July 28, 2020
Some parents, upon discovering a white dot on the gum of an infant or older child, immediately begin to panic. Taking care of your baby's health is the right thing to do, but a symptom is not always a threat. In any case, you first need to figure out what triggered the appearance of a spot, pimple or lump, and then act, but, of course, without unnecessary nerves and preferably by consulting a doctor. And journalists from the UltraSmile.ru portal will tell you about the main reasons why white spots might appear on your baby’s gums.
Reason No. 1. Epstein's pearls, or palatal cysts
White spots on a newborn's gums can be completely harmless if they are Epstein pearls. They are usually located on the upper jaw and palate. Outwardly they look like yellowish or white beads. Size – no more than 3 mm in diameter. They appear in 60–85% of newborns. They are nothing more than a cluster of epithelial cells. The formations are noticeable when yawning and opening the mouth. They do not cause babies any unpleasant sensations or discomfort, and 1–2 weeks after birth they go away on their own.
Epstein's pearls appear in 60–85% of newborns
“A white spot on a baby’s gum or spots that appear during the first days after birth are often caused by the accumulation of estrogen, a hormonal crisis and the body’s adaptation to new conditions. This phenomenon certainly requires careful monitoring, but does not require treatment and should not cause serious concern on the part of parents. If the baby develops normally, then during the first months of life the spots disappear on their own,” explains pediatrician A.V. Skromnova.
Reason No. 2. Bon's knots
White dots on the gums of a baby, as in the photo below, are Bon's nodules. A person who is not related to medicine is unlikely to be able to distinguish them from Epstein’s pearls outwardly, especially since they also consist of keratinized epithelium, but they take longer to disappear - within 3 months after birth. Benign and completely painless nodules got their name in honor of the famous German pediatrician who first described this phenomenon back in 1886.
Bohn's nodules consist of keratinized epithelium
Reason #3: Neonatal teeth
This is a very rare phenomenon (occurs in 1–2% of cases), but it still occurs. Neonatal, or congenital, teeth appear as white balls on a baby's gums. They may appear immediately or a month after birth. Most often they are localized on the lower jaw in the incisor area.
What does a neonatal tooth look like? The white hard point on the gum of a baby resembles a regular milk unit in appearance, but it is distinguished by mobility, since its roots are too short or absent.
A white hard spot or swelling on the gum of a child who is already 4-6 months old may indicate the imminent eruption of the first milk units. Usually during this period the baby becomes restless and may develop a cough and nasal discharge. If the formation on the gum has a bluish tint, and the tooth does not break out for a long time, then this situation may indicate an eruption cyst in which blood and fluid have accumulated. Contact a doctor who will cut the gum and help the milk unit come out quickly.
Doctors recognize the phenomenon as a deviation from the norm, which is random in nature. Less commonly, the appearance of neonatal and congenital teeth is associated with developmental defects. However, there is no rush to remove such elements, since as a result they are often included in a number of milk units, of which in total the baby erupts only 20 pieces.
This pathology is very rare
But sometimes neonatal teeth are supernumerary, interfere with the baby’s eating, cause pain for the mother when breastfeeding, and in these cases they are removed. An indication for removal can also be severe mobility of the unit, because if a tooth falls out on its own, it can lead to aspiration and respiratory arrest in the baby.
Why does white plaque appear?
Timely diagnosis allows you to quickly get rid of the problem.
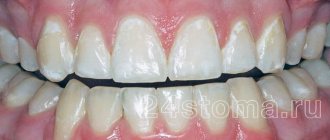
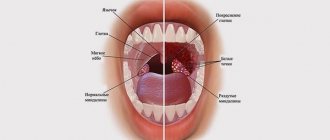
White plaque on a child’s gums or on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is a fairly common phenomenon and can occur in children of all ages, including newborns. There are quite a few reasons that provoke the appearance of white plaque on the gums.
Such a symptom can be a sign of both relatively harmless diseases and serious diseases, sometimes even having an oncological profile. Learn more about this in the video in this article.
