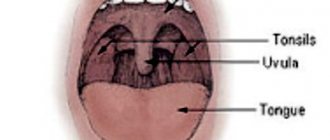
The term "tonsillitis" comes from the Latin name for the tonsils or tonsils. These are special paired rounded almond-shaped formations located on both sides between the palate and the root of the tongue, on the border of the oral cavity and pharynx. Their basis is lymphoid tissue; it is responsible for the maturation of lymphocytes (immunocompetent cells) and the development of an immune response with their help.
The palatine tonsils belong to the peripheral immune organs and, together with other tonsils, form the protective lymphopharyngeal ring of Pirogov-Waldeyer. Their task is to recognize and subsequently destroy pathogens and create an immune barrier at the level of the pharynx. Such protection works both against infectious agents penetrating from outside and against one’s own opportunistic flora.
In most cases, this process is asymptomatic. But sometimes it is not possible to quickly destroy the pathogens; they begin to multiply in the natural recesses (crypts and lacunae) of the tonsils and provoke inflammation. This condition is called tonsillitis.
There are 2 forms of the disease:
- Acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis, the duration of the disease usually does not exceed 10–14 days. The nature of the inflammation can be catarrhal, follicular or lacunar. After the pathogen is destroyed, all symptoms of the disease are leveled, and the tonsils are cleared and return to their previous state.
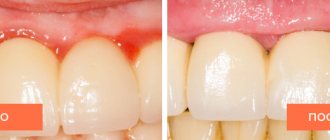
- Chronic tonsillitis, characterized by prolonged inflammation of the tonsils. The tonsils are enlarged, and a purulent-microbial (caseous) substrate is constantly preserved in their recesses.
Chronic form of tonsillitis, why the tonsils become inflamed
Infection is the main cause of inflammation of the tonsils. The acute form of the disease in 70% of cases is caused by viruses, the remaining 30% is caused by bacterial and fungal flora. Therefore, sore throats most often accompany acute respiratory infections and are seasonal.
Damage to the tonsils in chronic tonsillitis in 80% of cases is of a bacterial nature. The main causative agents of the disease:
- β-hemolytic streptococcus.
- Group A streptococcus.
- Staphylococcus aureus.
- Haemophilus influenzae.
- Rarely encountered bacteria: mycoplasma, chlamydia, etc.
Viruses in the chronic form of the disease have a predominantly provocative, destabilizing effect. Acute and chronic recurrent viral infections weaken the immune defense, which creates conditions for the activation of bacterial flora. Hypothermia, acute intoxication, and ingestion of cold or irritating food lead to the same result.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptoms of tonsillitis in children that require immediate treatment are:
- pain when swallowing and yawning;
- heat;
- general intoxication of the body (weakness, decreased appetite, headaches);
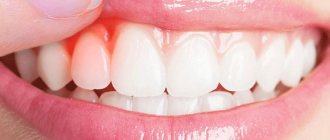
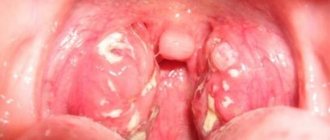
- swelling and redness of the tonsils;
- formation of whitish or yellowish plaque on the tonsils;
- blisters, sores on the throat;
- loss of voice, hoarseness;
- bad breath;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes (this sign can indicate not only tonsillitis, it accompanies many other diseases in children).
Features of the chronic form of the disease
Chronic inflammation of the tonsils can have several clinical variants:
- Latent form, when the patient does not experience significant discomfort in the throat and does not experience signs of exacerbation of the disease. Such people consider themselves healthy and are not aware of the dormant infectious-inflammatory focus in their throat.
- Periodically relapsing type of disease. Sluggish exacerbations and episodes of clearly defined inflammation of the tonsil itself, adjacent palatine arches and the pharyngeal wall are possible. Between periods of exacerbation, the inflammatory process subsides, but is not completely eliminated.
