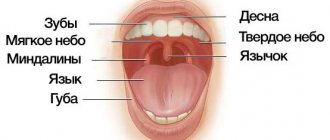
The lymphatic system is the protective barrier of the entire human body and is the first to encounter germs and viruses that can infect a person.
The general function of the lymphatic system is to destroy bacteria and viruses that enter the blood from outside. As soon as the virus enters the body, the lymphatic system immediately begins to react to this with peculiar processes.
- Causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes Diagnostic methods
- Can a child's lymph node become inflamed?
One possible reaction may be inflammation of the lymph node behind the ear, in the groin area or on the neck. The lymph system is as important for the body as the circulatory system. It helps to cleanse the cells and tissues of the body, and also regulates metabolism in the body.
Content:
- Causes of pathology
- Signs of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes 1.1. First stage 2.2. Second stage 2.3. Third stage
- How to cure an enlarged lymph node in the submandibular area
- Prevention of the inflammatory process
Inflammation of the submandibular lymph node is one of the most common types of lymphadenitis.
Its development is caused by inflammatory processes occurring in the oral cavity and less often in other parts of the body. Often the problem occurs with advanced caries, pulpitis, gingivitis, and inflammatory lesions of the tonsils. It is also caused by throat diseases. Let's take a closer look at why the submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged and what should be done to normalize the situation.
Contact our clinic!
“Ear, Nose and Throat Clinic” offers you consultations with doctors of the highest category, constantly developing in their specialization and working with advanced diagnostic and therapeutic equipment. A quick and competent diagnosis of enlarged lymph nodes is a guarantee of successful recovery with minimal risk of exacerbations. To make an appointment, you can leave an online application on our website or call us by phone. You should not postpone a visit to the doctor, as a protracted inflammatory process can lead to negative health consequences.
Causes of pathology
If the lymph node changes its size, it can be assumed that a viral or bacteriological infection has spread. Taking into account the localization of the lesion, the doctor understands exactly where the source of the disease is located and which organs need urgent medical attention.
Among the dental provocateurs of enlarged submandibular lymph nodes:
- inflammation of the salivary glands;
- gingivitis;
- pulpitis;
- flux;
- stomatitis;
- alveolitis;
- periodontitis;
- deep caries;
- inflammation occurring under the crowns.
But the violation is not always associated specifically with dental diagnoses. Its reasons are:
- Respiratory diseases: pharyngitis, laryngitis, rhinitis.
- Pathologies related to the bone structures of the skull: damage to the bone structures of the lower jaw, damage to the temporomandibular joint, articular capsule.
- Infections: sore throat, measles, tonsillitis, otitis media, chicken pox, mumps. In all these cases, the lymphatic tissues swell a few days after the first symptoms of the disease appear.
- Specific pathologies caused by pathogenic pathogenic agents: toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea.
- Oncological neoplasms. Lymphatic tissue always reacts very sharply to tumor growth. Enlarged submandibular lymph nodes sometimes indicate the presence of a neoplasm in the area of the tongue, neck, or salivary glands.
- Autoimmune disorders. Always associated with disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. Then, by mistake, lymphocytes begin to treat healthy cells as dangerous pathogens. They destroy them, causing inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Hyperthyroidism. With an exacerbation of this disease, the neck and cheek area swells, the lymph nodes become more voluminous.
In young children, parents may notice large round “balls” under the jaw during the period of active teething. This often causes an increase in body temperature. There is no need to be afraid of such symptoms. It is associated precisely with the inflammatory process provoked by the eruption of milk units. But, if the situation does not return to normal within three to five days, it is still worth showing the baby to a pediatric dentist, surgeon or pediatrician.
Preventive measures
Prevention of inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes lies in a healthy lifestyle. General strengthening of the body, hardening, playing sports and giving up bad habits - these well-known rules help the body to be more resistant to any diseases.
Leading a healthy lifestyle
You should not ignore systematic annual visits to doctors for preventive examinations, which help to identify health problems in time and eliminate them without delay, without waiting for them to manifest themselves in full force. Do not try to treat even a “harmless” cold yourself: incorrect treatment or its absence is a starting step towards lowering the body’s protective barrier, and, therefore, provoking its defenselessness against viruses and bacteria.
Signs of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes
How the disorder manifests itself depends on how far the disease process has progressed. If you do not carry out the necessary therapeutic measures, one stage will quickly pass into another.
First stage
The size of the lymph nodes changes very slightly, but the person already feels that they hurt when pressed. Discomfort occurs when turning the head. Body temperature often rises and a sore throat appears. A tickle or dry, unproductive cough is annoying. Pain occurs only on one side of the neck or on both sides at once. The first case is more likely if it is a viral disease.
Second stage
It is called “acute lymphadenitis”. Now the lymph node can be distinguished visually - it becomes convex and protrudes forward. Externally it resembles a subcutaneous ball. Its diameter reaches three centimeters, but can be more impressive.