But you shouldn’t worry too much about this, because most often, white plaque on the gums is easily treatable. The main thing is to notice the problem in a timely manner and show the baby to a specialist. The doctor will be able to quickly and accurately determine the nature of the pathology and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Important: Under no circumstances should you self-medicate if white plaque appears on your baby’s gums.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis can have a different nature.
If you notice a white coating on your baby's gums, one of the most common reasons for this is stomatitis. It is especially common in babies under one year of age, who, in order to explore the world with their own hands, pull into their mouths everything that comes their way.
Not all such objects are sterile; some of them may contain pathogenic bacteria, fungi or viruses, which can trigger the development of stomatitis.
Pathogenic microorganisms can be found on any object.
The incubation period of this disease is 4-8 days, after which the following symptoms are observed:
- weakness and drowsiness;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of a white or yellowish coating, white dots or spots.
If there is no treatment, plaque and white spots can degenerate into bleeding ulcers, which will cause particular discomfort.
The listed symptoms may manifest themselves to varying degrees, depending on the form of the disease:
| Type of stomatitis | Causes | Peculiarities |
| Most often caused by the herpes, measles, rubella virus. | First, bubbles form on the mucous membranes; after they burst, erosion appears, which is covered with plaque. |
| Contact with a sick person, caries, chronic diseases. | Redness of the area of the mucous membrane affected by bacteria, followed by ulcers. |
| Most often caused by fungi of the genus Candida. | It is characterized by white dots that grow and merge into a single white plaque. After its removal, bleeding erosions appear. |
| When there is local contact with an allergen, or when the allergen gets into the blood. | The mucous membrane becomes bright red, irritated and painful. |
| Caused by damage to the mucous membrane by high or low temperatures, chemicals, and various objects. | Redness, swelling and soreness of the mucous membrane in places of contact with the irritant. |
Stomatitis is not a dangerous disease, but it causes a lot of inconvenience and causes special discomfort. The child may become capricious and even refuse to eat completely. If stomatitis is not treated, ulcers appear, which cause severe pain to the baby. Therefore, at the first manifestations of such a pathology, you should immediately consult a doctor.
At the initial stage, it is not at all difficult to cope with this disease; the use of local anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antimicrobial drugs is sufficient. Medicines for stomatitis, which are most often used in infants, are presented in the photo.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis affects the gums, tongue and inner cheeks.
Another common cause of white plaque on the gums of babies is a disease such as thrush, or candidiasis. Its development is provoked by microscopic fungi of the genus Candida. These microorganisms are considered opportunistic.
This means that any healthy person has them, without causing any discomfort, and they exhibit their pathogenicity only under certain conditions:
- imbalance of normal microflora;
- stressful situations;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- decreased immunity due to other diseases;
- infection through the birth canal of a sick mother.
Candidiasis can be either an independent disease or accompany other more serious diseases.
The causative agent of thrush is fungi of the genus Candida.
The main manifestation of thrush is a white coating on the child’s gums, as well as on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. This plaque consists of waste products of fungi and pseudomycelium. After removing the plaque, damaged mucous membranes are revealed, with bloody ulcers.
In addition to white plaque, candidiasis may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- burning;
- dryness;
- soreness;
- temperature increase;
- weakness.
Candidiasis is quickly treated with antifungal agents.
Thrush is easily treated with antifungal and antiseptic topical agents. Together with them, it is recommended to use drugs that help accelerate the healing of the mucous membrane.
It is important to understand that the earlier the disease is detected, the easier it is to get rid of it. The drugs that are most often used in infants to treat candidiasis are presented in the photo. But their independent use is unacceptable, since any drug has contraindications and side effects.
Important: The appearance of thrush or candidiasis in a baby is the reason for a thorough examination of the baby’s body for hidden causes of decreased immunity.
Calcium deficiency
A lack of calcium can lead to rickets.
Calcium is one of the most important microelements. Breastfed babies receive calcium from mother's milk, which is always adjusted in composition to the needs of each individual child, in accordance with his age.
