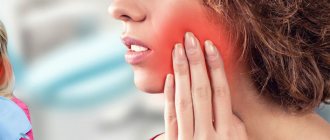
Ear pain is a fairly common symptom. Painful sensations in this case give the patient a lot of unpleasant moments, and it is very difficult to simply “endure” such pain. It is noteworthy that pain in the ear is not always associated with diseases of the hearing organ. Such painful sensations can also be caused by other organs that radiate, that is, “giving off,” to the ear. A condition in which the ear hurts, but there is no inflammation in it, is called otalgia.
Otalgia can be caused by many reasons:
Temporal arteritis
The disease is an inflammation of the vessels of the temporal artery.
If the inflammatory process spreads to the ear artery, the patient will also experience pain in the ears. This disease is typical for older women. It causes blurred vision, headaches, pain in the temples, and increased fatigue. Make an appointment right now! Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Along the branches of the vagus nerve, pain can radiate to the ear from the esophagus, thyroid gland, and organs of the cardiovascular system.
If you have ear pain, you should definitely consult with an otolaryngologist, since this condition may signal the presence of serious diseases in the body. If the ear is healthy, no abnormalities have been identified, and the pain does not go away, it is necessary to diagnose the nose, larynx, pharynx and, if necessary, other organs to identify the cause of otalgia. Further treatment will depend on the diagnosis.
Acute otitis media
According to statistics, acute forms of otitis media account for 30% of the total number of ENT diseases. Most often it occurs in preschool children.
Symptoms of acute otitis media
The disease is characterized by an acute onset with the appearance of the following symptoms:
- earache;
- ear congestion or hearing loss;
- increased body temperature;
- anxiety;
- disturbance of appetite, sleep;
- headache and toothache.
Causes of development of acute otitis media
In most cases, the disease can be caused by various pathogenic microorganisms - viruses, microbes, fungi, etc. In exudate obtained from the middle ear, respiratory viruses are found in 30-50% of cases. The most common causes of otitis are parainfluenza viruses , influenza viruses, rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, enteroviruses, respiratory syncytial viruses, etc.
In 50-70% of patients with acute otitis media, bacteria are detected in the exudate from the middle ear (most often Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis).
Often the cause of otitis is a mixed (viral-bacterial) infection.
When making a diagnosis, a differential diagnosis is made with myringitis (inflammation of the eardrum) and exudative otitis media.
The occurrence of otitis media is directly related to the condition of the nose and nasopharynx: rhinitis and tonsillitis often provoke inflammation of the middle ear.
Otitis often occurs against the background of decreased immunity and immunodeficiency states.
1 Diagnosis of otitis in MedicCity
2 Diagnosis of otitis in MedicCity
3 Diagnosis of otitis in MedicCity
Routes of infection
The most common route of infection into the middle ear is through the auditory tube during rhinitis and sinusitis.
It is possible that infection can penetrate through the blood during influenza, scarlet fever and other infectious diseases.
In rare cases, the infection enters the middle ear through the ear canal due to injury (rupture) of the eardrum.
Stages of acute otitis
There are 5 stages of the disease:
- stage of acute eustachitis: feeling of congestion, noise in the ear, normal body temperature (if there is an infection, it may increase);
- stage of acute catarrhal inflammation in the middle ear: sharp pain in the ear, low-grade fever, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear, increasing noise and congestion in the ear;
- pre-perforative stage of acute purulent inflammation in the middle ear: sharp unbearable pain in the ear, which radiates to the eye, teeth, neck, pharynx, increased noise in the ear and decreased hearing, increased body temperature to 38-39 degrees, the blood picture becomes inflammatory in nature;
- post-perforation stage of acute purulent inflammation in the middle ear: pain in the ear becomes weaker, suppuration appears from the ear, noise in the ear and hearing loss do not go away, body temperature becomes normal;
- reparative stage : inflammation is stopped, perforation is closed with a scar.
