Why do you need a tongue?
The uvula in the throat is a palatal process that resembles a small bell. Its main function at the junction of the larynx and palate is protective. It prevents bacteria, viruses and pathogenic microorganisms from entering the throat and lower respiratory tract. The tongue covers the throat from cold air when walking on a frosty day. It also distributes air flow.
The tongue is located above the larynx, and when it enlarges, the functions of swallowing, breathing, and speech are impaired. The swollen organ can increase in size by 5 times. Because of this, it falls on the tongue, causing gag reflexes.
What is uvulitis?
Uvulitis is understood as chronic or acute nonspecific inflammation of the uvula in the throat.
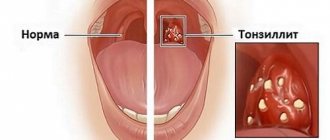
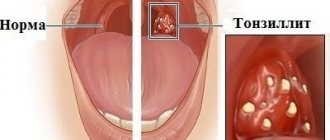
Since uvulitis is most often based on an infectious-inflammatory process, the disease is often accompanied by pain, swelling and pronounced hyperemia of the uvula. The uvula is a small organ, which is represented by the terminal part of the soft palate.
It is localized above the root zone of the tongue, strictly in the middle - between the palatine tonsils (tonsils) and the arches.
The uvula consists of smooth muscle fibers and is covered on the outside with a delicate mucous membrane. The organ is also rich in small capillaries, arterioles and venules.
The main functions in which the uvula is involved are:
- sound production, speech creation;
- redistribution of inhaled air flows;
- preventing food lumps from entering the lumen of the larynx and other organs of the respiratory system;
- warming and purifying inhaled air;
- participation in the processes of formation of cough and gag reflexes.
Thus, despite its small size, this organ takes part in such important processes as sound production and the distribution of food and air. Its inflammation may be accompanied by a violation of one or several of the listed functions.
Classification
In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, uvulitis does not have its own specific code; it is classified in a large group - sore throat. Consequently, inflammation of the uvula has a conventional code according to ICD 10 - R 07.0.
In the modern classification, uvulitis is divided primarily into acute and chronic (according to the nature of the disease). Acute inflammation usually lasts a maximum of 2 months, while chronic inflammation bothers the patient for 6 months or more and tends to recur.
Depending on the etiological factor, uvulitis is divided into the following types:
- Viral – when the disease is based on a viral infection that affects the epithelium of the oropharynx and respiratory tract.
- Bacterial - in this case, the causative factor of the disease is bacteria: streptococci, staphylococci, Klebsiella, etc.
- Traumatic - this type of disease is associated with injury to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, including the uvula (burns, exposure to rough, hard food, less often - fractures of the hyoid bone).
- Allergic is a type of uvulitis in which immune inflammation of the uvula and often the mucous membrane of the larynx occurs in response to exposure to allergens (food, medications, pollen, etc.).
- Medicinal – occurs as a result of the aggressive effects of certain drugs or their improper use.
Specific forms of uvulitis caused by certain microorganisms are extremely rare. They can develop against the background of an atypical course of syphilis, tuberculosis, AIDS, etc.
Causes of swelling
Swelling of a small organ is a symptom indicating the development of an infection or other pathology. In 25% of cases, an inflammatory process develops on the uvula, even in this case the disease is a consequence of inflammatory reactions, for example, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis.
Swelling is caused by the development of bacteria: streptococci, staphylococci. Viruses, especially influenza, parainfluenza and adenoviruses, are also causes. Only in 20% of cases can the uvula become swollen due to the spread of a fungal infection.
One of the reasons for swelling of the tongue is an allergic reaction. It can develop through contact with various substances or as a result of taking medications.
A tumor of the uvula develops from factors:
- pathologies of the oral cavity and nasopharynx;
- neoplasms, benign and malignant uvula or adjacent elements;
- surgery to remove tonsils;
- throat surgery;
- injuries, burns of the tongue;
- inhalation of toxic substances, dust;
- drinking hot drinks and food.