But in some cases, the calcium in milk may not be enough, for example, if the mother is not eating well or has bad habits. In this case, the baby may develop hypocalcemia.
How does this pathology manifest itself:
- increased sweating;
- excessive hair rolling out;
- chin tremor;
- white plaque in the form of a film on the gums;
- flinching at sharp sounds.
Taking vitamin D3 is recommended by Rospotrebnadzor.
Important: Hypocalcemia can develop not only with insufficient calcium intake in the body, but also with a lack of vitamin D3, which is important for the absorption of calcium. Therefore, in the autumn-winter period, pediatricians often additionally prescribe this vitamin.
In the absence of timely corrective treatment, calcium deficiency can lead to very serious consequences that can no longer be completely cured. Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to the prevention of hypocalcemia and follow all doctor’s orders if this disorder is suspected.
Improper hygiene
It is important to observe the rules of oral hygiene from birth.
It is necessary to monitor the condition of the oral cavity from the very birth of the baby in order to prevent the development of pathological processes. Typically, in the first months after birth, when the baby is exclusively breastfed, no additional procedures are required to cleanse the oral cavity.
Wipes for cleaning the oral cavity.
But if parents notice a white coating on the child’s gums after eating or frequent regurgitation, then it is necessary to clean the oral cavity of such sediment daily to prevent the development of pathogenic microflora in it. To clean, you can use a gauze pad soaked in a weak soda solution, or purchase special baby wipes for the oral cavity.
The instructions for such hygiene products contain complete information on how to use them correctly. They are very convenient both for home use and on the road, and their price is quite affordable.
Other reasons
Sometimes plaque on the gums indicates diabetes.
The reasons listed above are among the most common pathologies accompanied by the appearance of white plaque on the gums.
But in rare cases, such a symptom may accompany more serious illnesses:
- HIV infection - transmitted from a sick mother to a child during childbirth, and it can also be acquired due to the negligence of doctors;
- Diabetes mellitus is very difficult to diagnose in children under one year of age; it is usually detected only when the level of glucose in the blood reaches critical levels. Therefore, it is important to know all the symptoms of diabetes in order to notice the problem at the initial stage;
- Gum cancer is more common in people over 40 years of age, but in very rare cases it can also appear in infants. In addition to white plaque, it manifests itself in bleeding and swelling of the gums.
Sometimes parents may mistake neonatal teeth for white plaque. They are extremely rare and most often doctors recommend removing them, because such teeth do not fully develop and will interfere with the eruption of baby teeth.
Reason No. 4. Stomatitis
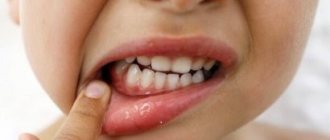
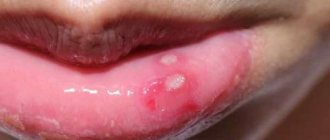
Often, a white pimple on a baby’s gum, as in the photo, gives reason to suspect a disease such as stomatitis. An inflammatory process on the mucous membrane can appear in both very young children and older ones. The main causes of the pathology: weak or unformed immunity, poor oral hygiene, injuries, allergies, infection of wounds and scratches in the mouth with dirty hands and foreign objects.
White dots may indicate stomatitis
A white spot on a baby’s gum, covered with plaque, most often indicates candidal stomatitis (in 90% of cases) caused by the Candida fungus, but aphthous, traumatic, drug-induced or herpes stomatitis can also be to blame. A dentist or pediatrician can determine what type of disease your child has and prescribe the appropriate course of treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis in children with mild and moderate forms is carried out on an outpatient basis. In severe cases and the development of complications, the baby is hospitalized. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a pediatric dentist or periodontist.
Children are prescribed bed rest and a diet with pureed, non-irritating food. He is given separate hygiene items and dishes. Plenty of warm fluids are recommended.
The following drugs are prescribed:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nise, Paracetamol, Nurofen) are used to relieve temperature and inflammatory reactions.
- Antihistamines (Clemastine, Loratadine) are used to relieve swelling of the mucous membranes.
