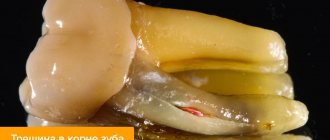
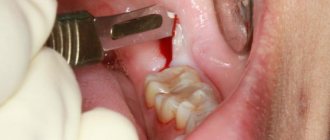
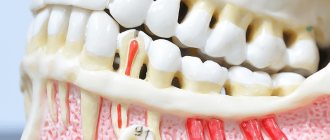
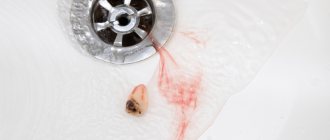
Causes of a crack in the root of a tooth
Not all patients understand why a root crack occurs in a living tooth. The reason lies in the uneven distribution of the load. Moreover, the load can be strong and sudden, or it can accumulate over years and lead to the appearance of a crack after some time.
Typically, the cause of a crack is caused by the following factors:
- domestic trauma
- blow, fall, sudden load while chewing; - improper treatment
- strong pressure when cleaning canals or filling the root can injure the walls and in the future, with the slightest excessive load, cause a crack in the root; - error during prosthetics
- strong pressure when installing a pin or the manufacture of inappropriate dentures that unevenly distribute the load during chewing, leading to injury; - Bruxism
- unconscious clenching of the jaws, for example, during sleep, leads to a load that the patient does not notice and cannot control.
What Causes Injury?
The main reason why tooth crown damage occurs is weakened enamel.
In such cases, microcracks and chips often form, which subsequently lead to a crown fracture. But even strong teeth can be injured under strong mechanical stress, however, this usually happens simultaneously. The reason for the weakening of the enamel can be:
- poor quality dental treatment;
- deficiency of calcium, phosphorus and fluorine;
- violation of nutrition rules;
- constant exposure to food acids;
- disruption of the pancreas with uneven release of acidity;
- the effect of different temperatures when eating food (hot-cold);
- jaw injuries.
With weakened teeth, a crack can also occur as a result of the habit of chewing hard objects or foods, nails, packaging, etc.
Dentists warn that those at greatest risk are patients who have had prior dental treatment with pulp removal or a filling placed on a large, diseased crown cavity.
Types of tooth root crack
Pressure can be applied both vertically and perpendicularly to the crown. The following types of cracks are distinguished:
- oblique crack of a tooth
- a diagonal fracture, usually the healthy part is much larger, and the doctor can save the tooth by removing the affected part; - transverse crack of a tooth
- part of the root is completely broken off and deprived of nutrition; the closer the crack is to the coronal part, the higher the risk of complications; - longitudinal crack in the root of a tooth
- the fracture runs vertically, along the axis of the root, often accompanied by a fracture of the crown; - comminuted tooth crack
- multiple root fractures intersecting with each other.
Complications after chipping
Restoring a chipped front tooth or a chipped molar (what to do in the case of different types of damage is discussed above) should be mandatory. Firstly, the aesthetic component suffers. A smile looks ugly, a person develops complexes, he is always afraid that others will notice the defect. Secondly, if you neglect medical intervention, you cannot avoid negative consequences (sometimes irreversible). These are problems such as:
- malocclusion;
- curvature of roots;
- increased sensitivity to external stimuli (cold, hot, sour, sweet);
- pulpitis, periodontitis and other diseases.
All of these conditions are considered very serious. Most of them often lead to the loss of units and affect the health of neighboring elements.
Oral diseases affect other organs. For example, if a large piece of a back tooth breaks off and the remaining fragment or the entire row hurts, this can later be associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, heart and blood vessels, and urinary system. Even microcracks can lead to such complications. Thus, unpleasant consequences can only be avoided with the help of timely intervention by a dentist.
Root crack diagnosis
Only a doctor can diagnose an injury. First, the specialist makes a preliminary diagnosis based on the patient’s symptoms and complaints. More detailed research is required to clarify.
- Instrumental examination.
By tapping the tooth, the doctor determines whether there are irregularities, fractures or bleeding in the root of the tooth. - X-ray.
The image clearly shows the tooth root crack, its location and the severity of the injury. - Electrical exposure
helps determine the condition of the pulp.
What kind of help will be provided at the clinic?
First of all, the dentist will conduct a diagnosis. The dentist will examine your mouth and take an x-ray. It will show:
- how deep is the crack?
- whether the root is affected;
- whether soft tissues are injured or not;
- what state the channels are in.
