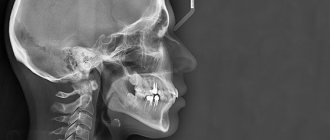
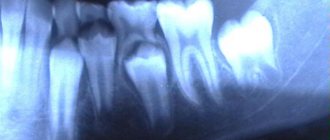
In dentistry, x-rays are one of the most popular types of diagnostics. An image of the teeth allows you to clarify the diagnosis, assess the general condition and internal structure of the tooth, the condition of the bone tissue and gums, and choose the right treatment tactics. To monitor treatment, it is also necessary to take dental x-rays. And prosthetics, implantation, root canal treatment and other operations are generally impossible without this examination.
Let's find out more about this indispensable diagnostic method.
Indications for dental x-rays
A referral for an x-ray is given by a dentist after a visual examination of the oral cavity and a survey of the patient. There are quite a few indications for radiography.
Root crack or fracture
The feeling of severe pain in a certain area of the jaw when biting or chewing food is a sign of a fracture of the tooth root (or a crack in it). Also, during an examination of the oral cavity, a swollen, hyperemic mucosa can be detected near the injured tooth.
On an x-ray, the fracture will appear as a small darkened stripe on the root of the tooth. The image will also allow you to determine which group of fractures a particular case belongs to: transverse, vertical, oblique, comminuted.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is the pathological process of inflammation of the supporting apparatus of the tooth. In the first stages, this process can be asymptomatic, while gradually destroying the bone tissue around the tooth, and then the tooth itself. Subsequently, the patient experiences bleeding gums, swelling, and slight mobility of teeth.
A pathology such as periodontitis has a very high frequency of manifestations (approximately 90% of the adult population is susceptible to this disease in one form or another). Periodic X-rays for preventive purposes (how often dental X-rays can be taken for children and adults will be discussed below) allows you to see periodontitis in its early stages and begin treatment on time. In the pictures you can see the degree of change in bone tissue, destruction of partitions, inflammatory and purulent processes.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process that affects the root membrane of the tooth, as well as the tissues surrounding it. This pathology is most often a consequence of prolonged caries and the lack of any treatment.
Periodontitis on an x-ray is visualized as a layer in the periapical region. With this pathology, fistulas with purulent contents appear. X-rays show foci of destruction with fuzzy, uneven contours.
Anomalies in the location of the dental joint
If teeth grow abnormally, or are positioned in a non-standard manner (with an inclination, with a rotation, etc.), a dentist or orthodontist may prescribe an x-ray to identify an anomaly in the location of the dental joint. It is better if such a diagnosis is carried out in childhood, when the position of the teeth can be changed without much difficulty with the help of braces. It should be noted that children should not have their teeth x-rayed as often as adults.
Neoplasms or abscesses
X-rays are the best way to diagnose tumors, such as dental root cysts. In the image, the cyst appears as a darkened area, which has a round or oblong shape with clearly defined contours.
An abscess is an accumulation of pus in a certain area of the dental system. It is also visible on x-rays.
Advantages of X-rays in dentistry
One of the most common diseases that occurs in almost every patient is caries. If the disease is detected at an early stage and treated, it is not dangerous. But in the absence of timely intervention, caries causes serious complications (pulpitis, periodontitis and others), which are accompanied by severe toothache and the treatment process in such cases takes a lot of time and effort. This is why it is so important to visit the dentist regularly for preventive examinations. It is recommended to undergo an examination every six months, which may include x-rays.
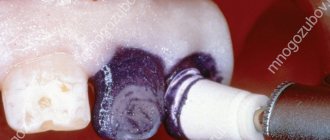
If a root canal filling is planned, the dentist needs to see its structure and possible individual characteristics. After filling, the specialist prescribes an x-ray for control. This is very important, because if a filling defect is not detected in time, inflammation will develop after some time, which can lead to tooth loss.
More information about caries treatment can be found here
Types of X-ray
After the examination, the doctor can prescribe the patient one of four possible types of x-rays
.
Prikusnoy
This method allows you to reflect the crown part of the tooth in the image. It is used to detect periodontitis and interdental caries. Bitewing can be used to obtain images of the upper and lower teeth.
Sometimes such a picture can be taken after prosthetics and crown installation to see how correctly the procedure was performed.