Inflammatory processes in the pharynx and pharyngeal ring develop due to dry mucous membranes, hormonal imbalances due to pregnancy, menopause, adolescence, or the use of hormonal medications. In this case, the greater damage occurs on the tongue.
Risk groups include smokers and people who drink alcohol excessively. If a person has reduced immunity due to chronic endocrine or systemic pathologies, a swollen uvula will be a consequence of illness.
Due to undeveloped immunity, children are primarily affected by swelling of the uvula. The symptoms are extremely severe. Elderly people are also susceptible to swelling of the uvula, but the signs are not obvious.
Poor treatment of respiratory diseases leads to tumors: if a person gargles with a concentrated soda solution and a decoction of medicinal herbs of various origins.
Causes
The most common cause of acute uvulitis in children and adults is an infection that can penetrate the membrane of the uvula by contact. There are hematogenous and lymphogenous routes of infection (with blood or lymph flow, respectively).
Also, many doctors argue that for the development of inflammation, the presence of a predisposing factor is necessary - a violation of the integrity of the venous plexuses of a small organ. This creates favorable conditions for the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms.
Main causes of the disease:
- carious lesions of teeth, gingivitis, stomatitis (inflammation of the gums and oral mucosa);
- acute tonsillitis (angina), pharyngitis (inflammation of the back wall of the pharynx), damage to the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis, ethmoiditis, frontal sinusitis);
- infectious diseases of the nasopharynx (rhinitis of various etiologies);
- allergic reactions from the oral mucosa.
The disease can also occur after drinking alcohol (like a chemical burn), against the background of inflammatory diseases of the peripharyngeal fatty tissue - phlegmon, abscesses. Provoking factors are burns of the oral cavity due to excessively hot food, acids, alkalis, trauma to the tongue with sharp objects, hard food, and snoring.
In some cases, the causes of damage to the uvula may be tumor diseases of the soft and hard palate (benign, malignant), injuries to this organ as a result of severe paroxysmal coughing and sneezing.
Symptoms
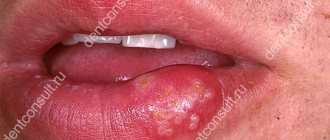
It is difficult to miss the swelling of the uvula: the feeling of a foreign body, gagging are unpleasant signs. Even a person who is far from medicine can visually examine the throat and find out that the appendage of the palate is swollen.
But if the tumor is not obvious, other symptoms may indicate a problem:
- increased salivation;
- speech disorder;
- labored breathing;
- pain and sore throat.
Depending on the pathology, severe fever, cough, and runny nose may occur. If a person suffers from allergies, a rash, itching, redness of the skin and swelling of the lips and tongue are possible.
Painful swallowing of saliva during a long conversation or after sleep may indicate a problem. An unpleasant symptom may subside within half an hour. Discomfort may occur when eating, drinking, or sneezing and coughing.
Symptoms of the disease
The disease develops very quickly. At the initial stage, the symptoms of uvulitis are not pronounced. Breathing is not impaired, there is a feeling of a lump in the throat, the voice changes, and discomfort occurs when swallowing and speaking. The tongue increases in size and swells slightly.
Moderate and severe uvulitis is characterized by more severe symptoms:
- dysphonia (voice disorder)
- false gagging
- increase in body temperature
- hypersalivation (increased salivation)
- swelling and tenderness of the soft palate
- pain when swallowing
- sore throat feeling
Most often, signs of uvulitis occur in the morning, after sleep. The first step is to carefully examine the oral cavity. If the tongue has acquired a bright red color and increased in size, the cause of discomfort is most likely uvulitis.
If the size of the uvula has increased several times and it reaches the tongue, it is possible to completely block the lumen of the nasopharynx. This can cause asphyxia and death, so in this situation the patient must immediately receive emergency assistance.
You need to be especially careful in the presence of this disease in young children, since in them all processes in the body proceed much faster, so an ambulance should be called immediately.
