Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mouth (but can also develop on the tongue and lips) that is most often diagnosed in children. Stomatitis in adults is usually a consequence of the introduction of viruses into the oral mucosa. In addition, this disease can occur in the presence of a number of other diseases, due to decreased immunity. For dentists, diagnosing and treating stomatitis in the mouth does not cause any difficulties, while attempts to get rid of the disease on their own can lead to unpleasant consequences
Causes of stomatitis
Stomatitis is both an independent disease and a manifestation of other diseases. The causes of stomatitis can be:
| CAUSES | A COMMENT | ||
| causes: | Viruses: | a comment: | herpes simplex virus, varicella-zoster virus |
| causes: | Mushrooms: | a comment: | yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. |
| causes: | Bacteria: | a comment: | fusobacteria, streptococci, gonococci, mycobacterium tuberculosis, mycobacterium leprosy. |
| causes: | Allergy: | a comment: | stomatitis can be a consequence of food, household and drug allergies. |
| causes: | Injuries | ||
| causes: | Hygiene: | a comment: | Poor oral hygiene, this includes both the presence of dental deposits (tartar and plaque), and the presence of many foci of infection (caries and its complications), old fillings and crowns. |
| causes: | A number of diseases: | a comment: | — diseases of the digestive system (Crohn’s disease2, gastroesophageal reflux disease3, gastritis4) — chronic heart failure5 — diabetes mellitus6 — vitamin C hypovitaminosis — chronic tonsillitis — insufficient pancreatic function |
Causes
The question of why stomatitis appears has several possible answers. First of all, this is the body’s weak resistance due to age, lack of vitamins, severe stress or heavy physical activity. In addition, the harmful effects of allergens, new or existing infections in the body, and traumatic damage to the mucous membrane are important. So, all the variety of reasons can be reduced to several groups:
- weakening of the immune system for any reason (age, illness, stress, strain, bad habits, poor nutrition or environment),
- insufficient oral hygiene (presence of untreated caries, periodontal disease, gingivitis, hard plaque, infrequent or improper brushing of teeth),
- allergies (not only to foods, but also to medications, denture materials, dental products and pastes, food or vitamin supplements),
- injuries to the mucous membrane - mechanical (biting, hard and sharp food particles, rubbing dentures, blows, etc.) and thermal (burns from hot food or drink),
- infection entering the body (in children this is “disease of dirty hands”), or activation of microorganisms present in the body.
Bad habits have a great influence: for example, smoking damages the mucous membrane (with hot smoke, chemicals from smoldering tobacco), reduces immunity, and irritates the mucous membrane of not only the mouth and nose, but also the bronchi. Avoiding excesses and unhealthy foods, alcohol and tobacco significantly strengthens the immune system and prevents repeated relapses of stomatitis.
Classification of stomatitis by the World Health Organization7
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | According to the degree of damage to the mucous membrane | a comment: | 1) Superficial (catarrhal, fibrinous) 2) Deep (ulcerative, necrotic) |
| classification: | Due to the occurrence: | a comment: | 1) infectious (viral, bacterial, fungal) 2) traumatic (mechanical, chemical or physical injury) 3) allergic 4) arising from systemic diseases |
| classification: | According to the clinical course: | a comment: | 1) acute 2) chronic |
Catarrhal stomatitis
Characterized by redness, slight swelling, burning of the mucous membrane. It is observed with influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, and drug-induced damage.
Fibrinous stomatitis
It manifests itself as single painful aphthae, which are covered with a white coating. Afta is a superficial defect of the oral mucosa of a round shape. It appears in mild forms of aphthous stomatitis.
Ulcerative stomatitis
manifests itself in the form of deep defects in the oral mucosa - ulcers. Observed in traumatic stomatitis.
Necrotizing stomatitis
Characterized by ulcers that are covered with necrotic plaque. It is observed in ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis, a complication of measles.
