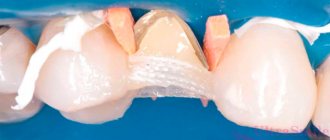
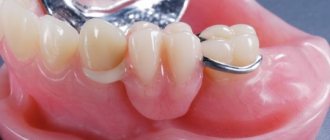
Common materials used to make veneers include photopolymer composites, porcelain, and zirconia. One of the most popular compositions is dental ceramics, used both in the creation of solid cast products and in the lining of metal frames. Ceramic veneers installed on the front teeth guarantee the restoration and preservation of smile aesthetics for a long time.
Dental ceramics are used to make feldspar veneers - a category of materials that combines various compositions based on quartz and feldspar. The main difference from porcelain used to create household products is the absence of kaolin, due to its vulnerability to coloring elements. The structure of the composition, as a rule, is a mixture of microcline and albite (feldspar) and quartz, in a ratio of 65/25%, as well as additional elements that ensure the strength of the finished microprostheses. Feldspathic ceramic veneers belong to the most affordable category in terms of cost, but their characteristics in most respects are not inferior to alternative models.
Indications
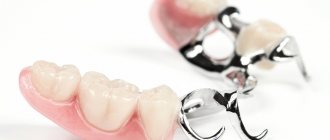
Ceramics are used to make aesthetic dentures with or without a metal frame. With its help you can make:
- thin veneers less than 0.6 mm thick and regular veneers (only made of glass ceramics);
- occlusal veneers;
- inlays and crowns;
- endocrowns;
- root posts (made of oxide ceramics);
- stump pin inlays (with a pin made of oxide ceramics);
- bridges supported on inlays (with a frame made of oxide ceramics);
- three-unit bridge-like dentures, as well as long-length bridges;
- dental implants (made of oxide ceramics);
- abutments;
- artificial teeth of removable dentures (made of glass ceramics);
- gingival part of conditionally removable and fixed dentures (glass ceramics).
E-max crowns: price 2022
How much does a ceramic crown cost per tooth in mid-price clinics? First of all, this will depend on which version of the E.max material the veneer or crown will be made from and, accordingly, what technology will be used (this can be either a pressing technique or CAD/CAM technology).
Ceramic crown for a tooth: price for 1 unit
- A crown made from Emax PRESS material will cost you an average of 21,000 rubles, and a veneer made from this material will cost you approximately 25,000 rubles. Moreover, most often when ordering 4 or 6 veneers at once, clinics give a discount of approximately 15-20%.
- A crown made of Emax CAD material will cost at least 30,000 rubles. 20,000 rubles.
Moreover, it should be taken into account that this cost usually does not include temporary crowns made of plastic (the cost of 1 temporary crown is additionally about 1500-2000 rubles). By the way, in the regions of Russia the price of the Emax PRESS ceramic crown will be slightly lower, for example, it can be about 18,000 rubles.
Contraindications to the use of ceramics
- Low-strength ceramics cannot be used under increased occlusal loads, including in patients with bruxism.
- It is prohibited to manufacture ceramic dental bridges if their bending strength is less than 350 MPa.
- Lithium disilicate ceramics are not suitable for the manufacture of bridges longer than three units.
- The material is also not used for deep subgingival preparations if adhesive fixation is required.
- It is contraindicated if the preparation depth is insufficient.
- It is not used if there is a need for subsequent non-destructive removal of the structure, with the exception of screw ones.
Classification of ceramics by level of transparency
The level of transparency of dental ceramics is indicated in Latin letters:
- HT (High Translucency) – high transparency;
- LT (Low Translucency) – low transparency;
- MO (Medium Opacity) – medium opacity;
- HO (High Opacity) – high opacity.
These four levels are typical only for glass ceramics. Oxide ceramics only meet the HO level. Zirconium oxide belongs to the MO level and does not correspond to the specified HT. The higher level of transparency of zirconium oxide is explained by a decrease in the porosity of the material. Less porous - scatters light less, acquires transparency and higher strength.
The choice of ceramics with a particular transparency depends on the type of denture and the color of the supporting tooth. Highly transparent ceramics are suitable for partial restorations and are not suitable for crowns due to the prospect of translucency of the dark oral cavity. Monolithic dentures are recommended to be made from HT and LT ceramics. To completely or partially cover the shade of the prepared tooth, HO and MO are used.
