Teething is one of the most important periods in a child’s life. This happens at about six months of age, but it is difficult to name the exact timing, since this process occurs individually for each baby. What do parents need to know about the names of their child’s teeth and the pattern of their appearance?
Name of a child's teeth
What are baby teeth?
Milk teeth are the teeth that are the first to erupt in humans. Their rudiments are formed in the womb, at approximately 5-7 weeks of pregnancy, and by the age of three the child already has 20 teeth. Milk teeth differ from permanent teeth in structure (they are smaller and have a different shape), and the bite does not contain small molars, or premolars.
X-ray of baby teeth
Timing of teething
One of the most common questions parents ask is: “How long does teething take for babies?” It is useful to know both the time frame for the appearance of the first tooth and the time frame for the eruption of all teeth. In general, teething is an ongoing process that occurs between 6 and 24 months of age. Although your baby has twenty baby teeth that will appear over the course of two years, teething fortunately only causes pain and irritation at the time the tooth is about to break through the gum. It is not known exactly how long it will take for a tooth to fully erupt, but on average experts say it can erupt within 1-7 days per tooth. However, teething symptoms usually only last a couple of days, so if your baby experiences discomfort for an extended period of time, it's safe to assume it's not teething.
Scheme of baby teeth eruption
Normally, baby teeth begin to appear after the child reaches 5-6 months, but this period depends on a number of factors, including the quality and characteristics of the child’s diet, the region of residence and even the weather. Some children are born with one or more teeth; most often they must be removed because they interfere with normal sucking.
On a note! Milk teeth erupt symmetrically according to the so-called antagonizing principle, that is, teeth of the same name appear approximately simultaneously, and the process begins from the lower jaw. The exception is the lateral incisors, which begin to erupt from above.
Numbering of baby teeth
First, the two lower central incisors are shown, then the two upper ones, which are located directly above them. This order of teething ensures contact between the teeth and gives the baby the opportunity to begin to practice chewing solid foods. By the age of one year, a child, as a rule, has eight teeth. Next, two fangs grow - first on the lower jaw, then on the upper, after which the teeth of the chewing group (molars) erupt. At three years old, children can already fully bite and chew solid food.
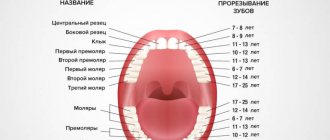
Approximate order and pattern of appearance of baby teeth
| Name | Age, months |
| Central incisors on the lower jaw | 6-7 |
| Central incisors on the upper jaw | 8-9 |
| Lateral incisors, upper jaw | 9-11 |
| Lateral incisors, lower jaw | 11-13 |
| Upper molars (first) | 12-15 |
| Lower molars (first) | 12-15 |
| Fangs | 18-20 |
| Second molars | 20-30 |
Types of teeth
Humans have the following types of teeth:
Incisors
Incisors are sharp teeth at the front of the mouth that bite into food and cut it into smaller pieces. They are flat, with a thin edge. They are also called front teeth. Both children and adults have eight incisors - the four incisors at the front of the mouth, and the lateral incisors located on either side of them.
Fangs
Fangs are sharp, pointed teeth that sit next to the incisors and look like a cone. Dentists also call them fangs or eye teeth. Canines are the longest of all teeth, and humans use them to tear food. Both children and adults have four canines. Children develop their first permanent canines between the ages of 9 and 12 years. The lower canines tend to emerge a little earlier than the upper canines.
Premolars
Premolars, or teeth, are larger than the incisors and canines. They have many ridges and help chew or grind food. Adults have eight premolars. The first and second premolars are the molars located next to the canine teeth. Children do not have premolar teeth. They first appear as permanent teeth at the age of 10-12 years.
Molars
Molars (molars) are the largest of all teeth. They have a large, flat surface with ridges that allow them to chew and grind their food. Adults have 12 permanent molars—six in the lower and upper jaws—while children have eight primary molars. Last molars
are wisdom teeth, or third molars, that usually appear between the ages of 17 and 21. They are located at the end of a row of teeth, in the far corners of the jaw. Some people do not have wisdom teeth, or the teeth may remain in the bone and never come out. Sometimes wisdom teeth only come out halfway or are in the wrong position, increasing the risk of infection or damage to surrounding areas. People may experience mild discomfort as wisdom teeth begin to emerge through their gums, but anyone who experiences severe pain or swelling should see a dentist. A dentist may remove wisdom teeth if a person has tooth decay, pain, or infection. Humans do not need these teeth for chewing and are difficult to keep clean due to their distant position in the mouth.