Acute stomatitis
It has pronounced symptoms, as a rule, it appears for the first time or recurs extremely rarely, once every few years. Also occurs due to acute trauma. Patients complain of severe pain, difficulty eating and sometimes even talking, general weakness, fever, and bad breath. Acute stomatitis with incomplete or improper treatment can become chronic.
Chronic stomatitis
Characterized by constant relapses, as a rule, this occurs when the immune system is weakened. May occur as a result of regular, moderate trauma. Clinical manifestations are less pronounced; this type of stomatitis always requires first of all eliminating the cause of the disease.
Viral stomatitis
Herpetic stomatitis
Caused by the herpes virus of the first, less often the second type.
It accounts for 80% of all stomatitis and occurs mainly in children, less often in adults. The prevalence of herpes simplex virus ranges from 65% to 90%8. Infection occurs through airborne droplets and household contact. More common is recurrent herpetic stomatitis, which is manifested by itching, burning, slight soreness in the oral cavity, then vesicles (bubbles) appear, which burst and heal after 7-10 days.
During primary infection, acute herpetic stomatitis occurs; it is characterized by general symptoms such as fever, weakness, aches in the muscles and joints, the degree of these manifestations depends on the severity of the disease. As a rule, the acute form occurs in children.
Varicella zoster virus infection
The mildest form, in which the mucous membrane of the tonsils is affected. The palatine tonsils are not very enlarged, the mucous membrane of the throat is red, there is no plaque or pus.
Stomatitis with measles
Measles is an acute viral, highly contagious disease that is caused by the Polinisa virus and is transmitted by airborne droplets. The disease is extremely contagious. It is characterized by a rise in temperature, symptoms of ARVI, a rash on the face, neck, and then the whole body. In the oral cavity, Filatov-Koplik spots and stomatitis occur, which is characterized by hyperemia, swelling of the mucous membrane and white plaque. Nowadays, thanks to vaccination, this disease practically does not occur.
Types of stomatitis: symptoms and treatment
Stomatitis is a general name for various inflammations of the mucous membranes in the mouth: on the roof of the mouth, the inner surface of the cheeks, under the tongue, in the throat, on the lips or gums. Therefore, with stomatitis, symptoms and treatment are determined by the causes of the disease and the affected area.
Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis)
It manifests itself in bleeding, swelling of the gums and discomfort when pressed. Accompanied by an unpleasant odor from the mouth. Sometimes it leads to tooth mobility. In case of gingivitis, professional hygiene is often carried out, and then the periodontist determines how to treat stomatitis in the mouth and strengthen the gums: he may prescribe rinses, recommend medicated toothpaste and an electric toothbrush with a special attachment.
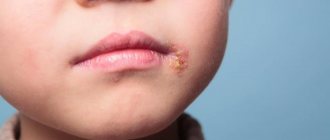
Stomatitis on the lip (cheilitis)
Symptoms can be different: a “cold” on the lip, severe peeling, inflammation of the lip border, cracks over the entire surface of the lips. How and with what to treat stomatitis on the lip in an adult depends on the nature of the inflammation. An integrated approach is practiced:
- elimination of acute symptoms: for pain, anesthetics are prescribed, for high temperatures - antipyretic drugs;
- local treatment: agents are used that relieve inflammation and promote tissue healing;
- correction of the immune system.
But before treating stomatitis on the lip, it is necessary to determine the cause of this disease, since without eliminating it, there is a high probability that the problem will soon recur. Taking into account the nature of the infection, medications (antibiotics, antivirals, etc.), vitamin therapy and a gentle diet are prescribed.
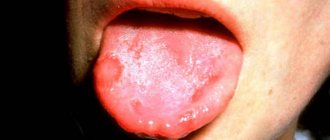
Inflammation of the tongue (glossitis)
Signs: swelling of the tongue, change in color to burgundy or bright red, the appearance of plaque, the formation of painful ulcers. The general approach to treating stomatitis on the tongue in adult patients involves two directions: relieving local symptoms (antiseptic rinses, applications, etc.) and influencing the main cause of inflammation.