Advantages and disadvantages of ceramics in dentistry
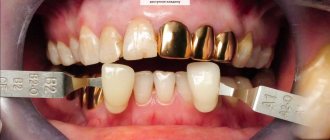
Ceramics make it possible to produce dentures that are almost impossible to distinguish from real teeth. In this indicator, it outperforms amalgams and metal alloys, unlike which it also has low thermal conductivity. It can be used to make dentures for vital teeth. Such designs do not have the disadvantages of metal dentures, however, prices for metal-free crowns are always higher. In addition, ceramics are more fragile than metal, and therefore require careful handling during preparation and do not tolerate sharp transitions.
Composite materials are in no way inferior to ceramics, but they have an undeniable advantage. It is more durable and has increased biocompatibility, since it does not contain organic components. Ceramic materials have record color and wear resistance, as well as bending strength, but they are more fragile than composites. Therefore, some authors recommend choosing composite materials for implant-supported prostheses.
Among the obvious disadvantages of ceramics is low repairability, especially in the oral cavity.
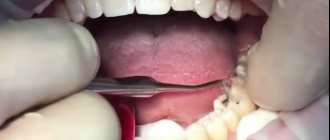
Tooth preparation
Treatment of the base prior to installation of the structure includes a number of sequential procedures:
- Initial examination, during which the condition of the dentition and root area is assessed, and a treatment plan is formed;
- Professional cleaning and selection of shade of the workpiece;
- Preparation of the unit on which installation is planned.
The development of technology makes it possible to carry out the process of grinding teeth using non-contact methods - for this, laser, ultrasound or air-abrasive treatment are used (not always used, if possible).
Manufacturing stages
To create veneers, a technique is used to bake several layers of ceramic material. The mixture is applied to a stamp or foil, in which a model is wrapped, replicating the anatomical structure of the tooth. Condensation of the product is carried out using grooved tools to remove excess moisture. After applying the enamel coating, re-firing is performed.
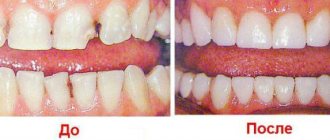
The finished onlay fully matches the shade of a natural tooth and is resistant to dyes and mechanical stress. Veneers are fixed using an adhesive that penetrates into the structure of the base.
Service life and cost
The service life of ceramic linings is at least ten years, and largely depends on operating conditions. Compliance with basic hygiene procedures allows you to extend the life of veneers and preserve their aesthetic properties. The cost of the service is determined by the complexity of the technology, and varies from 25 thousand rubles per unit.
Application of fireclay clay
To finish the external surface of buildings, fireclay made from white clay is used. To acquire the quality of heat resistance, the clay is thermally treated. After heating, kaolin becomes stone, it is crushed to produce fireclay clay, which is used for the manufacture of any heat-resistant construction and the production of refractory bricks and various decorative products. Note that there are several compositions for the production of fireclay mass; the components are taken in different percentages of water and mass; in one version, coarsely ground powder is used, in the other, finely ground. The addition of calcined powder differs in different mixtures. All compositions are selected in accordance with the requirements of the characteristics of the declared technological maps.
Hybrid ceramic options
Other, “intermediate” versions of ceramics are also used in dentistry. For example, glass infiltrated ceramics are a sintered porous oxide variety impregnated with special glass after milling the frame. In this technology, scientists tried to combine the strength of oxide ceramics and the transparency of glass ceramics, but they failed to achieve good results. Therefore, only frame parts are made from this material.
Recently, new hybrid materials have appeared - composite blocks containing an organic matrix, for example Lava Ultimate (3M Espe) or Enamic (Vita). They cannot be fired in a kiln and have nothing in common with ceramics.
History of appearance
The history of dental ceramics goes back more than 200 years.
The first researchers to study the possibility of using porcelain as teeth and to leave their mark on the documents were the Frenchman Alexis Duchateau and the Italian Nicholas De Chemant. In 1774, they tried to make artificial teeth from traditional green porcelain.
The first dental ceramics that vaguely resembled natural teeth in color was produced by Elias Wildman. This happened in 1838.
Is it correct to call amorphous ceramics glass ceramics?