Treatment is carried out depending on the defect.
Chips and cracks in enamel
The mildest degree of damage. Teeth react to irritants and ache when eating. The restoration is carried out with filling material; before this, the corners and sharp edges are polished. According to indications, veneers are installed on damaged enamel. They are made either from a composite, covering the surface layer by layer, or from ceramics. Ceramic veneers are made from individual impressions in a dental laboratory. They are more expensive, but last longer and retain their attractive appearance for years.
Some patients believe that it is not necessary to treat the back teeth; they are still not visible. But enamel damage is a gateway for pathogenic microorganisms. To prevent serious diseases, the enamel must be restored.
Loss of part of a tooth
If a front tooth breaks off, it will be built up with a composite material. These teeth look natural and can last for many years. When chips and cracks are very noticeable, the tooth is replaced with a veneer or it is ground down and a crown is put on. If part of a front tooth is broken, ceramic restorations will disguise the problem so that others will not realize that the crown is artificial. They imitate tooth enamel as accurately as possible.
If the wall of a chewing tooth has broken off, veneers will not help. Here you need prosthetics on a pin or stump tab (if half of the tooth or more has broken off). A pin (fiberglass pin) is inserted into the canal. It provides stability to the tooth, and a crown is placed on top for its protection and aesthetic purposes. Prosthetics with an inlay requires taking impressions. Inlays are made in a dental laboratory. The root end is inserted into the canal, and the prosthesis is put on the coronal part.
A tooth with a filling broke off
The doctor assesses the condition of the canal using an x-ray. If the canals are well sealed, then they immediately move on to prosthetics or extensions. If the canals are poorly isolated, an inflammatory process can begin there, so before extension, endodontic treatment is carried out - the canals are re-treated, the inflammation is eliminated, and only then the tooth is restored.
Broken tooth crown
When the enamel is fractured, patients complain that the sharp edge has injured their cheek or lip, but do not experience pain. The dentist grinds down the sharp edges and restores the tooth with composite.
A fracture of the crown (dentine) most often occurs due to injury, and it cannot be done without pain. The fracture can run along the tooth or break it in half.
Treatment depends on whether the pulp (nerve) is involved or not.
In case of a fracture without damage to the pulp, a pad with calcium hydroxide is placed in the pulp chamber and a temporary filling is placed. They observe how the pulp behaves, whether there is pain, and whether the neurovascular bundle has retained its viability. If events develop favorably, the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one. The half tooth is built up with a composite; in case of large damage, a veneer or crown is used.
If a tooth breaks in the gum, this most often means that the pulp is exposed. In such cases, the treatment plan and its outcome are influenced by the time of treatment and the age of the patient. For unformed roots in children, direct pulpotherapy is performed with a calcium-containing pad. The sooner a patient sees a doctor (the first 24 hours
), the greater the likelihood of saving the pulp before necrosis begins. If the incisors are fractured or if a molar tooth is broken and hurts, it is important for children to see a doctor as quickly as possible. The pulp can be preserved, the tooth will remain alive, tissue exchange and normal blood supply will continue to occur in it. This is important for the formation of permanent roots.
In cases of late presentation, treatment begins with the removal of moving fragments and amputation of the pulp. The canals are then isolated with gutta-percha. Prosthetics are performed with an inlay and a crown.
When wisdom teeth are fractured, they are most often simply removed.
In adults, the exposed pulp is removed immediately, then the canals are filled and the coronal part is restored.
If the crown is completely fractured (the tooth is broken under the gum, but the root remains), it can be used with a pin. In cases where the natural crown has not been preserved, prosthetics are performed on the stump inlay.
The root broke
The most difficult of injuries. Restoring a chipped tooth is quite simple; putting the root fragments back together is much more difficult. First, the pulp is checked for viability. To do this, electrical and temperature tests are carried out. If the nerve responds to stimuli, the root fragments fit together like a puzzle. A splint is then applied to ensure immobility. The patient wears the splint for approximately 3 months
, with control checks
after 1 and 2 months
. After this, the debris is checked for mobility. If they move, the tire is reinstalled. In a stationary state, a mineralized connection is formed between the fragments and the root can perform its functions.
If the pulp is dead, the tooth is removed followed by prosthetics or implantation.
Fracture after prosthetics
The reason that a tooth under the crown has broken may be that:
- excessive loads were placed on the tooth;
- preparation before prosthetics was carried out poorly;
- treatment before installing the crown was incorrect;
- hard tissues are eaten away by caries, the tooth under restoration is rotten.
Treatment is carried out based on diagnosis. If the roots of the tooth are preserved, then the canals are re-treated, and then prosthetics are performed on the stump inlay (if the tooth is destroyed by half or more). In the case when the root is inflamed, the pathological process has gone far, tissue necrosis has begun, and the tooth is removed. Then implantation is performed or a bridge is installed.
With bridge prosthetics, it is not possible to stop the loss of bone tissue; adjacent teeth have to be ground down, before which the nerves (pulp) are removed from them. Such units do not receive minerals, become brittle, and quickly collapse. A pulpless tooth is considered dead.
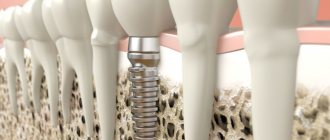
The implant functions as a natural root, completely restores chewing function, and prevents bone tissue atrophy.
Crack in the root of a tooth: what to do
After diagnosis, patients are concerned with the question of whether it is possible to cure a crack in the root of a tooth. It all depends on the severity of the injury, the type of fracture and location. But there is no therapeutic treatment - tablets, ointments and injections; in any case, surgical intervention is necessary.
Ⅰ.
In case of a transverse fracture, the tooth can be saved, but the pulp is removed without exception. The doctor cleans and fills the root canals, and fastens the crack with a pin. Now the tooth needs rest and a minimum of chewing load - to reduce mobility, the teeth are splinted, that is, fixed in the correct position with a special splint-onlay.
Ⅱ.
Splintered, vertical and oblique cracks in most cases are only the initial stage of destruction of the root system, and over time the fault will grow. Therefore, depending on the severity of the injury, the doctor removes either part of the root with a crown or the entire tooth. A partially lost tooth can be restored using an inlay on a pin, or a complete tooth can be restored by installing a prosthesis or implant.
Treatment of a crack in the root of a tooth requires following the following recommendations:
- limit the chewing load - it is better to eat soups, cereals and other soft foods, avoid hard foods;
- monitor the temperature - all foods and drinks should be slightly warm, ice cream or hot tea have an undesirable effect on the injured root;
- eliminate pressure - do not open your mouth wide, do not close your jaw too tightly, brush your teeth carefully, avoid blows.
Methods of treatment and restoration
If a tooth is cracked, whether it can be saved will depend directly on the nature of the injury and the time after which the person went to the dentist. With a high probability, you can save a tooth with small chips and microcracks. The use of composite materials will allow you to restore the crown without visible aesthetic defects.
The situation is much more complicated with extensive cracks. Crown restoration and treatment are carried out only if at least a third of the tooth root is preserved and there are no inflammatory or infectious processes.
In case of significant vertical or diagonal cracks, dentists remove one part of the crown and build up the second half or install a prosthesis on implants. Such manipulations are necessary, because even if the crack has not reached the base of the tooth, under load it will still crack the tooth and its integrity will require re-treatment after some time. Damage to the root system, jaw tissue, and pulp is performed by tooth extraction. Extraction is also used for damaged wisdom teeth.
If a tooth is cracked in half, it can be saved, but only partially if there is no serious damage. You should not delay your visit to the doctor. Modern dentistry has enormous possibilities for restoring teeth; even if removal is required, the crown can be restored with the help of prostheses that will not differ from the rest of the teeth.
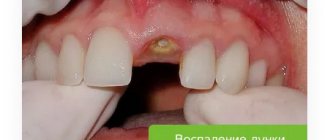
Complications and consequences of a root crack
In this situation, timely treatment is important: seeing a doctor at the initial stage will help avoid consequences. If this is not done, you may encounter the following complications:
- abscess.
A crack without treatment can provoke an inflammatory process, which in the future will turn into suppuration of soft tissues and lead to the formation of an abscess. Treatment of a purulent cavity is much longer, more expensive and unpleasant than treatment of a fissure; - phlegmon.
Suppuration, which, unlike an abscess, does not have clear boundaries and does not flow into the formation of a cavity. Cellulitis is a decay of cells that can spread to any tissue in the cavity; - periodontitis.
Inflammation of the periodontium, that is, the tissues surrounding the tooth, leads to their death and the inability to hold the tooth in the gum. The result is the complete loss of one or more teeth; pulpitis. The death of the pulp - the neurovascular bundle of tissues in the tooth through which it receives nutrition. Pulpitis is quite painful and can affect neighboring tissues; - tissue injury.
A root fragment can injure soft tissue. In this case, the doctor will have to extract a piece of the root and remove the infected tissue.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms are:
- pain that does not have an exact location (radiates to different parts of the dentition);
- increased sensitivity of the enamel (this is strongly felt when eating hot or cold foods);
- severe discomfort while chewing food.
If vertical damage leads to pulpitis, then the patient develops a characteristic putrid odor from the oral cavity, which cannot be gotten rid of even after cleaning.
As tissue necrosis develops, the color of the enamel may change, the gums may swell, and become very painful when pressed. Very often the damage affects the root, and this leads to severe loosening of the tooth.
Let's talk about what you can do when your front teeth are loose - how to strengthen them at home and in dentistry.
Prevention of root injuries
The best treatment is disease prevention. To prevent cracks at the root, try to follow a few recommendations:
- be careful and attentive, because half of the cases of root cracks are household injuries, which can be avoided if you take care of yourself and your health;
- carefully choose a clinic and a doctor - before visiting a dentist, check the reviews and ratings of the clinic, certificates and specialist diplomas, do not go to questionable dentists;
- strengthen your teeth - eat healthy foods, do not forget about the importance of calcium and fluoride in strengthening your teeth, choose suitable dental hygiene products.
If symptoms of a root crack occur, do not self-medicate and do not wait for the pain to go away on its own. See your doctor. If the pain is caused by a temporary phenomenon, you will be calm, and if a crack is discovered at the root, treatment at the initial stage will help maintain the health and beauty of your smile, avoid complications and unnecessary expenses.
Dentists' recommendations
If a tooth is cracked, you can save it, but you should make an appointment with your dentist right away. The sooner professional help is provided, the less likely there are complications.
Before visiting a doctor, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- the load on the injured tooth is completely eliminated;
- take only soft or ground food of medium temperature;
- Every hour, rinse your mouth with antiseptic agents, saline solutions or herbal decoctions.
Experts strongly advise against touching a damaged tooth with your fingers or tongue. You should not loosen it or try to use any popular recommendations. When a tooth is cracked, it can only be saved by going to the dentist.
Service life of a tooth after repeated restoration
Service life depends on many factors:
- depending on the restoration method: the most reliable and durable is considered to be prosthetics with a crown or restorative inlay - especially if it is made using high-precision CAD/CAM systems. Here, all internal tissues are reliably protected by the shell of the prosthesis, which is functionally and aesthetically identical to the tooth. And such a restoration will last at least 15 years. A less reliable method is considered to be re-building a filling, because it is most susceptible to chipping, shrinkage and peeling,
- on the material: if we talk about crowns, then the most durable are those made from metal ceramics (last 10-12 years) and zirconium dioxide (last about 25 years). Ceramic or composite veneers, as well as composite crowns, are inferior in strength and have a short service life (from 5 to 7 years). Such dentures will have to be changed more than once - they quickly lose their integrity, break off and darken,
- on the condition of the patient’s teeth, gums and the presence of chronic diseases: as well as severe chronic diseases - for example, diabetes mellitus, systemic or oncological diseases, vascular and neurological pathologies,
- How long veneers or artificial crowns will last depends on the patient’s compliance with wearing recommendations: proper care and compliance with safety measures determines how long veneers or artificial crowns will last. In dentistry, cases are described when products designed for 5-7 years served patients for 10 and even 15 years,
- on the qualifications of the doctor installing the prosthesis: the more experience the doctor has, the less likely it is that he will make a mistake in installing the prosthesis.
Why is extension needed?
Aesthetic or artistic restoration (extension) is one of the ways to restore a damaged tooth. As a rule, its coronal part has some defects: chips, cracks, pathological destruction - but no more than 30% of the total volume of the supragingival part. To restore aesthetics and functionality, it is returned to its original shape.
Direct extension1 is carried out by layering light-curing filling materials on the problem area. As a rule, such extension is recommended in the following situations:
- with a wedge-shaped defect,
- for chipped enamel,
- for carious lesions (in which case a pin can be additionally installed),
- with enamel hypoplasia.
The extension is done in just 1 visit to the dentist. But restoration of one defect can last about 2-2.5 hours, because... The dentist needs to very accurately convey the natural shape, relief, color and translucency. And the person himself must subsequently remember that gnawing hard foods and objects is no longer allowed, and he should also take care of injuries.