How does the process work?
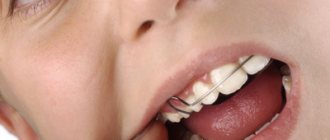
When the time comes for teething, the baby usually becomes restless, begins to put toys and other things in his mouth, bites his chest with his gums, and begins to salivate profusely. Parents may notice a small bump on the gum filled with fluid; the mucous membrane in this place becomes red and swollen. After some time, white spots clearly appear through the soft tissues - this means that the tooth is ready to be born.
Milk and permanent teeth
Important! If the lump becomes too large and causes serious discomfort to your baby, you can ask the doctor to cut it to “help” the tooth get out.
The body's reaction to teething depends on its individual characteristics. In some children this process is asymptomatic, in others the temperature rises, a runny nose, redness of the throat, diarrhea, sleep and appetite worsen.
Attention! If teething is difficult, accompanied by fever and other symptoms, it is better for parents to consult a doctor. Typically, in such cases, antipyretic and analgesic drugs are prescribed, as well as ointments and gels that reduce discomfort in the gums.
Types of teeth
You can relieve discomfort from teething by massaging your gums (performed with a clean finger) or by purchasing a special stimulator ring at the pharmacy.
- When do children's fangs change to permanent ones?
Timeline of teething
Most babies' first teeth emerge between 6 and 7 months of age, but this may happen earlier or later. In general, your baby's teeth will most likely appear in the following timeline windows:
6-7 months
During this time, the process of erupting the first teeth begins. The first teeth to emerge are usually the lower central incisors, which are the two middle teeth at the bottom. Children at this age become more active. They begin to grab and pull objects towards themselves, transfer objects from one hand to another, and may even begin to crawl. It is important to keep an eye on small objects within your baby's reach as he will want to put everything in his mouth during teething!
From 8 to 13 months
Between 8 and 12 months, your baby's upper central incisors will emerge. Additionally, sometime between 9 and 13 months, they will have upper and lower teeth next to their upper central incisors (called lower and upper lateral incisors). In addition to teething, it is important to understand that other important gross motor milestones are reached during this developmental window. Most babies are able to sit up, stand up without assistance, take their first steps, pick up and throw objects, roll a ball, and grasp objects.
From 13 to 20 months
Typically, between 13 and 16 months, your baby's first molars will appear on the bottom and top at about the same time. Soon after this, their canines will appear on both the top and bottom rows, around 16 to 20 months.
From 20 to 30 months
At the final stage of teething, the baby's back teeth or second molars appear in the bottom row. Although most teething symptoms appear the same in both babies and toddlers, there are some differences as your baby gets older. First of all, your baby can now tell you about his discomfort and pain, unlike non-verbal babies. On the other hand, many babies will not show any signs of discomfort and will not complain at all about pain when moving their molars. For other babies, the pain may be significantly worse because their first molars are larger than their other molars. They may even complain of headaches or jaw pain!
What to do if baby teeth are delayed?
The absence of signs of teething in a child at a time when other children already have several teeth is not a cause for concern. The exact timing depends on several factors, including:
- genetic characteristics;
- climate and living conditions;
- feeding habits (in children who are breastfed, teeth usually appear later than in “artificial” children);
- quality of child care;
- nutrition and living conditions of the mother during pregnancy;
- the presence of chronic diseases and pathologies.
Numbering of teeth in dentistry for children
A situation where teeth are completely missing in a one-year-old child should be a cause for concern - sometimes this is a variant of the norm, and sometimes it indicates disorders in the body.
Important! The most common pathologies that can affect the timing of teething are dysfunction of the endocrine system and rickets.
Less common is a disease called edentia, or the absence of tooth buds, which can be diagnosed using x-rays.
The structure and significance of teeth
Teeth in mammals are divided according to their shape and purpose into incisors
,
canines
and
molars
.
