X-ray diagnostics during dental implantation is required to identify diseases and contraindications. Using images, the implantologist assesses the condition of the bone tissue, and based on this, selects the appropriate method for installing implants. After the operation, X-ray diagnostics determine whether the structure is installed correctly and whether treatment adjustments are required. For a complete picture, several images are taken using different methods - a targeted image, an orthopantomogram, a computed tomography. Our clinic has its own certified radiology department.
The importance of X-ray diagnostics before implantation
The images allow you to identify obstacles to the installation of implants. They identify problems that can complicate the operation.
Using images, the implantologist determines:
- distance to the mandibular nerve and maxillary sinuses;
- density, volume of bone tissue to select the shape and size of the implant;
- the condition of adjacent teeth to prevent infection from entering the surgical area.
Lack of diagnosis can lead to:
- damage to the nerve and sinuses;
- unstable fixation of the artificial root;
- infection of the operation area;
- reducing the service life of the implant and replacing it with a new one;
- increased sensitivity of the gums due to incorrectly selected orthopedic design.
X-ray diagnostics makes it possible to exclude complications and install implants according to the correctly selected protocol in accordance with the patient’s clinical situation.
Why do you need a CT scan before treatment?
Many patients, when studying the possibilities of modern dentistry (deriving information on their own from Internet sources or attending consultations with dentists), most have an idea of why a preliminary research procedure is needed before starting any treatment - a computer tomogram. But it is still not uncommon for this question to cause confusion, disagreement and denial among some patients.
Let's try to figure out the question together: why do you need to do a CT scan of your teeth? Some of the patients believe that this is done on purpose to “lure out” more money.
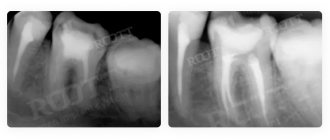
Computed tomography (CT) is necessary for almost any dental treatment, excluding professional oral hygiene and dental treatment in children. Even superficial caries can hide a large affected cavity in the tooth, which cannot be seen either visually, or on a targeted image, or on an orthopantomogram (OPTG).
Treatment of caries.
There are often cases when a patient has secondary caries under a filling, but a targeted or panoramic image does not always show the entire volume of affected tooth tissue. This can only be seen on a CT scan. And after this visualization, we can assume whether it will be possible to remove the affected areas without touching the nerve, or whether the inflammatory process is already in a borderline state between deep caries and pulpitis.
Canal treatment.
There is such a definition in diagnosing dental root canal disease as periodontitis (granuloma, cystogranuloma, cyst) - this is when the inflammatory process extends beyond the apex of the tooth root and the inflammation already passes into the bone tissue.
What degree of diagnosis does a panoramic or targeted image give us in this case? Imagine how a baby looks at the moon: yes, it exists, it is round, but the fact that it has the shape of a ball and what its true dimensions are is not in his mind.
It’s the same with a cyst; a panoramic image shows that it is there, but what size it is, this image does not make it possible to see, because it only shows the image in one plane. Using a computed tomogram, you can understand whether it is advisable to treat such a tooth or the extent of the inflammation is such that there is no longer any chance of saving the tooth.
Sometimes, without a computed tomography scan, it is completely impossible to see the inflammatory process, because the roots of the teeth are located in such a way that in other types of images the image is superimposed on each other and the affected tissue is visible on one root, while the inflammation on the other root canal is hidden.
Prosthetics.
Not a single orthopedist who values his reputation as a specialist will begin drawing up a treatment plan, not to mention the treatment itself, without a CT image. He, as the main conductor of the entire process, needs to understand the condition of the teeth, bone tissue, and periodontal tissues before starting to talk about prosthetics. Because the orthopedist is the final link in the dental treatment process and is responsible for the “foundation” on which he installs certain prostheses.
It happens that a patient comes and says that “at another clinic they looked at OPTG and said that implantation can be done without problems.” Our dental prosthetics specialists in Moscow, orthopedic dentists and implant surgeons, do not work “by touch.” Before starting to draw up a treatment plan, they need to see the condition of the oral cavity on a computer tomogram in order to maximally assess and eliminate all “icebergs” that will not float out unexpectedly during the process of implantation or prosthetics, but will be eliminated before problems arise during the treatment process.
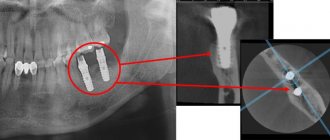
Implantation.
We move on to the implantation stage. On the OPTG we see that the height of the bone is acceptable, but if we expand the image on a CT scan, it becomes clear that the bone crest is so narrow that there is simply physically no place to install the implant. Imagine a board beam. In order to screw in a screw of the required size, it must be not only the required height, but also the width; a screw of the required diameter cannot be screwed into plywood.
Computed tomography in our clinic, along with other advantages, also makes it possible to carry out virtual implantation, that is, an implant surgeon, using a special program, can clearly demonstrate before your eyes whether it is possible to install an implant of the required size in the volume of bone tissue that you have. You have a. If not, then the question arises about preliminary preparation for implantation: sinus lift or bone grafting.
Periodontology.
There are many nuances in periodontal treatment, when the doctor, using the latest equipment and various instruments, can determine the diagnosis and stage of the disease. But often the periodontist also needs a CT scan to understand the source of the problem.
"Shelf life" CT
Sometimes it happens that a patient comes with a CT image from 6 months or a year ago and refuses to take a new one. Or he comes with a panoramic image (OPTG) and insists that “this image can also be used for treatment.” We have no choice but to refuse treatment to such a patient than to begin treatment with the possibility of causing harm to health. The “shelf life” of CT is a maximum of 3 months. Even within six months, both minor and serious changes can occur in bone tissue, root canals, formation of periodontal pockets, etc.
We strive for excellence in our work. Our clinic has the most modern Planmeca ProMax 3D cone beam computed tomography equipment.
This creates a number of advantages for you:
- There is no need to go or travel anywhere else for this type of diagnosis, without which no self-respecting doctor would begin treatment.
- During complex treatment, our specialists can always see your picture and know by heart your clinical picture of the disease. And if they need to discuss any related details about your treatment, they can do this without your presence, and discuss it with you as a scheduled appointment.
- They can always clearly show and tell you on the spot what is happening in the oral cavity and what needs to be done to prevent it.
- At any stage of treatment, if necessary, you can take a CT scan and evaluate the results of treatment: be it deep caries, treatment of a canal with a cyst, periodontal treatment, bone grafting, open sinus lift, implantation, prosthetics, preventive examination.
Sight shot
A 2D image makes it possible to analyze the condition of 1-3 teeth. For this purpose, a digital radiovisiograph is used.
Allows you to identify inflammatory processes in neighboring teeth, monitor the condition of sealed canals, diagnose damage, and detect pathologies. It can be periapical (study of the tissues around the tooth) and interproximal (analysis of the crown).
Advantages:
- clear image of 1-3 teeth with image magnification;
- safety for the patient, several tests can be done in a row without harm to health.
Flaws:
- 2D image giving only one perspective;
- small visible range.
In our Center, the procedure is performed in a separate X-ray room. The patient is put on a protective apron, the position of the head is fixed, and the radiologist directs a beam of rays to the area being examined.
The procedure takes a few seconds, is painless, and does not cause discomfort.
Panoramic photograph of teeth OPTG
An orthopantomogram gives an idea of the general condition of the dental system - it shows the external and internal condition of the dentition and bone tissue. Performed on an orthopantomograph, a flat two-dimensional panoramic image is obtained - the device combines several images taken in different planes into one. Therefore, OPTG does not accurately convey the image.
The procedure defines:
- ratio of jaw, sinuses;
- location of nerves;
- hidden carious formations;
- damage to seals;
- dental diseases (cyst, periodontal pockets).
Pros:
- full picture of the jaw;
- consideration of a local problem;
- the price is lower than CT.
Minuses:
- two-dimensional images;
- likelihood of misstatement;
- does not determine the angle, thickness of the alveolar processes, structure, position of the jaw.
Before the examination, you need to remove metal jewelry and accessories. To perform OPTG, the patient bites on a special plate to keep the jaws motionless. The orthopantomograph rotates around the patient's head. The procedure lasts from 8 to 20 seconds and does not cause discomfort.
Computed tomography CT
CT scan is performed on a 3D tomograph. The device's detector generates two-dimensional images, which are combined into a three-dimensional 3D image in a special computer program. The method is more informative than 2D images and allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the jaw in high resolution.
CT diagnostics are carried out at the preparatory stage of implantation to identify contraindications and after installation of implants to prevent complications. It is applied for:
- identifying pathologies of the maxillary sinuses;
- determining the condition of bone tissue;
- assessing the location of the mandibular nerve;
- analysis of temporomandibular joints;
- detection of impacted teeth that may interfere with the installation of implants;
- diagnostics of fractures, neoplasms on the jaw.
Advantages:
- accuracy, information content;
- clarity of the picture.
Flaws:
- high price compared to other types of x-ray diagnostics.
The procedure is performed while standing, the patient bites the plate of the device and remains motionless for up to 40 seconds until the device rotates around the head.
What is 3D dental scanning?
3D dental scanning is a modern and very accurate diagnostic technique that allows the dentist to examine the patient’s jaws and teeth from any angle.
The dentist scans the teeth with a special device - an intraoral (intraoral) 3D scanner. Unlike a conventional X-ray machine, the device takes not one picture, but thousands and transfers them to a computer, where a three-dimensional model is formed from the images.
Just a few minutes - and a digital 3D image of the oral cavity is ready
Safety
According to the established SanPiN requirements, the annual exposure rate should not exceed 1000 microsieverts. Modern X-ray equipment is safe - the table below shows the radiation exposure during one image and the permissible number of procedures per year.
| Radiation exposure per 1 procedure | Safe number of procedures per year | |
| Sight shot | 1-3 µSv | 500 |
| OPTG | 13-17 µSv | 80 |
| CT | 50-60 µSv | 20 |
| Type of diagnosis | Radiation exposure per 1 procedure | Safe number of procedures per year |
| Sight shot | 1-3 µSv | 500 |
| OPTG | 13-17 µSv | 80 |
| CT | 50-60 µSv | 20 |
X-ray diagnostics are not recommended during the first and last trimester of pregnancy.
Our clinic uses a safe device that meets international standards
The digital X-ray system with a minimum level of radiation SIEMENS SIRONA GALILEOS allows you to perform the most accurate studies for patients. The device is intended for the study of bone tissue, tooth roots, temporomandibular joint, nasopharynx, and upper spine. An analysis of local problems and the condition of a large volume of jaw tissue is carried out.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Chief physician, Ph.D.
Orthopantogram of the dentition: what is it and how is it done?
28.05.2020
Orthopantogram of the dentition: what is it and how is it done?
- The essence of the OPTG method
- Indications and contraindications for the dental orthopantomogram procedure
- Advantages and disadvantages of the panoramic dental photograph method
- X-ray OPTG in modern dentistry
Diagnostic imaging is an integral part of modern dentistry. It helps doctors timely identify oral problems, plan dental treatment and monitor its effectiveness. The most popular method in this area is a dental orthopantomogram. This is a panoramic x-ray of the upper and lower jaw, showing all the teeth at once, including those that have not yet erupted. The OPTG also gives the doctor an idea of the condition of the jaw bone and temporomandibular joint.
The essence of the OPTG method
Sometimes an external examination of the oral cavity is not enough for a doctor to make a diagnosis or choose a treatment method. It is in such cases that an orthopantomogram is prescribed; you will find out what it is below. OPTG is an x-ray of the lower part of the face. Like any x-ray test, it uses ionizing radiation to create images of the body's internal structures. During the procedure, the patient places their chin on a small rest in front of the X-ray machine and gently bites down on a sterile mouthpiece. This ensures you remain still while shooting. The procedure is performed very quickly, the patient does not feel anything.
The standard method involves shooting directly on film. When conducting digital OPTG, information is processed on a computer.
Indications and contraindications for the dental orthopantomogram procedure
The procedure allows the doctor to assess the condition of all the patient’s teeth, determine their number, position and degree of eruption. Dental orthopathograms are also used to plan orthodontic treatment and examine the jawbone.
Additionally, orthopantomography reveals:
- caries or pulpitis;
- dental injuries and jaw fractures;
- sinusitis; periodontitis, periapical abscess;
- tumors, radicular cysts;
- disease, fracture or dislocation of the temporomandibular joint;
- foreign bodies;
- sialolithiasis (salivary duct stones).
Sometimes dentists use this method to diagnose children. In this case, OPTG of the dentition is used to monitor the growth and development of children's teeth (determining their location, shape, angle, etc.).
The only contraindication to the procedure is pregnancy. In this case, the doctor decides how much the benefits of the diagnosis outweigh the possible risks.
Advantages and disadvantages of the panoramic dental photograph method
A panoramic photograph of teeth in Kursk makes it possible to collect detailed information about the condition of the patient’s oral cavity. Compared to other types of dental diagnostics, an orthogram has a number of advantages:
- wide coverage of facial bones and teeth;
- low radiation dose;
- convenience and speed of examination;
- the ability to examine patients who are prohibited from opening their mouths;
- quick results;
- minimal number of contraindications;
- painlessness.
