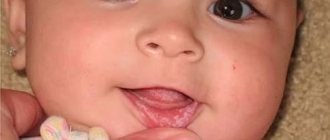
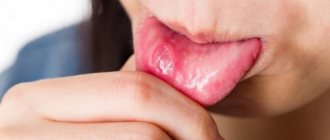
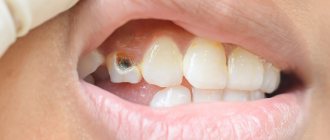
The problem occurs several weeks before the eruption of a baby or permanent tooth. The appearance of a cyst is indicated by a bluish-purple spot (hematoma). This is due to difficulty in tooth eruption.
An eruption cyst is a type of soft tissue benign tumor that appears when a tooth has already begun to erupt through the gum. Scientists and doctors have not agreed on why it occurs. The most likely causes: infection, trauma, improper development of teeth, which causes a lack of space for the “newbie”. In addition, it may be a consequence of caries and improper care.
Eruption cysts occur during the growth of baby teeth or, more often, at 6–9 years of age, when permanent teeth emerge. The fact is that, due to its anatomical structure and location, the chewing group of teeth is the most difficult to erupt.
If you notice a large formation in your baby’s mouth, in the place where a tooth should appear, consult a doctor. Do not resort to self-medication under any circumstances. Infusions, rinses and even strong antibiotics most likely will not help, but ruining a child’s health in this way will cause serious harm.
If you contact a specialist, treatment can follow one of two scenarios. In the most favorable option, the doctor will advise giving the child toys, special teethers, crackers - everything that the baby can chew. This will help break through the mucous membrane.
In difficult situations, surgery may be necessary. Then the surgeon will cut the gum under local anesthesia. This will make teething easier.
It is forbidden to try to cut or tear the mucous membrane on your own; you can cause a serious infection or injure your baby.
Causes of Teething Cysts in Children
During teething, a hematoma is formed; it occurs due to the fact that the tooth cannot break through the mucous membrane and thereby injures the gums and ruptures blood vessels. The longer the formation is in the oral cavity, the larger its size; in addition, the amount of swelling will depend on the group affiliation of the tooth.
The main causes of the tumor:
- pulpitis;
- caries;
- periodontitis;
- improper tooth treatment or lack thereof;
- eruption injuries.
The baby’s body tries to limit the source of infection, which is why a dense protective capsule is formed, which eventually develops into a cyst. The occurrence of such formations is quite common. An infection caused by carelessness, an unsuccessful attempt to chew hard food, a fall that led to a tooth injury - all this can serve as a starting point for gum inflammation and further development of a cyst.
Another fairly common mistake parents make, which can lead to the appearance of a tumor during teething, is negligence in caring for baby teeth.
It is generally believed that you should take serious care of your dental health after changing them. Since there is no point in treating non-permanent baby teeth - they will soon fall out. In fact, not taking things seriously leads to many problems. Any gum diseases and oral infections should be eliminated in a timely manner, regardless of how many teeth the baby has and whether they are permanent or not.
How to help a child at home with suppuration?
If suppuration and the formation of a lump on the gum appear, it is recommended to contact a dentist as soon as possible, but, unfortunately, for various reasons this is not always possible.
If an adult can endure pain (although, of course, situations are different), then it is much more difficult for a child to endure painful sensations, and it is not easy for parents to watch their child suffer. There are ways to alleviate the baby's condition. Naturally, they will not replace full-fledged treatment, so you can resort to them only in situations where going to the doctor is impossible right now.
These include:
- take as much warm liquid as possible, which reduces intoxication of the body;
- eat liquid food (moderately warm, but not hot!), as it injures already damaged gums;
- If the pain becomes severe, you can use painkillers. For example, Nurofen or Paracetamol - the exact dosage depends on the age of the child, so before use you should carefully read the instructions for the drug;
- to reduce swelling, you can resort to cold - any frozen product from the freezer compartment of the refrigerator is wrapped in a soft cloth and applied to the cheek;
- use rinsing solutions that temporarily relieve pain - chamomile decoction or the drug chlorhexidine, which reduces irritation.
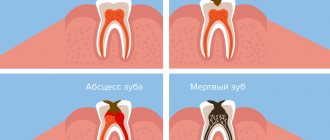
Complications with cyst growth
Tooth trauma, advanced caries, nasopharyngeal or periodontal disease, dental malformations - one or more of these factors can lead to the development of a cyst. The danger is that the cyst grows unnoticed. It usually does not hurt and at the initial stage does not cause discomfort or reaction of the lymph nodes. With further development, suppuration and various unpleasant sensations may appear. But even if there is no pus, the cyst is very dangerous. Therefore, do not delay treatment.
A cyst can lead to intoxication of the body due to the fact that waste products of harmful microorganisms enter the blood. The consequence of this can be headaches, high fever and, in the worst case, sepsis.
In addition, complications are caused by local problems - phlegmon, abscesses, osteomyelitis. These complications are inflammatory in nature and often occur when the cyst suppurates. The spread of pus can lead to destruction of the jaw bones, damage to the internal organs of the digestive system, liver, and heart.
It is impossible to avoid the appearance of a cyst, but if you properly care for baby and permanent teeth and treat infections in a timely manner, you can reduce the likelihood of its occurrence. In addition, periodic visits to the dentist will allow you to notice the problem at an early stage, when treatment will be as simple and easy as possible for the body.
A lump on an area of the gum where there is no tooth yet: what to do in this case?
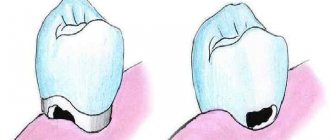
A couple of weeks before the tooth erupts, a cyst may appear on the gum, looking like a lump filled with a clear or bluish liquid. Such bumps are by no means common: dentists do not consider such formations to be a pathology requiring treatment. In addition, such formations on the gums in no way indicate an inflammatory process.
According to statistics, a small percentage of children are affected by the appearance of such a cyst. The child may not even suspect that he has a lump in his mouth, because if he touches it, there is no pain. However, a dental examination is still necessary, because the inflammatory process may still begin, in which case intervention will be required. The presence of inflammation is indicated by such signs as increased body temperature, pain when touching the lump, and swelling of the mucous membrane.
Most parents do not like the fact that their child has a lump in his mouth: in this case, you can ask the dentist to make an incision under anesthesia, as a result of which the fluid inside the cyst will come out. As a rule, when part of the cyst is removed, the crown of the tooth about to erupt is visible.
Cyst treatment
A dental cyst is treated either with therapeutic methods or with surgical intervention. The first ones are used in simple cases.
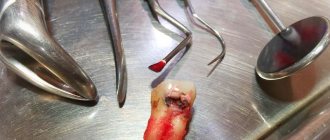
Surgery involves two types of operations - cystotomy and cystectomy. In both cases, local anesthesia is used. With cystomy, only the anterior wall of the cyst is removed. This is a less traumatic option, as it allows you to preserve the rudiments of permanent teeth during surgery on milk teeth.
Cystectomy is performed if the size of the cyst does not exceed 1.5 cm. This operation is more difficult, but postoperative recovery is much faster.
No matter how small and insignificant the swelling may seem to you, contact your dentist. This will avoid complications. And the problem will be resolved more easily and in a short time. Remember that no rinses, infusions or other folk remedies can guarantee recovery.
If the causative tooth is permanent –
In this case, the tooth is not only possible, but also necessary to be saved.
If permanent teeth in children have already formed roots, then treatment of permanent teeth with periodontitis will be carried out as in adults. However, treating a permanent tooth with incomplete root formation will present some difficulty, because such teeth may have very wide root canals as well as gaping apical foramina (see photo below). And this poses a great difficulty for high-quality filling. Permanent tooth with incomplete root formation –
Currently, in pediatric therapeutic dentistry, there are 2 main approaches to the treatment of periodontitis in permanent teeth with incomplete root formation. The first method is based on temporary filling of root canals with materials based on calcium hydroxide or calcium oxide. This requires a long, months-long exposure of these materials in the root canals (with periodic replacement of the material with fresh portions). This will narrow the width of the apical foramen by creating an osteocement apical barrier, after which it will be possible to perform permanent filling of the root canals.
The duration of such treatment usually ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 years. If a water-based material with calcium hydroxide is used, then it needs to be changed in the root canals monthly, but if it is oil-based - only once every few months. The disadvantage of this method is the need for frequent repeat visits, and the effectiveness is only about 70-90%, because the emerging osteocement barrier has a loose porous structure and does not guarantee 100% reliable sealing of the root canal lumen.
The second method is a one-step technique for forming a barrier in the area of the apical foramen using materials from the MTA group (mineral trioxide aggregate). An example of such material is “Pro Root”. The method assumes that the apical part of the root canal for 3-4 mm will be permanently sealed with MTA. Thus, in this case, only 1 visit is required, but it is best to use this method only in the last stages of root formation (otherwise, it will be best to combine temporary filling with calcium hydroxide-based material for 1-2 months + subsequent permanent filling with MTA) .
How to avoid complications
To avoid missing a cyst in the early stages, check with your dentist at least once every six months, especially if your child has chronic pulpitis or periodontitis. The occurrence of cysts is most likely between the ages of 6 and 12 years, especially during the formation of the first molars in the lower jaw.
Teach your child proper and regular oral hygiene. This will reduce the likelihood of inflammation and caries in both milk and permanent teeth. For this, use high-quality children's toothpaste for a specific age. Asepta has developed Baby, Kids and Teens pastes that take into account the dental needs of children of different ages. For the little ones, specialized Asepta wet wipes designed in the form of finger pads are suitable - wipe the gums after each feeding.
It is necessary to treat infections and caries in a timely manner so that they do not lead to the formation of a cyst in the future.
Preventive measures to prevent the formation of lumps on the gums
To reduce the likelihood of an abscess to a minimum, a child from childhood should be taught to carefully observe oral hygiene.
The list of the most effective measures includes:
- Brushing your child's teeth twice a day. First, parents should brush their child’s teeth themselves, showing how to do it correctly, gradually giving the child more independence in this matter;
- rinsing your mouth after every meal;
- minimizing sweets in the diet - it is important to ensure that the child keeps caramel and candies in his mouth as little as possible;
- Do not introduce your child to chewing gum (the product is especially harmful if it contains sugar).
conclusions
Having noticed inflammation, in no case should you engage in independent treatment or hope that everything will go away over time on its own. Even if the cyst opens, this will only slightly reduce the inflammatory process, but bone tissue destruction will begin in the upper part of the tooth, which will ultimately cause the tooth to be removed, since it will become impossible to cure it. Remember that at the site of the opened cyst there remains a hole through which pus will flow into the mouth: those around you will clearly smell this discharge, and the patient himself will also “enjoy” its taste. Treatment in case of cyst formation should begin with a visit to the dental surgeon, who will first take an image to make the correct diagnosis.
Symptoms and diagnosis
At the initial stage of development, the only symptom of the disease can be pain. Obvious symptoms can be noted at the progressive stage:
- biting is accompanied by complaints of pain;
- swelling and hyperemia are visible on the gums. The formed characteristic tubercle with noticeable spots (pus) may have a bluish tint;
- when you press on the gum, pus will come out - this is evidence of the formation of a fistula.
When a child’s dental cyst is mature, it manifests itself:
- painful sensations when palpating enlarged submandibular and cervical lymph nodes;
- headache;
- loss of appetite;
- general weakness;
- increased temperature in the evenings.
A dental cyst at the Novostom clinic is diagnosed:
- when the dentist conducts the initial examination;
- using extended radiography to determine its type;
Stages of development
Due to the ongoing formation of immunity, the child’s cyst has the opportunity to develop. The child's body produces a violent reaction when faced with even minor exposure to a pathogen. The formation of a fibrous capsule can go through three stages:
- Initial. Pain syndrome is characteristic.
- Progressive. The swelling becomes noticeable, but the pain subsides. Specialists at the Novostom center suggest that this is due to the death of the nerve.
- Suppuration. It is not advisable to let things get to this point. Timely removal of a tooth cyst in a child will relieve his body of immune and toxicological overload.