- Antiviral drugs (Famciclovir, Acyclovir, Zovirax) are used at the beginning of treatment or in severe cases.
- Immunomodulators (Lysozyme, Gamma globulin, Thymogen) are used to enhance immunity.
During treatment, vitamin-mineral complexes and fish oil are used in monthly courses.
Local drugs that act directly on the mucous membrane are widely used.
For local treatment of herpetic stomatitis the following are used:
- antiseptics (Hexoral, Miramistin) - they are used to rinse the mouth every four hours for two weeks;
- ointments and gels with anesthetics (Kamistad, Lidochlor gel) are used for pain relief, they are lubricated with mucous membranes three times a day for up to two weeks;
- antiviral agents (Ganciclovir, Acicovir) - destroy the viral cell, gums are treated with these ointments five times a day, two weeks;
- proteolytic enzymes (Trepsin, Chymotrypsin) are used to cleanse the necrotic surfaces of ulcers; they are washed with these solutions twice a day.
- rinsing with decoctions of medicinal herbs (calendula, chamomile, sage) is carried out after each meal for up to two weeks;
- epithelializing ointments (Solcoseryl, Methyluracil) are used to enhance the healing of erosions and ulcers, used in the recovery stage, used up to four times a day for ten days.
Physiotherapy is applied locally. Irradiation of affected mucous membranes with ultraviolet and infrared rays is used.
Reason No. 5. Lack of oral hygiene
White spots on a baby's gums and plaque may simply be remnants of formula or breast milk that the baby was fed with. Or indicate that the baby recently burped. How can I check this? Take a special napkin, silicone brush or cotton sponge and wipe the palate, gums and mucous membranes.
It is important to remember that even the smallest children need hygienic oral care, since their diet contains sugar, and in the mouth, just like in adults, plaque and bacteria accumulate, which can provoke an infectious and inflammatory process.
Is research necessary?
Usually, thrush in the mouth of a baby does not require additional research, since it is not difficult for an experienced specialist to diagnose it based on obvious signs. But sometimes, in case of serious lesions, additional studies may be prescribed:
- microscopic: in this case, the doctor will take scrapings from the oral mucosa to examine the yeast-like fungal cells more carefully;
- bacteriological: during such a study, a scraping is also taken and then bacteria are cultured to understand how large the volume of fungal colonies is and how amenable to treatment they are with antifungal drugs; in addition, bacteriological testing helps determine which drug is the most effective in treatment, because some of them may not have an effect in the treatment of thrush;
- serological: this study requires a blood test, in the serum of which antibodies to fungal infection are examined.
Reason No. 6. Advanced dental diseases
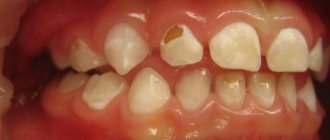
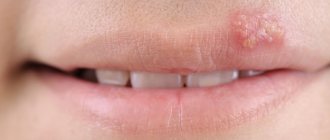
Of course, dental diseases in newborns are an exception. However, in children who have already acquired baby or permanent teeth, this is far from uncommon. If a child has a white dot on the gum next to the tooth as in the photo, then this may be associated with the development of periodontitis, periostitis (flux), fistula, cyst1 or abscess. These pathologies occur in cases where teeth with caries or pulpitis are not treated for a long time.
The photo shows a milk tooth cyst
Such white spots on the gums contain serous fluid or are filled with pus. They pose a serious danger to the child’s body and can lead to damage to the rudiments of permanent units, dysfunction of internal organs, blood poisoning and even death.
What is this disease?
Herpetic stomatitis is a pathological process that develops in the mucous membrane lining the oral cavity. The causative agent of this disease is herpes simplex virus type 1. In children under the age of five, this virus is detected in 60% of all cases. By adolescence, it is detected in the vast majority of people. Herpes stomatitis in children develops during the baby’s first contact with the virus. This occurs most often before the age of three.
The high incidence is explained by:
- low level of production of own antibodies;
- immaturity of cellular immunity;
- the fact that the baby does not receive antibodies from mother's milk;
- high reactivity of the child's body.
