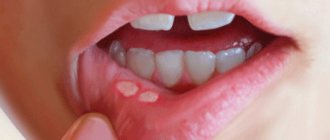
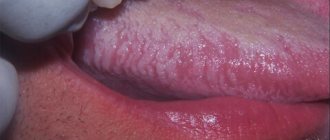
Lateral pharyngitis is one of the types of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx, affecting its side walls located behind the tonsils. The second name of the pathology is lateropharyngitis.
Lateral pharyngitis has symptoms similar to classic pharyngitis, and it is extremely difficult for a non-doctor to determine it. Inflammation may be unilateral or bilateral. When affected, the patient experiences redness and swelling of one lateral ridge or both. The general symptoms of the disease are in many ways similar to the catarrhal manifestations of tonsillitis. In children they are brighter, and the intoxication of the body is stronger. Treatment of the disease must be carried out by a doctor. Self-therapy with home methods greatly increases the risk of complications.
Causes
The causes of lateral pharyngitis are tissue damage by pathogenic fungi, viruses or bacteria. In order for a disease to occur, it is necessary not only for the pathogen to enter the throat, but also for the presence of provoking factors that significantly reduce the body’s defenses. The following negatively affects the functioning of the immune system:
- poor nutrition, in which the body does not receive enough necessary substances;
- smoking in active or passive form;
- abuse of alcohol and even light alcohol;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the body;
- presence of carious teeth;
- breathing through the mouth, especially in the cold season;
- viral infections on the legs;
- overwork;
- lack of sleep;
- chronic stress;
- emotional shock;
- living in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions;
- regular consumption of very hot food and drinks, which causes a drop in local immunity;
- taking medications that reduce the activity of the immune system (such drugs are required for a number of autoimmune diseases).
In children, the problem occurs somewhat more often than in adults, since the child’s immune system is not yet mature and cannot sufficiently resist viruses, bacteria and fungi.
Doctors also identify advanced catarrhal pharyngitis, which affects the back wall of the pharynx, as a fairly common cause of the disease. Taking this into account, the classic form of the disease should be fully treated by seeking medical help.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
The appearance of neck pain on the right or left can be a sign of various pathological conditions, so the patient needs to consult a specialist. Until an accurate diagnosis is established, the patient must maintain physiological rest for the neck, avoid heavy physical exertion and prolonged work at the computer. In case of severe pain, taking painkillers and NSAIDs is allowed. The use of physiotherapeutic methods of treatment and warm compresses until the cause of the disease is determined is prohibited.
The Shants collar fixes the neck and eliminates pain
Conservative therapy
Medical tactics for neck pain depend on the cause of the disorder. If cervicalgia is short-lived, caused by sudden turns of the head, uncomfortable position of the neck during sleep or work, you can limit yourself to physical therapy. To relieve muscle spasm, it is recommended to wear a Shants collar for 2 weeks. After excluding the tumor cause of pain, thermal procedures and compresses are prescribed. For chronic pain, reflexology and exercise therapy are used. The following medications are used as etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy:
- Analgesics
. The drugs are indicated for all types of severe neck pain that causes discomfort and impairs performance. NSAIDs, in addition to analgesic, have an anti-inflammatory effect. - Antibacterial agents
. Purulent processes in the retropharyngeal space serve as the basis for the initiation of massive antibacterial therapy. Antibiotics are selected taking into account the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms. The course usually lasts at least 14 days. - Local remedies
. Blockades with injection of anesthetics are recommended for unbearable pain that cannot be treated with NSAIDs. Compresses with topical corticosteroids and anti-inflammatory drugs diluted with dimexide can also be applied. - Chondroprotectors
. For osteochondrosis, preparations of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate are indicated to slow down degenerative processes in the cartilage tissue of the vertebrae. The products improve the nutrition of cartilage and promote rapid regeneration. - Cytostatics
. To treat the oncological cause of neck pain, drugs from the group of antimetabolites and alkylating compounds are used. If necessary, chemotherapeutic agents are combined with radiation therapy.
