21.07.2021
Author: Dentist-periodontist, therapist Stopinskaya Ulyana Yurievna
Modern dentistry is impossible without reconstructive surgical interventions. Almost all of our patients undergoing dental rehabilitation have encountered one type of surgical treatment or another: implantation, closing recessions, replanting grafts, etc. The success of such treatment depends on many factors. We will look at some of them in more detail.
To begin with, it should be noted that for quick and high-quality healing, the doctor must meet the following conditions:
- Healing by primary intention (bringing together the edges of the wound with sutures). Wound healing refers to all the physiological and regenerative processes that occur when restoring the integrity of damaged tissues. Surgical wounds are created under relatively controlled conditions, i.e. The surgeon can influence certain factors to a certain extent, for example, the type of incision, the method of creating the flap, the width of the receiving bed, and the method of suturing.
The photo shows a view of the wound on the 14th day after surgery. The seams are visible. Healing by primary intention.
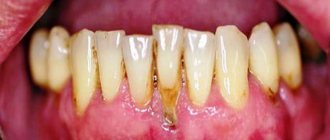
- Good blood supply to the intervention area . The difficulty of healing after implantation or plastic periodontal surgery is often due to the fact that the wound is located in the projection of the surface of the tooth or implant, which does not contain blood vessels. This reduces local immunity and makes it difficult to deliver nutrients.
- Cleanliness in the intervention area. The oral cavity is colonized by a large number of bacteria that can directly affect wound healing. The doctor must ensure that on the eve of the operation the patient undergoes professional hygiene and is trained in postoperative oral care.
The photo shows the view before and after professional hygiene
Now let's take a closer look at the factors influencing wound healing. They can be divided into general and local.
Causes of sores in the mouth
Purulent ulcers in the mouth can appear for various reasons. They are often the result of dental diseases.
The list of reasons may include the following:
- viral infections (herpes simplex or herpes zoster);
- fungal and bacterial infections;
- irritation of the mucous membranes from smoking and certain foods (nuts, cheese, citrus fruits);
- ulcerative stomatitis;
- chemotherapy drugs;
- frequent stress and nervous tension;
- oral injuries;
- hormonal changes.
The occurrence of ulcers due to diseases/damage to the soft tissues of the mouth and tongue
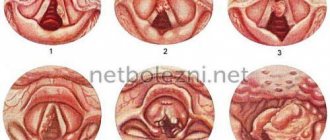
1. Recurrent
aphthous stomatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that is characterized by periodic eruptions of aphthae (small ulcerations) on the oral mucosa. Aphthae can be localized on the tongue, buccal mucosa, hard and soft palate, and also on the mucous membrane of the lips. They are painful. In some cases, with constant injury, aphtha can turn into a long-term non-healing ulcer, after epithelization of which a scar is formed.
Patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis usually suffer from colitis. Nervous strain, minor injuries to the mucous membrane, for example, when brushing teeth, as well as menstruation, can also predispose to the onset of the disease. The aphtha heals within 7 - 10 days. In case of complications of the disease, the number of ulcerations may increase, then the healing period is extended by 2 - 4 weeks.
2. Herpetiform stomatitis
characterized by the appearance of numerous small ulcers. In appearance they resemble the sores of herpes simplex. As a rule, they occur in women under 30 years of age. They are localized mainly on the lower surface of the tongue and in the area of the floor of the mouth. They do not have clear boundaries, the base is gray. The healing process is completed largely without scarring within 7 to 10 days. In simple forms of stomatitis, white ulcers in the mouth are observed (or rather, the center of the ulcer is covered with a thin, loosely fitting white or grayish film). Also, a white ulcer in the mouth can form in children in cases where there is candidal, or fungal, stomatitis.
As for the treatment of stomatitis, in this case the form of the disease and the severity of the lesion are taken into account. General and local treatment depends on this. But for almost all forms of stomatitis, vitamin C is prescribed to improve immunity.
3. Recurrent necrotizing peryadenitis
(Setton's aphthae) is characterized by the formation of a compaction in the submucosa, then painful ulcers with raised and compacted edges form in this place, as well as the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate (accumulation of cellular elements mixed with blood and lymph). Ulcers are localized on the upper and lower lips, cheeks, and lateral surfaces of the tongue. Eating food becomes extremely difficult for many patients, even to the point of giving it up. The same severe pain can be observed when talking. The ulcers do not heal until several months, and the disease lasts for years.
4. Afty Bednar
occur exclusively in children and are defined as traumatic erosions (ulcerations). The cause is poor oral hygiene or rough mechanical rubbing of the mucous membrane of the palate (this is where they are located). Covered with a whitish-yellow coating.
5. Traumatic ulcer
in the mouth is most often the result of physical impact, hence its name. As a rule, such an ulcer occurs as a result of an accidental or intentional bite of the mucous membrane, damage by a toothbrush. The presence of a traumatic ulcer in the oral cavity can provoke dental treatment (with careless use of dental instruments or, for example, with pointed temporary crowns).
Also among traumatic ulcers are the so-called prosthetic ulcers, which arise from exposure to complete or partial removable dentures, the dimensions of which are larger than necessary, or their surface is poorly processed and has sharp edges. Such ulcers can be located directly under the prosthetic structure. As a rule, healing takes place within 10 - 14 days, provided that the traumatic factor is eliminated. Treatment may not be necessary, since traumatic ulcers are often painless and small in size. In the case of the opposite, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and the use of an ultrasonic brush is recommended, which not only cleans, but also has an antibacterial effect.
Also, the presence of ulcers can be caused by the effects of alkalis, acids, and certain medications on the oral mucosa.
How can you get rid of sores in your mouth?
How to treat wounds in the mouth if they appear and cause discomfort. Initially, you need to determine the true causes of their occurrence. This will help not only choose the right treatment, but also reduce the risk of relapse. If simply stomatitis has formed, it is not difficult to recognize it, but a purulent wound in the mouth of unknown pathogenesis is a reason to consult a doctor. Particular attention should be paid to lesions that do not heal for more than 10 days.
For a quick recovery, use:
- medicinal ointments with anti-inflammatory effect;
- antibiotics if the cause is a bacterial infection;
- complex of vitamins;
- rinsing with oral antiseptics;
- protective applications;
- painkiller injections;
- laser cauterization.
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis is a chronic pathology characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa. Its main symptom is a rash of aphthae or ulcers, which are noticeably painful. Aphthae usually appear periodically in the following areas:
- Language;
- Cheeks;
- Hard and soft palate;
- Mucous membrane of the lips.
If ulcers are periodically injured, they can develop into full-fledged, difficult-to-heal wounds, in place of which noticeable scars remain. The normal healing time for aphthae is no more than a week from the moment of its appearance.
The prerequisites for the occurrence of aphthous stomatitis are as follows:
- Chronic colitis;
- Diseases of the nervous system;
- Chronic stress;
- Injury to the mucous membrane;
- Hormonal imbalance during menstruation.
With a normally functioning immune system, ulcers heal on their own in one, or in extreme cases, two weeks. If healing does not occur, you must visit a doctor to prescribe the correct treatment. As a rule, the basis of therapy is taking vitamin C, which has a positive effect on the immune system.
Tuberculosis of the oral mucosa
Tuberculosis of the oral mucosa is a complication of standard pulmonary tuberculosis. The cause of the pathology is the penetration of bacteria into the oral cavity through damaged soft tissues. Localization of ulcers occurs in the following places:
- Cheeks;
- Language;
- Floor of the oral cavity.
At the affected sites, standard tuberculous tubercles first form, and then ulcers appear in their place. They do not heal and gradually increase in size. Aphthae are shallow, but very loose with slight bleeding. Their edges are soft, but despite this, the ulcers are noticeably painful.
Usually, along with the appearance of tuberculous ulcers, the patient feels a general deterioration of his condition, which manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- Loss of appetite and weight;
- The appearance of a white coating on the tongue;
- Sweating;
- High body temperature.
Treatment of such a pathology involves staying in a special closed dispensary. As a rule, during the period of weakening of the symptoms of the disease, sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out, as well as treatment with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs.
Special recommendations for the treatment of white ulcers on the oral mucosa
To quickly get rid of unpleasant ulcerations in the mouth, you need to follow a diet. Your diet should include vegetables, fruits, red meat, and fish. It is important to avoid spicy and sour foods, such as citrus fruits, until complete recovery. Any rough food (nuts, etc.) that can injure the mucous membrane is also excluded. Sweets (cakes, jam, chocolate), crackers, chips, coffee are also prohibited.
It is important to pay attention to the quality of the water consumed. The heavy metal salts and other impurities it contains can cause constant bleeding from the gums and contribute to infection. If the pathology is provoked by some disease, it is necessary to eliminate it.
Afty Bednar
Bednar's aphthae is the appearance of small wounds on the oral mucosa. The pathology manifests itself exclusively in children due to poor hygiene or accidental injury.
The location of the ulcers is the palate. They have a slightly yellowish coating and heal quite quickly - up to 5 days. For the pathology to go away, it is enough to normalize oral hygiene.
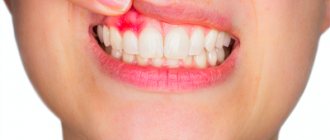
The gums become inflamed due to insufficient oral hygiene and lack of regular visits to the dentist. The result is an excessive accumulation of plaque on the teeth and pathogenic microorganisms. Pathogenic microorganisms trigger a process in which their own toxins and inflammatory mediators are generated. Treatment of diseases of the mucous membranes and gums with the Vector device
Acute necrotizing gingivostomatitis
Acute necrotizing gingivostomatitis is a viral infectious pathology in which ulcers form on the surface of the entire oral mucosa, including the tonsils. The prerequisites for this disease are:
- Deterioration of the immune system;
- Injury to the oral mucosa;
- Lack of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- Chronic severe fatigue;
- Sudden hypothermia;
- Complication of ordinary stomatitis or viral pathologies.
The risk group is mainly men under 30 years of age. Ulcers are wounds with a loose bottom, uneven edges and a dirty green coating, which has an unpleasant odor and can be easily removed if desired. All the soft tissues around them are swollen and inflamed, and the wounds themselves bleed slightly. As a rule, the appearance of such ulcers is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Acute pain while eating and talking;
- Very bad breath;
- Heavy secretion of saliva;
- A sharp increase in body temperature;
- Swelling and soreness of the gums;
- Bleeding gums;
- Yellowish plaque on the surface of the gums.
Treatment of the disease should be carried out under the strict supervision of the attending physician. The treatment regimen depends on how poorly the patient feels and at what stage the disease is. Typically treatment involves the use of:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- Antiallergic drugs;
- Vitamins C and R.
Additionally, the inclusion of high-calorie food and drink in the diet is prescribed. Sometimes, if necessary, heart medications are added to the treatment regimen.
Local treatment of pathology is also carried out by surgical removal of damaged tissue under anesthesia. After this, the oral cavity is treated with anti-inflammatory, antiseptic drugs, as well as a solution of white clay. When a positive result is achieved, professional oral hygiene is performed.
White ulcer on the oral mucosa: how to deal with the problem
White sores in the mouth appear quite often. Although the problem cannot be called critical, it causes significant discomfort. Difficulty talking, chewing, swallowing and smiling. In some cases there is pain. Therefore, everyone who has ulcerative formations wants to get rid of them as quickly as possible. In this case, you cannot self-medicate. To determine the cause of the ulcers and prescribe effective therapy, it is necessary to undergo examination by a specialist.