Perforation of the maxillary sinus (or, as it is also called, the maxillary cavity) is an iatrogenic complication that occurs during dental procedures on the upper jaw. It consists of perforating the bottom of the sinus, which causes an abnormal communication to appear between it and the oral cavity. Air begins to flow into the mouth through the hole, bleeding from the hole and a feeling of compression in the projection of the cavity are possible. If infectious agents get into the wound, sinusitis develops.
The CELT Dentistry Department invites you to undergo a course of treatment for perforation of the maxillary sinus in Moscow. Our multidisciplinary clinic welcomes leading domestic dentists with decades of scientific and practical experience behind them. They have a modern equipment base for accurate diagnosis and treatment in accordance with international standards. Our dental department has all certificates and licenses, treatment is carried out on the basis of an official contract with guarantees. We use the most effective methods for closing maxillary sinus perforations that provide the best results.
Consultation with a dental surgeon - 1,000 rubles.
Plastic perforation of the maxillary sinus - 7,500 rubles.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a consultation with a dental surgeon is 1,000
Make an appointment
Structural features
The maxillary (maxillary, main) sinus is located inside the bone of the upper jaw. It is delimited from the oral cavity by the alveolar process. It forms the bottom of the cavity. The volume of the cavity of the upper jaw can be up to ten cubic centimeters. She has a communication with the nasal cavity. The inside of the cavity is lined with mucous tissue.
The structure has features that make it easy to damage:
- Sometimes the thickness of the bone plate between the bottom of the cavity and the roots of the teeth does not exceed one millimeter.
- There is a variant of the location of the roots of the second and first molars, when they penetrate into the cavity and are delimited from it only by the mucous membrane that lines the sinuses.
- The bone plate quickly thins out during inflammatory processes.
- Small thickness of trabeculae of the upper jaw bone.
Such structural features cause slight damage to its wall, even when the doctor did not violate any rules and did not apply significant force.
Features of the maxillary sinus
The maxillary, or maxillary, sinus is a cavity inside the skull, bounded on all sides by bone tissue. In adults it is quite voluminous, sometimes reaching 10 cm3. Its shape and location in the bones determine the unique pronunciation inherent in humans. The cavity, resonating, forms the timbre of sound.
The paranasal sinuses are lined from the inside with a thin mucous membrane and are connected to the nasal cavity by thin tubules for drainage of mucus and ventilation. If the holes become clogged, inflammation develops - sinusitis.
There are a number of known features that explain the appearance of a hole in the bottom of the maxillary sinuses:
- The size and thickness of the walls separating the maxillary sinuses from the oral cavity are individual for each person. With thinned bone (up to 1 mm thick), the sinus is easily perforated when the dentist works. This is also facilitated by the proximity of the roots of the front teeth.
- It happens that the roots of distant teeth penetrate into the sinus area and are separated from it only by a thin film of mucous tissue. As long as the tooth is healthy, everything is fine. If the doctor begins to manipulate the canals of such teeth, the mucous membrane breaks through and penetration occurs.
- Even healthy bone can atrophy and become thin and weak with persistent periodontal and periodontal diseases. Or the trabeculae of the upper jaw - the plates that form its skeleton - are insignificant from birth. It is easy to perforate such an obstacle with sharp instruments.
Therefore, it cannot be unequivocally stated that the doctor is always to blame for the development of complications.
What is perforation of the maxillary sinus?
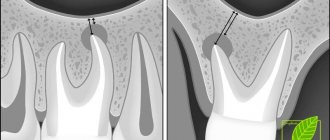
The formation of a defect in the maxillary sinus is a complication during manipulations on the upper jaw. A hole is formed between the oral cavity and the main sinus. This can happen when removing the molars of the upper jaw (molars and premolars) or during prosthetics. And also for complex endodontic treatment of tooth roots and removal of cystic formations. The defect is formed at the site of the tooth socket.
General overview
The maxillary sinuses, or sinuses, are located in the bone voids present in the structure of the maxillary region, and through a small opening they are connected to the nasal passage. The cavity bottom is located next to the tissues that provide attachment to the root parts of the lateral units of the dentition.
Dental intervention involving interaction with the upper jaw, in some cases, leads to the formation of an open canal - perforation, which is a consequence of damage to the sinus. Factors causing negative consequences include:
- Extraction of an element, the root part of which has fused with the sinus during development;
- Thinning of bone structure due to chronic inflammation;
- Removal of an extensive cyst located on the apical part of the root;
- Failure to comply with safety precautions during tooth implantation or extraction;
- The presence of chronic diseases affecting the structure of the jaw.
In addition, manipulations that increase the risk of perforation include treatment of teeth and gum tissue, which involves deep immersion into the structure of the affected area.
Causes of perforation.
The dentist is not always to blame for this complication. It can often appear due to the individual anatomical characteristics of the patient. It may also be due to the course of the inflammatory process in the tissue surrounding the root.
The causes of perforation may be the following:
- Perforation of the maxillary sinus during tooth extraction occurs most often. Its bottom is perforated when a tooth is suddenly removed with great force.
- In some patients, the roots of the upper teeth penetrate into the sinus cavity. When teeth are removed, the integrity of the bone plate is automatically violated. During treatment, filling material may enter the cavity.
- For technically complex endodontic treatment. With this type of treatment, the inflammatory focus is located deep in the gums or under the root of the tooth. Instead of removing the diseased tooth, the dentist tries to save it. During this type of treatment, the bone plate is easily damaged.
- In the process of installing an implant in the upper jaw bone with subsequent dental prosthetics, the maxillary cavity can be easily damaged. This is because the implant is similar to a screw and must be screwed into the bone. If there are defects in this manipulation or anatomical and topographical features, the patient’s bone plate of the upper jaw may be damaged (the size of the implant was incorrectly selected, there were defects in preparation for implantation). Before placing an implant, the doctor does not take into account the fact that when a tooth is removed, the thickness of the bone plate quickly decreases.
- Perforation can occur due to chronic inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth (periodontitis). With this pathology, the bone plate delaminates and becomes thin. If a tooth has to be removed in such a situation, perforation almost always occurs.
- Carrying out manipulation to remove an impacted tooth from the maxillary cavity.
- Perforation often occurs during tooth root resection procedures. The need for this manipulation arises when extracting a root with a festering cyst.
Prevention
Perforation of the maxillary sinus is a problem that is easier to avoid than to fix it later. Since perforation is caused by dental intervention, preventing the problem falls on the shoulders of the dentist. He is obliged:
- responsibly examine the patient before performing procedures;
- clearly understand the anatomical features of the client before major intervention;
- strictly adhere to the intervention technology.
The dentist is also obliged to respond adequately to any signs of perforation that has just occurred due to his fault. If for some reason the doctor has not fulfilled his own duties, then it is up to the patient - he must refuse self-medication and put aside the fear of dentists, in no case try to “endure” the discomfort, but immediately seek help.
Symptoms of perforation of the maxillary sinus
How does perforation of the maxillary sinus manifest itself? There are specific symptoms when this happens.
Signs of perforation:
- Bleeding from the tooth socket with the inclusion of air bubbles. When you exhale through the nose, the number of bubbles will increase.
- With perforation, bleeding occurs not only from the tooth socket. It may come from the nasal passage, which is close to the sinus.
- The patient speaks “in his nose” or nasally.
- Then there is a feeling of free passage of air through the tooth socket.
- The patient sometimes notes distension and a feeling of heaviness in the middle third of the face on the affected side.
If the perforation was not recognized immediately and treatment was not carried out, then the symptoms of sinusitis are added to the previous clinic.
Sinusitis manifests itself:
- Body temperature rises.
- The feeling of fullness in the projection of the maxillary sinus intensifies.
- Nasal breathing is difficult.
- The nasal mucosa on the affected side is swollen.
- General weakness increases.
- Aching pain in the nasal region.
- Purulent discharge from the nasal passage on the side where the manipulation took place.
Symptoms
It is important to understand that the maxillary sinus is not isolated. Air circulates constantly in it. Therefore, if there is this pathological condition, then the flowing blood will contain air bubbles. In addition, part of the blood mass will penetrate into the sinus.
To make a correct diagnosis, you need to contact a highly qualified specialist who, based on the test results, prescribes the most effective therapeutic measures.