Surgery
In severe cases of osteochondrosis, it is necessary to carry out surgical interventions aimed at decompressing the spinal canal. Discectomy, laminectomy and foraminotomy are used. If the disease is complicated by an intervertebral hernia, surgical removal is necessary. For retropharyngeal abscesses, surgical opening of the abscess is performed and subsequent rinsing of the cavity with antibiotic solutions. To correct torticollis, dissection of the fibers of the damaged muscle and excision of keloid scars on the skin are used.
Kinds
The disease can be acute or chronic. The second type is much more difficult to eliminate, since with it the damage to the mucous membrane is more severe and deep.
Also, depending on the clinical picture of the disease, lateral pharyngitis is divided into three types.
1. Chronic lateral pharyngitis, atrophic. During the disease, the mucous membrane becomes thinner, and the lymphoid tissue is partially replaced by connective tissue. The mucous membrane is hidden by epithelial tissues, some of which are prone to keratinization and peeling. This type of disease is difficult to treat. In advanced forms, only maintenance therapy is possible, which minimizes discomfort in the throat and reduces the likelihood of complications.
2. Subatrophic. It is often called not an independent form, but the first stage of atrophic lateral pharyngitis. The patient experiences diffuse damage to the pharyngeal mucosa, against which tissue atrophy develops. With such a lesion, treatment can completely solve the problem.
3. Hypertrophic. Against the background of pathology, the mucous membrane becomes loose and thickened. There is also a dilation of the vessels of the mucous membrane and an increase and thickening of the lymphoid nodules.
Depending on what type of problem is diagnosed, the treatment of the pathology is selected. The sooner a patient seeks medical help, the higher the likelihood that the disorder will be completely eliminated.
During pregnancy
During the period when a woman is carrying a child, against the background of hormonal changes, a sharp decrease in immunity occurs. This is a normal and necessary process that ensures the preservation of pregnancy, since without it the body’s natural protective barrier will recognize the fetus as a foreign object that needs to be removed from the body. For this reason, various viral and bacterial throat infections are becoming a fairly common problem. For some women, classic or lateral pharyngitis is a constant companion of pregnancy.
Since any inflammation poses a danger to the fetus, treatment should be carried out from the first symptoms. Self-medication is strictly prohibited, as it poses a serious danger and can cause serious consequences for the unborn child. In the early stages, due to general intoxication, there is a risk of miscarriage, and in the later stages, there is a risk of premature birth. It can also cause disturbances in the development of the child, both physical and mental.
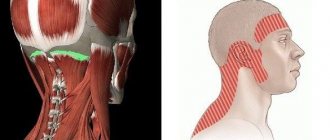
Neck pain
Arthritis
30250 09 June
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Neck pain - causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Almost two thirds of people have experienced neck pain – cervicalgia – at least once in their lives. Such pain does not always indicate a serious illness. But if relapses occur more and more often, this may be a warning sign.
Types of pain
Conventionally, the causes of cervicalgia are divided into two groups:
- arising as a result of spinal diseases (herniated intervertebral discs, arthrosis, dysfunction of intervertebral joints) and vertebral subluxation (whiplash injury). The effects of such injuries can last a lifetime;
- arising due to other reasons: infectious and endocrine diseases, tumor processes, rheumatism.
Possible reasons
Myofascial syndrome
Prolonged strain of the neck muscles, sprains, and hypothermia lead to pain that is of moderate intensity and short duration. In this case, there is often a restriction in head mobility and spasm of the neck muscles, in which tightness and pain when pressed are felt.
As a rule, pain with myofascial syndrome goes away on its own within a few days.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the spine that occurs as a result of deformation and destruction of the intervertebral discs. Loss of elasticity, compression and destruction of discs lead to overload of intervertebral (facet) joints, arthrosis, pinched nerve roots and pain. With age, due to drying of cartilage, the distance between the vertebrae decreases, which causes damage to the intervertebral joints and ligaments.
Facet joint dysfunction
Damage to the structure of the intervertebral, or facet, joints is one of the most common causes of pain in the neck.