Possible complications of otitis externa
As a rule, otitis externa does not cause complications and is easily treated. However, if complications do occur, they may include the following:
- temporary hearing loss in the affected ear. Goes away after recovery from otitis media;
- chronic external otitis. It usually occurs when there are difficulties in treating external otitis, for example, in fungal and mixed bacterial-fungal forms;
- spread of infection to deep tissues - cellulitis of the neck, lymphadenitis, osteomyelitis. Similar complications (malignant otitis media) can occur in patients with immunodeficiency conditions, diabetes, and those receiving chemotherapy. Such complications can be life-threatening.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce otalgia, ear drops with local anesthetics or oral tablets with analgesics are used before visiting a doctor. Medicines can be used if the pain does not occur due to injury. The pathological process that affects the ear quickly involves the bones of the skull and the brain, so self-medication is unacceptable. A qualified ENT doctor should provide assistance to patients with otalgia.
Conservative therapy
Treatment involves the use of local or systemic medications, or a combination of both. For otitis, ear drops containing antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic substances are used, and the ear is toileted. To improve the outflow of exudate from the tympanic cavity, vasoconstrictors are instilled into the nose. To reduce pain in the first days (before the eardrum ruptures), heated 96% alcohol is dripped into the ear.
To eliminate the consequences of taking ototoxic drugs, ATP and galantamine are prescribed, which stimulate regeneration processes. Nootropics help improve the nutrition of the auditory analyzer structures. To influence the neurological causes of otalgia, sedatives, anticholinergics, metabolic and vasoactive drugs are recommended. Severe painful paroxysms require the use of anticonvulsants.
Physiotherapy methods are effective in practical otolaryngology. To stop the inflammatory process and stimulate local immunity, microwave therapy, laser therapy, and UHF are performed. To prevent hearing disorders during the recovery period, pneumomassage of the eardrum is performed. Reflexology and amplipulse therapy help eliminate paroxysms of neuralgia of the ear node.
Surgery
The tympanic cavity is cleared of pus during myringotomy, followed by washing the ear with antibacterial solutions. In case of chronic otitis and the absence of effect from conservative measures, anthrodrainage is performed in the mastoid area. Indications for surgical treatment are external cholesteatomas, exostoses, and abscesses.
To eliminate the consequences of middle ear trauma, reconstructive surgeries are prescribed: myringoplasty, tympanoplasty, mastoidoplasty. In case of damage to the inner ear, otosurgical interventions are performed to restore the integrity of the anatomical structures. In case of severe illnesses and injuries accompanied by hearing loss, the patient requires selection of a hearing aid or cochlear implantation.
Why does the jaw hurt near the ear: the main causative factors
Soreness in the jaw with radiation to the ear can provoke various pathologies.
Dental problems
Dental diseases are often accompanied by pain, which can radiate to different parts of the head, including the area near the ear. Possible reasons for the appearance of an unpleasant symptom:
- caries at different stages of development, pulpitis;
- abscess;
- damage to prostheses - crowns or implants;
- glossitis - inflammation of the tongue;
- cyst or granuloma of the tooth root;
- gum disease – gingivitis, periodontitis;
- periostitis is an inflammatory process in the periosteum.
Pain in the jaw is often associated with procedures performed by the dentist, for example, teeth cleaning or whitening, their treatment or removal, implantation, or installation of braces. Irradiation into the ear is observed when the figure eight erupts and its position is incorrect.
A problem such as bruxism can also provoke pain. When it is present, the jaw muscles unconsciously contract, causing severe teeth clenching and friction. A characteristic grinding sound occurs. Often a person is not aware of the presence of bruxism, since it usually occurs at night. A disorder can be suspected by the presence of discomfort in the facial muscles in the morning. Due to the strong tension, pain is also felt in the jaw, and microcracks form on the enamel.