Stomatitis in the throat
Inflammation in the throat is characterized by painful sensations when swallowing, headache; the temperature may rise. To understand how to treat stomatitis in the throat in adults, blood tests, saliva testing (bacterial culture), and cytological smear tests are often prescribed. For treatment, antiseptic sprays and rinses, drugs aimed at eliminating the causative agent of stomatitis, and anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
In addition to following the doctor’s recommendations, for stomatitis in the throat, it is advisable to drink herbal decoctions, avoid overheating (baths, saunas, hot baths) and physical activity.
Acute herpetic stomatitis
Caused by the herpes virus and usually occurs with fever, vomiting and diarrhea; Bubbles appear on the mucous membranes, turning into ulcers that heal after a few days. When diagnosed with herpetic stomatitis, treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms and immunocorrection.
Fungal stomatitis
Stomatitis caused by candidiasis (fungal infection) is characterized by the appearance of a white coating with a curd consistency, a feeling of dryness and burning in the mouth. During treatment of candidal stomatitis, it is important to maintain hygiene: thoroughly wash your hands and dishes, rinse your mouth before and after eating. The diet should consist of warm food and plenty of fluids; smoked, salty, and spicy foods should be excluded. The oral cavity is treated with antifungal and anti-inflammatory agents.
Drug-induced stomatitis
This type of stomatitis is a consequence of an allergic reaction to antibiotics and other medications. Symptoms include the formation of spots, blisters and ulcers on the mucous membrane, accompanied by pain and bad breath.
Complex treatment of medicinal stomatitis consists of several stages:
- exclusion of the drug that caused stomatitis;
- taking antihistamines;
- diet correction;
- To heal the affected areas, sprays or ointments are used, often containing an anesthetic to relieve pain.
Stomatitis caused by fungi
Candidal stomatitis is a fungal disease caused by fungi of the genus Candida.10 Young children and the elderly are more often affected; people with diabetes and xerostomia (dry mouth), pregnant women and people with weakened immune systems are also at risk. Elderly people wearing removable dentures often get sick.
The main symptom of fungal stomatitis is a burning sensation and the presence of a white, cheesy coating, when removed, a swollen, red mucous membrane appears. The general condition of adults with candidal stomatitis is practically not affected.
Bacterial stomatitis
Vincent's ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis
It manifests itself as ulcerations of the mucous membrane, strong odor from the mouth, fever, weakness, pain when eating. In severe forms, ulcerations can occupy almost the entire oral cavity, and the temperature rises above 38°C.
Gonorrheal stomatitis
Caused by Neisser's gonococcus. The mucous membranes of the lips, gums, lateral and lower surfaces of the tongue are mainly affected. The mucous membrane has a brightly hyperemic color and a large amount of gray purulent plaque with an unpleasant odor. But, as a rule, there are no complaints.
Acute streptococcal gingivostomatitis
It is characterized by general damage to the gums, severe pain, fever, enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes. The mucous membrane of the mouth and tonsils is hyperemic, abscesses may form.
Is treatment possible at home?
Treating stomatitis at home is quite possible, especially if it is not severe. However, it is still necessary to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and choice of medications than to treat stomatitis at home.
To treat herpetic stomatitis at home, local remedies are sufficient: rinsing with miramistin (3-4 times a day) or hexoral. To suppress inflammation, you can use Cholisal gel, for faster healing of ulcers - solcoseryl gel (or Actovegin), sea buckthorn or rosehip oil, oil solutions of vitamins A or E. If rashes appear on the lips or skin around the mouth, you can use Zovirax cream or acyclovir. In severe cases of the disease, it is necessary to use drugs against the herpes virus, but they must be prescribed by a doctor.