The thinning of cartilage on the articular surfaces leads to the appearance of bone growths - osteophytes. They narrow the lumen of the intervertebral foramina and compress the nerve endings. As a rule, this causes a dull pain (gradually increasing, of low intensity), especially in the morning after sleeping in an uncomfortable position (on a high pillow, lying on the stomach). When moving it increases, and at rest it weakens. The pain may radiate to the back of the head, ear, temple or shoulder.
Hernias and protrusions of intervertebral discs
Compression of intervertebral discs that have lost their elasticity leads to their protrusion (protrusion) into the spinal canal and the subsequent formation of a hernia.
As a result, compression of the spinal cord occurs, leading to impaired sensitivity of the hands (numbness, burning, weakness) and pain. Shooting (irregular one-sided) pain intensifies when tilting, rotating or throwing back the head, so that the person instinctively tilts the head forward and to the side opposite to the localization of the pain.
Cervical myelopathy
Prolonged compression of the spinal cord herniation leads to disruption of the spinal circulation.
Painful sensations arise not only in the neck, but also radiate between the shoulder blades and into the shoulders. They intensify with movement and do not stop even after taking painkillers. Characteristic signs include the appearance of goosebumps, numbness in the limbs, and problems with fine motor skills. Dizziness, memory impairment, and gait changes are possible.
Whiplash
A whiplash injury to the cervical spine occurs in a person when the neck is sharply bent forward or backward with subsequent kickback in the opposite direction. This type of damage most often occurs during an accident. This causes stretching and damage to muscles, ligaments, intervertebral discs and cervical vertebrae. In the most severe cases, dislocations and fractures of the cervical vertebrae occur.
The consequences of injury can be pain in the cervical region and shoulders, migraines, spasms of the neck muscles, and impaired mobility.
Associated symptoms include blurred vision, fatigue, and headaches.
Neck pain due to muscular-tonic syndromes
Muscular-tonic syndrome is a condition that is caused by prolonged spasm of several muscle groups in the head, neck and chest. Compression of the neurovascular bundles leads to nagging, sometimes severe pain. In particular, scalene muscle syndrome is a symptom complex in which the innervation and blood supply to the scalene muscles of the neck, running from the cervical vertebrae to the first and second ribs, are disrupted. This syndrome is characterized by pain and stiffness in the neck, more often in the morning, and a certain position of the head (the head is tilted forward and slightly towards the tense muscle). The pain can be mild, aching, but sometimes sharp, intensifying at night, with a deep breath, or when tilting the head to the healthy side. Sometimes pain is transmitted to the shoulders, to the axillary and interscapular areas, to the anterior parts of the chest.
Neck pain due to other causes
Constant and prolonged neck pain can be caused not only by diseases of the spine.
First of all, infectious diseases should be excluded, in particular, nonspecific or tuberculous spondylitis, epidural abscess. Persistent pain that increases rather than decreases with rest may be a sign of metastatic damage to the vertebrae. These symptoms are accompanied by increased body temperature, general weakness, and sweating. When pressing on the spinous processes, local pain occurs.
Damage to the spine is also possible with rheumatoid arthritis. As a rule, at an early stage of the disease, pain occurs in the neck, back of the head and head. The pain can radiate to the forehead and eye sockets, and intensifies when bending and turning the head. Sensation in the neck and arms is lost.
Diagnostics and examinations
First of all, the doctor pays attention to clinical symptoms: localization and distribution of pain, impaired sensitivity in the neck, shoulders, arms, decreased reflexes, general condition, nature of the pain (increases with movement or at rest).
The doctor may prescribe:
- general blood analysis
No. 5Clinical blood test
Blood analysis. General blood test (without leukocyte formula and ESR) (Complete Blood Count, CBC) A general blood test is a comprehensive study, during which a quantitative assessment of the content of blood cells (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets), hemoglobin is carried out, hematocrit and red blood cells are calculated indexes (MCV, MCH, MCHC, RDW).
Up to 1 business day
330 RUR Add to cart
- blood chemistry
No. OBS74Biochemistry of blood
Blood biochemistry: minimum profile The minimum biochemical complex includes studies that help make an initial assessment of the state of health and determine the course of further examination. For use as part of a clinical examination and as prescribed by a doctor.