The disadvantages include the fact that the OPTG x-ray does not show small anatomical details, as well as the overlapping of teeth images on the photograph.
X-ray OPTG in modern dentistry
Orthogram is a highly accurate diagnostic method widely used in modern dental clinics. The study involves the use of a low dose of ionizing radiation. A digital orthopantomogram is used more often (how this study is done is described above). The procedure allows you to obtain a detailed image of the dental structures. Also, the Le-Dent clinic provides dental prosthetics services.
Price
Diagnostics in our Center is included in the cost of implantation consultation:
- drawing up a treatment plan, CT scan with examination on a computer screen without decoding and recording on DVD - 3000 rubles. ;
- drawing up a treatment plan, CT scan with interpretation, recording on DVD - 5200 rubles.
When installing implants in our Center, consultation and x-ray examination are included in the package, diagnostics after surgery is carried out free of charge. Funds spent before the start of treatment are credited to the patient’s account in the form of an advance.
You can view pricing at our clinic here.
Types of X-rays in dentistry
Dr. Kizim
>
Articles
>
Types of X-rays in dentistry
The work of a radiologist in dentistry is very important; only high-quality radiographs allow doctors to draw up correct treatment plans for patients in the shortest possible time.
In dentistry, there are several types of x-ray examinations:
— targeted shot;
— orthopantomogram (panoramic image);
— cone beam computed tomography (3D image).
At the Center for Dentistry and Basal Implantation, all these examinations are carried out by radiologist Ruslan Albertovich Baterikov. In our clinic we use equipment from the Finnish company Planmeca Pro max 3D of the highest precision with minimal radiation doses. You can find out the cost of services in the “ Prices ” section.
Find out details
A targeted image allows you to establish the true causes of the patient’s complaints, outline an effective treatment plan and monitor its results. The image gives an idea of the anatomical structure of the tooth, the condition of all its internal elements, and the presence of an inflammatory process both in the tooth itself and in the periodontal tissues.
A targeted photograph is prescribed by a dentist:
- for high-quality treatment of caries - to determine the depth of carious lesions;
- when removing teeth - to determine the state of tooth eruption and determine the number of tooth roots;
- during endodontic treatment, treatment of tooth canals, pulpitis and periodontitis - allows you to assess the condition of the canals before treatment, the quality of their preparation for filling and the correctness of filling.
Orthopantomogram is a type of X-ray examination of the entire dental system or a panoramic photograph of the jaws showing all teeth, as well as soft tissues, sinuses, maxillary sinuses, and the temporomandibular joint. The image is displayed in two-dimensional format.
The examination of each patient begins with this image, since, having an orthopantomogram, the doctor can give a comprehensive consultation about the condition of the patient’s oral cavity and begin timely treatment of diseases that have not yet manifested themselves.
An orthopantomogram is prescribed by a dentist:
- at the initial consultation when the patient comes to the clinic for the purpose of a complete diagnosis of the condition of the oral cavity, drawing up a complete rehabilitation plan and full treatment of the patient;
- when removing wisdom teeth, especially if these are complex removals of impacted and dystopic teeth;
- to assess bite pathology during orthodontic treatment;
- to determine anomalies of occlusion during orthopedic and orthodontic treatment for the full restoration of the bite and chewing process.
Cone beam computed tomography is the latest method of three-dimensional diagnostics of the entire dental system. With this study, you can see any part of the maxillofacial region from different angles. This type of x-ray diagnostics provides the most comprehensive information about the condition of the patient’s dental system. When planning dental implantation using CBCT, the operation is bloodless and with the least trauma to the body, since the surgeon has determined in advance a safe place and angle for installing the implant, which completely eliminates the possibility of touching dangerous areas of the jaw. Osteoplastic and maxillofacial surgeries are also greatly simplified.
Cone beam computed tomography is prescribed by a dentist:
- for complex diagnostics of the dental system to determine a comprehensive treatment plan;
- to determine the degree of infection of the tooth canals in complicated caries, pulpitis, periodontitis;
- to identify cysts and neoplasms in the jaw bone, during inflammatory processes in the maxillary sinuses;
- to determine the condition of bone tissue, the location of nerve canals and the level of pneumatization of the maxillary sinuses;
- when planning implantation, osseoplastic and maxillofacial operations;
- to determine occlusion anomalies during orthopedic and orthodontic treatment for complete restoration of the bite and chewing process;
- to assess bite pathology during orthodontic treatment;
- for diagnosing the temporomandibular joint in case of its dysfunction.