Human teeth are similar to the teeth of mammals. They are also located in special
holes called
alveoli
, and
are divided
into
incisors, canines
and
molars
.
An adult usually has 32 teeth: 4 incisors, 2 canines, 4 molars
and
6 large molars on each jaw
. Teeth have a characteristic shape and structure and occupy a certain position in the dentition.
Incisors
located in the front parts of the jaws, have an upper cutting edge and are intended mainly for grasping and cutting food.
The canines
follow the incisors, they are pointed and usually serve to hold and tear food.
Behind the canines are the molars
. They have an extensive chewing surface and are used to crush and chew food.
Teeth are necessary for holding and grinding food, take part in the formation of speech sounds and are an important part of the mouth.
Structure of teeth
A tooth consists of
a crown
(
the part of the tooth that protrudes above the gum
),
a neck
and
a root
(
the part of the tooth located deep in the alveolus and covered by the gum
).
The basis of the tooth is hard tissue
-
dentin
.
On the crown it is covered
with enamel , and on
the neck and root
-
with cement
.
Dentin
and
cement
are types of bone tissue. The neck of the tooth is covered with the thinnest layer of enamel.
Enamel
- the hardest tissue in the human body. This is explained by the high content of inorganic substances in it - up to 97%. However, even this can wear out and crack. Healthy enamel also contains 2 - 3% water and 1 - 2% organic substances (proteins, lipids and carbohydrates).
There is a cavity inside the tooth - a root canal
filled with dental pulp, or
pulp
.
It is represented by loose connective tissue containing blood vessels and nerves
.
Newborn babies have no teeth. At the age of 3 months, children begin to erupt baby teeth.
.
From about 6 years of age, children begin to develop permanent teeth
.
Their rudiments appear at the roots of baby teeth. The permanent teeth begin to grow and squeeze the roots of the milk teeth, blocking the path of blood. Deprived of nutrition, the roots of baby teeth dissolve. Baby teeth gradually fall out and are replaced by permanent teeth. This process ends by 10–12 years. The exception is the last pair of large molars, the so-called “ wisdom teeth.”
Their appearance is delayed in some people until 20–30 years, and in some they may not appear at all.
The closure of the upper teeth with the lower ones is called
a bite
.
With a correct bite, the upper canines block the lower ones, and the upper incisors are located in front of the lower ones
. This enhances their cutting action.
Healthy teeth are one of the important conditions for the normal functioning of the digestive system. A damaged tooth can cause a variety of diseases. Infection and inflammation can spread throughout the body.
The digestion process is disrupted, as food that is insufficiently chewed and not prepared for further chemical processing enters the stomach.
Causes of dental disease. If you do not properly care for your teeth, food particles remain between them, which undergo fermentation, resulting in the formation of lactic acid. It acts on tooth enamel and causes the dissolution of minerals.
A yellowish coating of microorganisms that live in the oral cavity appears on the affected area of enamel. They continue to destroy the minerals of the tooth. As a result, a carious cavity
. Microorganisms penetrate into it and cause caries - the gradual destruction of the tooth. If you do not put a filling on the damaged area, the tooth will gradually collapse. In such cases, you need to consult a dentist.
Caries
- the most common human disease. It occurs in 93–95% of people. In childhood, it ranks first among chronic diseases and occurs 5–8 times more often than the second most common disease - bronchial asthma. According to various authors, about 80% of adolescents have carious cavities at the time of graduation.
Eating food that is too hot or cold, biting nuts, chewing hard candy, and drinking hot food with cold drinks lead to enamel cracks.
. They easily become trapped by food particles on which bacteria multiply. Gradually, the cracks increase and carious lesions occur.
The tobacco tar contained in tobacco causes great harm to teeth and gums. It settles on the teeth and forms a yellow plaque, which after some time turns into tartar.
To avoid dental damage, it is important to maintain oral hygiene
.
It is necessary to brush your teeth with a brush and toothpaste 2 times a day after meals (morning and evening). The main procedure is to brush your teeth in the evening before going to bed, since unremoved plaque and food formed during the day contribute to the rapid proliferation of bacteria and, consequently, the development of caries. Remaining food particles between the teeth are removed using dental floss
. Metal objects, such as needles, should not be used, as they can damage the enamel.
