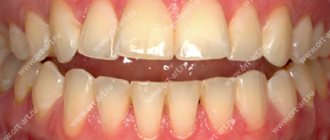
One of the most common orthodontic disorders found in adults and children is deep bite. This is what experts call the type of closure of the dental arches, when the upper teeth cover the lower teeth by more than 1/3. In this case, the cutting-tubercle contact between them is disrupted.
This deviation in dentistry is also called vertical deviation of occlusion. Also used are names such as traumatic or decreasing bite, deep frontal or incisal overlap, as well as deep incisal occlusion or diocclusion. All these synonyms mean the same violation.
Causes
The reasons why such a deviation occurs can be congenital or acquired. The most common of them:
- genetic predisposition;
- congenital facial anomalies – cleft palate, cleft lip, etc.;
- a case of severe infectious disease of the mother during pregnancy;
- pathological childbirth with a period of fetal hypoxia;
- diseases in infancy and preschool age associated with dysfunction of the endocrine and respiratory systems, gastrointestinal tract, metabolic disorders;
- incorrect posture and pathologies of the development of the musculoskeletal system;
- gum tumors;
- injuries to the oral cavity or facial part of the skull;
- impaired swallowing and chewing;
- bad habits such as thumb sucking, biting the lower lip, or prolonged pacifier sucking.
Most problems, such as incorrect attachment of the frenulum of the tongue and lips, untimely replacement of primary teeth, early loss of primary molars and premolars, and dental diseases can be prevented or corrected by timely preventive care at the dentist.
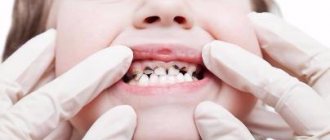
In adulthood, this deviation most often results from pathological abrasion of teeth caused by looseness of bone tissue or uneven load when chewing on individual areas of the dentofacial apparatus. Incisal occlusion can result from an accident or other trauma to the skull, for example, after unsuccessful rehabilitation of rhinoplasty and other plastic surgery on the face.
Tooth wear due to deep bite
Symptoms
The list of characteristic signs is determined by the severity of the pathology. Thus, in the early stages, the only form of manifestation is the formation of small chips and cracks on the surface of the enamel, almost invisible to the naked eye. The cause of mechanical damage is the pressure of the elements of the lower row on the tissues of the palatal surface adjacent to the base of the upper teeth, as well as constant contact with the area of the cutting edge, whereas in normal condition the load is distributed evenly.
Untimely contact with an orthodontist is often due to the absence of pronounced symptoms that could cause the patient significant physical inconvenience. Manifestations characteristic of the middle stage include:
- Intensive abrasion of enamel from the lingual side of the upper incisors and the frontal covering of the mandibular elements, caused by constant contact, and leading to an aggravation of sensitivity in problem segments.
- Changes in facial contour, reflected in a decrease in the height of the lower third, as well as associated problems with diction and food processing.
- Development of TMJ dysfunction. Accompanied by extraneous sounds, painful sensations, and limited mobility.
- A noticeable deviation in the position of the lips, leading to impaired closure.
A severe degree is characterized by the diagnosis of pronounced anomalies of the skeletal structure, including a combination of macrognathia and microgenia, disturbing the proportions of the face (“bird-shaped”). The incisors constantly injure the palate, which causes chronic tissue inflammation, painful sensations when eating, as well as other negative consequences that require medical intervention.
Signs
Deep bite causes a number of visual aesthetic defects and functional disorders. A person with vertical incisal occlusion has a shortened lower part of the face, the lower lip may be slightly turned outward, and a sharp groove appears above the chin. When smiling, the lower dental arch remains hidden behind the lip.
The main symptom of deep incisive occlusion is the overlap of the lower teeth by the upper teeth by more than 1/3. In this case, the upper jaw looks overhanging. Due to the disorder, the oral mucosa is chronically injured, so the patient periodically experiences episodes of stomatitis; gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease may occur. In most cases, diocclusion causes hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles.
Result
Photos before and after correction of the anomaly illustrate the possibilities of modern orthodontics. In most cases, it is possible to correct the bite, change facial features, and get rid of functional disorders. A competent orthodontist will select the optimal correction method. The patient must strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and come for examination on time. The results of treatment last a lifetime. To consolidate the effect, after removing orthodontic appliances, retainers are installed on the inner surface of the teeth to prevent the incisors from returning to the wrong position.
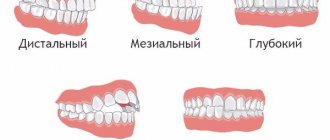
Kinds
Orthodontists distinguish the following types of this pathology:
- incisal overlap – contact of the cutting edge of the lower arch with the palatine tubercles is preserved;
- deep bite – there is no incisal-tubercle contact;
- deep traumatic - the cutting edges of the lower teeth rest against the palate.
If treatment is not carried out, then all these stages in most cases alternately replace each other in the indicated order, therefore the incisal overlap is considered the beginning of pathological changes, and the traumatic type is the result of a long course.
Depending on the amount of crown overlap, the following 3 degrees are distinguished:
- I – overlap up to 5 mm deep;
- II – overlap 5-9 mm;
- III – overlap over 9 mm.
A distinction is made between anterior occlusion, when the overlap is observed in the frontal zone, and lateral, if the violation is detected in the lateral region. With this deviation and simultaneous reduction of the anterior teeth of the lower jaw, we are talking about sagittal disocclusion. This phenomenon is often observed in children with a milk supply.
Abnormal occlusion of the dental radii in the sagittal direction (lateral segment)
Orthodontists also distinguish distal and neutral types of pathology. With distal, the oval of the face seems narrower, and the chin remains unchanged, while with neutral, the oval looks shortened. Distal is usually more noticeable, while neutral requires an orthodontic examination to confirm.
Diagnostics
To clarify the diagnosis and severity, the doctor prescribes a detailed diagnosis. Depending on the situation, this may include:
- symmetroscopy – detailed reproduction of the dentition;
- electromyotonometry - study of the tone of the muscles that move the lower jaw;
- occludogram – a model of the closure of the patient’s dentition;
- MRI – visualization of the structures of the temporomandibular joint.
The patient is photographed in profile and frontal. A model of the dental-maxillary apparatus is made from the alginate mass, on which all the necessary parameters will be measured.
Additionally, fluoroscopy and 3D cephalometry may be needed.
Treatment
The question often arises as to whether deep bite treatment should be performed. It is necessary to choose a tactic together with an orthodontist, who can determine whether he is dealing with a progressive or stable form. In the case of the distal form, a set of measures aimed at restoring the bite is clearly recommended. But when it comes to neutral deep bite, the doctor may advise a wait-and-see approach if the existing clinical picture does not cause negative consequences.
The selection of therapeutic measures depends on the indications and age category of the person.
In children
On average, a deep bite elimination program takes about 6 months, but can vary significantly, either shortening or lengthening the course. The general pattern is that the younger the patient’s age, the faster the correction will take place.
For ages 2 to 6 years, the program consists of the following items:
- surgical excision of the frenulum of the tongue or lips (if necessary);
- mandatory consumption of solid foods - carrots, apples, etc.;
- weaning from bad habits - pacifier, finger sucking, etc.;
- sanitation of the oral cavity and removal of all foci of caries for normal distribution of load during chewing;
- expansion of the frontal part of the dental arches;
- correct positioning of the front teeth;
- mesial movement of the mandibular bone.
After the beginning of the loss of baby teeth, bite separation requires the use of dental plates, silicone trainers, bite blocks, and activators. The Brückl apparatus is used among functional orthodontic devices.
Bruckle orthodontic appliance
In adults
In adults, deep occlusion is treated with braces. The course of wearing them can range from one to several years, but it all depends on individual characteristics. If the pathology is caused by congenital or acquired adentia (the absence of a tooth), then prosthetics are prescribed. To achieve an ideal result after wearing braces, veneers or lumineers are used.
If a deep bite is caused by changes in the jaw or the situation is complicated by other indications, braces will not be enough, since they only affect the positioning of dental elements. This clinical picture indicates the need for surgical treatment. In the Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, complex surgery is performed under general anesthesia with a long rehabilitation period.
FAQ
Why is an open bite dangerous?
This anomaly is dangerous not only due to the presence of an aesthetic defect, but is also a threat to the general health of a person. Gastrointestinal disorders, respiratory diseases, pain in the jaw joints - this is not the entire list of complications that abnormal bites lead to.
What happens if an open bite is not treated?
Abnormal bites will not correct themselves. The situation will only get worse. Teeth under increased stress will deteriorate until they are completely lost. In this case, the problem can be solved with prosthetics, but this can also be problematic until the bite is corrected. Therefore, you should not delay correcting abnormal bites. And it is advisable to do this as early as possible. In children and adolescents, the dentofacial apparatus is not yet fully formed, which increases the chances of doing without surgery.
How long does it take to treat an open bite?
It all depends on the severity of the disease and what treatment methods were chosen. If we are talking about orthodontic treatment, then this is 1.5-2.5 years. It is possible to increase the treatment period if the dynamics of changes lag behind those expected. Remember that after braces there comes a retention stage during which you need to wear retainers.
How much does open bite treatment cost?
The cost of open bite correction is influenced by the following factors: severity of the disease, type of treatment (orthodontics and/or surgery), dental clinic and others. As a rule, the price for treatment is announced to the patient only after diagnosis.
Consequences
Lack of treatment for deep disocclusion causes many functional disorders. Some of them can be eliminated at any time after the start of recovery, while others remain with the patient for life.
The most common consequences:
- difficulties with biting and chewing food well, which in turn causes gastrointestinal disorders;
- diction disorders;
- breathing problems;
- hypertonicity of the maxillofacial muscles;
- arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint;
- psychological discomfort due to disturbances in the smile zone and speech disorders.
How to fix an open bite
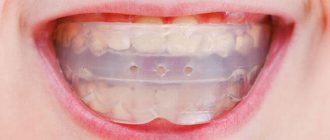
To prevent deformation of the dentition, their destruction due to mechanical pressure on each other, the appearance of caries and diction disorders, it is recommended to correct the bite from early childhood. Many patients experience fear due to discomfort when wearing braces. These structures are uncomfortable and require regular correction. Not many people know about a painless alternative to braces - aligners.
Sign up for free 3D modeling of your future smile!
Make an appointment
*By making an appointment you consent to the processing of your data
Essentially, this is a therapeutic mouthguard used for a corrective and fixing effect. They are made from soft polymers that are safe for humans. Aligners help move teeth in the desired direction. The patient is recommended to wear the device for up to 20 hours a day, removing it only for hygiene procedures and while eating. The product is easy to put on and take off. Another advantage of aligners over braces is that they are completely transparent and invisible to others. The average correction period is 3-6 months; to correct complex violations it will take up to a year. During long-term treatment, the aligners are replaced with a new set every 2-3 months.