11/24/2017 As you know, a person’s teeth grow twice throughout their life. By the age of 6-7 years, the primary bite is fully formed; by the age of 12-13 years, “children’s teeth” are replaced by “adult teeth” - by this time the formation of a permanent bite is completed. Somewhat later, up to the age of 20, 4 more “wisdom” teeth may grow. Their name reflects the late period of growth. They are the last in the row, but very often there is not enough space for them and their growth is associated with many problems.
How do dental tissues develop in humans?
Anatomically, a human tooth consists of a crown, neck and root. The visible part of the tooth is surrounded by hard tissues - enamel, dentin and cement, which protect the soft tissue - pulp. It extends from the crown of the tooth to its roots, has a large number of vessels and nerve endings and is directly involved in the nutrition of the entire tooth. Unfortunately, all tooth tissues undergo age-related changes, so in this case we are dealing with complex aging.
Dental development begins in the prenatal period. Already in the second month, the fetus develops an oral cavity with a dental plate. The rudiments of baby teeth form on it. By the fourth month, clear cell differentiation occurs. We can find anameloblasts, which are responsible for the formation of enamel, and dentinoblasts, which form the basis for dentin. By the sixth month, the outer and inner layers of dentin with a network of tubules are formed, and the gradual formation of pulp occurs, in particular the formation of collagen fibers.
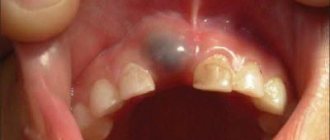
If a new tooth does not grow in place of a baby tooth
The loss of baby teeth, as well as their appearance, does not occur simultaneously, but in accordance with the development of the jaws and the growth of permanent replacement. The concept of a protracted renewal is quite relative, because for some the radical will show itself in a week, and for others in a month or two. And in the second case, we are not always talking about deviation.
Often baby teeth are “pushed out” by molars, which almost immediately make their way out, but if a child’s tooth falls out and a new one does not grow and is not visible, you need to wait a few weeks.
Reasons to see a doctor:
- lack of replacement 2-3 months after the loss of a baby tooth;
- swelling and redness of the gums, pain without signs of germination of a molar;
- sequential loss of other teeth without the appearance of new ones.
Reasons why a child’s tooth does not grow for a long time:
- Infectious diseases, including past ones.
- Lack of calcium in the body.
- Oral diseases.
- Mechanical injuries.
A child’s tooth has fallen out and is not growing, but the situation does not correspond to the reasons indicated? Perhaps the delay is provoked by poor ecology, incorrect or poor-quality diet, stressful situations, or even genetic preconditions.
Until what age do human teeth grow?
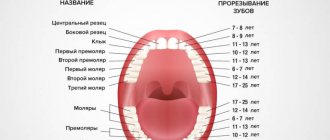
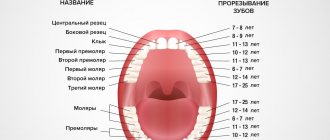
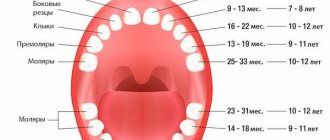
Baby teeth begin to erupt before one year of age. As a rule, at 2-2.5 years a child receives a full set of baby teeth. The molars are located immediately behind the milk teeth: between them there is a partition that is destroyed during the eruption of permanent teeth. The change of teeth in a person begins at the age of 6-7 years: the upper incisors usually fall out first. The milk bite is replaced by a permanent one at about 12-13 years of age. Molars develop more slowly than baby teeth, and the roots of wisdom teeth can continue to form up to 23 years of age and even later.
Typical problems
Usually in this age period the formation of the dental-jaw system proceeds without problems. There is not a single temporary tooth left in the mouth of a twelve-year-old child, and this period is the most favorable for treating malocclusion with braces. Since jaw growth begins to slow down by the age of 15, orthodontic treatment must be carried out before this age in order to avoid the removal of permanent teeth.
Lack of space for the eruption of the canine and permanent premolars occurs if temporary molars were removed in childhood and the corresponding correction was not carried out. The canine is the last one to erupt and it is the one that lacks space. Crowding of teeth is formed in the anterior part of the jaws and the fangs in this case can erupt closer to the lip outside the dental arch.
The formation or aggravation of crowding of teeth is possible in the case of incorrect location of the rudiment of the third molar on the lower jaw. As a result, the pressure exerted by the wisdom tooth on the second molar can lead to an anterior displacement of the entire dentition. Since there is not enough space in the row for an incorrectly positioned wisdom tooth, its complete eruption is impossible. And its retention, that is, incomplete eruption, leads to poor oral hygiene and, as a consequence, the development of carious processes both on the eighth tooth and on the adjacent second molar.
Age-related changes in dental growth and development
As soon as teeth (both milk and permanent) begin to erupt, they become vulnerable to the external environment, but at the same time they acquire a protector in the form of saliva, which not only helps destroy bacteria, but is also directly involved in saturating the teeth with various minerals. The first to experience age-related changes are enamel and dentin. Every year, due to the erosion of enamel, our teeth decrease in height. The average is about 0.035 millimeters per year, but some people experience increased tooth wear due to anatomical features and bad habits. The color and structure of the enamel change: more and more dyes accumulate in it, which leads to yellowing and loss of shine. Cracks and microdamages form on the surface of the enamel, where plaque penetrates. Over time, it mineralizes and prevents the penetration of organic substances and beneficial microelements into the enamel. It should be remembered that enamel cannot be restored, so in case of damage or illness, you should consult a doctor promptly and not wait for complications to arise. As for dentin, over the years it regenerates more and more slowly, and the quality of replacement dentin also becomes worse.
University
DOSSIER 'KP'
Naumovich Semyon Antonovich, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor. 1990-1994 – Deputy Dean of the Faculty of Dentistry. In October 1991, he was elected to the position of associate professor, from 1993 to the present time he has been the head of the department of orthopedic dentistry of BSMU. Author of more than 500 scientific papers, including 9 co-authored monographs, 12 patents.
— Semyon Antonovich, is it true that Belarusians have bad yellow teeth because of chlorine water from the tap?
— Teeth are primarily heredity, genes, even how the fetus developed in the womb is important. But after birth, nutrition and lifestyle come to the fore. Health depends primarily on yourself, and only 11-12% on medicine. Environment, nutrition, lifestyle - these are the three pillars on which health rests.
In addition, dental health can be improved. The republican prevention program contains the main idea - the use of fluoride preparations, it strengthens the enamel. To strengthen teeth, fluoridated table salt is produced in Mozyr.
From 2003 to 2008, I was the chief dentist of Belarus, the main thing is that we did not destroy what was accumulated during the Soviet era: even now in kindergartens and schools, children are examined by dentists, preventive measures are carried out, they are taught oral hygiene, and, if necessary, treatment. If it weren’t for this, our dental health indicators - the KPU index: caries-filling-extracted tooth - would be much worse. Today we are leaders in the post-Soviet space.
There are WHO requirements for each age regarding the number of remaining teeth. Let's take the indicative age category of 65-74 years: the latest European requirements for this age are 20 teeth. But our indicator is quite high: in 2013-2014, Belarusians of this age had up to 15 teeth.
- Is it true that Americans have good white teeth because they eat and drink everything with ice?
— No, rather because a small filling there costs about 100 dollars. The patient is motivated to get a filling, because the next stage is a crown for $600. And if you engage in prevention from a young age, you may not have to pay.
A lot depends on the person himself: how he takes care of his oral cavity, whether he brushes his teeth correctly, chooses a brush and paste. Universal advice - which is better? - no: each has its own characteristics, it all depends on the condition of the mucous membrane and enamel.
“It happens that young people remove 15-20 teeth”
— I heard that every tooth pulled out brings a person closer to old age: they say, the brain receives a signal and rearranges its work...
— The absence of even one tooth is of great importance, especially if it is a front one. But the absence of the so-called “six” is also a problem. If the defect is not closed, the neighboring teeth begin to move, and this is due, as you say, to signals from above. Teeth can move vertically, transversely, or in any other direction - along the line of least resistance. They can also shift at an angle of 5-7 degrees. As a preventative measure, we recommend making a temporary prosthesis – popularly called “butterflies” – to close the defect so that the teeth do not move. And then decide: to make an implant or a bridge based on nearby teeth.
— But the absence of one tooth is not an indication for intervention, or would you still not advise leaving even one hole?
— I wouldn’t recommend it, especially the sixth teeth. As a rule, they are the first of the permanent teeth to appear and the first to wear out; the load on them is colossal. When they are removed, people sometimes do not pay attention and live without a tooth. And after 10 years they come to us with complaints: “Doctor, the muscles on my face hurt.” If a person has lost key teeth, deformation of the dentition begins, and the temporomandibular joints become sensitive. The absence of even one tooth will manifest itself as unpleasant symptoms within 4-7 years.
— Some people are afraid to insert implants - it’s an operation! – especially now, when the number of cancer diseases is growing. And it’s scary to put on “crowns” - they say the teeth under them rot and collapse...
— If the supporting crowns are made with high quality, there will be no damage for 8-10 years. Yes, if the crowns are made poorly - we call them “pans” - a “greenhouse effect” develops under them: food and saliva get in, which leads to tooth decay.
Implants can be installed if the patient has sufficient bone tissue, the bone structure allows for manipulation and there are no contraindications. These include diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases, and cancer.
Another contraindication is severe forms of periodontal disease, previously called periodontal disease. This is the exposure of the gingival margin, loss of bone tissue, loose teeth, which we most often remove. With such a disease, the implantologist will also refuse you: your own tooth does not take root, how will someone else’s tooth take root? Periodontal disease - when the bone is lost, but the tooth is intact, but must be removed - this is scary. Here, first of all, professional hygiene is important: removal of dental plaque and anti-inflammatory therapy of the gingival margin. Removing visible tartar is easy, but there are also stones under the gum. Sometimes it’s so far away that you can’t take a picture right away. Then they perform a patchwork operation: they peel off the gingival margin and this is the only way to remove the stone. Otherwise, it will mechanically destroy first the gum and then the bone.
The first signs of such a problem are bleeding gums, both while brushing your teeth and without. Plus visible changes: swollen gingival margin with a bluish tint. To recognize the problem at an early stage, every self-respecting person should go to the dentist twice a year.
- But they say that exposure of the roots of the teeth is an age-related feature, no?
— Yes, but often there is also a general pathology, for example, diabetes, blood diseases, and thyroid diseases. Young people with such diagnoses come to us at both 25 and 27 years old. I write the conclusion: “Remove 15-20 teeth.” And even more! There are teeth, but there is no bone tissue where they would be fixed. The teeth move even from a “gust of wind.” As a rule, we provide prosthetics for such patients only with removable dentures.
“If a dentist enters the profession with a counter in his eyes, he will not make a good specialist.”
“But even in such situations, when all the teeth have been removed, there is no need to panic. Yes, you need to get used to removable dentures, but life goes on. Let me give you the example of my grandmother: she had full dentures made in 1933, she was only 35 years old. As a result, she lived happily for 97 and a half years, 60 of them with complete dentures. When I offered to make her new ones, she just waved her hand: “They don’t make them like that now...” But I still reconstructed them several times, since such prostheses must be remade every 5-6 years. And as a specialist, I understand well that she would never have lived this long without them...
— I have a friend who, before leaving for America about 10 years ago, made himself new teeth: he pulled out his own and inserted beautiful, white implants. Two years later, the first thing that caught my eye was how his face had changed, how it was swollen or something. He complained: his joints hurt and it was difficult to eat. Is this poor-quality work or is it rather the body’s fault that it rejects something foreign?
- More likely, both. Unfortunately, this happens. The first attempts to make implants began in Minsk at the 13th dental clinic back in 1989. I then worked as deputy dean of our dental faculty, I was appointed chairman of the commission for evaluating those first experiments. The methods were rather weak, but our specialists were trained in Vilnius. The first steps were with problems, today I understand that those implants were not installed very well...
But 26 years have passed, and today there are practically no such problems, we are among the world statistics: implants serve the patient for 9-12 years or more. Yes, it happens that patients come to us - they were promised a lot, implants were installed, then crowns were made on them, people paid a lot of money - and after a year we remove and remove everything. It happens that prosthetics are carried out with numerous errors: in the upper jaw, for example, the implant is removed into the maxillary sinus, in the lower jaw - into the mandibular canal, inflammatory processes begin. But, thank God, such cases are rare.
The best school graduates come to our dental faculty, over the last 10-15 years - with a score from 370 to 400. Previously, the medical faculty was the best, now we have practically no competitors. We train general dentists who, after graduating from university, not only have good theoretical knowledge, but also have excellent practical skills in all areas of dentistry.
— It’s logical, I heard that dentistry is the easiest way to earn good money in medicine, the main thing is to open your own private office.
— Unfortunately, I also hear about this often. But this is not such an easy bread, it is associated with occupational hazards and great psychological and physical stress. If a person enters a profession with a calculator in his eyes, he will not make a good specialist...
“We once reduced the size of the lower jaw.”
“I would never have thought that a beautiful smile can be achieved with the help of braces: a person hasn’t smiled for half his life because of ugly, uneven teeth, and then one day he starts to shine!”
— I have been dealing with this problem for almost 40 years. When I started working in the late 70s, there was only one orthodontist in the entire Minsk region. At the regional dental clinic, he saw 80 patients in 6 hours of work: 40 patients had impressions taken, 40 had ready-made orthodontic plates applied. There were no braces yet, only removable devices.
Nowadays, with the help of braces, you can manipulate your teeth and dentition quite widely: move, reduce, expand. But braces can be used when the bite is formed: no earlier than 11-13 years.
In complex cases, an integrated approach to the treatment of such patients is needed. First, they undergo preparatory surgical operations. So, for a student from Syria - his chin protruded four centimeters forward - my teacher, Professor Chudakov, and I reduced the size of the lower jaw. And only then they installed orthodontic devices, straightened the remaining teeth and completed the treatment with dentures.
—What incident impressed you the most?
“Once a LAZ driver came to me; there were buses like this that were produced in Lvov. The rotating iron handle of the starter crushed half of his face, knocking out almost all his teeth, along with the alveolar processes (the part of the jaw where teeth grow from). My teacher, Professor Velichko, and I restored his jaws and made luxurious ceramic removable dentures. Later, years later, he came and thanked them for helping him improve his life: he got married and looked great.
I also remember when I was just starting to work, a young man approached me and asked me to do his wife’s teeth. They looked and gasped: she had 28 rotten roots and not a single tooth. And she is only 25 years old! We had to remove all the remains, it was impossible to restore them, and make removable ceramic dentures. In those days, no one did implants in our country. It turned out that my husband didn’t even know what was in her mouth, and we didn’t tell him either. She was a nice girl, I remember, I also advised her: “You know, don’t take them off at night - just for hygiene - don’t let her know anymore...”
Photo: DMITRY LASKO Komsomolskaya Pravda , February 9, 2016
Age-related changes in dental pulp
Regressive and age-related changes in the dental pulp also affect dental health. Over the years, the pulp decreases, and fibrous changes are often observed in its tissues. Mineral deposition negatively affects the condition of blood vessels and capillaries. Atherosclerosis of pulp vessels occurs in many people over 50 years of age. Because of this, tooth tissues no longer receive proper nutrition, which is why they become more fragile and vulnerable. Many people are interested in how to determine a person’s age by looking at their teeth. Only a medical examination can provide more or less accurate data. It is very difficult to determine a person’s age by looking at their teeth, since even relatively young people’s teeth can be in very poor condition, and vice versa.
Pathological causes of delay
If a child’s teeth have fallen out and new molars do not grow for a long time, the reasons for the delay should be sought in pathologies:
- Retention is a complete or partial delay in eruption. Partial retention is observed when the crown of a molar tooth appears in the socket of a milk tooth, but growth stops there. Often the cause is early loss of a baby tooth, accidental or surgical. That is, a replacement for him has not yet been formed.
- Adentia – absence of teeth. This rare problem is common in older people, but can also occur in children. As a rule, it is triggered by taking strong medications during pregnancy.
Age-related changes in bone tissue and gums
In addition to age-related changes in teeth, over the years a person, as a rule, decreases bone density and its height. Osteoporosis of the jaw often occurs in older people. The clinical picture is aggravated by adentia (partial or complete) and poor-quality dentures, due to which the distribution of the chewing load is disrupted. Changes can affect not only hard but also soft tissues. Age-related gum recession occurs both due to previous diseases (for example, periodontitis), and due to poor genetics, poor lifestyle and bad habits, especially smoking. At an advanced stage, this leads to loosening and loss of teeth.
No teeth at one year of age
Why does a child’s teeth not grow after a year of life?
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Unsuitable climate.
- Poor quality of food and water.
- Diseases and infections.
- Vitamin and calcium deficiency.
To dispel or confirm suspicions, you need to take your baby for examination to a therapist and dentist. To determine the causes of delayed jaw development, blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound examinations of organs, and testing of thyroid function may be necessary. To exclude edentia (lack of teeth) from the diagnostic field, fluoroscopy is performed.
How can you avoid age-related changes with the help of modern dentistry?
Even though our teeth age along with the rest of our bodies over the years, this does not mean that it is impossible to maintain an attractive and healthy smile in old age. Rule number one is good daily hygiene. Rule number two is regular preventive visits to the dentist. Professional cleaning will help remove hard plaque and prevent the development of caries, and the remineralization procedure improves the condition of the enamel. Laser and physical therapy are now actively used to strengthen gums, therefore, if you have problems with periodontal disease, it is recommended not only to visit a specialized specialist, but also to monitor the health of your gums at home. Rule number three is a balanced and healthy diet, coupled with taking vitamin complexes. This will help not only the teeth and oral cavity, but also other systems of the body.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Author of the material: Yaroslav Ikonnikov
Taking care of your child's health
Parents often turn to dentists asking how to relieve teething pain in babies. There are several ways to help your child, including:
- application of a special gel for gums with a cooling effect
- using pacifiers or rubber toys, which help relieve itching from the gums for a while and distract attention
- massaging baby's gums
We also recommend cleaning your baby’s gums twice a day, morning and evening, using a special cloth fingertip soaked in boiled water.
Domostom family dentistry employs attentive and experienced doctors who find an approach to almost every child. At the appointment, the doctor will conduct a thorough examination and answer all the parents’ questions.
What are molars?
They are formed from the epithelial dental plate: molar rudiments appear only by the fifth month of the mother’s pregnancy. They are divided into two types: replacement - incisors, canines and molars, and additional - molars. The first ones repeat similar teeth in the “milk” set, the second ones have no predecessors.
The rudiments of replacement molars grow in the same alveolus as milk teeth, behind the lingual surface, and over time they are isolated by bone tissue. The rudiments of additional ones are formed only after a year, since the jaw by that time increases in size.
In what cases may they appear earlier/later and why?
If at least one tooth has grown by the age of one year, there is no reason to worry.
According to statistical data, in modern babies the period of eruption of the first teeth differs slightly from generally accepted normative indicators. White surfaces of the incisors are observed from 8.5 months of age.
Accordingly, the process of replacing dairy units with permanent units is also shifting. Pediatric dentists do not see any problems if by the age of one year the child has at least one tooth , and by the age of three the entire milk group has been formed.
In the complete absence of units, a thorough examination of the baby is carried out to identify provoking factors.
A discrepancy in the timing of teething may be due to a genetic factor or other reasons. Among the main provocateurs of process delays:
- previous infectious diseases;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract that occurred over a long period of time;
- problems with the metabolic functions of the body;
- lack of vitamin D (when diagnosing rickets);
- pituitary insufficiency.
It is not only the late teething that is alarming, but also their earlier appearance. Most often this occurs as a result of a disorder of the endocrine system (for example, Albright's syndrome, hyperthyroidism, hypergonadism).
A growing tumor (for example, eosinophilic granuloma) can provoke the eruption of one or a whole group of incisors before the age of six months.
Features of the development of dental tissue
The structure of each molar includes a crown - the outer part, a neck, as well as a root section, which ensures fixation in the bone tissue and nutrition of the element. The crown is covered with a protective layer - outer enamel, cement and dentin, designed to protect the pulp chamber from external influences. The sufficiency of nutrients entering the dental tissue depends on the condition of the pulp; in addition, it contains nerve endings that go to the root of the tooth, therefore, during inflammatory processes or damage affecting this layer, severe pain occurs. Age-related changes in dental tissue are an integral part of the natural aging of the body.