Pain under the tongue can serve as one of the main symptoms of a whole range of problems, from banal mechanical injuries to a number of pathologies of the oral cavity, nervous system or internal organs. Depending on the cause and location of the pain, it can have a different nature and intensity.
If you or your loved one has pain under the tongue, there is no need to panic or self-medicate - this can only lead to aggravation of the situation. Contact a dentist at a dental clinic, he will conduct a diagnosis, determine the exact cause of the discomfort and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen to effectively eliminate the pain.
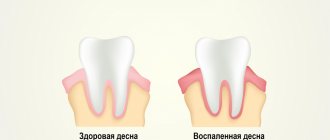
What is in the sublingual area
The tissues located on the lower jaw under the tongue are called the floor of the mouth. Due to the complexity of the structure, as well as the natural functionality of this area, a person often experiences problems accompanied by pain.
Structure of the sublingual region:
- Hyoid muscles - have an elastic structure and are responsible for the motor function of the area;
- Hyoid bone - has an anatomical shape in the form of a horseshoe, located in the muscle layer. It is the only bone in the human body that has no connections with other bones of the body;
- Nerve endings are elements of the peripheral nervous system, responsible for the sensitivity of the sublingual area to various physical, mechanical and thermal stimuli;
- Salivary glands - responsible for the production of saliva, which is involved in the process of wetting the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and the digestion process;
- Blood vessels - provide nutrition to the tissues of the sublingual area;
- Frenules are connecting folds in the sublingual area, responsible for connecting the sublingual tissues with the tongue.
Each of the above elements ensures the natural functionality of the dentofacial apparatus and participates in all physiological processes of the oral cavity.
If inflammation of the salivary gland begins
Our body is designed very thoughtfully. There is practically no process for which only one organ is responsible. Most of them complement and support each other's work. At the same time, a number of organs are responsible for one function at once, forming an entire system. For example, not just the stomach, but the entire digestive tract is responsible for digestion. Digestion of food begins from the moment it enters the mouth.
The salivary glands are responsible for the process of secreting saliva, which is so important for us. There are as many as three pairs of them in our mouth. Saliva is very important for digestion of food, normal swallowing and maintaining the alkaline balance in the mouth. The salivary glands can be susceptible to various diseases. Doctors consider the parotid gland to be the most vulnerable. Inflammation can also affect the sublingual and submandibular glands. Do not underestimate the danger of such inflammation. The inflammatory process in the tissues of the salivary glands is dangerous both due to its symptoms and severe complications. These can result from untimely or incorrect, delayed treatment.
Complications of inflammation of the salivary glands are extremely dangerous. It could be:
- Nephritis.
- Neuritis.
- Myocarditis.
- Meningitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Encephalitis.
This is why it is so important to start treatment as soon as possible. It must be intensive and systematic. Then the disease will pass quickly and without complications.
And it is best not to bring the salivary gland to a state of inflammation at all. Follow simple rules of prevention.
Often, inflammation of the salivary glands begins due to the closure of the excretory duct. There is simply a colossal amount of bacteria in our mouth. If the duct is closed and saliva is not excreted. Then these bacteria quickly penetrate inside the ducts themselves and infect them. A focus of the inflammatory process develops.
If you have undergone surgery in the oral cavity or have had severe flu, encephalitis, typhoid, or pneumonia, your risk of inflammation of the salivary glands increases. Be as attentive as possible to your health and consult a doctor at the first warning signs. In these diseases, the glands under the tongue are often involved in the inflammatory process. An important role is played by what pathogen led to the disease, as well as how it progresses. In this case, inflammation can be gangrenous, purulent, catarrhal.
Causes of pain under the tongue
Modern medicine knows dozens of different reasons that can cause unpleasant and painful sensations under the tongue in an adult, teenager and child: from a banal mechanical injury to the frenulum, leading to tissue damage, to allergic reactions causing swelling. At the same time, there is a list of the most common causes observed in most patients.
The main causes of pain under the tongue:
- Mechanical injuries to the frenulum and muscle tissue are the most common cause of sublingual pain. As a rule, it is observed in people with a short frenulum. It is injured due to stretching, as well as in the event of mechanical trauma to tissues, for example, during eating, hygienic brushing of teeth, etc.;
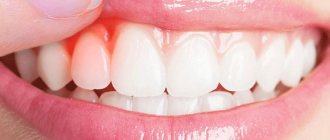
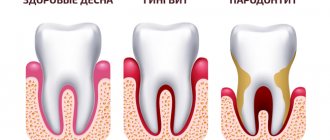
- Dental pathologies of the oral cavity – stomatitis, dental problems (caries, periodontitis, periodontitis), gumboil, etc.;
- Infectious inflammation of the oral cavity - pain often manifests itself with sore throat. During this period, it is painful for a person to eat, swallow water and saliva, stick out his tongue or simply chew;
- Cellulitis or abscess of the floor of the mouth is a significant accumulation of pus in a small area of the floor of the mouth. Causes “bursting” of internal tissues, putting pressure on peripheral nerves - this provokes pain and tactile discomfort;
- An allergic reaction can be the body’s response to various irritants. Causes swelling of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, accompanied by discomfort or pain in the sublingual area;
- Asymmetry of the hyoid bone - an anatomical disorder in the growth of the hyoid bone, can provoke excessive or nonspecific pressure on the peripheral nerves, causing pain;
- Neuralgia is a general disease of the nervous system that manifests itself in its various parts. It is often a consequence of nervous shock and is accompanied by a feeling of painful numbness in the oral cavity;
- Diseases of internal organs and body systems - some areas of the tongue may reflect (irradiate) pathologies of internal organs, which is accompanied by painful sensations in the sublingual area;
Note! Most of the above problems that provoke the development of pain in the sublingual area can be caused by bacterial infections (streptococci), fungi (candidiasis), and herpes.
Possible consequences
If the swelling is not eliminated in time, then negative consequences will not keep you waiting. They may appear as follows:
- chronic or acute respiratory dysfunction;
- violation of a person’s aesthetic appearance (almost constantly open mouth with tongue hanging out);
- psychological discomfort;
- speech distortion;
- malocclusion;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- copious amounts of saliva;
- tooth decay and loss.
Symptomatic features of pain under the tongue
Pain in the sublingual area can have various symptomatic manifestations. First of all, they are accompanied by different types of pain (sharp, aching, throbbing), as well as constancy or frequency.
If you consult a doctor, it is very important to correctly characterize the pain - this will allow the specialist to narrow down the range of symptoms for differential diagnosis. For example, you may have pain in the frenulum under your tongue or pain under your tongue on the right/left.
One of the characteristic manifestations of stomatitis or candidiasis is a white pimple under the tongue. Its presence may indicate the development of a fungal or bacterial process. If such a symptom is detected, treatment will include antifungal and antibacterial therapy with the prescription of antibiotics or special antiseptic rinses. The presence of pimples of a different color may indicate the presence of a wide range of problems, the identification of which requires a thorough diagnosis of the oral cavity or the entire body.
How inflammation develops
To prevent such inflammation, teach your child to follow simple hygiene standards. It is very important to brush your teeth regularly. If a child finds a wound in his mouth, it should be immediately treated with brilliant green or iodine. Invite your child to rinse his mouth thoroughly with a decoction of chamomile, calendula, sage, a weak solution of potassium permanganate or soda. All these products have an antibacterial effect. If swelling or painful redness appears, take your child to the doctor immediately. He will recommend how to proceed further. Don't risk your child's health and don't waste time on self-medication! Under no circumstances should this swelling be rubbed, iced, or heated. Because of this, the abscess can burst inside.
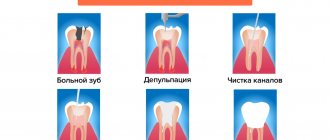
Features of diagnosis and treatment of pain under the tongue
Treatment of pain in the sublingual area should be carried out after a high-quality diagnosis to determine the root cause of the problem. Sometimes, pain in the frenulum under the tongue or in the surrounding tissues is treated by therapists or allergists, but in most cases this is done by dentists, because about 90% of all cases of treatment are associated with a dental problem.
Diagnosis of pain under the tongue is carried out in several stages:
- Initial appointment - the doctor collects anamnesis, finds out information about the nature and location of pain, and also examines the patient’s oral cavity;
- A complete diagnostic examination is carried out in the absence of characteristic symptoms of common dental diseases. It is possible to use hardware techniques (X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.);
- Differential diagnosis – a specialist differentiates the underlying pathology from similar diseases;
- Making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment - based on the data of the initial examination and diagnosis, the doctor establishes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes an adequate treatment regimen.
Note! The method of treatment and the choice of drugs to eliminate pain in the sublingual area directly depend on the root cause of the symptoms. For example, if your frenulum hurts due to a mechanical injury, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions for mouth rinsing will be prescribed, including: chlorophyllipt, hexoral, stomatophyte, alcohol tincture of calamus, stomatidine or others. If the pain is associated with the development of bacteria or fungi, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.
How to treat an abscess in children
To identify an abscess, a puncture is often performed. This will make it possible to find out which specific pathogen caused the abscess. Also, the doctor will immediately determine which antibiotic is most effective against it. Most often, treatment is surgical. The doctor opens the abscess, cleans it, treats it with antibacterial agents, prescribes antibiotics and other drugs. Physiological procedures support the treatment. For a superficial abscess, the doctor will administer anesthesia with novocaine. Once the autopsy is performed, treatment will be the same as for normal wounds.
As a result, we emphasize once again that it is easier to avoid such inflammation than to treat it later. Just don't forget about basic hygiene. Well, if symptoms of the disease appear, immediately go to the doctor.
HPV vaccinations
HPV vaccine
You can protect yourself from the formation of growths in the oral cavity by getting vaccinated against the papilloma virus. There are many different rumors around this vaccine, but they have no basis in terms of effectiveness.
The product contains substances of organic origin that promote the production of cells in the body that resist the development of condylomatosis.
Effective means are used for vaccination:
- Cervarix;
- Gardasil.
These vaccines are not used in the treatment process; they are intended solely for preventive purposes. The procedure must be performed before sexual activity begins; the maximum age of the patient is 26 years. When using the product at an older age, the effectiveness decreases significantly.
One vaccine protects the body from the papilloma virus for 8 years.
Do I need to follow a diet?
If any of the reasons listed above have been medically established as causing the appearance of a cosmetic defect, it would not be a bad idea to reconsider your own gastronomic preferences.
Each of these conditions requires at least a slight adjustment of the diet , especially if a person prefers to eat “junk” food. The adjustment is as follows:
- in increasing the volume of consumption of products of plant origin - vegetables, fruits, herbs in fresh, baked form, as well as in salads;
- excluding excessively fatty meat, spicy, salty and fried foods from the menu. When cooking food, you should choose baking, boiling or steaming;
- in regular consumption of sea fish and seafood, as the main source of saturated acids;
- in choosing pasta made from durum wheat or vegetables as a side dish for meat or fish dishes, depending on individual preferences;
- You can’t give up cereals; they are a source of vitamins and microelements. The most useful are buckwheat, oatmeal, and pearl barley;
- You should use olive or any other vegetable oil as a salad dressing. As an exception, it is allowed to consume homemade mayonnaise once a week for this purpose in limited quantities - no more than 30 ml.
Preventive measures
Use mouthwash after meals.
Preventing the development of a disease is always easier than fighting harmful microorganisms and the results of their vital activity. To prevent the formation of growths in the oral cavity, the following measures are recommended:
- perform hygienic cleaning of the mouth at least 2 times a day;
- after eating, use a mouthwash;
- develop a diet so that it contains mainly fresh vegetables and fruits (to strengthen the immune system);
- regularly visit the dentist for preventive examinations;
- do not borrow other people’s household items (dishes, towels, cosmetics);
- undergo an annual examination with an oncologist;
- lead an active lifestyle (if you work sedentarily, include morning exercises and twice-a-day workouts on simulators in your daily routine).
Removal methods
There are several ways to remove growths under the tongue. In each individual case, the specialist selects the best option, taking into account the localization of the formation and the extent of the affected area. Whatever method is used, it is complemented by antiviral therapy to prevent relapses. Only an integrated approach, including taking medications, will help get rid of the problem in the oral cavity.
| Treatment of growths under the tongue | |
| Method name | Process description |
| Surgical removal | An effective way to remove growth by cutting it off from soft tissue using surgical instruments: scalpel, scissors, electric knife, conchot. Sutures are subsequently placed on the wound. |
| Cryodestruction | The growths are removed using liquid nitrogen. The method copes with the task, but this type of influence can provoke malignancy of the formation, that is, have the opposite effect. |
| Laser removal | The essence of the method is to cut off the growth with a laser beam. The advantages of the method: quick and effective elimination of formations, absence of pain for the patient and bleeding, which prevents infection. The likelihood of relapse is very low; after the procedure, the process of cell regeneration is stimulated. |
| Radio wave therapy | The method is low-traumatic and painless; the procedure does not even require the use of a local anesthetic. Removal of growths occurs under the influence of high frequency radio waves. The specialist directs them to the base of the growth and cuts off the affected tissue. The rehabilitation period lasts 7-10 days. |
| Electrocoagulation | This method efficiently and quickly removes pedunculated growths on the tongue. The essence of the method is to throw a loop of special fiber over the formation and apply high-frequency current to the material. The hot fiber cuts off the growth, simultaneously soldering the microvessels, which prevents bleeding and infection of the wound. Electrocoagulation prevents further development of the virus. At the site of the removed growth, a crust forms, which after some time comes off on its own. |
| Galvanocaustics | The location of the small growth is cauterized with platinum wire heated under the influence of current. The method is fast, eliminating bleeding and infection of the wound. |