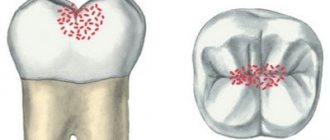
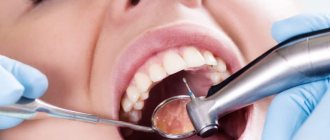
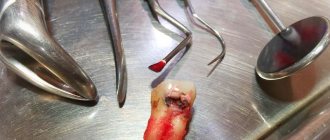
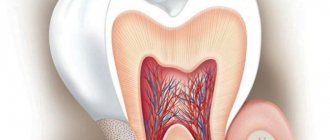
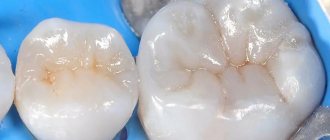
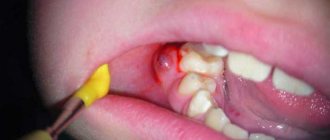
Cervical caries is a type of carious lesion that affects the area at the neck of the tooth directly below the gum line. Dental disease itself is characterized by demineralization and destruction of dental tissues (enamel and dentin) in the area of the crown and tooth root. Often it does not manifest itself in any way in the initial stages, which makes diagnosis difficult... However, as it develops, the patient begins to experience pain symptoms when exposed to temperature and chemical stimuli. The disease is dangerous because it develops rapidly, since the enamel of the cervical area is quite thin. This is why it is very important to detect it early and begin treatment as quickly as possible.
The therapeutic department of dentistry CELT invites you to undergo diagnosis and treatment of cervical caries in Moscow. Our multidisciplinary clinic has been operating in the capital's paid medical services market for more than a quarter of a century. Contacting our dentistry is the key to correct diagnosis and treatment in accordance with international standards. For this, we have everything necessary: specialists with decades of experience in scientific and practical work and a powerful diagnostic and treatment base. The department has the appropriate licenses and certificates. The price of treatment for cervical caries is determined individually after making a diagnosis and developing tactics for its elimination. You can view the basic prices by going to the “Services and Prices” tab or by contacting our information line operators.
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | price, rub) |
| Restoration of the crown part of the tooth (long-term temporary restoration) | 9 000 |
| Using a rubber curtain to isolate the mouth | 1 500 |
| Composite veneer | 8 000 |
| Composite retainer with support | 7 500 |
| Therapeutic pad for the treatment of deep caries | 500 |
| Light-curing composite filling (1-plane) | 4 000 |
| Filling made of light-curing composite (2-plane) | 5 000 |
| Filling made of light-curing composite (3-plane) | 6 000 |
| Glass ionomer cement filling | 2 000 |
| Polishing the filling | 350 |
| Placing a temporary filling | 400 |
| Light-curing temporary filling | 1 000 |
| Removing an old filling | 300 |
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a consultation with a dentist-therapist is 1,000
Make an appointment
More information about cervical dental caries
Carious lesions are considered the most common disease in the world, and for good reason. Today, they affect more than 95% of the world's population, and this figure continues to increase. The name “caries” itself, translated from Latin, means “rotting,” and in fact it says everything about the pathological processes occurring with hard dental tissues. The difference is in the localization: not on the crown or in the root region, but in the area of the neck of the tooth near the gums. Another designation for cervical dental caries is “cervical.”
It affects the surfaces of the frontal and chewing units from the cheeks, lips and tongue. It is most often diagnosed in patients between the ages of thirty and sixty. At the same time, there are many cases where carious processes in this localization affect baby teeth in children. Often they encircle the tooth, turning into a circular shape. Dentists believe that the localization of pathology at the border of the dental crown and root is still dangerous because:
- The enamel and dentin in this area are quite thin and vulnerable, which is why pathological processes quickly spread to deeper tissues;
- Changes in the dental surface during cervical caries are not always visible, so the patient seeks professional help only when toothache appears;
- This type of disease, more often than others, can cause complications in the form of inflammation of the pulp and periodontal tissue, which increases the risk of losing the entire tooth;
- Due to the fact that the pathological area is close to the gum line, treatment is significantly more difficult (especially for molars).
Complicated caries in children
In children and adolescents, complications, like the caries that precede them, develop at lightning speed. This is due to insufficient mineralization of enamel in childhood and the tendency of young patients to infectious diseases caused by streptococci - sore throat, bronchitis, measles and scarlet fever.
Advanced forms of caries in children lead to:
- the development of its circular shape, when, starting from the neck of the tooth, decay spreads around its crown, and over time the tooth breaks off;
- spread of infection along the surface of the crown (planar caries). In this case, the tooth completely darkens, the child complains of aching pain;
- acute and chronic pulpitis;
- infection of the rudiments of permanent teeth, resulting in multiple caries after their eruption.