Disorders of the temporomandibular joint
TMJ problems are the most common cause of non-dental pain in the facial area. Joint dysfunction is provoked by various disorders in the mobility of the system of muscles, ligaments, cartilage and bones. Pain may appear on the left or right, as well as on both sides. The main symptoms of TMJ dysfunction:
- pain near the ear when swallowing, chewing, yawning, talking;
- dizziness;
- visual impairment;
- noise in ears;
- headache.
The disease is also diagnosed by a characteristic click when opening the mouth. TMJ injuries (dislocations, fractures) are accompanied by bruising, swelling, and redness. You can get them from a blow or bruise. Often the jaw disc is displaced forward, and the head of the lower jaw is shifted backward. This provokes stretching of the anterior and posterior disc ligaments and pressure on the bilaminar area of the joint, where pain receptors are located.
The TMJ can be affected by arthritis and arthrosis. In the first case, severe night pain, crunching and clicking, and stiffness in the morning appear. In the second, the pain is aching and chronic in nature and increases with yawning and opening the mouth. Pathology is provoked by various reasons: age-related changes, stress, inflammation, trauma and genetic predisposition.
Disturbances in the functioning of the TMJ are observed with the habit of clenching or moving the jaw, with bruxism, and constant chewing of gum (the joint does not have time to rest after eating food). Causes wear and tear and malocclusion. Chewing food on one side provokes increased pressure in this area. Over time, damage to the TMJ affects the nerve endings, which explains why pain occurs.
Neurological diseases and vascular pathologies
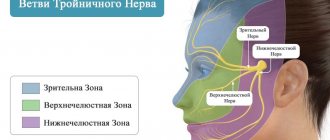
Trigeminal neuralgia is a disease that causes sharp pain in different parts of the face. It all depends on which branch is affected (there are three of them). Unpleasant symptoms may intensify when chewing, talking, pressing on the face, or brushing teeth. In addition to the trigeminal nerve, pain near the ear can provoke damage to other nerves:
- wandering;
- glossopharyngeal;
- occipital
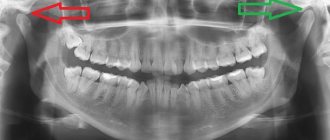
Arteritis, in which acute pain appears due to muscle spasms, can provoke malaise. Deformation is visually observed, and compaction is visible on the x-ray. Characteristic symptoms include swelling and redness of the affected area. Pain in the jaw, which radiates to the ear area and other areas of the face, may indicate diseases of the brain, in particular, circulatory disorders of this organ.
Painful sensations near the ear can be the result of damage to blood vessels, for example, the carotid artery. In this case, the neck, jaw and facial part are affected.
Oncological factor
As cancer develops, pain often appears on the right side. The tumor can be malignant or benign. In the first case, the nerve endings first lose sensitivity, and numbness of the face appears. After this there is pain in the jaw. In the second case, unpleasant sensations in this area are also observed. A lump appears near or behind the ear - a consequence of the growth of a lymph node. In this case, it is important to take measures to prevent an inflammatory or purulent process from starting. In addition to pain near the ear, other symptoms associated with a benign tumor include:
- deterioration of general condition;
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- redness of the tumor.
If suppuration occurs, this already poses a danger to the patient’s life. Lack of proper care can lead to infection entering the bloodstream.
Causes of chronic pain in the throat and ear
Pain in the throat and ear, without or with fever, is one of the most common complaints of patients visiting an otolaryngologist. On average, about 15% of patients seek professional help. As already mentioned, most often the pain occurs on one side; There are also cases when it covers both sides.
The reasons for this phenomenon lie in pathological processes affecting several anatomical structures, but not necessarily. There are often cases when the pain radiates to the ear when the throat is affected. The features of human anatomy are such that the ear, throat, mouth and nose form a communicating system, interconnected by channels.