If the baby is bottle-fed, he may get sick in the first months of life. Viral infection often goes into a latent state. It persists in the nerve ganglia.
Reason No. 7. Wen, or lipoma
A white dot on the gum of a baby may indicate the accumulation of fatty tissue under the mucous membrane and the formation of a benign lipoma. The reasons for its appearance are varied: poor oral hygiene, trauma, past illnesses.
The neoplasm itself is not painful or dangerous, but after a long period of time it can greatly increase in size and begin to cause discomfort, be constantly injured, and even degenerate into cancer. If a baby has a wen, the doctor usually monitors its condition over time and, if necessary, may recommend removal using a laser or the traditional surgical method - with a scalpel.
A white dot on a baby's gum may be an accumulation of fatty tissue
What to do if a child has a lump, spot or dot on his gum
If you find a white spot on the gum of a baby, then you should not make a diagnosis yourself, relying on photos from the Internet, and, moreover, start self-medication. To begin with, it is recommended to thoroughly clean the mouth of a small child in order to get a good look at the growth and make sure that the problem is not caused by the accumulation of plaque and food debris. To do this, you need to use a soft silicone finger brush, specialized wipes or gauze soaked in warm water. To maintain hygiene, newborns should be given some water after each feeding.
The first step is to thoroughly clean your baby's mouth.
“If you have pimples and bumps in your mouth, run to the dentist, not to the pediatrician! Of course, there may not be anything dangerous at the points on the gums, but we have a not very pleasant situation. My daughter had a kind of pimple pop up next to a baby tooth, which looked healthy, and the pediatrician waved it off and said that it would go away on its own, but didn’t really explain anything. And the lack of intelligible explanations alarmed me, so I decided to go to the dentist. It turned out that the tooth was carious, but there was only destruction on the back side, and the pediatrician took a superficial look. I couldn’t even see it without a special mirror, normal lighting and tools! And in general, pediatricians have little education in matters of dentistry, they may not care, but your child will end up suffering!”
Gela, review from woman.ru
What if the problem is not caused by poor hygiene? Parents are advised to monitor the condition of the tumor and the well-being of the baby, and if serious pathologies are suspected and alarming symptoms appear (fever, moodiness, loss of appetite and sleep, bad breath, bleeding, etc.), they should consult a doctor. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective and safe treatment.
1Kushner A.N., Lapkovsky V.I., Petrovich N.I. Odontogenic cysts in children: epidemiology and treatment // Modern dentistry. – 2013.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
gum disease
Possible complications
The initial stage of the disease is easy to treat.
Most often, the initial stages of diseases accompanied by the appearance of white plaque on the gums proceed unnoticed. That is why there is a problem of early diagnosis of such a disease, which can sometimes be very serious.
In an advanced stage, this symptom causes severe pain in the child, and then even the most inattentive parent will notice the problem. But treating the disease at this stage is much more difficult and longer.
In addition, in the absence of timely and correct treatment, various complications may arise:
- dysbacteriosis;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- damage to internal organs;
- transition of the disease to a chronic form;
- diseases of ENT organs;
- development of sepsis, etc.
Such complications can arise not only due to lack of treatment due to late diagnosis, but also during attempts at self-medication, when parents may mistakenly believe that they are able to cope with the disease on their own, without the help of a doctor. But in the end, this only makes the situation worse.
Comments
My child has developed a white dot on his gum right next to his front baby tooth. The teeth are healthy, without holes, the child is 7 years old. What could it be?
Alexey (08/02/2020 at 00:22) Reply to comment
- Dear Alexey, perhaps your child’s permanent tooth has begun to erupt, and since the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, it simply does not have enough space and has changed the direction of growth. In this case, the baby tooth will have to be removed, otherwise there is a risk that the permanent tooth will move into the second row or will be severely curved, and the bite may be disrupted. Contact your pediatric dentist to clarify the situation and agree on a further plan of action.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (08/04/2020 at 09:12) Reply to comment
I still don’t understand whether it is possible to independently treat a child if such a white spot occurs. After all, it usually goes away quickly when you spread it with brilliant green.
