when baby teeth begin to change to molars.
- Do not neglect the treatment of oral diseases, regardless of their severity and area of distribution.
In our clinic you can not only sign up for regular preventive examinations, but also receive the right treatment.
Where do teeth come from?
Teeth begin to form and develop when the fetus is still inside the womb (at about 6 weeks). They have their source - the epithelial dental plate. Already by 14 weeks, active formation of dental tissues, which are hard, occurs. Initially, this occurs in the area where the crown will be, and later at the root.
Molars, namely their first rudiments, appear by the 5th month of the embryo. They are located higher than the child’s baby teeth or lower. By the time the child is born, the rudiments are already practically formed in the tissues of the jaw.
Teeth that belong to an additional group (have no predecessors) are formed later. This occurs after about 1 year of life. Why? Because the baby's jaw is still very small and there is not enough space for them.
Features of teething
Teething can be painless, without disturbing the baby’s well-being or changing his behavior. However, in most cases, this process is accompanied by hyperemia, fever, refusal to eat and many other symptoms.
At this stage of child development, all dads, and especially moms, need to be patient and prepare themselves for the fact that the period of teething may be accompanied by severe symptoms.
Modern parents are very worried about this problem, so they try to carefully read the necessary literature, learn from the experience of relatives, in order to prepare for the appearance of the first incisor. More often, mothers find plans that provide the required number of teeth at a given period of age, and if there are no expected results within the specified period, they begin to panic.
Is it possible to know in advance which tooth will make itself known first? In what order do children's teeth appear? It is quite difficult to answer questions with accuracy, since each organism is special and its development occurs in its own way.
What does a dental formula look like?
To make it more convenient to describe teeth and their number, special formulas are usually used. Each tooth has its own number, which is used to decipher its location.
When describing a milk bite, Roman numerals are used:
- incisors – I, II;
- canine – III;
- molars – IV, V.
If we talk about the formula for adult teeth, here the teeth are counted starting from the center:
- incisors – 1.2;
- fang – 3;
- molars (small) – 4.5;
- molars (large) – 6,7,8.
8 is a wisdom tooth; not every person has it.
Teething in children: symptoms
The first signs of the imminent appearance of teeth appear about a week before their appearance. The symptoms will not stop until the tooth breaks through the gum lining.
Signs of teething in a baby are as follows:
- the child becomes irritable for no reason;
- sleep deteriorates (if the child cries at night and tosses and turns, there is no need to immediately start rocking him to sleep - it is better to give the baby the opportunity to calm down on his own);
- the gums become very swollen and swell at the site where the tooth appears;
- the appetite deteriorates, the baby may even refuse to eat altogether, feeling hungry;
- the child begins to chew on various objects to relieve severe itching in the gums;
- salivation increases;
- Due to drooling, a rash may appear around the mouth, chin and chest.
There are also additional ones, i.e. optional symptoms of teething in infants:
- heat. If the temperature has increased, this most likely indicates an inflammatory process that develops in parallel with teething and is in no way connected with it (it could be stomatitis or any cold).
When the temperature rises, you need to carefully examine the oral mucosa. If there are small bubbles filled with a cloudy liquid, erosion, and the gums themselves are bright red, then the child has herpetic stomatitis. Any baby receives antibodies to the herpes virus from its mother, but usually by the time the first teeth appear, their effect ends. Often the catalyzing factor in the development of stomatitis is trauma to the mucous membrane, which is inevitable when teeth appear. If the above signs cannot be detected, then it is recommended to give the baby Panadol (suppositories are the preferred form of medication). As practice shows, it is useless to call a pediatrician, since this is not their specialization. Only a dentist can determine the specific type of stomatitis (aphthous, herpetic, etc.).
- hematomas on the gums. Sometimes the gums become swollen, turning an eerie shade of blue. Despite their frightening appearance, hematomas do not require treatment. Doctor intervention is allowed only for large hematomas that do not decrease over a long time.
- vomit. The only acceptable cause of vomiting is excess saliva entering the stomach and esophagus. If vomiting begins against the background of elevated temperature and, especially, diarrhea, then these symptoms have nothing to do with teething - you need to call a doctor.