Complications
If the uvula on the roof of your mouth is swollen, you must urgently seek medical help, otherwise there will be a rapid development of edema, asphyxia and death.
If the swelling is insignificant, a person may experience difficulty speaking or eating: the feeling of a foreign body causes nausea, as a result the patient refuses to eat and does not receive microelements for the body.
Difficulty breathing slowly but surely leads to dysfunction of internal organs and tissues. The respiratory and cardiovascular systems and meninges are affected.
Solutions for inhalation
One of the most effective methods of therapy is therapeutic inhalations. It is necessary to make a decoction based on thyme, eucalyptus oil and pine buds. 20 grams of kidneys are poured into a glass of water and boiled for 30 minutes. Then mix 10 grams of thyme with a glass of boiling water and leave to infuse for 40 minutes. The decoction and infusion are combined in one container and 20 grams of eucalyptus oil are added. The resulting product is poured into a nebulizer and inhaled at home.
Inhalation with vasoconstrictor drugs is also good for relieving swelling.
Diagnostics
If signs appear, you should consult a doctor: a therapist or an otolaryngologist. If hypersensitivity to one of the components is indicated, the patient will be referred to an immunologist or allergist. If a reactive tumor of the uvula is suspected due to the development of an infection, an infectious disease specialist is also involved in the study.
Visual diagnosis is not enough. It is important to identify the degree of swelling and symptoms, and determine the condition of the body. Therefore they carry out:
- laryngoscopy;
- pharyngoscopy;
- Ultrasound;
- radiography.
It is necessary to prescribe laboratory tests of blood, urine, and scraping of the mucous membrane. If purulent ulcers are visible on the uvula, their contents are examined.
Diagnostic features
Diagnosis of the disease is not difficult. It is enough for the doctor to listen to the patient’s symptoms and examine the oral cavity.
If the diagnosis requires clarification, then the following procedures must be performed:
- Take a clinical blood test. This procedure will help determine the nature of the infection (viral or bacterial), as well as the presence of infection in the body. If the disease is infectious, the number of leukocytes in the blood will increase. With the allergic nature of the disease, an increase in eosinophils occurs.
- Take a bacterial culture from the throat to determine the microflora that caused inflammation of the uvula. The analysis will help determine the type of pathogen, as well as its susceptibility to the main types of antibiotics.
- If you suspect an allergy, you need to conduct an allergy test.
- Conduct histological studies of uvula tissue, X-rays and tomography to exclude oncology.
Select equipment
Treatment
If the uvula is swollen, you cannot self-medicate: incorrect actions will lead to a sharp deterioration of the condition. If swelling develops quickly, you should call emergency medical care, the paramedic will give injections with antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs and refer the patient to the intensive care unit.
If the tumor of the palatine process is insignificant, you can consult an otolaryngologist yourself. After the examination, the doctor will determine the cause of the pathology and develop a treatment program.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment methods are chosen if the patient's condition does not cause concern. If the inflammation is caused by a bacterial infection, the first-line drug is an antibiotic. If the disease began due to the development of a viral or fungal infection, choose the appropriate medication.
A group of medications will help relieve symptoms:
- Antihistamines. If the swelling is not caused by contact with an allergen, medications help relieve swelling.
- Anti-inflammatory. Help eliminate swelling, redness, and pain. At the initial stage, non-steroidal drugs are prescribed; in difficult situations, steroids (hormones) are used.
- Diuretics. They are aimed at relieving puffiness, but the drugs must be taken carefully.
Antiseptics will help eliminate pathogenic microbes. In difficult situations, doctors prescribe injections of antihistamine and anti-inflammatory solutions. For small and moderate tumors, tablets and capsules are used. If swallowing is inconvenient, sprays, gels, solutions, syrups and suspensions are used.
Inhalations with different compositions are remedies for the treatment of uvula swelling. But the compositions for the devices must be chosen by an otolaryngologist.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to strengthen the body when the main symptoms have already been reduced. To normalize metabolism the following is prescribed:
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- UHF;
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- applications.
