Update date: 01/13/2021 15:33:37 8224 Share:
Author: Maria Feldshtein
*Review of the best according to the editors of simplerule.ru. About the selection criteria. This material is subjective in nature, does not constitute advertising and does not serve as a purchase guide. Before purchasing, consultation with a specialist is required.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used in the treatment of acute and chronic pain of various origins. They differ in composition and potency - and you need to know which drug will be more relevant in a particular clinical situation. In this article we will consider two remedies - Ketanov and Nise. We'll tell you how they differ and what nuances you should pay attention to.
| The drug and its characteristics | Nise | Ketanov |
| Pharmacological group | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) |
| Active substance | Nimesulide | Ketorolac tromethamine |
| Release form | Tablets and dispersible tablets, granules for oral suspension, gel and spray | Film-coated tablets, solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration, |
| Manufacturer | Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. (India) | SC Terapia SA (Romania) |
| Price | 150-400 rub. | 60-200 rub. |
The drugs are dispensed at the pharmacy with a prescription.
Indications for use
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used where it is necessary to relieve pain, remove inflammation and thereby alleviate the patient’s condition. They do not treat the disease - they do not eliminate its cause, but they influence the mechanisms of its development and reduce the severity of symptoms.
For the drug Ketanov, the instructions indicate that it can be used for pain of varying intensity and origin:
- condition after surgery and injury;
- toothache;
- muscle and joint pain;
- neuralgia;
- rheumatic diseases;
- pain due to malignant tumors.
Nise is used primarily for diseases of the musculoskeletal system. It relieves pain from injuries and inflammation of the joints, including those associated with rheumatic diseases, and alleviates the condition of osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome. Can be used in the postoperative period.
Possible causes of acute toothache
It is worth remembering the most common reasons:
- Caries. Bacteria destroy the surface of the tooth, resulting in a tooth reaction and discomfort when eating, eating sweets, or cold foods.
- Pulpitis. This is an inflammatory process that appears due to the fact that the patient did not treat caries in time. Pulpitis provokes acute toothache, which intensifies when drinking hot, cold drinks or food.
- Periodontitis. This is inflammation that occurs as a result of infection. Toothache has a pulsating form. It intensifies when mechanical stress is applied to the tooth.
- Periostitis. This is a special inflammation, it is accompanied by swelling of the gums. Afterwards, swelling and pain increase. Sometimes with periostitis, the upper jaw swells and the temperature rises. A pulsating toothache can be felt in the ears, eyes, and temples.
How do drugs work?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs work according to the same scheme:
- They block the production of the COX-2 enzyme.
- Slow down the production of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues - modulators of pain sensitivity, inflammation and temperature regulation.
- Prevents the development and progression of the inflammatory process, relieves pain and reduces high body temperature.
Ketorolac in the drug Ketanov is one of the most powerful analgesics. In terms of potency, it is comparable to morphine and superior to other NSAIDs. At the same time, the drug compares favorably with narcotic analgesics (including morphine) - it does not affect opioid receptors, does not depress breathing, does not cause drowsiness, drug dependence and addiction.
Nimesuldide (Nise) is a weaker drug - and unlike Ketanov, it is not prescribed where it is necessary to relieve really severe pain (after surgery, for cancer). But it has other advantages:
- It blocks the production of histamine, which makes it possible to recommend nimesulide to patients with bronchial asthma (many NSAIDs are prohibited for this disease).
- Has antioxidant activity against free radicals.
- It has a targeted effect on joint tissue. The analgesic effect of nimesulide is comparable to the gold standard - diclofenac.
Description of Ketanov
The drug Ketanov is included in the list of NSAIDs, derivatives of acetic acid. It is available in tablets, solution, gel, and ophthalmic drops. In terms of pain relief, the drug is comparable to morphine, but is not addictive and does not have a hypnotic or sedative effect. Manufactured by Ranbaxy in India and SC Terapia SA in Romania.
Research and effectiveness
The potent drug Ketanov is used to relieve pain in oncology. It copes with moderate pain that occurs as a result of tumor metastasis and bone damage.
An hourly dose of Ketanov can relieve pain and improve the quality of life of patients with malignant neoplasms. The advantage of the drug is that it does not cause dependence or addiction. This is an alternative to narcotic analgesics.