In chronic tonsillitis, the drainage and natural self-cleaning of crypts (folds) and lacunae (recesses) are disrupted in the tonsils; pus, living and dead bacteria, and toxins are constantly stored in their depths. This maintains constant inflammation, overstimulates sentinel immune cells, and provokes toxic-allergic reactions.
The immune response that forms during chronic tonsillitis is not sufficient to completely suppress the infectious process; it only restrains the activity of pathogens. Disruption of this delicate balance leads to exacerbation of the disease or triggers immune disorders.
Risk factors
The risk of developing chronic tonsillitis of the throat increases if the patient has a hereditary predisposition to the disease. About 3% of all recorded cases are transmission of the inflammatory process from parents to children. Also, the protracted course of infectious diseases is caused by formations in the nasal cavity, polyps and sinusitis. The source of infection can be a carious tooth, gum disease, or periodontitis. Additionally, the body is weakened by poor nutrition, bad habits, constant stressful situations, and prolonged use of potent drugs.
Why treat chronic tonsillitis?
Chronically inflamed tonsils become a constant source of infection. With a decrease in immunity, it can spread to other tonsils and peripharyngeal tissue, invade the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, and descend into the underlying parts of the respiratory tract.
But the inflammatory reaction of the tonsils is not the main problem of chronic tonsillitis. Constant irritation of the immune forces not only weakens the protective response, but also creates the preconditions for the occurrence of abnormal reactions. Antibodies appear in the body, which are initially produced against β-hemolytic streptococcus, but show aggression towards connective tissue.
This secondary pathology is called rheumatism or Sokolsky-Buyo disease. It is a systemic acquired disease with an autoimmune mechanism, with the favorite targets for antibodies being heart valves and the synovium of small joints.
The key focus of streptococcal infection and the site of primary formation of rheumatic autoantibodies is the inflamed tonsils. Therefore, competent treatment of chronic tonsillitis is an effective prevention of rheumatism and its complications.
Causes of tonsillitis development
The main factors that trigger the pathological process are:
- infectious diseases that the patient tried to cure with home and folk methods;
- frequent pharyngitis, which reduces the body’s immunity and causes inflammation of the throat mucosa;
- allergic reactions that weaken the body;
- dental diseases, treatment of which has been postponed indefinitely;
- low immunity after suffering serious illnesses or prolonged stressful situations;
- congenital pathologies of the structure of the respiratory tract, curvature of the nasal septum.
All of the listed causes of tonsillitis are summarized by one main factor – weakening of the immune system and deterioration of the body’s condition. Having lost the ability to resist infections, it becomes vulnerable to pathogenic microorganisms that cause prolonged colds and inflammation of the mucous membrane.
How to be treated correctly
Competent treatment of chronic tonsillitis includes a set of measures to eliminate infectious inflammation and deep sanitation (cleansing) of the tonsils. This is necessary to prevent relapses of the disease, suppress allergic and autoimmune processes, and restore the protective function of the pharyngeal lymphadenoid ring.
Common mistakes when treating tonsils:
- Only local medicine for sore throat is used, with the rejection of recommended systemic antibacterial therapy.
- The drug is selected by the patient independently, without taking into account the nature of inflammation, composition and sensitivity of the microflora.
- Drugs for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis are taken haphazardly, or instead of recommended medications, a folk remedy for the disease is used.
- Early cessation of treatment, therapy is completed soon after the sore throat subsides and other symptoms of exacerbation decrease.
- Avoidance of treatment between periods of exacerbation, refusal of proposed surgery.
- Late visit to the doctor, at the stage of complications.
This approach is the main reason for the protracted and complicated course of the disease and the formation of drug resistance in pathogens. Treatment of chronic tonsillitis in adults should be carried out comprehensively, under the supervision of a physician.
When to see a doctor
Frequent cases of sore throat, prolonged recovery from respiratory infections, and persistent cough are reasons to immediately seek help from an otolaryngologist. The specialist will not only conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of the body, but will also tell you how to quickly and without consequences cure chronic tonsillitis. For additional consultations and examinations, you can contact the doctors of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitber) in the central district of Moscow at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10 (metro stations Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya) . Experienced ENT doctors will offer an effective course of treatment for tonsillitis, taking into account the age and characteristics of the patient’s body. The selection of antibiotic drugs and physical therapy will be made based on the results of the examination and a history of diseases.
Treatment without surgery
Conservative treatment includes general and local drug therapy, physiotherapy, lavage of lacunae and other methods of cleansing the tonsils. Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, and immunomodulatory agents are prescribed.
Conservative therapy is widely used in modern otorhinolaryngology. But it does not always completely cure tonsillitis. The tonsils may remain enlarged even after drug suppression of the infection and deep cleansing; the risk of relapses and complications remains. In approximately 1/3 of patients, it becomes necessary to treat the disease surgically.
Treatment of tonsillitis in children
With properly selected medications, treatment of tonsillitis in a child takes about a week. The patient is prescribed bed rest, plenty of fluids and a gentle diet, excluding spicy and fatty foods. Medicines are selected according to the type of tonsillitis, accompanying symptoms, and the age of the child. Medicines should only be prescribed by a doctor.
The treatment program includes:
- painkillers;
- washing and rinsing;
- sprays and lozenges;
- physiotherapy. Source: T.V. Spichak Diagnosis and treatment of tonsillitis in children from the perspective of evidence-based medicine // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2010, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 130-135
Antibiotics are prescribed to children only in severe cases, as they cause side effects (abdominal pain, diarrhea, etc.).
Removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) is used in exceptional cases, if frequent relapses of the disease are observed, conservative treatment is ineffective, and complications from internal organs are identified.
In case of exacerbation of the chronic form of tonsillitis, the child requires bed rest, diet correction with the exception of fatty, fried, smoked, sweet foods, as well as drug therapy, which includes antibiotics, vitamins, desensitizing drugs, and immunomodulators.
Necessary:
- wash the lacunae of the palatine tonsils with antiseptics;
- treat the back wall of the pharynx and tonsils with solutions of fucorcin, Lugol;
- the child should regularly gargle with antiseptics and herbal decoctions.
You also need to do inhalations, use antiseptic aerosols, and take antimicrobial lozenges.
Physiotherapy may be prescribed :
- Ural Federal District;
- UHF;
- microwave;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- laser therapy.
Complications of the disease:
- descent of purulent infection into the heart sac;
- abscess;
- bleeding from the tonsils;
- eustacheitis;
- otitis;
- purulent inflammation;
- swelling of the larynx with the development of asphyxia, which can be fatal.
Operations for tonsillitis: from traditional methods to modern techniques
Indications for surgical treatment:
- The presence of episodes of exacerbation of the disease 2 or more times a year, with a predominance of purulent inflammation.
- Frequent (more than 4 times a year) exacerbations of tonsillitis, even if they occur without complications.
- Exacerbations are rare, but there are signs of complications from the heart, joints, kidneys or other organs.
- The disease is latent (hidden), but has become the cause of the development of rheumatism and other systemic diseases.
For a long time it was believed that chronically inflamed tonsils should be completely removed. This operation is called tonsillectomy. It allows you to eliminate the source of infection, but makes an uncorrectable hole in the protective lymphoid ring of the pharynx.
Currently, tonsillectomy is rarely performed, mainly in cases of severe purulent-destructive changes in the tonsils. In all other cases, ENT doctors give preference to organ-preserving operations, trying to leave an island of functionally active tonsil tissue.
But resection (partial cutting off of the tonsils) carries the risk of relapse of the disease. After all, such a procedure does not guarantee the elimination of all inflamed and infected tissue. The use of a laser improves the result due to an additional disinfecting and immunomodulating effect in the surgical area, but still does not completely solve the problem of relapses. Nevertheless, laser technologies are recognized as a priority in the treatment of tonsillitis.