Facial neuritis - symptoms and treatment
Neuritis (neuropathy) is a disease of the nervous system, manifested in dysfunction of a nerve or a certain group of nerves.
In recent years, the Greek word “pathos”, which means “suffering”, has been used to denote syndromes of damage to the peripheral nervous system, and previously used terms, for example, “neuritis”, have been replaced by “neuropathy”, “sciatica” by “radiculopathy”, etc. d. If several nerves are inflamed, then it is polyneuropathy, if one nerve is inflamed, then it is mononeuritis. When the cause of inflammation of the nerves is, for example, diabetes, we talk about diabetic polyneuropathy, [1] and if there is an infection, then about infectious polyneuropathy (for example, herpes, diphtheria, etc.); [2] if the factor is hereditary, then it is hereditary polyneuropathy; if associated with a nutritional disorder, for example, alcohol abuse, then alcoholic polyneuropathy; if polyneuropathy appears against the background of reduced immunity, then it is idiopathic polyneuropathy, etc. [3]
Many types of peripheral neuropathy are often caused by exposure to toxic chemicals, malnutrition, injury and nerve compression, and also occur as a result of certain medications, such as those used to treat cancer and HIV/AIDS. [4]
As an example, consider such a common type of neuritis as neuritis of the facial nerve, also called Bell's palsy, the incidence of which is 23 people per 100 thousand, in all age groups, regardless of gender. The average age of patients is 40 years.
Most often, facial paralysis occurs as a result of local hypothermia. The source of infection is often chronic processes in the mouth, throat, and ear. In acute otitis media, nerve damage is caused by perineural edema of vascular origin. But more often, facial paralysis is caused by the herpes zoster virus in the area of the external auditory canal and eardrum. [5]
Facial neuritis develops as a result of:
- tumor processes in the cerebellopontine angle and posterior cranial fossa, temporal bone, parotid gland;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- acute, chronic otitis, mastoiditis;
- infections - syphilis, tuberculosis, Lyme disease, HIV infections, malaria, diphtheria, typhus, etc.;
- sarcoidosis, collagenosis, amyloidosis;
- Guillain–Barré syndrome;
- multiple sclerosis and many other diseases.
- Sometimes the development of neuropathy of the facial nerve is observed during pregnancy against the background of nephropathy.[6]
Indications and contraindications
A course of massage therapy for facial neuralgia is prescribed in the following cases:
– for neuritis caused by infection;
– after surgical removal of tumors compressing the facial nerve;
– after rehabilitation of acute purulent inflammation of the middle ear.
Before removing the cause of neuritis (tumor, inflammation), massaging the paresis is contraindicated.
Method of treating facial neuralgia using massage
The course of treatment is divided into three stages, established in accordance with the objectives.
- At the first stage (first 7 days) of the disease, when movement in the affected half of the face is absent or weakly expressed, attention is paid only to the healthy side. The patient is taught to relax the muscles at rest, after speaking, and then during speech. In addition, the amplitude of facial expressions of the unaffected half is limited.
- At the second stage, when muscle activity appears, attention is paid to the affected side, limiting the activity of healthy muscles.
- The third stage is characterized by residual effects in the form of muscle weakness and insufficient motor coordination.
Since nerve functions return unevenly, movements are not restored at the same time. In some cases, the lower half begins to function first, in others – the upper. Uneven recovery is fraught with the occurrence of contractures, so it is not recommended to force events with the help of massage and exercises.
Therapeutic gymnastics for facial muscles
When performing exercises with facial muscles, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Exercises are performed in front of a mirror. Before each exercise, relax the facial muscles, especially on the healthy side. It is not allowed to perform gymnastics only on the affected half, as this may impair general motor coordination.
- It is necessary to make symmetrical movements. The range of motion of the half of the face not affected by neuralgia is limited by holding it with the hand.
- The affected half of the exercise is performed passively, helping with one hand. When motor functions appear, the effect increases. As they are restored and activated, the same exercises are performed, creating resistance with the hand.
- Exercises for facial expressions are repeated 4–5 times with breaks, for eyes – 2–3 times. Gymnastics are performed 2-3 times daily.
- In the absence of full facial expressions, muscle movements of the healthy side are limited in order to mask the defect.
In case of complications of the disease, at the first signs of synkinesis (friendly movements), massage is limited, excluding physical activity for 3-5 days.