The node is painful to the touch. Because of this, it is difficult for the patient to turn and tilt his head, and open his mouth wide. The mobility of the upper and lower jaw is significantly limited.
The pain may radiate to the cheek or ear. Body temperature increases. Overall performance decreases.
Third stage
Called purulent lymphadenitis. Here, the inflammatory process even affects structures adjacent to the lymph node. The patient complains of pain in the throat, collarbone, armpit, and head. The nerve endings of the teeth may become inflamed. Then acute toothache occurs.
Pus formed in lymphoid tissues consists mainly of necrotic cells. If it gets into the blood (and such a possibility always exists), the outcome can be extremely unfavorable, so the inflammatory process should not be started.
Patients can understand that the submandibular lymph node is inflamed and needs treatment as soon as possible by the following signs:
- the “ball” enlarges and becomes red or bluish;
- every day it becomes more dense and solid;
- the skin located above the lymph node takes on a red tint and is hot to the touch;
- the lower jaw area swells.
Complications and consequences
Lymphadenitis behind the ears is a dangerous disease for both children and adults. Most often, if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the disease begins to recede immediately after the start of therapy for the provocateur of the disease and goes away after it is completely cured.
If you do not contact a specialist in time, the inflammation will progress, spreading to adjacent tissues. During the inflammatory process at the site of infection, lymphoid tissue dies and is replaced by connective epithelium. As a result of this process, the lymph node irretrievably loses its functional abilities: in the future, the problem node will no longer be able to perform the filtering function, which, with subsequent infection of a person, will provoke the direct entry of viruses into the body through its unprotected area.
Even more dangerous not only for health, but also for life is purulent lymphadenitis. The purulent formation, after maturation, opens on its own inward or outward. The second option in this situation is the most favorable, although it is accompanied by the danger of the onset of a septic process.
When an abscess ruptures into the internal muscle tissue, it is almost impossible to predict where the pus will come out. Near the parotid lymph nodes there are vascular connections that can transport pus specifically to the brain, which is almost 100% fatal.
The transition of lymphadenitis into a chronic form also carries hidden dangers for human life: impaired circulation of lymph in the body, expansion of the connective epithelium near the affected area, systematic swelling will become regular companions of the sick person.
How to cure an enlarged lymph node in the submandibular area
Therapy must be carried out under medical supervision. Its main goal is to eliminate the infection that caused the disorder. If the root cause of the condition is not established, it will not be possible to be completely cured.
If the problem is related to an oral disease, mandatory treatment is carried out. For severe inflammatory pathologies of internal organs, antibiotic therapy is carried out. For pathologies of a viral nature, patients are prescribed antiviral drugs.
If the examination reveals that pus has accumulated inside the tissues, it is drained using a drainage tube. Additionally, a puncture is taken to recognize the pathogen and understand whether the disease has a benign or malignant course.
As soon as the infectious focus disappears, the lymph nodes begin to shrink, stop hurting and gradually reach their normal state.
Prevention of the inflammatory process
To reduce the risk of developing lymphadenitis, you must strictly follow the recommendations:
- Have annual preventive examinations at the dental clinic. Treat all emerging oral diseases in a timely manner. Avoid caries and take care of your gums.
- Do not ignore the presence of infections and treat them. During therapy, strictly follow all medical prescriptions.
- For any damage to the skin, treat wounds with antiseptics. This minimizes the risk of contracting an infectious disease.
- If you feel unwell, consult a doctor and get laboratory tests. This simple measure allows you to detect violations at the earliest stages.
It is necessary to understand that using “grandmother’s” methods for inflamed lymph nodes is dangerous. So, under no circumstances should you heat the inflamed area or apply cold compresses to it. It is unacceptable to massage him or put pressure on him. All of these actions can make the situation worse. Then it will be much more difficult to reverse the disease.
Features of the treatment of illness in children
The progression of parotid lymphadenitis in school-age children and adolescents is a fairly common occurrence. The causes of the pathology can be infectious and viral provocateurs, as well as the characteristics of the child’s body in the process of its physiological formation.
If symptoms of lymphadenitis appear behind the ear in a child, you should immediately contact your pediatrician to prescribe appropriate treatment. The fact is that children suffer more painfully from any form of lymphadenitis behind the ear; the disease is accompanied by the appearance of fever, severe malaise, and lack of appetite.
The methodology for treating lymphadenitis in children is practically no different from the treatment of adults. A feature of the treatment of pathology in pediatric patients is the selection of drugs according to age indicators, as well as their dosage.
Even if the problem lies in age-related changes, and not in the patient’s infection, the child should receive medical care. As the pathology progresses due to age, the patient may not be prescribed aggressive antibacterial drugs. In this case, methods of health therapy, including taking drugs to enhance immunity, vitamin complexes, and physiotherapeutic procedures, may be sufficient; however, the treatment methodology in each individual case should be selected only by a doctor, taking into account the course of the disease, associated factors and the prevailing symptoms.