Cervical caries: causes of development
On the one hand, caries in the cervical region occurs for the same reasons as its other types of localization:
- Insufficient oral hygiene (especially in hard-to-reach places) and accumulation of dental plaque;
- Eating simple carbohydrates, from which streptococci synthesize a glucose polymer that causes demineralization;
- Growth of cariogenic microflora of the oral cavity (acid-forming streptococci Mutans, Viridans, Sanguis);
- Reduction of anti-carious microflora and the ability of hard dental tissues due to changes in the composition of saliva, a decrease in its antibacterial properties and deficiency.
On the other hand, its development is initiated by a number of other specific factors characteristic only of the cervical region:
- Anatomical features that may manifest themselves as disproportionality of the gingival margin to the height of the dentition or its pronounced severity. The latter accelerate the accumulation of plaque in these areas;
- Inaccessibility of the cervical area and difficulty in ensuring effective hygiene. As in the first case, this leads to the rapid accumulation of plaque, the formation of tartar, and even the development of inflammation of the gum mucosa;
- Frequent use of toothpastes with whitening properties and toothbrushes with hard bristles, which have an abrasive effect on the enamel in the cervical area, which is already quite thin (0.1 mm compared to 1.7 mm in the area of the dental cusps or 0.7 mm - in the area of fissures);
- An unbalanced diet, in which there is a lack of vitamin B1, as well as too frequent consumption of sweet/acidic foods or pharmacological drugs that make tooth enamel porous and susceptible to negative influences.
You need to be especially attentive to your health if cervical caries has affected several units at once. Why? Often this phenomenon indicates a disruption of the endocrine system and pathologies of the thyroid gland or the development of such a serious disease as diabetes. It also happens that pathological processes manifest themselves due to poor heredity: if one of the parents suffered from them, then the risk that they will occur in the child is quite high.
Why does caries form?
There are two groups of factors that provoke the development of caries - local and general.
There are several theories explaining the mechanism of this disease. Among the most well-known reasons for the formation of caries: - crowding of teeth does not allow high-quality care of the oral cavity, which contributes to the processes of fermentation and decay;
- excessive consumption of foods rich in carbohydrates and lack of solid foods in the diet;
- low pH of the oral cavity;
- fissures and tartar.
The appearance of carious lesions is facilitated by a lack of minerals (fluoride, calcium, phosphorus), weakened immunity and chronic gastrointestinal diseases, heredity and poor-quality drinking water.
Stages of cervical caries and its clinical manifestations
The stages of cervical caries are the same as those of other types in terms of localization. Each has its own symptoms, by which the dentist can determine it:
- At the spot stage, a white chalky spot appears in the cervical area, the surface of which is initially smooth, but gradually becomes rough, which indicates that the enamel is beginning to deteriorate. At the same time, the spot itself becomes more noticeable and stands out against the background of unaffected areas. There are usually no clinical manifestations at this stage;
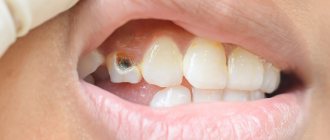
- At the stage of superficial caries, the spot darkens, the enamel continues to deteriorate, and the patient experiences short-term pain in response to exposure to temperature (hot or cold food) or chemical (sweet, sour food) stimuli. As soon as the influence of the latter is eliminated, the pain symptoms also go away;
- The middle stage manifests itself as the formation of a carious cavity deep into the tooth. Food particles get stuck in it, causing pain. Sometimes they occur during conversation or oral hygiene activities;
- At the stage of deep cervical caries, serious destruction of dental tissues and pain symptoms are observed in response to exposure to irritants. If treatment is not started promptly, the process will spread to the dental cement and reach the pulp. Thus, pulpitis will begin, which will manifest itself in severe pain.
At later stages of development, when pathological processes involve the deep layers of dentin and cement, the cavity becomes even deeper. Dead tissue, pieces of food and pathogenic microflora get into it. Failure to adequately treat cervical dental caries at this stage will lead to serious complications in the form of pulpitis and periodontitis. The latter consists of inflammation of the connective tissue around the tooth root and its apex. Ignoring this problem will cause the development of a jaw cyst, abscess or fistula, as well as a very high risk of losing a tooth.
What is caries - main aspects
Dental caries is a long-term process of demineralization of enamel and destruction of hard tooth tissues. The disease is characterized by several stages of development. With a long course, a cavity defect is formed, which can be seen upon careful examination. A dental examination can detect caries at the chalk spot stage, an early stage of defect formation.