- To treat residual effects (severe contracture, synkinesis), before the massage session, a thermal procedure is performed using Sollux, paraffin, and poultices. Massaging should be stroking and rubbing.
- Kneading and vibration movements are contraindicated. When fixing the correct position, bandages with adhesives are used.
Duration of treatment
Massage procedures are carried out every day for 14–21 days, achieving complete recovery. The procedure lasts from 5 to 12 minutes.
If the expected effect is not achieved, massage sessions are suspended for 8–10 days, after which a new course of 25–30 procedures is established. Therapeutic gymnastics are performed at the same time.
Massage is combined with all types of medicinal and physiological therapy (electrophoresis, electrical stimulation using galvanic or exponential current, electroUHF, diathermogalvanization, darsonvalization, inductothermy, as well as applications with therapeutic mud, paraffin and mountain wax). Ultrasound treatment is carried out on the day of therapeutic exercises, alternating with the day of massage.
Features of massage for other diseases of the facial nerve
Properly selected manipulations, taking into account indications and contraindications, help:
- improve local blood circulation;
- eliminate muscle spasms;
- will restore facial activity;
- correct speech defects that have arisen under the influence of pathology.
The speed of obtaining therapeutic results depends on timely seeking medical help.
Facial nerve paresis
To solve the problem, experts use rubbing in the form of semicircles with constant stroking. Vibration and ultrasonic therapy methods show good effectiveness for paresis.
Neuralgia of the facial nerve
Requires separate techniques:
- stroking the face and back of the head;
- rubbing the shoulders, neck until the dermis becomes slightly red;
- small vibrating movements in the area of the cheekbones and forehead;
- weak effect on the skin of the nose, eyebrows, nasolabial triangle.
Important! A professional massage therapist will be able to enhance metabolic processes, blood circulation in the problem area, and accelerate the removal of decay products.
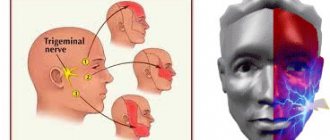
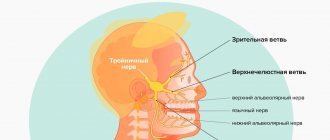
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
The pathology requires treatment of the facial, head, and cervical-collar areas. Massage of the trigeminal nerve on the face and these areas leads to:
- normalization of blood circulation;
- lymph outflow;
- stable nutrition of tissues.
The course is conducted with the utmost care. If the rules are violated, a new attack is possible due to the impact of trigger areas.
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Symptoms
The following symptoms of inflammation of the facial nerve are distinguished:
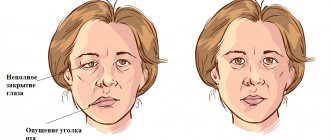
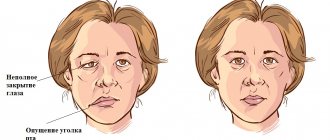
- partial or complete impairment of facial muscle movements;
- the corner of the mouth lowers, the nasolabial fold on one side is smoothed out;
- the face becomes asymmetrical;
- the eyelid does not close completely;
- the eyeball protrudes and turns upward;
- pain in the ear, taste disorder;
- watery or dry eyes;
- hearing loss or sensitivity to loud sounds;
- the patient cannot whistle or stretch out his lips with a straw.
How effective is massage?
Regular, properly performed massage is an effective remedy for restoring facial activity. However, each patient's nervous system reacts to it differently: some patients have an almost instantaneous response, while others have a delayed reaction.
Depending on the severity of pain and the severity of nerve damage, the massage therapist adjusts the massage parameters:
- Impact force;
- Speed;
- Duration of the session.
The longer the massage is done, the greater the effect it will have.
Main indications for massage treatment
Timely massage for neuritis is a very effective procedure. Combined treatment with massage and medications helps restore lost muscle function in a shorter time than using drug therapy alone.
Massage treatment should begin no earlier than 7-14 days after the first symptoms of the disease appear. The main indications for the treatment of facial nerve neuritis with massage are:
- inflammatory process in the nerve of an infectious or toxic nature;
- mechanical nerve injury;
- impaired motor function of the facial muscles in the postoperative period.
Massage should be used with caution in case of concomitant purulent diseases of the ENT organs. Massage movements improve blood flow in facial tissues, which can contribute to the spread of infection. Therefore, the procedure is carried out only as prescribed by the attending physician.