Due to the presence of the glass phase, this type of ceramic is often called glass ceramic, which is not entirely true. Glass ceramics, or glass ceramic, is a material made by directed crystallization of glass. Sitall is a term that combines “silicate” and “crystal”. The process of formation of crystals into a glass phase is called sitallization. In dentistry, instead of “ceramic glass” they say “glass ceramics”.
Factors Affecting Porcelain
Factors affecting porcelain:
- chemical composition of components;
- the degree of their grinding (dispersity);
- temperature, firing duration.
Ceramic mass
Preparation is done in different ways: semi-dry, or dry, or wet, depending on the composition of the mass. Preparation is carried out by mixing the prepared enriched raw materials with water. Depending on the volume of water added (for a specific process), the desired consistency is achieved. The quality of the product depends on the quality of the ceramic mass, so the mass must meet certain requirements: technological (no foreign inclusions, impurities), physical (strength), biological (no toxins and allergens), aesthetic (beautiful, transparent, color-fast).
Features of the technology.
The manufacturing technology of products comes down to four main operations: FORMING, DRYING, DECORATING, FIRMING.
MOLDING. Products are obtained from masses by plastic molding, slip casting, and pressing. The first option includes modeling, stuffing, rolling on machines with a template, and stretching on a potter's wheel. If the mass is well suited for a particular molding method, it is usually called: “pottery clay”, “clay for modeling”, “fireclay for stuffing”. However, almost any mass can be molded in any way if the molder has sufficient experience. Many masses can be adjusted in composition. For example, to improve plasticity, you can add 3-10% lump clay, to reduce deformation and improve drying properties - fireclay chips.
DRYING. Responsible operation. The main requirement for drying is uniformity. Those. All areas of the product should dry at the same speed. If necessary, quick-drying thin edges should be isolated from air flows (cover with rags, polyethylene). The faster the drying, the less shrinkage. The thicker the walls of the product, the longer they will dry: if 1 cm dries in 2 days, then 2 cm dries in 4 days, and 3 cm dries in 9 days. Large, heavy items need to be dried on dryers.
DECORATION. Ceramic paints, glazes, etc. are applied to the dry (or scrap) product. decorating materials. See relevant sections.
BURNING. The raw product is fired 5-20 hours in advance, usually 8-12 hours before the maximum temperature. It is important that the start of firing is slow enough to avoid the product exploding from the released water vapor. A good start is up to 200 degrees in 2-3 hours. Next, the usual heating rate is 1-3 degrees per minute to the final temperature.
Reviews
The use of dental ceramics allows dental laboratory specialists to create dentures whose appearance is as close as possible to the natural elements of the jaw row.
Thanks to the improved composition, these products are only slightly inferior in strength to metal structures.
Sources:
- https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnyie-p/naznachenie-stomatologicheskoy-keramiki.html
- https://stomatology.su/stomatologicheskaya-keramika.html
- https://ppt-online.org/554131
- https://ppt-online.org/380042
- https://stomatology.su/klassifikaciya-stomatologicheskoy-keramiki.html
- https://stomweb.ru/articles/keramicheskie-materialy-v
- https://zubovv.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnyie-p/stomatologicheskaya-keramika.html
What types of clays are there?
Nature surprises us with its diversity. They exist in different quantities: gray, white, red, yellow, green, blue, dark blue, black clay. The variety of colors is explained by the fact that in different clay deposits, certain minerals are present, which give the rocks different colors.
For example, the color of red clay is explained by the presence of an admixture of hematite (a compound of iron and copper); white clay contains kaolinite; blue – cobalt and cadmium salts; yellow – sodium compounds; black color, iron substances and carbon compounds are present.
The demand for all types of clay (construction, ceramic, fired, powder, abrasive, refractory, natural red, fireclay) is explained by physical and chemical properties:
- good ductility, porosity, swelling, shrinkage (air and fire), fire resistance, dispersibility;
- property of water resistance, stable water insulator is actively used in construction and landscape design.
Types of ceramic masses
There are natural ceramic masses, consisting of one rock, and artificial ones, which are obtained by mixing different types. Regardless of what kind of ceramic mass is being prepared (natural or artificial), mandatory preparation is required: crushing, mixing, moistening.
Depending on the location of the formation deposits, clay has different physical and chemical characteristics and the color is determined by the presence of the corresponding components. The use of a specific color of the starting material determines the color of the ceramic mass.