Alisa (08/21/2020 at 06:38) Reply to comment
Stomatitis will probably be treated in a baby with some safe ointments or pastes? Are such remedies completely safe for children or can they offer another method of treatment?
Olga (08/21/2020 at 08:56) Reply to comment
Hello, my child is 5 years old, the front tooth is much lighter than the rest, it is very noticeable (the rest of the teeth are normal white, but the front one is just snow-white.) Tell me, what is this connected with and what to do?
Vladimir (08/21/2020 at 08:58) Reply to comment
Recently we were talking to a girl on the playground and she said that her daughter often has stomatitis. I would like to know if this is contagious to other children? After all, they play with the same toys and can transmit bacteria through them.
Olga (08/21/2020 at 09:35) Reply to comment
Hello! Thanks for the useful article. After reading the article, I thought about it: my son had small dots right on his gums with a size of 0.5 mm, very small. I thought it was teething and didn’t pay much attention. The teeth are cutting through, everything is fine, thank God. I have a question: can such dots just appear before teething? Or should I also contact a pediatrician or dentist?
Kamila (08/21/2020 at 10:56 am) Reply to comment
My son has white spots on his gums and mucous membranes, has a slight fever, eats poorly, he is 1 year and 2 months old. It looks like stomatitis. Can I buy medicine for stomatitis at the pharmacy, or is it better to go to the dentist?
Olesya (08/21/2020 at 11:08 am) Reply to comment
Could white spots be an allergic reaction of the baby to spicy and salty foods in the diet of a nursing mother? The habit of generously salting and peppering food has been around for many years. For now, I’m trying to eat more neutral in taste, but sometimes I break down.
Alina (08/21/2020 at 11:26 am) Reply to comment
Why did my one-month-old baby start to have white spots on his gums, although this had never happened before? What measures would you recommend to take in this case and will these white dots harm the child?
Laima (09.23.2020 at 14:43) Reply to comment
How can white pimples on the gums and oral mucosa cause harm? These white spots have been formed for several weeks; what should the baby’s oral cavity be treated with to get rid of them?
Tanya (09.23.2020 at 14:45) Reply to comment
Tell me, can these white spots on the gums cause stomatitis in an infant? How to treat these white spots in a baby if the child is still breastfed?
Kira (09.23.2020 at 15:29) Reply to comment
The child suffers greatly due to the appearance of small white spots on the gums, as well as on the inside of the cheek. In appearance, these white dots look like leftover milk from a baby; they cannot be removed with a cotton swab; the child is constantly capricious. Please advise what can be done to rid the child of these white spots in the mouth?
Lyudmila (09.23.2020 at 15:41) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Prevention of white pimples in the mouth of a baby
To reduce the likelihood of acne and spots appearing in a baby’s mouth, you must adhere to the following preventive rules:
- Breastfeeding provides the baby with all the substances necessary for its full growth and development. Therefore, a nursing mother should eat well and foods that are harmful to the baby should be excluded from the diet.
- After feeding, you need to carefully clean your baby's mouth. After teething, you need to use special children's silicone brushes to clean them; as the child grows, you should teach him to maintain hygiene.
- Pacifiers and bottle nipples must be clean and washed immediately after use. Excessively long use of pacifiers negatively affects the condition of baby teeth and the formation of the bite, so it is necessary to wean the baby from this habit in time.
- Parents should regularly examine the child’s mouth, but if a pathology is detected, they should not self-medicate - they should take the baby to a pediatrician or pediatric dentist as soon as possible.
- The baby should be regularly taken to see a pediatrician, and once every six months to a dentist. If a pearl mussel or other benign formations are detected in a baby, you need to visit the doctor more often.
A white pimple on a baby's gum is not a reason to panic. This symptom does not always indicate the development of a serious pathology. But if the mucous membrane of the gums not only turns white, but is also covered with plaque and swollen, the disease that led to such symptoms should be urgently diagnosed and treated.
Dr. Komarovsky on the treatment of oral thrush in infants: