Pathology of the connecting joint between the lower jaw and the temporal bone. In the acute stage, the following symptoms are noted:
- intense pain in the affected area;
- swelling of the skin over the joint;
- restriction of movements when opening and closing the jaw;
- increased basal temperature.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines the patient’s medical history, conducts an examination, and prescribes computer tests.
Methods of treating the disease:
- jaw immobilization;
- antibiotic therapy;
- local administration of corticosteroids;
- myogymnastics;
- physiotherapeutic measures.
General characteristics of the pathology
What is jaw arthritis
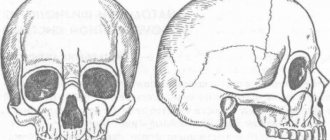
In medicine, this pathology is called arthritis of the temporomandibular joint, or TMJ arthritis. Due to this joint, the lower jaw moves and makes it possible to make movements with the mouth.
Arthritis of the maxillary facial joint is a disease that is a complex inflammatory process of this joint.
The pathological process can occur in both acute and chronic forms. A distinctive feature of the development of the anomaly is the limited mobility of this structure.
The disease is complex, it is treated by specialists of different profiles.
According to ICD 10, the specified pathological process is assigned code K07.6.
There are several forms of this disease, depending on the location of the pathological process. This:
- arthritis of the upper or lower joint;
- arthrosis of the upper jaw joint. The disease occurs when there is severe deformation of the joint. In this case, the lesion spreads to both areas of the jaw node, destruction of cartilage tissue occurs
The pathological process is characterized by the unilateral nature of the lesion. During the first stages of the pathological process, inflammation of the joint capsule and surrounding soft tissue occurs. As the pathological process spreads, cartilage tissue and articular surfaces are damaged. Because of this, lesions with connective tissue are formed.
Predictions and prevention
The disease is serious and requires timely consultation with a specialist. In infectious and acute forms, the prognosis is favorable, but only if all treatment conditions are met. The chronic form, even with treatment and compliance with recommendations, often develops into bone ankylosis. In this case, surgical intervention is indicated, since the problem cannot be eliminated by other means.
At risk are patients with rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, and people with jaw injuries. For prevention, it is recommended to carry out timely sanitation of purulent foci, if present, to protect against repeated injuries. It is necessary to monitor your health and treat developing specific infections. The following situations should also be avoided:
- physical exercise;
- bad habits that load the jaw, for example, it is forbidden to chew seeds and nuts;
- stress;
- bruxism;
- breathing through the mouth (you need to try more with your nose).
Complexes of therapeutic exercises and massages are performed independently or in the office. This allows you to strengthen muscle tone, improve jaw mobility, and eliminate crunching when moving. In addition, such measures speed up the recovery process.
About Us
The MY ORT clinic offers treatment for diseases of the jaw, including acute or chronic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint. We offer our patients the following benefits:
- modern methods of therapy;
- use of certified materials;
- full range of services, including diagnostics;
- control of treatment, guarantee of results;
- attentive attitude towards everyone, creation of comfortable conditions;
- affordable prices.
You can make an appointment or consult with our specialists by phone. Leave a request on the website, choose a convenient time to visit or send a request by email
Risk factors
A number of reasons can lead to the development of arthritis of the jaw.
Violation of the structure occurs due to the following reasons:
- traumatic factor. The cause in this case may be a blow, a fracture, or a sudden opening of the mouth;
- infectious diseases of the ENT organs or lower jaw. Arthritis of the maxillary joint is caused by streptococci, chlamydia, mycobacterium tuberculosis, and various viruses;
- osteomyelitis;
- untreated caries or periodontitis;
- otitis, mumps. Arthritis is a complication of these pathologies;
- gout;
- reactive arthritis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- metabolic disorders;
- diabetes;
- thyroid diseases;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
Sometimes inflammation is a consequence of hypothermia.
Classification
TMJ arthritis can be:
- Spicy;
- Chronic;
- Bilateral;
- Unilateral;
- Infectious;
- Rheumatoid;
- Purulent;
- Deforming osteoarthritis;
Infection may result from direct spread or hematogenous spread. The area becomes inflamed, movement is limited, and pain appears. Bone destruction may be diagnosed. Acute traumatic arthritis can sometimes be associated with severe removal of the masticatory organ. Creaking and stiffness can occur in old age when bones rub against each other. Common manifestations of rheumatism are pain, swelling, and limited movement. Secondary degenerative pathology most often develops after injury. The patient has difficulty opening his mouth, and the pain is usually one-sided. The disease code according to ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) is K07.6.
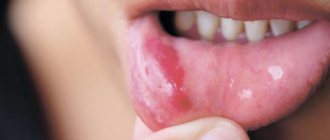
Clinical picture (symptoms)
Arthritis is accompanied by pain and discomfort.
The disease manifests itself in the following characteristic symptoms:
- pain in the jaw area, which radiates to other parts of the face and intensifies with movements and opening the mouth;
- dizziness;
- sleep disorders;
- limited movement in the joint;
- feverish condition;
- inflammation of the skin and soft tissues around the joints;
- elevated temperature;
- clicking in the jaw area when it moves;
- temperature rise up to 38 degrees, sometimes higher;
- pain when palpating the affected area (joint pain);
- deformation of the contours of the face due to the fact that the chin “goes” to the side;
- feeling of weakness, increased fatigue;
- hearing impairment.
Important! With arthritis of the jaw joint there is a risk of the formation of purulent inflammation. In this case, the joint swells and the skin becomes red and hypersensitive. A lump is felt in the area of the mandibular joint. The shade of the skin changes, speech and chewing functions are impaired.
Classification of arthritis
TMJ arthritis is a nonspecific disease, despite its widespread occurrence. The forms and types of the disease are classified according to the nature of development and the nature of the course of the pathology.
Due to their development, the following types of arthritis are distinguished:
- infectious;
- non-infectious;
- traumatic.
Infectious arthritis, in turn, is divided into contact and hematogenous. Contact arthritis develops due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the joint against the background of infection of organs located in close proximity to the TMJ. Hematogenous arthritis is a consequence of the spread of infection in an ascending direction through the bloodstream. This form of the disease develops in tuberculosis, measles, syphilis, and other severe bacterial pathologies.
The cause of the development of traumatic arthritis of the TMJ are injuries, bruises, fractures, and tendon compression. This form of the disease can occur after severe road accidents or in athletes who have injured their jaw.
Non-infectious arthritis can be traumatic, rheumatoid (autoimmune) or reactive. Reactive arthritis develops against the background of existing infectious diseases, but no pathogenic microorganisms are found in the synovium of the joint.
Separately, dystrophic arthritis is distinguished, which is a consequence of disruption of local metabolic processes. In this case, there is a lack of nutrition of the cartilage tissue, its gradual degeneration and loss of elasticity of the cartilage.
According to the nature of the course, the inflammatory disease is divided into chronic and acute. Acute TMJ arthritis is characterized by pronounced symptoms and a general deterioration in well-being. The disease may be accompanied by suppuration in the joint capsule and infection of the periarticular tissues. Chronic TMJ arthritis is characterized by moderate severity of symptoms, but with periodic exacerbations.
In the absence of adequate therapy, acute arthritis can become chronic, which is difficult to treat.
With arthritis of the temporomandibular joint, symptoms depend on the type of inflammatory reaction and the form of the disease. Regardless of the cause of TMJ arthritis, the symptoms require attention, so you should consult a doctor if you experience the slightest discomfort in the jaw, since the advanced form of the disease is difficult to cure.
Types of deviations in the maxillofacial joint
The clinical picture of this disease depends on the form in which arthritis of the jaw joint occurs.
Types of disease:
| Type of pathology | Characteristics |
| Acute form | The predominant symptoms in this case are severe pain in the affected area and swelling of the soft tissues. Typically, acute arthritis of the jaw joint occurs after traumatic injury. |
| Chronic arthritis | With this form, aching pain is constantly observed in the jaw joint. In the morning, jaw mobility is limited. Body temperature usually does not increase, the general condition of the body is satisfactory. |
| Infectious arthritis of the TMJ | Usually this type of pathology is a consequence of previous diseases - influenza, tonsillitis. In the infectious form of arthritis, severe pain is observed, during which it is impossible to open the mouth freely. Unpleasant sensations radiate to the area of the ear, back of the head, and temple. |
| Traumatic | This is the most common form of arthritis of the maxillary joint. It occurs against the background of an injury. |
| Specific | This type of disease occurs quite rarely. Typically, specific arthritis is a consequence of previous diseases - syphilis, gonorrhea, tuberculosis. |
| Non-specific | In this case, the inflammatory process occurs due to traumatic or rheumatoid factors. |
| Purulent | This form of pathology is a consequence of acute arthritis, which has been neglected. A thickening appears in the area of the mandibular joint, and body temperature rises. |
| Rheumatoid | The disease manifests itself in constant pain localized in the area of the maxillary joint. In this case, the clinical picture is often supplemented by pain that is localized in the area of the knee, hip or elbow joint. |
Depending on what exactly caused the development of the inflammatory process, the following paths are distinguished:
- hematogenous . In this case, the pathogen penetrates the joint area along with the blood flow. This method of infection is possible with tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea, scarlet fever, measles;
- contact . The disease develops against the background of damage to the sections that are located next to the maxillary joints. A similar thing is observed with otitis media, purulent mumps, phlegmon or abscess of the parotid-masticatory area;
- straight . Arthritis of the maxillary facial joint in this case develops due to direct infection, which occurs due to injuries or fractures of the jaw.
It is possible to determine the form in which the pathological process occurs only after carrying out specific diagnostic measures.
Causes of TMJ dysfunction
Conventionally, we can distinguish 3 main reasons for the development and etiology of the clinic of TMJ jaw joint dysfunction:
- Imbalance and disruption of the nervous coordination of the jaw muscles that raise and lower the lower jaw. Most often, the tone and tension of the muscle fibers in the right and left masticatory muscles are first disturbed, and then their imbalance occurs, irritation of the bilaminar zone and pain when chewing and swallowing.
- Chronic stress, over a long period of time (from a year or more), caused by a disorder of the central nervous system and higher nervous activity.
- Malocclusion and occlusion (closing) of teeth, coupled with non-standard sizes and position of the jaws relative to each other and the base of the skull.
As a rule, all of the above factors, to a greater or lesser extent, occur if a diagnosis of TMJ dysfunction syndrome is made. Reviews from patients and a forum on the Internet confirm this.
A hereditary predisposition to dysfunction of the jaw joints has been proven, with genetic anomalies associated with malocclusion, especially with micrognathia and macrognathia of the lower or upper jaw.
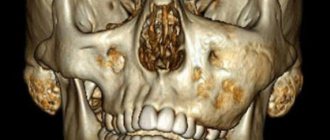
Methods for diagnosing arthritis of the jaw joint
Arthritis on x-ray
Diagnosis and treatment of the inflammatory process in the jaw joint area can be carried out by different specialists, which depends on the cause that caused its development. This could be an ENT doctor, a dentist, a traumatologist, an infectious disease specialist, or a dermatovenerologist.
The main diagnostic measures include:
- radiography . During this diagnostic exercise, widening or narrowing of the joint space is detected, which indicates acute or chronic arthritis of the TMJ, respectively;
- magnetic resonance imaging . The method allows you to study the condition of soft tissues, estimate the amount of fluid in the joint cavity;
- CT scan . This method of research makes it possible to differentiate between healthy and damaged tissues;
- ultrasound diagnostics . Using this research method, it is possible to visualize the fluid in the joint cavity. However, it is impossible to fully study the structure of soft tissues in this way.
Note! Acute arthritis of the TMJ is differentiated from such pathologies as acute otitis media, trigeminal neuralgia, gout.
After obtaining the necessary data and making a diagnosis, an individual course of treatment is developed.
Diagnostics
During an in-person examination, the dentist reveals a limitation, and a significant one, in the opening of the mouth, as well as a significant narrowing of the amplitude of jaw movement. To confirm the diagnosis, such patients are prescribed orthopantomography, teleradiography or computed tomography. A blood test will show signs of inflammation. If TMJ arthritis is rheumatoid, C-reactive protein increases. According to indications, magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed, which reveals disc displacement and degenerative changes. Primary damage to the muscle tissue is confirmed when the pain becomes stronger upon palpation.
As a result of the studies, purulent-septic diseases are excluded, the range of motion and functions of the joint are assessed. The minimum norm when opening the mouth is about 40 millimeters. Sound phenomena are common, but their occurrence does not indicate the need for therapy. If pain occurs with clicking and limited movements, therapeutic procedures are performed.
Treatment options
Pathology is treated in the following ways:
- Fixation
fixation . The first thing that is done when arthritis of the jaw joint is diagnosed is to ensure the immobility of the affected structure. To do this, apply a bandage. On the side of the diseased joint, between the teeth, a special plate is placed, which should remain there for 2-3 days;
- taking medications . The patient is prescribed analgesics to suppress pain and reduce temperature (Nurofen, Analgin), antibacterial drugs (Tetracycline, Amoxicillin), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Celecoxib, Nimesulide). Immunosuppressants may be prescribed, which is required for rheumatoid arthritis. The group of such drugs includes Etanercept, Leflunomide;
- drug blockade . The goal of therapy is to relieve pain in the affected joint. Novocaine injections may be prescribed;
- ointments, compresses . For pain in the affected joint, topical agents are prescribed, for example, ointments containing bee or snake venom. Ointments, by heating the affected area, restore joint mobility and suppress muscle spasms;
- sanitation of the oral cavity . This method is required for rheumatoid arthritis.
Drug blockade
Exercise is another way to restore the mobility of an inflamed joint at home. The specialist prescribes a course of therapeutic exercises for the patient. The most effective and common exercise is to open the mouth using only the upper part of the jaw.
Physiotherapy helps with TMJ arthritis. Effective measures include:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- mud therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- cryotherapy.
Therapeutic massage sessions are also available .
Surgical intervention is carried out in case of development of a purulent process, rupture of the joint capsule, fractures of the articular surfaces. During the operation, the specialist installs a drainage system.
Traditional methods of treatment include the following:
- cabbage leaf compress . You need to take one sheet, iron it with a heated iron, and apply it to the affected area. Carry out the procedure 1-2 times a day;
- compress with sea salt . It is necessary to calcinate natural sea salt in a frying pan, then wrap it in a piece of linen cloth. Apply to the affected area. Repeat application up to two times a day;
- infusion of yarrow . Pour 4 tablespoons of raw material into 400 ml of boiling water. The product should sit for 2 hours. You need to take it 4 times a day, 50 ml each time.
The condition must be corrected with the help of a doctor.
Treatment
Effective treatment of TMJ osteoarthritis requires an integrated approach.
In particular:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapeutic procedures to relieve symptoms.
Drug treatment
- The patient is prescribed non-steroidal drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of serious violations, the treatment protocol includes chondoprotectors that have a restorative effect.
- To relieve acute pain, potent analgesics are prescribed in various forms.
- In combination, the patient is recommended to install orthopedic structures (braces, mouth guards).
- It is recommended to limit your intake of solid foods.
Physiotherapeutic manipulations
- Ultrasound procedures.
- Laser therapy.
- Impact of dynamic currents.
- Electrophoresis.
- Microwave.
Surgery
If conservative methods do not bring the expected result, the patient is prescribed surgery. As a rule, surgical elimination of the problem is indicated only in complex cases when strong medications are ineffective. The operation is performed as an emergency if there is a purulent focus in the joint.
Instead of a conclusion
Statistics show that every third resident of the country has one or another joint pathology. Limitation of motor functions can lead to general complications, such as disruption of the metabolic and endocrine systems, hernias, limited mobility, etc. The earlier treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of recovery.
After successful treatment, a period of remission begins. The patient needs to remember that TMJ osteoarthritis is a chronic disease, so after the therapeutic course it is important to follow a diet and listen to the state of the body. Even minor infections can cause an exacerbation of the disease.
Prevention
To minimize the risk of developing a pathological process, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- promptly treat diseases in which the formation of purulent foci occurs;
- protect yourself from traumatic factors;
- avoid hypothermia;
- promptly treat nasopharyngeal pathologies;
- treat acute infectious processes;
- eliminate dental problems.
To prevent the pathological process from worsening, it is important to seek help from a medical facility as quickly as possible.
Specific symptoms
Treatment for temporomandibular joint arthritis depends on the form of the disease
The following symptoms are characteristic of TMJ inflammation:
- pain in the affected joint;
- limitation of jaw mobility;
- swelling of the skin around the affected area;
- severe hyperemia.
The pain syndrome intensifies when opening the mouth, while chewing food and with any other load on the joint. The pain intensifies in the first half of the day and gradually disappears in the evening. When the TMJ is affected, difficulty opening the mouth is observed. This is due to muscle stiffness due to pressure from the inflamed joint.
When you try to open your mouth wide, there is a noticeable skew of the jaw towards the healthy half. This is one of the characteristic symptoms of TMJ arthritis.
With infectious inflammation, the pain is acute and excruciating. A person may feel a feeling of fullness in the jaw or a pulsating joint. In this case, the skin turns red and the temperature of the epidermis around the inflamed joint rises.
Suppuration in the joint capsule is accompanied by a general deterioration in health. Patients complain of increased body temperature, decreased appetite, and severe fatigue.
Symptoms and treatment of temporomandibular joint arthritis depend on the form of the disease. In acute arthritis, excruciating pain is observed and the patient requires urgent drug therapy. With chronic arthritis, patients experience discomfort when trying to open their mouth, problems chewing food, and aching pain in the jaw. In this case, treatment should be aimed at normalizing metabolic processes in the joint and relieving swelling.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
The difficulty of identifying pathology is determined by the anatomical specificity of the joint structure, as well as the polyetiological nature of the disease. It is important not only to identify the presence of arthrosis, but also to determine the cause of its occurrence. Diagnostic methods include:
- Conducting an initial visual inspection;
- Instrumental examinations of the oral cavity;
- X-ray and computed tomography;
- Collection of samples for laboratory research.
The treatment plan is drawn up based on the results obtained during the formation of the clinical picture, and may include drug treatment, physical therapy (including electrophoresis), orthopedic treatment, as well as surgery.
During the treatment period, it is recommended to establish a dietary regimen that reduces the overall load on the jaw joint. As part of dental intervention, the causes that influence the formation of excess jaw pressure are eliminated, including bite defects and dentition anomalies.