You should visit a dentist several times a year.
Lesson summary. Teeth are involved in the mechanical processing of food. Between 6 and 12 years of age, baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth. A person usually has 32 teeth, which include incisors, canines and molars. Teeth need daily care. They should be brushed twice a day after meals. Caries is the most common dental disease. Sick teeth need to be filled.
Caring for baby teeth
Children should be taught oral care procedures from early childhood. After the first teeth appear, it is recommended to gently wipe them once a day with a clean piece of gauze soaked in boiled water. As your baby gets older, you can purchase your own soft-bristled brush and brush your teeth with water. After the baby reaches one year of age, it is recommended to purchase a special paste and teach him how to care for the oral cavity on his own.
Teeth of the upper and lower jaw
Milk teeth, like permanent teeth, are susceptible to decay and caries, which can appear even in children under two years of age.
On a note! The main feature of childhood caries is multiplicity, that is, it often affects not one, but several teeth, penetrating into the deep layers of tissue.
At the spot stage, the disease is treated with fluoridation; in case of an extensive pathological process, cleaning of carious cavities and removal of infected tissues is necessary.
Formula for recording baby teeth using the Haderup system
Comparative characteristics of teeth
| Name of teeth | Location in the dentition | Qty | Characteristics of teeth | Function |
| 1. Incisors | Located in front of the upper and lower jaws. | 8 (4 in each row) | The most “graceful”. They have one root. The crown is chisel-shaped with a narrow cutting edge. A single cone-shaped root is compressed from the sides. | Used for grasping and biting food. |
| 2. Fangs | Located lateral to the incisors. | 4 (2 in each row) | Larger than incisors. They have one root, which is usually the longest. The crown rises conically from the edge of the hole, so the upper end practically turns into a point. The crown has two cutting edges. | Used for tearing and splitting food. |
| 3. Small molars (premolars | Lie behind the fangs | 8 (4 in each row) | The crown is oval in shape. The height of the crown is less than that of the canines. There are two conical chewing tubercles on the chewing surface. Usually one root is conical in shape. At the top, the root may be forked. | Chewing tubercles contribute to the crushing and crushing of food and its grinding. |
| 4. Large molars (molars) | Located behind the premolars, i.e. deeper (dorsal) than other teeth. | 12 (6 in each row) | The shape of the crown approaches cubic. There are 3-5 chewing tubercles on the chewing surface. The lower teeth have two roots, and the upper teeth have three. | Chewing tubercles provide multiple contacts when the jaws are closed, which contributes to the grinding of food and its grinding. |
Now let’s get acquainted with the general plan of the tooth structure.
It is more convenient to consider it using the example of a sagittal section through a tooth. Task: make a schematic drawing of the tooth (sagittal section).
Teeth are built primarily from hard tissues - dentin, enamel, cement . Only in the cavity of the tooth crown and in the canal is the dental pulp (soft tissue) - pulp .
The following parts are distinguished in the tooth:
· crown;
neck;
· root.
The crown of the tooth is covered with enamel. Enamel is the densest substance in the human body. The enamel contains about 96-97% inorganic salts (phosphoric acid and calcium carbonate, calcium fluoride). It has no cells or nerve endings. The enamel is covered with a thin shell - the cuticle. To some extent, enamel is permeable to water, vitamins, glucose, and amino acids coming directly from the oral cavity.
In the area of the neck and root, the enamel disappears, so the root of the tooth is covered with another solid substance - cement . Cement in composition and structure resembles bone tissue (it contains 30% organic substances and 70% mineral salts).
The neck of the tooth is surrounded by gum.
Dental roots grow tightly together with the surface of the alveolar sockets (cells for teeth) through the periosteum - periodontium. The periodontium is a thin layer of connective tissue containing a large number of blood vessels and nerve fibers.
Extreme pain in the tooth area, redness and swelling of the gums, swelling of the cheeks and lips, even a slight increase in temperature can be accompanied by inflammation of the tissues around the cement - periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontium). This process is popularly characterized as flux.
