Causes of bleeding Classification How to stop?
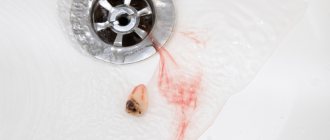
Dentist's help Prevention Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure that cannot be performed without damaging tissues and blood vessels. This causes bleeding from the tooth socket. The blood forms a clot that protects the wound from bacteria. Usually, it stops coming out of the wound after a few minutes, but there are cases when bleeding continues for several hours or even days.
Local reasons
- Vascular rupture during traumatic surgery;
- breaking off the root septum or alveoli (socket);
- inflammation in the area of the tooth that was removed;
- the effect of adrenaline (after the narrowing of blood vessels, the second phase begins - their expansion);
- melting of blood clots clogging blood vessels under the influence of purulent secretions;
- local hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels). Occurs from hot food, drinks, rinses or compresses.
Under no circumstances should you apply heat to the wound after extraction!
Thus, the occurrence of bleeding can be provoked not only by a doctor’s error, but also by the patient’s actions.
Why do my gums bleed?
Bleeding from the gums can occur for mechanical or pathological reasons.
The first group includes a blow to the jaw area or minor injuries due to an incorrectly selected crown or filling. In this case, bleeding goes away immediately after the problem is eliminated. Only a doctor can assess whether a crown has been chosen correctly or a filling has been installed during a face-to-face consultation, because it is difficult to see such nuances on your own. Gums can also be damaged by a brush that is too hard, intensive use of dental floss, or careless impact with other objects in an attempt to completely remove food debris. In this case, bleeding appears only after the procedure and disappears after a few minutes.
Pathological causes are associated with diseases of the oral cavity and other organs. Bleeding is a symptom:
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums;
- stomatitis - ulcers on the oral mucosa;
- periodontitis - inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth (localized - in several units, or generalized with damage to the entire jaw);
- leukemia (leukemia) - blood cancer with a characteristic decrease in immunity;
- intoxication with heavy metals (lead, mercury);
- diabetes mellitus, which causes weakness of the gums and blood vessels due to characteristic angiopathy.
Often gums bleed due to hormonal changes. It can be caused by pregnancy, menstrual irregularities, and puberty.
When your gums bleed when brushing your teeth
Most patients' gums do not bleed constantly. Symptoms only appear when brushing your teeth or eating hard foods. This occurs for several reasons:
- inflammation of the gums makes them more vulnerable to injury;
- the process of desquamation of the epithelium of the oral mucosa intensifies, which thins the tissue;
- capillaries located close to the gums become more permeable and bleeding occurs more easily.
The combination of all three factors leads to the fact that when brushing your teeth, your gums begin to bleed. This symptom should not be ignored. Cure the disease at an early stage is much faster and cheaper than in an advanced form. And the appearance of blood when brushing your teeth is not considered normal; it is always a sign of pathology.
Common reasons
The most common of them is a sharp rise in blood pressure as a result of a hypertensive crisis, excessive physical activity, and thermal procedures (bath, sauna, hot bath).
In second place are diseases that affect blood clotting: hemophilia, leukemia, hemorrhagic diseases.
Profuse bleeding occurs with unrecognized vascular tumors (hemangiomas). Therefore, it is important to conduct an X-ray examination, which shows such changes.
Taking anticoagulants can also provoke socket bleeding after removal.
Classification of bleeding
Bleeding is divided into primary, which begins immediately after surgery, and secondary, when bleeding begins after some time.
The intensity of bleeding is determined depending on how much the hole bleeds after removal:
1st degree
– blood flows
for 20-30 minutes
, saturates the tampons and colors the saliva.
2nd degree
– bleeding continues for more than 40 minutes, blood and saliva mix intensively.
3rd degree
– the bleeding does not stop for more than an hour, the patient spits blood.
With prolonged bleeding, the patient's general condition worsens. Weakness, dizziness appear, and the skin turns pale. Blood pressure drops, the heart begins to beat less frequently. In case of bleeding, dentists advise not to delay a visit to the doctor so that he can take measures to stop the bleeding and prevent the condition from worsening.
How to prevent perforation
If patients with anatomical features of the location of the roots in the sinus are treated according to the standard protocol, the threat of rupture of the membrane is very high
The doctor must have the necessary information about the anatomical and topographical features of the patient and be prepared for an emergency situation.
- To prevent perforation of the sinus membrane, computed tomography is required. After studying the CT image, the doctor selects the optimal treatment tactics. But not every equipment allows you to identify all the nuances. In our Center, diagnostics are carried out using a modern 3D tomograph Sirona Galileos with ENT mode settings. Provides high quality images, allows you to evaluate the structural features of the upper jaw and sinus, calculate the height of the septum, find out the location of the roots, their anatomy.
- When working with the canals of teeth located in the sinus, all manipulations must be extremely careful. The dental canals are very thin, sometimes tortuous, the doctor must control every action. Endodontic dental treatment in our Center is carried out using a Seiler dental microscope. Multiple magnification expands the view, allows you to examine the entire length of the dental canal in great detail, and prevent the filling material from leaving the root.
- The experience of a specialist is of great importance so that he can give an adequate assessment from a CT image, choose tactics, and calculate efforts. Our Center employs highly qualified endodontists, with excellent clinical thinking and honed manual skills. Qualifications and skills allow us to prevent complications and act promptly in the event of an emergency situation.
We have minimized the likelihood of complications after dental treatment
. Advanced CT diagnostics in ENT mode and work using a dental microscope allow us to select competent tactics to prevent perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich Chief physician and founder of the Doctor Levin center
After endodontic treatment, control CT diagnostics is mandatory! This preventive measure allows you to timely identify perforation (even if the doctor did not notice it during treatment) and take measures to eliminate the consequences.
If a piece of instrument or filling material gets into the sinus, removal of the foreign body must be prompt and urgent ! Otherwise, there is a high risk of infection, development of inflammatory processes and neoplasms.
How to stop bleeding from a socket after tooth extraction
After the tooth is removed, the dental surgeon cleans the wound and applies a sterile swab. The patient is asked to tightly clamp the tampon with his teeth and hold it for about half an hour. If the tampon quickly becomes saturated with blood, it should be changed.
If the bleeding does not stop after 20-30 minutes
, the dry swab is replaced with one moistened with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
A cold compress can be used to constrict blood vessels. Ice is applied to the cheek, after wrapping it in a towel so as not to freeze the skin. Keep the compress for 10-15 minutes
, then take a break and repeat the procedure.
After surgery, the dentist recommends painkillers. You should follow these recommendations to avoid accidentally taking a product containing aspirin, which thins the blood and can cause bleeding.
If after all the manipulations there is still bleeding from the tooth socket, you need to contact a dental clinic.
Preventive crown care
The prosthesis installed in the mouth is influenced by food chemicals, saliva, and microbes. Without systematic proper care of crowns, they become covered with plaque, lose their original color, and become a breeding ground for infection.
Prevention of the development of infection in the oral cavity, especially under fixed dentures, involves strict adherence to the following hygiene rules:
- Teeth should be brushed at least 2 times a day: morning and evening, and if possible, more often. Brushing technique: movements of the toothbrush are performed from the gum to the top of the tooth at an angle of 45°. The procedure time is at least 3 minutes.
- Rinse your mouth with clean water after every meal.
- For better cleaning of teeth and dentures, it is recommended to actively use additional devices: interproximal and tuft brushes, dental floss.
- Use irrigators. To rinse the oral cavity, various agents with an antibacterial effect are used that destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
A well-installed prosthesis with good care will reliably and for a long time protect the tooth from external factors. But if a tooth infection does occur and decay begins, without proper treatment the pathological process will only progress, which will lead to serious complications. To eliminate the consequences, long-term treatment with significant financial costs will be required.
What does a dentist do?
First of all, the doctor will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis. In accordance with it, the dentist will carry out treatment.
First aid is to stop blood loss. To do this, local anesthesia is performed, blood clots are removed, the wound is dried and the place where the blood is coming from is determined.
Methods to stop alveolar bleeding depend on its cause and location:
- if there is a rupture of the gums or mucous membrane, they are sutured;
- a ligature (a special thread for ligating blood vessels) is applied to the bleeding vessel;
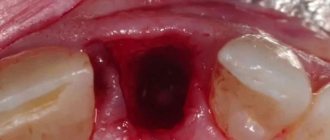
- If there is bleeding from the alveoli (socket), a tampon of iodoform gauze is placed on it. It is left in the wound for several days.
Tamponation is used as a prophylactic measure if there is a risk of bleeding. The tampon is left in the hole for several days. Then they take it out and see how well the wound has healed.
Removing wisdom teeth is potentially dangerous. Such operations are often difficult. Sometimes you have to cut the gum, saw the roots or the tooth itself and remove it piece by piece. Bleeding after such complex operations occurs more often than after ordinary ones.
Measures taken when a hole bleeds after wisdom tooth removal are the same as after regular removal. If there is a history of blood diseases, preparations are made for such an operation in advance. A blood test is carried out, in some cases calcium chloride injections and vitamin C
and
K.
_
If the cause of alveolar bleeding is systemic diseases, general hemostatic agents are used (calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, aminocaproic acid, dicinone, vikasol).
For hypertension, antihypertensive therapy is prescribed. After the pressure normalizes, the bleeding usually stops.
Symptoms of tooth decay under the crown
The first sign of an inflammatory process under a prosthesis is not pain, as many people think, but an unpleasant odor. This happens because at the stage of preparation for prosthetics, the tooth is usually depulped, that is, the neurovascular bundle, which is responsible for sensitivity, is removed.
- An unpleasant taste first appears in the mouth, then a putrid odor is added, which cannot be masked by any chewing gum or mouthwash.
- The patient discovers a gap between the crown and the gum, where food debris gets in, which becomes a breeding ground for microbes.
- Often, inflammation of the gums develops near the tooth with the formation of soft tissue swelling.
- If the tooth has not been pulped, then severe pain is present.
- Blackening of the tooth under the crown.
All these symptoms indicate an advanced putrefactive process in the tooth covered with a crown. You should immediately seek medical help from a dentist.
Ignoring the problem leads to dire consequences:
- formation of a purulent cyst at the apex of the root;
- complete tooth destruction;
- the formation of periostitis or gumboil;
- spread of purulent infection along with blood or lymph flow to other organs.