Sighting
With the help of a targeted image, it is possible to discern a specific affected tooth or several. Moreover, such a picture cannot include more than 4 teeth.
Panoramic
Using panoramic images, you can monitor the quality and effectiveness of the treatment already performed. They allow you to see a complete picture of the state of the entire dental system, and this is not only teeth with obvious problems (for example, caries, chips, etc.), but also roots, periodontal tissue, paranasal sinuses and the lower jaw joint.
On a panoramic image, the doctor will be able to see the presence/absence of filling material, hidden carious cavities, inflammation of the peri-root tissues, cysts, tumors, as well as teeth that have not yet erupted.
Digital or 3D X-ray
This type of x-ray is considered the most modern and safe. Using 3D X-rays, you can get a clear image of the entire row of teeth and a specific tooth. The result is a three-dimensional image that is displayed on the monitor.
Where can I do it?
Most dental clinics have an X-ray room where the patient can undergo this procedure without leaving the building and return to his dentist with the images. State clinics also have such installations, but they are exclusively of the old type. This means that you will have to go through the procedure several times and pay less. Old equipment also has high radiation doses. Unfortunately, many private dentistry are also equipped with such equipment. Sometimes a private doctor may refer you to another diagnostic center to obtain data. Cone beam computed tomography is only available in progressive private clinics, but the accuracy of the results fully pays for itself.
The price of the service will depend on the type of examination. Thus, bitewing radiography costs from 3 to 10 dollars, depending on the number of images. At the same time, prices are almost the same in both public and private institutions. A panoramic image will cost approximately $20-25. It can only be done in private institutions, but some clinics can provide this service for free if the patient is being treated by them. The most expensive diagnostic is CBCT, which is done in single diagnostic and dental centers. Its cost will be 50-60 dollars.
Description of the procedure
There is a certain algorithm that describes how to properly take a dental x-ray:
- the patient must remove metal jewelry;
- then he is brought to the X-ray machine and asked to bite down on the photosensitive film so that the tooth being examined is between the film and the machine;
- a picture is taken.
If required, the picture can be taken in a different projection. In cases where x-rays are performed using a computer radiovisiograph, the patient puts on a special apron, and then a sensor connected to the device is placed on the area of the dental system being examined. The photo is displayed on the computer.
Another option for x-rays is using an orthopantomograph. The subject stands at the device and places his chin on a special support for complete fixation. Next, he bites the block with his teeth, which will prevent the jaws from closing. Pictures are taken while the device rotates around the patient's head.
Usually the procedure takes only a few minutes, after which the finished images are described and transferred to the patient.
X-ray for pregnant and lactating women
Women during pregnancy should see a dentist as part of a routine checkup. The fact is that destructive and inflammatory processes in the gums and roots of teeth can lead to negative effects on the entire body. This situation is extremely undesirable when carrying a child, so a pregnant woman is sometimes prescribed x-rays. To examine the expectant mother, only minimal doses of radiation are used; they try not to take panoramic photographs, replacing them with targeted ones. However, radiation is still present, which raises the question among patients: is it possible to do an X-ray on a pregnant woman?
During pregnancy, of course, it is better to avoid such diagnostics. Manufacturers of new technology claim that it is absolutely safe for women even during this period. But still, the opinions of doctors on this matter remain skeptical. Such an examination can be prescribed only when the disease threatens life more than the possible negative impact of radiography on the fetus. In the third trimester, such diagnostics can be carried out without harm to the fetus. In the process of obtaining images, the patient’s chest, neck, abdomen, and pelvic area are tightly covered.
After childbirth, women often experience dental problems, mainly due to the loss of beneficial microelements. Nursing mothers should not be afraid of x-rays. This does not affect the structure of milk at all (this does not apply to studies of the abdominal and thoracic cavity). During lactation, women undergo X-rays under a protective apron. You can feed your baby after the x-ray on the same day.
How often can dental x-rays be taken?
As everyone knows, a large dose of X-ray radiation can harm human health. That is why there are some restrictions on dental x-rays. If we talk about how often an adult’s teeth can be x-rayed without harm to health, then the optimal answer would be: 3-5 times a month (if required). In general, the dose of dental x-rays (as shown by SanPiN) should not exceed 150 mSv per year.
To the question, is it harmful to have dental x-rays for children, the answer is yes. Such diagnostics are prescribed only in extreme cases, when dental pathology requires precise study. It is better to conduct digital research, then the harm will be minimal. It is also important to protect the child’s body with a special vest or apron before taking the photo.
Is it possible to carry out diagnostics during pregnancy?
According to SanPiN, X-ray examinations are allowed in the second half of pregnancy using protective equipment, provided that the radiation dose does not exceed the same 1000 μSv. However, it is recommended to refrain from taking x-rays in the first and last 12 weeks, i.e. in the first and last trimesters.
Do not be afraid of undergoing diagnostic procedures during pregnancy. Even ordinary caries is an infection that, if not properly treated, can spread throughout the body and lead to infection of the fetus. Therefore, it is better to receive a small and completely safe dose of radiation than to carry out complex dental treatment blindly, not knowing how deep the inflammatory process is.
After the baby is born, i.e. During breastfeeding, dental x-rays can be taken, even more than once (within reasonable limits). Radiation doses are minimal, so radiation does not accumulate in breast milk, and there will be absolutely no harm to the baby. There is also no need to pump or skip feedings.
Problems with X-rays
In some cases, dental X-rays (the attending physician will tell you how often they can be taken if the first image is unsuccessful) cannot be performed properly due to the patient’s body losing contrast. This can happen for several reasons.
A granuloma, abscess or cyst has developed on a separate part of the jaw
Abscesses, cysts, granulomas can greatly obscure the image, making its accurate description and diagnosis impossible.
A radicular cyst has appeared
A radicular cyst can hide other pathological changes in bone and dental tissues.
Improper canal filling
Incorrect use of filling material or filling of canals after removal of nerves leads to exposure of the image. Accordingly, it is not possible to see anything on it.
Why does a dentist refer a patient for dental x-rays?
An x-ray gives the doctor the opportunity to most accurately assess the condition of the problem unit or all organs of the oral cavity. And also study the clinical picture in detail. In particular:
- detect foci of inflammation that have not yet manifested themselves;
- identify neoplasms in the bone and soft tissues of the dental system;
- establish the signs and stage of development of periodontitis or periodontal disease;
- establish linear dimensions, volume, structure of bone tissue before implantation;
- more accurately assess the correctness of occlusion (tight closure of the dentition);
- detect anomalies of the dental system organs;
- determine the position of erupting wisdom teeth.
As a rule, radiography is prescribed before the start of orthodontic treatment, when planning implantation and prosthetics, before and after filling the tooth canals. This study is also used to evaluate the results of conservative and surgical treatment.
Free consultation
30-40 minutes
inspection and diagnostics
treatment plan and cost
Make an appointment
Frequently asked questions from patients
Are x-rays harmful?
Radiography is based on radiation exposure. This sounds quite threatening to the average person. Meanwhile, every person receives a dose of radiation every day, even our bodies are radioactive. The background radiation level per day is 10 μSv (microsieverts). To obtain 4 photos with a bitewing X-ray, the patient receives 20-51 μSv. A panoramic image gives 5-25 μSv. CBCT is accompanied by a higher radiation dose; in one session a person receives from 20 μSv to 700 μSv. The level of radiation will depend on the settings and type of device, and the width of the area being studied.
Thus, there is no direct threat in the procedure. However, radionuclides can accumulate, so diagnostics are prescribed if necessary. After the session, the radiologist must write down how many sieverts the patient received, this will make it possible to calculate the next dosage with minimal harm to the person. After the examination, it is advisable to eat more carrots, apples, radishes, beans and citrus fruits. These products will help remove radionuclides from the body.
How often can it be done
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
The type of x-ray and its frequency depends on the condition of the oral cavity and the complexity of the treatment. It is better to do CBCT no more than 3 times a year. Bitewing film photographs are prescribed no more than 7 times a year; the new technology uses lower radiation doses, so there may be more digital diagnostics. The acceptable norm is 7 diagnostic studies per year. When changing dentists, it is not necessary to take new photographs; it is enough to take the ones you already have with you to the appointment. If digital data has been lost, it can be requested from the clinic that conducted the examination. CBCT results are stored for up to a year in the archives of medical centers.