In general, it is dangerous to treat severe forms of stomatitis at home, especially such as Vincent’s ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis. To combat it, antibiotics will be required, which should be selected by the attending physician.
Traumatic stomatitis
Traumatic stomatitis develops as a result of mechanical, thermal or physical trauma. This type of stomatitis occurs:
- superficial (burn of the mucous membrane by hot tea)
- deep (burn with a strong alkali or acid, strong biting of the mucous membrane)
Acute mechanical stomatitis: rare, it can be caused by trauma to the mucous membrane when biting the cheek, tongue, lip while eating, an attack of epilepsy, a blow, trauma during dental treatment and other traumatic factors.
It is manifested by pain, hyperemia, swelling at the site of injury, erosion. With secondary infection, the wound can develop into long-term non-healing ulcers. Most often, traumatic stomatitis is acute, but can also be chronic, for example, constant biting of the cheeks under stress, chronic injury from braces, a sharp tooth edge, or a bad crown. As a result of trauma, painful erosions or ulcers with jagged edges form on the mucous membrane, which can become infected.
The cause of physical injury is most often a thermal burn due to contact with hot liquid, inhalation of steam, or exposure to fire, the latter, as a rule, accompanied by damage to the respiratory tract. The lesion is most often located on the tip of the tongue, lips, and the front of the palate. The mucous membrane becomes swollen, red, painful, and blisters may form, which then burst. With deep damage, the mucous membrane dies, and the damage involves muscles and even bone.
Chemical stomatitis occurs when burned with acid or alkali. In everyday life, this is most often acetic acid; also at a dental appointment, burns can occur with various drugs (phenol, formaldehyde, alcohol, hydrofluoric acid, etc.). The depth of damage depends on the damaging substance and its concentration, and the duration of exposure. First, the mucous membrane becomes bright red and painful, and with severe lesions, foci of necrosis then appear within a few hours.
In case of burns with acids, alkalis, or thermal burns, it is recommended to call an ambulance!
Symptoms of the disease
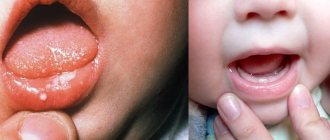
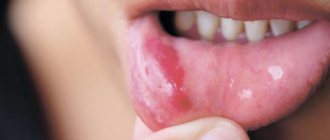
Symptoms depend on the type of pathology, but there are common clinical manifestations. As a rule, the disease does not begin acutely. The mucous membranes become red, swelling, pain, and a burning sensation appear in the affected area. You can see what stomatitis looks like in the photo.
If it is a bacterial infection, then after a day an ulcer appears at the site of infection with a red halo radiating from the center. The ulcer is covered with a white coating. During this period, salivation increases and an unpleasant odor appears. Pain bothers the patient not only when eating, but also at rest.
Pimples and ulcers appear anywhere in the oral cavity; in severe cases, stomatitis develops in the throat. Stomatitis on the tongue is especially painful, since there are many nerve endings there. Some types are characterized by bleeding gums.
With further development of the pathology, the temperature may rise, the lymph nodes may enlarge, and symptoms of intoxication may appear - weakness, nausea, lack of appetite.
Allergic stomatitis
They arise as a reaction of the mucous membrane to an allergen. An allergic agent can be toothpastes, mouthwashes, food, medicines, materials for crowns, fillings, etc. Allergies often occur to removable dentures. The mucous membrane is affected precisely at the point of contact with the damaging agent, for example, the hard palate under a removable denture. With allergic stomatitis, the mucous membrane is swollen, red, bubbles appear, which burst with the appearance of painful erosions.
Allergic stomatitis also includes chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis , it begins with swelling and burning, then a painful aphtha appears, and then a healing period begins. This disease is characterized by constant relapses with a certain frequency.
Prevention of stomatitis
Consists of the following items:
- strengthening the immune system, giving up bad habits, hardening, playing sports, eating with a sufficient amount of macros and vitamins (especially vitamin C)
- regular visits to the dentist
- adequate brushing of teeth at home, as well as removal of dental plaque in the dentist’s office once every 6 months
- identifying the allergen and avoiding contact with it
- undergoing medical examination for timely detection of diseases
- treatment of systemic diseases
- taking antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor, together with a course of probiotics, to avoid dysbiosis
- vaccination (against measles, chickenpox)
Tantum® Propolis
It is worth paying attention to Tantum Propolis, since propolis has an immunostimulating effect, promotes healing, and vitamin C, which is part of it, is responsible for regeneration, participating in the synthesis of collagen.
Propolis also has antiviral and antifungal effects. Therefore, vitamin therapy Tantum Propolis is an effective means of preventing stomatitis.12 Find out more
Treatment of stomatitis
Treatment of stomatitis depends on the severity and cause of the disease and includes the following measures:
1. For bacterial stomatitis, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. For fungal stomatitis - antifungal drugs, for viral ones - antiviral drugs
Important! Antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal drugs are prescribed only by the attending physician!
2. For high fever and pain, antipyretic and painkillers are prescribed
3. Vitamin therapy. It is especially important to take vitamins A, C, E
4. Immunomodulatory drugs
5. Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity. Antiseptics are used in the form of solutions, sprays, tablets, ointments
6. Epithelializing agents are used after acute phenomena have subsided
7. Sanitation of the oral cavity, removal of dental plaque
8. A gentle diet
9. Eliminating allergens and taking antihistamines
Important! Stomatitis is treated by a dentist, in some cases together with a therapist, infectious disease specialist, allergist and dermatologist. If you have symptoms, consult a specialist.
Treatment of stomatitis in adults at SM-Dentistry
The SM-Dentistry doctor will carefully collect anamnesis and develop an individual treatment program aimed at eliminating symptoms, increasing immunity, and preventing relapses. If it is necessary to identify the systemic cause of the disease, you will be offered consultations with general and related doctors.
The most common types of this disease that our specialists encounter are bacterial and ulcerative. We also provide treatment for herpetic, aphthous, and candidal stomatitis. If the illness is of an allergic nature, we will refer you to a qualified allergist for consultation.
Treatment at SM-Dentistry includes a range of tools:
- imported high quality antiseptic preparations;
- antiviral, antifungal drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs (gels, ointments) for healing the mucous membrane;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- vitamin therapy;
- developing a diet to improve immunity;
- if necessary - removal of plaque, stone, treatment of caries and other dental diseases.
In addition, you will receive detailed recommendations on oral hygiene.
Stomatitis causes a lot of unpleasant and painful sensations. In order to quickly and effectively get rid of them, contact SM-Dentistry (from 9 a.m. to 9:30 p.m. on weekdays, until 9:00 p.m. on weekends). To make an appointment, fill out an application on the website or call: +7.
Dentist consultation Professional teeth cleaning Plaque removal Treatment of caries Tartar removal
Answers to popular questions
Which doctor treats stomatitis?
The dentist, if necessary, can refer the patient to other doctors.
Do I need to take antibiotics for stomatitis?
Some forms of stomatitis require the use of antibacterial agents, but in most cases this is not only useless, but even dangerous, since it can lead to dysbacteriosis. Antibiotics should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor in the prescribed dosage.
How long does it take to treat stomatitis?
Depends on the severity and form of the disease. On average 7-10 days.
Is stomatitis contagious?
Not all forms of stomatitis are contagious. Traumatic stomatitis is absolutely not contagious. If stomatitis is caused by viruses, such as herpes or measles, the risk of infection is very high.
Is stomatitis contagious?
Whether stomatitis is transmitted or not is a question that worries many. Ulcers are not contagious if they are the result of:
– mechanical injuries;
– allergies;
- during intoxication.
If the cause of stomatitis is an infection, then the disease can spread to other people. These types include fungal, herpetic, and infectious stomatitis.