Symptoms of the early period of destruction of dental tissue are mild. On the surface of the enamel, spots ranging from pale yellow to gray are barely visible. Increased reaction to temperature and chewing of food. Medium and deep caries increases the intensity of symptoms, pain appears during exercise or at rest.
The disease can be complicated by the formation of retention cysts, pulpitis, and periodontitis. Complications from progressive caries are the main cause of tooth loss. According to WHO statistics, the incidence reaches 97%, with children accounting for 35% of the population. The largest number of cases are recorded in economically developed countries.
Diagnosis of cervical caries
Often the first question that patients ask is “How much does it cost to treat cervical caries?”... There is no definite answer to this, since each case is individual and requires the same individual approach to treatment. Before developing its tactics, CELT dentists carry out diagnostics, which make it possible to determine the stage of the disease, the extent of the pathological process and the amount of tissue destroyed by it. Based on the results obtained, they determine treatment methods, the need for intervention by an endodontist (if the pulp is affected) and an orthodontist (if a crown is needed). Depending on this, the exact price for treatment of cervical caries is calculated.
- Finding out from the patient information about pain symptoms, its nature and the circumstances under which it appears;
- Carrying out temperature tests, which make it possible to differentiate caries from other dental diseases;
- X-ray of the affected unit, from which one can determine the size and depth of the lesion, the presence/absence of a boundary between cement and dentinal tissue;
- Electroodontometry, thanks to which it is possible to determine the condition of the pulp and its reaction to exposure to a current of a certain strength.
Cervical caries must be differentiated from:
- Local destruction of the vestibular surface of hard dental tissues of canines, incisors and molars in the shape of a wedge (“wedge-shaped defect”);
- Non-carious lesions of the vestibular surface of fangs, incisors and molars, which is characterized by defects of dentin and enamel (“erosion”);
- Damage to tooth enamel that occurs due to constant, prolonged exposure to excess fluoride in the body (“fluorosis”).
How many teeth with caries can be cured at one time?
The decision is made by the attending physician after a thorough examination. Factors such as the complexity and technical features of the procedure, the patient’s health status, and the presence of allergic manifestations are taken into account here. In some cases, it is prohibited to treat even two teeth at the same time.
Previously, dentists used the rule “One appointment, one tooth treated.” Today there are no such restrictions, but only a few teeth with caries can be treated at a time. Other diseases require more attention from a doctor.
How is cervical caries treated?
As already mentioned, treatment tactics are selected individually, since they depend on the stage and extent of the process, as well as the volume of affected tissue.
Remineralization
In the early stages, remineralization therapy is carried out, which eliminates dentin excision. In the process, it is exposed to drugs containing sodium or tin fluoride, or calcium drugs, as well as agents with an antiseptic effect. The technique gives good results provided that the patient uses toothpastes for cervical caries, brushes teeth correctly and regularly, and also changes his diet to provide his body with all the necessary substances to restore hard tissues.
Infiltration using “Icon” technology
Another conservative treatment method that eliminates the excision of hard dental tissues. Just as in the first case, its use is limited to the initial stage of development of the disease. It consists of soaking the affected tissues first with a special gel, and then with an infiltrate, which, penetrating into the smallest capillaries of enamel and dentin, blocks the affected areas, preventing them from growing further. Thus, the pathological process will be stopped without drilling and filling. Its advantages are obvious: being 100% effective, it is absolutely safe and does not require anesthesia. The patient needs to visit the dentist once and spend no more than forty minutes in his chair. The technique can be used for young children and pregnant women.
Treatment of cervical caries with filling
It is indicated at the middle stage of development of the pathological process and provides for the following:
- Removal of affected hard tissues with bur;
- Thorough disinfection of the carious cavity;
- Her preparation for placing a filling;
- Filling with new generation composites;
- Surface grinding and polishing.
If units of the frontal region are affected, special attention is paid to selecting the color of the composite to accurately imitate the native tissue.
Treatment of cervical caries with prosthetics
Most often, it is required at the stage of a deep process, if there is significant destruction of the coronal part of the tooth. Algorithm of the dentist’s actions if the pulp is not affected:
- Most often, it is required at the stage of a deep process, if there is significant destruction of the coronal part of the tooth. Algorithm of the dentist’s actions if the pulp is not affected:
- Disinfection of carious cavity;
- Application of therapeutic and insulating pads with calcium;
- Installation of a temporary filling for three to four days;
- Its removal in the absence of pain and installation of a denture.
If the process has affected the pulp, endodontic treatment will be required: it is removed, the root canal is cleaned and filled. The tooth is strengthened with a pin or inlay and a prosthesis is placed.