When inflammation develops in any of the organs, the process spreads through these channels, affecting other structures of the system - the organs of hearing and the pharynx - which provokes pain in the throat and ear. The patient may complain of a sore throat radiating to the ear - or, conversely, the appearance of pain in the organ of hearing and spreading to the throat. It also happens that the patient cannot accurately determine the source of pain.
Symptoms in the form of pain are characteristic of a wide range of pathological conditions, which you can learn about by reading our tables presented in the following sections.
Common diseases that cause pain in the throat and ear
| Pathology | What is it characterized by? |
| Diphtheria | An acute infectious disease that develops as a result of exposure to bacterial agents. It is manifested by the development of fibrinous inflammatory processes in the area where the latter is introduced. Most often these are the upper respiratory tract, bronchi or oropharyngeal mucosa. |
| Measles | An acute infectious viral disease, manifested by the appearance of a rash on the skin, fever and pain in the throat, radiating to the ear. Its complication is often otitis media, which also causes pain. |
| Scarlet fever | Acute infectious processes that begin with a sore throat and are characterized by primary damage to the oropharynx, as well as pronounced intoxication. |
What is otitis externa?
This is an inflammation of the tissues of the external auditory canal, eardrum and auricle. Otitis externa is widespread. It is considered acute if it lasts less than 4 weeks, chronic if it lasts longer and/or occurs more than 4 times a year.
IMPORTANT! Information from the article cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication! Only a doctor can prescribe the necessary examinations, establish a diagnosis and draw up a treatment plan during a consultation!
Why do pathologists of the temporomandibular joint provoke ear pain when chewing?
Often, the prerequisite for the appearance of severe pain in the organ of hearing is disturbances in the functioning of the joint, which is the point of contact between the temporal bone of the skull and the movable jaw.
Dysfunctional disorder in this area can occur for several reasons:
- defects of the lower dentition (partial or complete absence of molars);
- mechanical impact (strong blow to the cheek);
- Constantly chewing gum.
The influence of these factors provokes the appearance of specific clicks in the chewing person that occur when closing or opening the mouth and a pain syndrome spreading to the ear located on the side of the damaged joint.
Diagnostics
If you have complaints about otalgia, you should consult an otolaryngologist. A preliminary diagnosis is made during a visual examination, when signs of injury to the outer ear, suppuration or liquorrhea, and tumor-like growths in the ear canal are detected. To establish the cause of pain, the examination scheme includes informative instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods:
- Otoscopy.
Examination with an otoscope is a simple method for diagnosing otitis media, neoplasms, and boils. The examination reveals skin hyperemia, bulging or retraction of the eardrum, and purulent discharge. If the disease is complicated by destruction of the auditory membrane, during otoscopy the doctor will see the structures of the tympanic cavity. - Audiometry.
A set of diagnostic methods is prescribed to determine the presence of hearing impairment and its severity. To obtain a complete clinical picture, several types of research are used: speech, tone or computer audiometry. - X-ray of the temporal bone.
X-ray methods allow us to study in detail the structure of the inner and middle ear. X-rays can reveal bone fractures, signs of inflammation or destruction of the mastoid process, and deformation of structures due to the growth of tumors. - Additional methods
. To clarify the localization of the pathological process in case of traumatic injuries to the ear area, a CT scan of the skull and an MRI of the brain are performed. The diagnostic search includes a study of the vestibular apparatus (vestibulometry, stabilography). If there is probable inflammation of the Eustachian tube, it is advisable to perform rhinoscopy and pharyngoscopy. - Laboratory research
. For otitis media, bacterioscopic and bacteriological analysis of discharge from the ear canal is indicated. Children with possible mumps are given serological tests (RSC, ELISA). To verify the diagnosis of a malignant tumor, a histological analysis of biopsy specimens is performed.
Otoscopy for ear pain
Our doctors
Gogolev Vasily Gennadievich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist
20 years of experience
Make an appointment
Zharova Galina Gennadievna
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, member of the European Society of Rhinologists, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Debryansky Vladimir Alekseevich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment