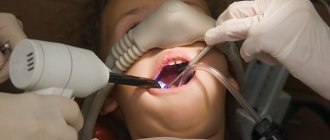
Many people have heard that it is possible to perform dental treatment under general anesthesia. This practice is especially often used in pediatric dentistry, when it is necessary to carry out a large amount of dental work, and the child does not communicate well with doctors or is simply afraid. However, sometimes patients confuse the concepts of dental treatment under sedation and treatment under anesthesia - these are two completely different methods.
Pediatric anesthesia in dentistry
First, let's figure out what anesthesia is. This is a reversible inhibition of the activity of the central nervous system, which we cause artificially.
Narcosis is characterized by:
- falling asleep and decreased reflexes;
- loss of consciousness and muscle relaxation;
- complete absence of painful sensations.
Translated into simple language, this means that during general anesthesia the child falls deeply asleep, lies motionless during the procedure and does not feel anything. And after waking up he doesn’t remember anything.
They are immersed in this state using a combination of several drugs, which ensures safety and comfort for the baby. At the same time, safety comes first. Modern methods of general anesthesia completely eliminate the negative impact on the mental and physical development of a small patient.
Unlike adult dentistry, in pediatric dentistry there is no intermediate option between superficial sedation and anesthesia. This means that for children under 16 years of age there are only two options for “sleep treatment”: superficial sedation, when the child remains awake during treatment, and general anesthesia (endotracheal anesthesia). This is due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of children. Because of them, deep intravenous sedation is impossible.
Expert opinion
Emir Romanovich Omerelli
Maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist
Experience: more than 13 years
To exclude the development of complications, before starting treatment it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination: ECG, X-ray of the lungs, consultations, if necessary, with a therapist, cardiologist and other doctors, collection of blood tests. All this is important to fully assess the patient’s condition and select the optimal type and drug of anesthesia.
They are as follows:
- Mask (inhalation), which is carried out by the patient inhaling a mixture of oxygen and anesthetic gases through a mask. This type of anesthesia is often given to children;
- Intravenous. By introducing anesthetic drugs into the blood.
Dental procedures that can be performed under general anesthesia:
- Removal of a tooth cyst;
- Removal of several wisdom teeth;
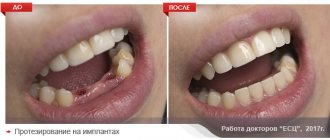
- Multiple dental implants.
Should children undergo dental treatment under anesthesia when they cry?
If your baby cries at the dentist, he may just be very emotional. And then, to calm him down, kind words are enough.
An experienced doctor knows how to find a common language with children, and there are usually no difficulties with treatment. There are many adaptive techniques when the doctor explains to the child in a playful manner that treatment is interesting and not painful at all. In addition, to cope with your baby’s fear, you can use the help of a psychologist.
If these methods do not help, then you can try the procedure under sedation. It muffles fear and temporarily dulls the baby's reactions.
Tears are not a good reason to perform dental treatment under anesthesia in children. It is worth resorting to it only if other methods of “agreeing” have not been successful. Anesthesia in pediatric dentistry is used if there are indications for it.
Treatment of baby teeth under anesthesia is carried out:
- if it is impossible to establish contact with the baby;
- dental treatment for children under 3 years of age;
- allergies to local anesthesia;
- mental illnesses or nervous system disorders: schizophrenia, epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, cerebral palsy, mental retardation;
- insurmountable fear of dental treatment (scientifically called dentophobia);
- strong gag reflex, which interferes with the treatment of distant teeth;
- extensive surgical operations: complex tooth extraction, abscesses, periostitis, lymphadenitis, serious jaw injuries.
When children should not use anesthesia for dental treatment:
✔
during the acute course of the infectious process;
✔
with decompensation of severe chronic diseases.
In general, there are no absolute contraindications to general anesthesia in children. Sometimes you just need to wait for the right moment or choose the most suitable technique. If the baby has an acute situation - pain or injury - there is always the opportunity to safely and comfortably undergo treatment under anesthesia.
Contraindications
Even with the use of modern anesthesia, which is due to excellent tolerability, a minimal percentage of complications and side effects, general anesthesia has a number of strict contraindications. The need for a one-stage large-scale correction of the dentition can delay or even make the presence of severe pathologies or certain physiological conditions inaccessible.
Thus, the following situations are unconditional contraindications for general anesthesia in dentistry:
- severe pathologies of the cardiovascular system in the acute and subacute period (myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, cardiac arrhythmias of various etiologies, uncompensated heart failure);
- dysfunction of the respiratory system (bronchial asthma, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a severe clinical stage), which is characterized by complete or partial obstruction that disrupts normal breathing;
- acute cerebrovascular accidents;
- the presence of acute infectious diseases;
- pregnancy in the 1st and 3rd trimester;
- state of alcohol or drug intoxication;
- consuming food and drinks before the scheduled procedure;
- psychiatric diseases in the acute period.
Some contraindications can be considered relative, since they can be easily eliminated, which in the future will allow dental correction to be carried out in full and painlessly, thanks to the effects of general anesthesia. Recommendations for preparing for the upcoming operation will definitely be given by the anesthesiologist at the clinic where treatment and dental restoration are planned.
How to prepare a child for dental treatment under anesthesia
- Before treatment, you should consult with an anesthesiologist. This can usually be done over the phone, but in some cases a face-to-face appointment is required.
To correctly administer general anesthesia, the anesthesiologist will need the following information:
- child development history;
- allergic reactions;
- past acute and chronic diseases;
- previous medical interventions and hospitalizations;
- anthropometric data (age, height, weight).
To clarify the child’s health status, you will need to undergo a series of tests. The anesthesiologist determines the full scope of the required examination based on the characteristics of the small patient and the type of upcoming treatment.
- Before anesthesia, diet is very important. The safety of anesthesia depends on its compliance.
The child who will best tolerate anesthesia is the one who:
- did not eat “heavy food” during the 6 hours preceding treatment;
- 4 hours before the procedure I had a snack;
- I drank water 2 hours before.
Dietary recommendations may vary, so the final meal plan will be discussed in consultation with the anesthesiologist.
- To help parents not be nervous, I also recommend asking the anesthesiologist what his qualifications are and what equipment he will use during the procedure. You definitely shouldn’t be embarrassed about such questions. Doctors with experience in pediatric anesthesiology should work with children, since the structure of the child’s body and its functioning have their own characteristics.
How is dental treatment performed for children under anesthesia?
During treatment under general anesthesia, the child does not feel anything. And he doesn’t remember anything after waking up. This is achieved by a combination of drugs. The main one among them is Sevoran.
The combination of drugs and their doses are calculated individually for each child. In this case, the doctor takes into account the age, weight and characteristics of the small patient. The use of combinations of anesthetics makes it possible to minimize their doses and carry out a high-quality and safe procedure.
The child falls asleep after a few breaths through the mask of the anesthesia machine. This happens in the arms of the mother. We perform induction of anesthesia as comfortably as possible for the baby. If a child comes with his favorite toy, we show her by example: inhalation from a mask is not scary.
In cases where parents warn the anesthesiologist that even a mask causes negative emotions in the child, premedication can be used. Then we administer a mild sleeping pill to the baby in the form of nasal drops, after which the child plays or watches cartoons for 30-40 minutes and gradually falls asleep in his mother’s arms. And then we begin induction of anesthesia.
An anesthesiologist and a nurse anesthetist are responsible for administering general anesthesia. Their interaction ensures the safety of the child. The baby is under constant control, precisely calculated doses of drugs are administered at the appropriate time. It takes approximately 30 minutes in addition to the treatment time for the anesthesiologist to induce anesthesia and wake up.
Reviews from parents and impressions of children
Irina
Dental treatment for a child under anesthesia is very exciting for parents. My daughter is only 4.5 years old, so I was looking for the best specialists. And I found it. Many thanks to the anesthesiologist at the Azabuka clinic, dentists and all the staff. Everything went just fine and with minimal stress for the parents. Thank you for helping!
I put Aza&Buka:
5
Anna
Alexandra and Evgeniy
We often visit Aza&Buka dentistry - we regularly bring our children for preventive appointments and dental examinations. I like the warm, even bright atmosphere in the offices and corridors, and especially the doctor. The clinic’s doctors are excellent specialists and even better psychologists. They easily negotiate with children, they immediately became friends. We recommend!
I put Aza&Buka:
5
Zhenya
Irina
The first appointment was planned in detail: we talked with our daughter, watched the video website. Lisa really liked the funny characters Aza and Buk, and at the appointment she only talked about them with the doctor. I decided that I would take care of my teeth like Aza and sat calmly in the chair throughout the entire appointment. Great idea, great execution. And the doctors are just great.
I put Aza&Buka:
5
Dasha
Svetlana
We were looking for a sincere and good doctor for our Vasya. The diagnosis of cerebral palsy often became a reason for refusal. The child is complex, the doctors could not find an approach. We have already started thinking about treatment under anesthesia. Aza&Buka dentists offered sedation, treatment while half asleep - they kindly and calmly agreed with the child. The teeth were cured quickly - without whims or fear. Thank you!
I put Aza&Buka:
5
Vasya
What is rehabilitation like after treatment under anesthesia?
After waking up from anesthesia, in the vast majority of cases, children feel well. Most often, the only thing that bothers them is numbness in the areas where the local anesthetic was injected.
As for behavioral changes, there are three types:
- excitement - the baby may be capricious and cry. This is accompanied by increased activity. But it quickly gives way to fatigue;
- fatigue - the child wants to sleep, refuses to eat, sits in the arms of the parents;
- no behavioral changes after waking up.
The first two scenarios are typical for children under the age of 7-10 years, the third - for adolescents and adults.
Hyperactivity and agitation upon awakening are unpleasant for both the child and those around him. To avoid it, we try to implement the second scenario; to do this, we put the baby to sleep and wake him up gently.
The child can eat immediately after waking up, unless the anesthesiologist gives other recommendations.
Very rarely, recovery from anesthesia is accompanied by nausea or a feeling of motion sickness. This lasts no longer than 2-3 hours. This reaction is typical for children who get motion sickness in transport. In this case, you will be able to eat and drink within an hour or after the nausea has passed.
There is no need to worry about the postoperative period - the anesthesiologist will always be in touch.