Features of the treatment of deep caries
Removing a carious cavity with deep damage to dental tissue is fraught with difficulties, and the choice of method depends on the degree of destruction of your own tooth. Treatment tactics:
- With pulpitis. Pulp damage involves deep preparation and removal of the nucleus pulposus along with nerve endings from the root canals. An antiseptic is placed into the lumen of the root canal, and the cavity is closed with a temporary filling or medication. This is necessary for etching and eliminating a secondary infectious process. After 1-3 days, the root canals are filled, and the defect is covered with a composite material.
- No pulp damage. Sometimes, with deep damage, the pulp remains intact, covered by a small layer of intact dentin. Preparation is carried out precisely to this tissue in order to preserve the integrity and functionality of the root system. Often the therapist has to leave this part of the dentin, despite its softening, friability and pigmentation. In such cases, a pad based on paste-like calcemin is placed at the bottom of the defect for antiseptics and restoration of dentin. An insulating gasket and a permanent filling are also placed into the defect cavity.
In case of significant tooth decay, patients are recommended to restore the body of the unit with a composite material. This method is not considered durable due to abrasion, destruction, and the formation of new carious cavities. The only alternative in particularly difficult cases is implantation, microprosthetics or prosthetics with a bridge structure.
Reviews about our doctors
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
Words cannot express my gratitude to Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva. This is the best doctor in the world. I got an appointment after many years of being ignored by the dentist’s office and with a bitter experience of treatment in another paid clinic, the mistakes of which had to be corrected in the first visits. Thank you for this... Read full review
Roman Stanislavovich Sh
25.07.2020
Root caries
Root caries
develops deep under the gum, violating the integrity of the tissues, while during visual inspection it may not be noticeable.
The basal species is localized on exposed roots and is characterized by a rapid course of the process. The enamel in the root zone has a minimum thickness, so it is quickly destroyed under the influence of external factors. How to treat root caries
is an important question that only a dentist can answer after an initial examination and a comprehensive diagnosis.
Preventive measures for cervical caries
It is important for patients to remember that this type of pathology develops very quickly, so if even minimal changes are detected in the cervical area, they should seek dental help as soon as possible. Modern techniques make it possible to completely restore the appearance and functionality of the affected tooth with uncomplicated caries. Treatment is cheaper, faster and easier for the patient, and the risk of complications is reduced to zero.
As for preventive measures, they consist of ensuring effective and regular hygiene measures for the oral cavity using individually selected toothpaste, brushes, floss and rinse. In addition, you should regularly visit the dentist for preventive examinations and professional oral hygiene, to prevent the development of gum diseases.
Professional treatment of cervical caries in CELT allows you to preserve the functionality and aesthetics of the dental unit. You can make an appointment with our specialists online or by phone: +7 (495) 788‑33‑88.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Locations
Interdental caries can develop anywhere in the dentition
. Patients turn to dentists both with caries between the front teeth and with damage to the chewing teeth. The photo below shows an example of the development of caries between the chewing tooth and the wisdom tooth.
Also, carious lesions can occur in both the upper and lower teeth. The infection affects not only permanent teeth, but also baby teeth. Therefore, both children and adults are at risk.
Is it necessary to treat caries at the initial stage if the tooth does not hurt?
It is necessary to treat caries, since the process of disease development has already begun.
As long as the destruction has not affected the pulp (tissue complex), you can quickly cope with the treatment and relieve the patient from unpleasant sensations and significantly save the family budget, since treating pulpitis is much more expensive. Treatment of a tooth that has only been affected by caries will take 10-15 years minutes and will cost 3-5 times less in a paid clinic than working on a tooth with pulpitis or other complex disease. To install a filling in a complex case, you will need to visit the clinic at least 2-3 times.
Tooth decay is contagious - fact or fiction?
Some scientists consider caries to be a contagious disease, since its occurrence and development is caused by pathogenic microbes. The microorganisms themselves are transmitted by contact, which means that caries is theoretically a contagious disease.
Other experts point out that each person has his own pathogenic microflora in his mouth, but it does not always cause caries. The disease appears as a result of poor hygienic care, as well as as a result of exposure to a number of other factors. It turns out that caries is not a contagious pathology, despite the existing theoretical calculations.
What is the difference between caries and pulpitis?
Caries and pulpitis are the most common dental diseases. They are very similar to each other, but there are also differences. The main difference is the depth to which inflammation has developed in the tooth tissues.
Caries appears at the initial stage of tooth damage. A small stain or darkening appears on the surface. This is called the first manifestation of caries. Subsequently, inflammation develops and moves deeper into the tooth. Caries that has reached the nerve is called pulpitis. Pulpitis already affects the nerve, and not just the tooth tissue. Pulpitis is characterized by severe pain, and caries can be accompanied by a painful reaction to sweets and cold foods.