Side effects of Ketanov are insignificant and incomparable with its positive effect. It can be used as an independent remedy for severe pain.
Source: “Ketanov in the treatment of chronic pain syndrome in cancer patients.” Isakova M.E. RMJ. 2011.
Contraindications
Ketanov has many serious contraindications for use:
- up to 16 years old;
- intolerance to components in the composition;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- peptic ulcer;
- before and after surgery;
- insufficiency of kidney and/or liver function;
- chronic pain;
- hemorrhage in the brain.
The medicine is used with caution for diseases of the heart, stomach, and respiratory system. Elderly patients may require dose adjustment.
Side effects
Possible undesirable symptoms from taking Ketanov include:
- gastralgia, loose stools, increased gas formation, abdominal pain, cramps;
- hearing and vision impairment;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- increase or decrease in the volume of urine excreted;
- drowsiness, poor sleep, cramps, muscle rigidity, hyperactivity, headache;
- difficulty breathing, laryngeal edema, bronchospasm, dyspnea;
- swelling, increased sweating, fever.
The risk of developing side symptoms increases with prolonged use of the drug and the presence of contraindications. The medicine must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable.
Dosage
Tablets are taken 10 mg 4 times. The dose per day should not be more than 40 mg. The solution is administered intramuscularly 10-30 ml depending on age. Course – 5 days.
If the recommended dosage is increased, symptoms such as nausea and vomiting are observed. There is a risk of peptic ulcers and gastritis, as well as metabolic acidosis and renal failure. In this case, gastric lavage is performed, enterosorbent is prescribed, and drinking plenty of fluids.
Who is it suitable for?
A potent analgesic is used for pain relief for injuries, dislocations, and fractures. Indications for use are also sciatica and osteoarthritis.
Assessing the effectiveness of drugs
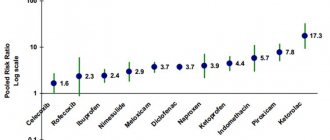
In 2013, the Russian Medical Journal published a review article highlighting the possibilities of using various NSAIDs in medical practice. In a number of studies, scientists compared nimesulide and ketorolac (as one of the most powerful drugs). Studies have shown that both drugs provide reliable relief of pain in various situations, including joint and toothache. According to many authors, the combined use of drugs is allowed: first, the strong NSAID ketorolac is prescribed, and after the condition improves, nimesulide is prescribed.
Application diagram
General rules for the use of NSAIDs:
- They are prescribed only in a short course – for 3-7 days. Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs increases the risk of adverse reactions.
- The effect of using the drug should be noticeable immediately - within 30-60 minutes (depending on the chosen product). A noticeable improvement in the condition is usually observed 2-3 days after the start of therapy. If there is no effect, you need to reconsider the treatment regimen.
- NSAIDs for oral administration are prescribed after meals. You need to take the tablets with plenty of water.
- For diseases of the digestive tract, NSAIDs are prescribed together with drugs that protect the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines.
- Nise is prescribed orally 1-2 times a day. The maximum daily dose for adults is 200 mg. For diseases of the joints and spine, Nise is used externally - in the form of a gel. Apply the drug in a thin layer to the affected surface 2 times a day.
- Ketanov is prescribed orally or parenterally. In the acute stage, with severe pain, treatment begins with ketorolac intravenously or intramuscularly. Next, the patient is transferred to tablets.
Description of Nise
NSAIDs Nise is available in the form of tablets and gel. It contains nimesulide. The medicine has an anti-inflammatory effect, reduces pain, and lowers temperature. Widely used in dentistry and other branches of medicine. Manufactured by Dr. Reddy's Laboratories in India.
The drug is used as a symptomatic drug to reduce pain and reduce inflammation. It does not affect the course of the underlying disease. Can be used once for mild to moderate pain.
Research and effectiveness
The drug Nise shows clinical effectiveness and safety in studies. There is a low percentage of adverse reactions and good tolerability in elderly patients.
Nise can be rationally used in neurological and general therapeutic practice to relieve pain. The average effective dosage for adults is 200 mg/day. The drug can be used for long-term therapy according to indications.
Risk factors when taking Nise are old age, peptic ulcer disease, combination with other NSAIDs, heart failure. In such cases, the risk of developing gastroenterological complications increases.
Source: “Possibilities of using the drug Nise in clinical practice.” Shavlovskaya O.A. RMJ. 2013.
Contraindications
The medicine Nise has many restrictions on its use. It is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the composition, under 18 years of age, during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Other contraindications:
- blood clotting disorder;
- alcohol addiction;
- insufficiency of myocardial function;
- gastrointestinal ulcer;
- Crohn's disease, irritable bowel syndrome;
- addiction;
- any active liver disease;
- simultaneously with hepatotoxic drugs;
- hyperkalemia;
- pregnancy and lactation.
Nise is used with caution for any diseases of the cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract. The substance is excreted primarily by the liver, so liver diseases will also be a limitation. Dose adjustment may be required in older age and in patients with kidney disease.
Side effects
Nimesulide is well tolerated in short-term treatment. The risk of adverse reactions increases with long-term use of the drug and when there are risk factors such as peptic ulcers, heart disease, and intolerance to the components in the composition.
Taking Nise may be accompanied by the following side symptoms:
- hypersensitivity reactions, anaphylaxis;
- increased sweating, dermatitis, erythema, urticaria, swelling;
- jaundice, cholestasis, hepatitis;
- exacerbation of asthma, shortness of breath;
- blurred vision;
- minor subcutaneous hemorrhages;
- hematuria, urinary retention, oliguria, nephritis, renal failure;
- eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia, purpura, pancytopenia;
- nervousness, nightmares, drowsiness, fear, headache, encephalopathy;
- arterial hypertension, hot flashes, tachycardia, hemorrhages;
- hypothermia, weakness.
Drug interactions must be taken into account. Simultaneous use with anticoagulants enhances their effect. Nimesulide reduces the diuretic effect of furosemide.
Dosage
The drug is taken after meals. It is recommended to use it in a short course. After 12 years and adults, 1 tablet 2 times is recommended. The maximum dose is 200 mg. For kidney disease, the dosage is reduced to 100 mg per day.
If you take a high dose of the drug, the side effects will increase. In case of overdose, drowsiness, vomiting, nausea, and apathy occur. Adverse symptoms are reversible and often do not require discontinuation of the medication.
As the dose increases, gastric bleeding, increased blood pressure, and breathing problems are also possible. In this case, you need to seek medical help. The victim is given gastric lavage, enterosorbents and symptomatic medications are prescribed.
Who is it suitable for?
The painkiller Nise can be taken for the following conditions:
- rheumatic diseases;
- psoriasis;
- osteoarthritis;
- myalgia;
- articular syndrome;
- dentalgia;
- inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Nise can be taken once for headaches, toothaches, and sprained muscles and ligaments. When long-term use of the product is required, you need to consult a doctor.
Adverse reactions
Adverse reactions are similar for all NSAIDs, but there are differences related to the strength of the particular drug.
Nise
most often causes the following symptoms:
- dizziness, nervousness;
- skin itching;
- swelling;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- dyspnea;
- arterial hypertension;
- tachycardia;
- allergic reactions.
Adverse reactions when taking Ketanov
:
- abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, nausea, flatulence;
- erosive and ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract;
- edema of renal origin;
- increased blood pressure;
- bronchospasm;
- ringing in the ears, hearing loss, visual impairment;
- skin rash;
- allergic reactions.
Contraindications
Ketanov and Nise have common contraindications. They are not prescribed when the following conditions are detected:
- a combination of bronchial asthma, nasal polyposis, intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs - there is a risk of developing a reaction to ketorolac or nimesulide;
- erosions and ulcers of the stomach and duodenum in the acute stage;
- gastrointestinal and other bleeding, as well as a high risk of their development;
- intestinal inflammation in the acute stage;
- liver failure and liver disease in the acute stage;
- severe kidney disease, including renal failure;
- bleeding disorders;
- pregnancy and lactation period.
Ketanov does not apply:
- for the treatment of chronic pain;
- as a means of premedication before and during surgical operations due to the high risk of bleeding;
- for pain relief during childbirth.