Usually choose one or two courses of 10 days.
Diet
Proper nutrition during treatment of any disease is the key to success. It is necessary to exclude allergens that caused the tumor, and also exclude:
- hot/cold food and drinks;
- spicy;
- pickled;
- sour.
Alcohol and carbonated drinks are prohibited. It is important for the patient to eat foods rich in vitamins, fiber, and carbohydrates.
Surgery
Otolaryngologists and surgeons are doing everything to delay surgery for partial or total removal of the uvula; this will lead to voice impairment. If a person’s life is at risk or the risk of developing disability is increased, then they resort to surgery.
Excision of the swelling is carried out using minimally invasive methods: laser, cryotherapy, ultrasonic scissors (scalpel). With these methods, stitches are usually not required because the edges of the wound are sealed using laser light or ultrasound. But if necessary, self-absorbing sutures are applied.
How to treat uvulitis?
Using these medications:
- Antihistamines and decongestants: Cetrin, Aleron.
- Diuretics (to rid the body of excess fluid) together with drugs that restore calcium levels in the body: Furasemide, Triphase.
- Glucocorticosteroids: Diprofos, Sondex, Medrol.
- Antimicrobial, antibiotics, antiviral drugs.
- Antiseptic sprays.
How to treat uvulitis? Using the following physiotherapeutic procedures:
- UHF;
- Inhalations;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Galvanic mud;
- Phototherapy;
- Electrophoresis;
- Speleotherapy;
- Electrotherapy;
- Acupuncture;
- Aromatherapy;
- Phytotherapy;
- Mechanotherapy;
- Ultraviolet irradiation.
Is it possible to be treated at home? Treatment is permissible, but only as a complementary therapy, not the main one. Used as folk remedies:
- decoctions of viburnum, raspberry, St. John's wort, thyme, which are used as a rinse for the uvula;
- ylang-ylang, eucalyptus, pine in the form of essential oils for inhalation procedures;
- Rosehip infusion gives a diuretic effect.
Is it necessary to follow a diet when treating uvulitis? There are no strict recommendations here, except for the following:
- Eliminate alcohol and cigarettes.
- Eliminate from the diet foods that irritate the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat: sour, hot, cold, salty, spicy.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
Important here are compliance with oral hygiene standards, humidification and purification of the air in the room where the patient is.
go to top
Prevention
To prevent the development of a tumor of the uvula, otolaryngologists and other specialist doctors recommend:
- Treat acute respiratory diseases. Follow doctors' recommendations for chronic pathologies.
- Avoid contact with allergens.
- Do not take medications uncontrollably.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Strengthen the immune system (hardening, moderate physical activity, walks in the fresh air, taking vitamin complexes).
Do not consume hot food or drinks, and avoid long-term consumption of cold foods (for example, ice cream).
- Premium Clinic Medical Center. Uvulitis. // [electronic resource]. Access date 06/23/2021
- Luchikhin L. A. Otorhinolaryngology. — 2012
- Blotsky A.A. Inflammatory diseases of the pharynx. — 2015.
- Head and Neck Institute. Uvula. // [electronic resource]. Access date: 05/22/2021
Author: Lyudmila Fedorova Pulmonologist, immunologist, therapist
Traditional medicine in the treatment of disease
The use of medications is necessary, but these drugs alone will not be enough. Rinsing with herbs, as well as taking infusions internally, have proven themselves to be effective.
The most commonly used mouth rinses are:
- Raspberry leaves. Pour boiling water over and leave for 30 minutes
- Onion peel. 1 tbsp. pour 700 ml of boiling water over the husks. Leave for about 4 hours.
- Dry viburnum fruits. 50 grams of fruits are poured into 1 liter of water and boiled for 30 minutes in a water bath.
- Garlic infusion. Grind 100 grams of garlic, pour in 150 ml of boiled water. Leave for 5 hours.