Massage techniques
For neuritis, several massage techniques are used, as well as a set of special exercises. Regardless of the chosen technique, the main movements are performed in the directions of the massage lines. The use of amplification techniques, as well as tapping and effleurage, is prohibited.
Segmental
Carrying out segmental massage aims not only to strengthen facial muscles, but also to relieve swelling and congestion in the nerve canal, as well as improve the conductivity and excitability of nerve endings. The massage technique for neuritis includes several techniques:
- vibrating soft movements;
- light stroking massage with fingertips;
- trituration;
- stroking.
All movements of the massage therapist should be light, without pressure. If there are no concomitant inflammatory diseases, then additional use of a vibrating massager is possible.
A segmental massage session for the treatment of neuritis begins with massaging the forehead. The forehead is stroked with an open palm from the central point to the temples, after which it is carried out with light rubbing. Vertical strokes are carried out from the eyebrows to the hairline. After stroking, apply light pressure with your fingers from the central point to the temples. Then they repeat the strokes and move on to vibrational patting of the entire surface of the forehead.
After the forehead, massage the area around the eyes. Using your fingers, they pass from the outer corner of the eye along the lower edge to the inner one. Use the middle and index fingers to lightly touch the upper eyelid. Then, with pointed circular movements, massage the outer edge of the eye socket, the lower edge towards the inner corner of the eye and the area above the eyebrows.
Move on to massaging the lower jaw, nose and lips. Usually the massage begins with the healthy half of the face, and gradually moves to the affected half. Techniques for this area are carried out using the index and middle finger along lines from the middle of the chin to the wings of the nose, along the sides of the nose to the bridge of the nose, along the back of the nose to its tip. Sequence of techniques:
- horizontal rubbing;
- vertical rubbing;
- point pressure;
- light point pressure;
- stroking;
- pincer-like stroking.
Finish the session by massaging the cheeks. The entire area is stroked with the palm of the hand, then rubbed linearly. Next they do:
- circular acupressure;
- forceps massage;
- zigzag stroking;
- point pressure with fingertips;
- tingling;
- light patting;
- horizontal active stroking.
All techniques alternate with soft relaxing strokes. The use of segmental massage in the treatment of neuritis requires a gradual increase in the load on the muscles. The first introductory sessions are always carried out in a gentle mode, selecting the optimal force of influence.
Spot
Acupressure facial massage is a simple but effective technique that is also suitable for independent use. The technique uses the impact of the surface of the fingers on biologically active points on the body, which are the projection of organs and systems. For neuritis of the facial nerve, massage is performed at the following points:
- between the eyebrows. The point is massaged for several minutes for pain, fatigue, or decreased concentration;
- below the inner edge of the eyebrows. The area is massaged to relieve nasal congestion, nerve pain and improve vision;
- above the corners of the lips. The points are massaged to relieve symptoms of stress;
- on the back of the neck along the spine. Massaging the points helps eliminate the symptoms of nerve inflammation, get rid of headaches, eye pain, and migraines;
- 2 cm above the auricle. Massage of the point relieves headaches and helps with neuritis of the auricular nerve.
After the massage, it is recommended to rest for a few minutes and do 2-4 breathing exercises . Do not perform acupressure if you have high blood pressure or chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Self-massage
At home, self-massage of the face is carried out using the classical method. Facial massage consists of several basic techniques:
- circling with fingertips;
- circling with fingertips;
- tingling.
All techniques are performed first on the muscles of the healthy half of the face.
The session begins with pinching at the base of the nose, gradually moving along the eyebrow line to the temples. Then pinching passes along the lower jaw from the midpoint of the chin to the bottom of the ears. Next, the face is massaged in circular movements with minimal pressure. Massage techniques affect the side of the nose, forehead, hairline area, temples, and chin. Then intense circular movements are made through the cheekbones to the temples. With slight reinforcement, they pass along the sides of the nose to the lower edge of the cheekbones and to the ears. Next, the pads of the middle fingers are pressed to the inner corners of the eyes and slowly move them towards the ears. The forehead is massaged with circular, slow and sliding movements.
The session is completed by massaging the entire surface of the head and face. They pass from the temples behind the ears to the back of the head, massaging the forehead, chin, cheeks, and the front surface of the neck with light pressure.