- coughing is not a natural cause when teeth appear, unless the child has swallowed saliva that has entered the respiratory tract.
- A runny nose is a sign of a cold, not teething.
Teething order
Typically, all children start teething at about the same time. Teeth emerge from the molar set at the age of 5, and it is the molars (large ones) that emerge. Then the diagram is as follows:
- Initially, the incisors on the lower jaw change, which are located in the center;
- then the central incisors appear on the upper jaw and the incisors on the sides on the lower jaw;
- at about 8-9 years old, the incisors on the top and sides change;
- up to 12 years of age, molars (small) grow;
- at the age of 13, the fangs change;
- after the child turns 14 years old, the second molars (large ones) come in. They were not included in the milk kit;
- and after another 1 year the third molars (large) appear. This is a wisdom tooth. But he may not appear at all.
Should I brush my newly erupted teeth?
Dentists strongly recommend starting to take care of oral hygiene from infancy. For newly emerging teeth, they offer special silicone brushes or wipes. A simpler option is a finger wrapped in gauze. You can simply moisten it with water or use toothpastes for children under 3 years of age (they are marked 0+ and can always be swallowed). The main thing when brushing your teeth is no violence! A little more cleanliness isn't worth the stress.
| Author Fedor Katasonov | Scientific editor Maria Gantman |
How to determine that a child will soon have molars?
There are certain signs that indicate that permanent teeth will soon begin to erupt:
- The spaces between the teeth increase. The jaw grows and the free space increases;
- baby teeth become loose as the root gradually dissolves. It cannot be firmly fixed in the jaw tissues;
- in case of loss of a temporary tooth. This confirms that the molar will soon come out as it has pushed out the previous one;
- The gums are slightly swollen and red.
When permanent teeth erupt, the child’s general well-being usually remains the same, the temperature does not rise, and there is no pain.
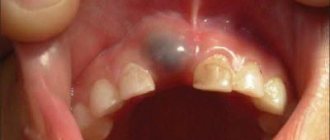
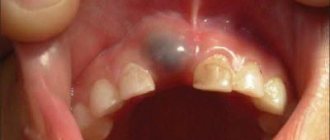
Teething in children and features of this process
Quite often, a few weeks before the appearance of a baby or molar tooth, a lump filled with a clear or bluish liquid forms on the gum. Naturally, it worries parents, but there is no pathology in this formation, and the lump, which does not look very aesthetically pleasing, does not indicate the beginning of the inflammatory process. In most cases, no intervention by a doctor is required. You can contact the dentist if the lump increases in size: the doctor will make a small incision and release the liquid.
Possible problems
Permanent teeth have just appeared, but this does not mean that there will not immediately be any problems associated with them. Parents should be aware of possible dental problems:
- lack of molars;
- pain in the molar area;
- crooked position of molars;
- molars fall out;
- injuries.
For any of these problems, it is important to contact a specialist in time to receive qualified help.
Complications during teething
- Delay in the appearance of permanent teeth.
This may be due to genetic characteristics, immune system problems and a number of other diseases. - Uneven teeth and other malocclusions.
- Hyperdentia.
The child’s molar tooth (or teeth) grows in the second row. Hyperdentia, or supernumerary of teeth, is a fairly rare phenomenon, but requires the intervention of a dentist to eliminate the risk of malocclusion in a child.
Molar protection and care
Considering all these features, doctors recommend that any child protect their molars and care for them in the correct form. It is best to get a detailed consultation from your dentist, who will tailor care to the individual characteristics of your baby’s teeth.
The main preventive protective measures include procedures such as professional cleaning, fluoridation, and fissure sealing. Take care of a healthy change of teeth and give your child no problems in adulthood!
Possible complications of molars
The main danger in the process of changing teeth will be insufficient oral hygiene. The child should brush his teeth regularly and properly and eat well. He should know that after eating sweet food he must brush his teeth or at least rinse his mouth.
A common problem after teething is the potentially dangerous pigmentation of fissures - depressions on the chewing surface of the teeth (not counting the canines and incisors). The fact is that the process of mineralization and formation of a strong tooth structure takes about 3 years after eruption. During this period, teeth are vulnerable and, with insufficient hygiene, can become pigmented and subsequently become infected with caries.
Let us remind you: if there were problems with your baby teeth, they will most likely affect the new molars. Also, possible complications of molars are associated with infections that can get inside the gums after baby teeth fall out. Therefore, hygiene during this period of the baby’s life must be strictly monitored.
Adentia and retention
Adentia and retention are specific problems that are possible when changing teeth. Edentia means the complete or partial absence of teeth, which is classified as a pathology and can be solved by installing dentures.
Retention means that the teeth have partially erupted, but remain under the gum. This is a very common occurrence during wisdom teeth eruption. The problem is solved by removing such teeth or by surgery on the gum to make room for complete eruption, if it is not a wisdom tooth.
How to improve your baby's well-being
When the unit cuts the gum, pain and burning appear. The tissues become inflamed and constantly itch. The inflammatory process can be so severe that the baby will have a fever for several days.
To help him, parents need to use:
- Special pharmacy teethers. These are safe silicone toys that contain a cooling solution inside. They must first be placed in the refrigerator and then given to the child. When the baby chews on the teether, it will create the effect of a massage and a cold compress, which will somewhat muffle the negative symptoms.
- Anesthetic dental gels. They usually contain benzocaine, an effective anesthetic. When applied topically, it reduces gum sensitivity. Also, group drugs may include lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate, herbal anti-inflammatory extracts. When choosing a medication, it is important to consult a pediatrician. Anesthetic dental gel can be applied only if it is not contraindicated for the child. It is important not to use the product too often, as it can cause allergies or other negative side reactions.
- Wipe off saliva in a timely manner. If you do not do this, the secretion of the salivary glands will irritate the delicate skin around the mouth and chin. Then the unpleasant symptoms of inflamed gums will be aggravated by a burning sensation on the outside.
- Give a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug if necessary. Ibuprofen-based products are suitable for children over three months of age. After using them, the body temperature drops and the pain goes away for a while.
- Massage the gums. Some guys have very strong itching. In this case, you can do a massage. The parent needs to wrap the index finger with a bandage, moisten it with water and gently massage the inflamed area. Thanks to these actions, the pain subsides. But, if the child does not allow this procedure, it is better not to insist.
The eruption of baby teeth is a long and complex process. You need to be prepared that ailments will soon be a thing of the past, and be attentive to the condition of the baby. If you have any questions regarding your general health or bite characteristics, you should immediately contact a specialist.
When do the first primary molars appear?
Molar teeth appear early in children. After a tubercle grows on the gum, little white spots appear. The milk molar organ appears between 1 and 2.5 years. They erupt painfully. By this time, the children’s chewing reflex has already developed. Children immediately use these chewing organs, because the consumption of solid foods without them was problematic. Tough food speeds up the process of jaw formation.
The deciduous bite contains eight molar units. Although the organs are located behind the fangs, they appear earlier from them. They come out in pairs. The chewing organ in the bottom row is shown first. Behind it appears a unit on the upper jaw. Second primary molars appear after 2 years of age. Sometimes it happens a little later or earlier. Dentists consider this normal. In order not to miss pathologies, if teething occurs later or earlier, it is worth showing the baby to a pediatrician and dentist. Deviation from the generally accepted pattern may be due to heredity or genetic predisposition.
The activity of the appearance of units increases by 24 months, that is, during the period of emergence of the second temporary chewing organs. The whole set appears by 30 months. Teeth replacement usually begins at age five and continues until age twelve. Molar units change the fastest. The order of replacement is the opposite of the pattern of appearance. Bone elements can grow in the free space that appears due to the fact that the jaw has grown. The first signs of loss of a time unit are swaying. You should wait until the rudiment falls out on its own. If it is removed, the permanent unit may appear in the wrong place, causing displacement of the masticatory organs.
Symptoms of appearance
Since the first molars are the largest rudiments, their chewing surface is extensive and their roots are large. Therefore, all mothers and fathers remember their birth, because they come out painfully. Only some babies do not experience discomfort. But this is a rare case. In other situations, many problems arise. Main symptoms:
- Rapid swelling of the gums.
- Increased salivation.
- The little ones become very restless.
- Sleep gets worse.
- Kids refuse to eat.
- Body temperature rises.
- If the body's defenses are reduced, a runny nose may appear.
- Sometimes babies suffer from diarrhea.
When tubercles with sharp edges sharply break through the gum tissue, babies suffer greatly from this. It happens that at the same time the growth of fangs begins. And these are the most painful sensations. The main symptom of the appearance of permanent units is the growth of the jaw, which entails the appearance of free spaces behind the temporary rudiments. At this point, permanent chewing organs will emerge. Gaps also appear between teeth. They ensure the even position of the indigenous bone organs.
To alleviate the condition of the little ones, pediatric dentists prescribe painkillers that will not cause harm to the body, and special rings for massaging the gums. A tasty syrup for toddlers is often recommended. When temporary rudiments change to permanent ones, the child needs to rinse his mouth. If the wound is bleeding, a soda solution will help. When severe swelling appears, the baby should be shown to the dentist. Dangerous complications can be avoided if you regularly visit the dentist and take good care of your oral cavity.
Baby's first teeth: when to expect?
Most babies erupt their first tooth between the fifth and eighth month of life. Breastfed children usually develop teeth several weeks earlier than formula-fed or formula-fed children. This is due to the fact that most infants receive breastfeeding “on demand,” and frequent and prolonged breastfeeding stimulates rapid thinning of the gum tissue through which the top of the tooth erupts.
During teething, the baby puts everything in his mouth
In children who receive breast milk substitutes as their main diet, their first teeth erupt at the age of 6-8 months. If the baby is already 8-9 months old and still has no teeth, there is no need to panic: late teething in some cases is a variant of the physiological norm and may depend on several factors, including:
- density of gum tissue at the site of eruption;
- time of introduction of complementary foods and composition of the children's diet;
- climatic conditions in the region of residence;
- the presence of chronic diseases and metabolic disorders.
Late teething occurs when teeth are retained in the jaw or alveolar ridge.
Of great importance in the timing of teething and in infants is the supply of essential minerals necessary for the health of bone tissue - calcium, phosphorus, iron and fluorine. If a child has endocrine disorders, the absorption and assimilation of these elements may be impaired, therefore, if the child is missing at least one tooth by 10-12 months, it is necessary to consult a specialist.
First tooth
Note! A hereditary factor can also influence the time of eruption of baby teeth, especially in the female line. If the mother or grandmother of the baby has teeth later than the established physiological norms, the probability of late teething in the child will be about 30%.
Features of molars
Large molars differ from other groups not only in external characteristics, but also have other features :
- these are the largest units in each dental arch;
- have the largest chewing surface;
- have a powerful root system;
- the upper molars are slightly larger than those on the lower jaw;
- have a stronger surface coating;
- able to withstand weight up to 75 kg;
- upper molars have 4-6 canals, while lower units generally have only 3 canals;
- maxillary molars have 3 roots (palatal, buccal-medial, buccal-distal), less often 4;
- the chewing teeth of the lower jaw have only 2 roots;
- wisdom teeth are the very last molars, which may appear by the age of 50 or not appear at all;
- the last molars are very often located not in the chewing arch, that is, they can grow horizontally or with a slight slope, located buccally or towards the tongue or palate;
- wisdom teeth have from 1 to 5 chewing cusps;
- the last molars often have a complex root configuration (curvature, fusion).
All this entails the peculiarities of treatment of such teeth. The presence of a large number of complex root canals, as well as difficult access compared to other groups of teeth, requires highly qualified doctors and modern equipment for high-quality therapy.
In dental practice, molars are considered the heaviest units, especially wisdom teeth. Proper care and regular preventive examinations will help keep them healthy. When the first signs of damage to the molars appear, we recommend that you immediately sign up for a consultation at our KAS+ dentistry. Timely detection of dental problems guarantees their high-quality treatment with minimal risk and long service life.