Up to 1 business day
RUB 3,840 Add to cart
- general urine analysis
No. 116Clinical urine analysis
General urine analysis (Urine analysis with sediment microscopy) General urine analysis is a comprehensive assessment of a number of physical and chemical parameters of urine, as well as elements of urinary sediment, aimed at identifying pathologies of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Up to 1 business day
RUB 370 Add to cart
- blood test for C-reactive protein
No. 43Markers of inflammation
C-reactive protein (CRP) The study of CRP in blood serum is used to detect inflammation and monitor the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Up to 1 business day
570 RUR Add to cart
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor will need the results of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging
In children
In childhood, the problem often appears and poses a threat, especially for children under 3 years of age. In them, due to the structural features of the nasopharynx, even mild swelling can cause suffocation. Also, intoxication at an early age is much more difficult to tolerate, which is why the child may develop convulsive seizures. With a significant increase in temperature due to pharyngitis, hospitalization is most often indicated for children under 3 years of age.
Pain, which is much stronger with lateral inflammation than with damage to the posterior wall, leads to loss of appetite. In some cases, this is the first symptom of the disease, a few hours after which an increase in temperature and other manifestations of pathology are observed.
What not to do
There are several common mistakes, by making which the patient puts his health at risk. Doctors categorically prohibit the following in case of illness:
- warming up the throat - the procedure is extremely dangerous, as it can contribute to the rapid spread of the inflammatory process, which is why there is a high probability of developing an abscess, phlegmon and sepsis;
- rubbing the throat area with vinegar or preparations containing alcohol is similar to warming;
- smoking during therapy - nicotine leads to serious damage to the mucous membrane, because of which, if you do not stop smoking, at least for the duration of the illness, treatment will be useless;
- the use of oil to treat the mucous membrane - by forming a film on its surface, oils only aggravate the condition, creating a favorable environment for pathogens;
- the use of alcohol infusions for gargling, since alcohol is a strong irritant to the throat, which will only further injure the mucous membrane;
- non-compliance with diet during treatment;
- self-medication.
Any violations in the treatment of the disease can lead to severe complications. If the patient does not comply with medical recommendations, then the specialist involved in treatment cannot guarantee a positive result.
Diagnostics
The cause of the pain syndrome is determined by the maxillofacial surgeon. According to indications, patients are examined by a neurologist, dermatologist, and other specialists. During the conversation, the doctor clarifies how long the pain has been bothering you, after which it appeared, how the disease developed, and what other symptoms were accompanied. During the examination, local changes are identified (hematomas, bruises, redness, swelling, the presence of infiltration), and the general condition is assessed for intoxication syndrome.
A dental examination is necessary if odontogenic pain is suspected. Helps to detect the causative tooth, alveolitis of the socket of an extracted tooth, etc. For superficial pyoderma, dermatoscopy is recommended to determine the depth of the lesion. To clarify the diagnosis, the following are prescribed:
- X-ray of the lower jaw.
It is a basic test for fractures and osteomyelitis. In the first case, the fracture line is visible on the photographs, the direction and degree of displacement of the fragments can be determined, and the optimal fixation option can be selected. In the second, radiographs show the corroded ends of fragments, areas of destruction, and sequestration. When using the technique, it is taken into account that radiological signs of osteomyelitis appear only a month after the onset of the disease. - Other visualization techniques
. Orthopantomography may be required in patients with stylohyoid syndrome and dental disease. For stylohyoid syndrome, MSCT of the temporal bone and radiography of the soft tissues of the neck are also performed to visualize the deformed styloid process and calcified ligament, ultrasound or contrast MR angiography to confirm compression of the arteries of the neck. - Microbiological research
. For superficial pyoderma, as a rule, it is not required. In other cases, the discharge or punctate is inoculated on nutrient media to determine the nature of the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics. In most cases, staphylococci are detected. - Other laboratory tests
. With purulent lesions, a general blood test reveals an increase in ESR, leukocytosis with a shift to the left. Patients with adenophlegmon and severe osteomyelitis require a comprehensive examination, including biochemical tests to assess the general condition of the body and blood culture for sterility to exclude sepsis.
Dental examination