The basis of the tooth is created by a special substance – dentin. 72% of the mass of dentin consists of calcium and magnesium phosphates, calcium fluoride and a number of other salts. Dentin contains collagen fibers and organic compounds (28%). Dentin is living tissue. Although it is similar in composition to bone, it is not as porous. Many dentinal tubules (tubules) pass through the mineralized base substance of dentin, which provide nutrition to dentin (the total length of all tubules of one tooth is approximately 1 km). Dentinal cells lie outside the dentin (in the pulp of the tooth). And only processes of these cells go into the thickness of the dentin along the tubules. Dentinal cells ( dentinoblasts ) provide life to the tooth; they produce prodentine, which is then mineralized.
There is a cavity inside the tooth - this is the dental canal . The canal is filled with soft tissue - pulp (tooth pulp), which is loose fibrous connective tissue. Blood vessels and nerve fibers pass through the pulp. Thus, due to the pulp, blood supply and innervation of all tooth tissues occurs, dentin is restored.
Milk teeth are built similarly to permanent teeth, but are approximately half the size. The roots of baby teeth are poorly developed, their neck is well defined. The enamel of baby teeth has a matte white and bluish color, in contrast to the yellowish tint of the enamel of permanent teeth.
When the jaws come together, the teeth of the upper and lower rows close together. This is called overbite . With a normal occlusion, the teeth partially overlap the teeth of the lower jaw due to the larger size of the upper alveolar arch and the outward direction of the teeth of the upper row.
The functional role of teeth is as follows:
· grasping and biting food;
· tearing food;
· crushing, crushing, grinding food.
Teeth also take part in the formation of articulate oral speech, giving a peculiar “color” to individual sounds.
When do permanent teeth appear?
The replacement of baby teeth with permanent teeth occurs once in a lifetime, in early preschool age. Permanent teeth are divided into two groups: replacement teeth, that is, those that have “twins” in the primary dentition, and additional teeth (premolars and molars). The timing of the eruption of permanent teeth is also individual and depends on genetic factors, region and living conditions, and quality of nutrition.
Structure of a baby tooth
| Name | Age, years |
| Molars (sixths) upper and lower | 6-7 |
| Central incisors on the lower jaw | 6-7 |
| Central incisors on the upper jaw | 7-8 |
| Incisors on the side of the lower jaw | 7-8 |
| Incisors on the side of the upper jaw | 8-9 |
| Fangs on the lower jaw | 9-10 |
| Fangs on the upper jaw | 11-12 |
| Premolars (4s) | 10-12 |
| Second premolars (5ths) | 11-12 |
| Second molars (7s) | 11-13 |
| Third molars (wisdom teeth) | 17-25 |
Dental formula
For reference! The eruption of permanent teeth usually does not cause children any discomfort - after the roots are reabsorbed, the baby teeth fall out on their own, and permanent teeth appear in their place.
During this period, parents need to monitor the child’s proper oral hygiene, as well as ensure that the permanent teeth grow evenly, without gaps or distortions. If the bite has defects, it is necessary to consult an orthodontist as soon as possible to correct it. Find out about the alveoli in the mouth from the article.
- Molars in children: order of eruption
Video - Baby's first teeth
Basic names of teeth in dentistry
Depending on their location, dental units have their own functional characteristics. The following important groups are distinguished.
- Molars. Placed in the top and bottom rows on the sides on the left and right. In the absence of pathologies, there are 12 of them. Their main purpose is to grind food and rough products.
- Premolars. In dentistry, such upper and lower teeth are called “four” and “five”. They perform an important function, grinding small and soft pieces of food. A healthy person has 8 of them.
- Fangs. In the standard picture, there are only 4 of them. They play an important role in chewing solid products. Leading chewing segment.
- Incisors. According to human anatomy, these front teeth are called and divided into lateral and medial. Usually there are 4 of them on both jaws. They take part in biting and biting.
We looked at the main names of human teeth based on their location. Elements of the dental system are also divided into temporary and permanent. The first are dairy ones, which grow within a period of up to 3 years. Permanent teeth develop in adolescence and form the final bite.
The names of a person's upper teeth depend on their location. An important chewing function is performed by the canines and molars; they are assisted by the premolars. It should be noted that polyodontia and edentia occur in practice. In the first case, a person has extra teeth, and in the second, their congenital absence.