If a person has any doubts about the presence of pathology, he should immediately visit a dental surgeon or ENT doctor.
Among the most common signs that may indicate that there is damage to the maxillary sinus are:
- Bleeding of the tooth socket, which occurs after the procedure for removing a dental unit. In this case, a large number of air bubbles are observed in the blood. Their number, as a rule, increases when the patient takes a deep breath.
- Bleeding from the nostril closest to the injury site. As a rule, with high-quality removal, blood flows only from the hole.
- Voice change. The man begins to nasal. This condition is not immediately noticed after removal of a dental unit, since a tampon is placed in the oral cavity, which prevents conversation.
- The sensation of air flow passing through the hole formed after tooth removal. In this case, the patient notes pressure in the upper jaw.
When perforation of the sinus occurs during the implantation procedure, it is as if the surgical instrument sinks deeper than the distance at which it should be located. If such a situation arises, a competent specialist will immediately determine that the bone membrane has been perforated.
For minor injuries that were not noticed by either the specialist or the patient, more dangerous symptoms begin to appear:
- severe inflammatory process;
- formation of extensive purulent contents;
- frequent migraines;
- constant pain in the upper jaw.
When inflammation begins, the patient has difficulty breathing. There is swelling on one side of the nose. In addition, this process is accompanied by general weakness and increased body temperature.
If these symptoms occur, you should notify your doctor about a recently pulled tooth or implant placement.
Methods for determining perforation
This pathology can be identified only on the basis of a characteristic clinic. If there is any doubt, a full range of diagnostic procedures is performed, including instrumental methods.
To diagnose a bone plate defect and subsequently eliminate it, it is necessary to perform the following manipulations when examining the patient:
- Carefully examine the tooth socket after the tooth root has been removed.
- Perform sounding of its bottom.
- Ask the patient to pinch their nose and exhale through the nose. The air will escape into the mouth through the tooth socket.
- If the patient puffs out his cheeks, air passes into the nasal cavity. But this technique can provoke sinus inflammation and should not be used frequently.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- probing the dental and perforation canal using a thin probe;
- CT scan;
- radiography, in the pictures you can see the defect and foreign bodies;
- general blood analysis.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of perforation of the floor of the maxillary sinus during tooth extraction is based on a typical clinical picture. In doubtful cases, as well as when such a complication is suspected during implantation or endodontic manipulations, it is necessary to use instrumental diagnostic methods:
- Probing the socket of an extracted tooth or perforated canal with a thin probe . This allows us to determine that there is no bone bottom in the wound. In this case, the instrument passes freely through soft tissues and does not encounter obstacles along its path.
- X-ray of the sinus area . In this case, the pictures can reveal both darkening of the cavity due to the accumulation of blood in it, as well as fragments of dental roots, implants or filling material. Sometimes it is advisable to conduct radiography with contrast, when a contrast agent is introduced into the cavity through a perforation fistula.
- Computed tomography , which allows you to determine perforations and the presence of foreign bodies in the sinus with maximum accuracy.
- If old perforations are suspected, general clinical blood tests , the result of which may indicate the presence of an active source of infection in the body.
Treatment of sinus perforation during tooth extraction
The tactics for managing a patient with perforation depends primarily on the condition of the sinus itself and the time of detection of this defect. This defect should only be treated by a qualified specialist.
Treatment of perforation of the main sinus of the upper jaw has the following objectives:
- Closing the defect.
- Prevent the process of inflammation in the sinus.
- Prescribe treatment if there is inflammation.
- If there are foreign particles, they must be removed.
If the perforation was immediately noticed and there are no signs of infection, then the treatment measures are as follows:
- Preservation of a blood clot in a tooth socket.
- Take measures to prevent its infection (application of a tampon with iodine solution).
- Apply stitches to the gums, if necessary.
- Treatment is carried out until the granulations grow and the defect is closed.
- The tampon is not removed from the hole.
- If the defect does not close on its own, it is covered with a plastic plate. It is fixed to the teeth.
- Prescribing a course of drug therapy aimed at counteracting inflammation.
If the perforation is complicated by gum rupture and penetration of foreign particles into the soft tissues surrounding the tooth socket, plastic closure of the defect is performed on the same day. Or after some time, when you are confident that the fabric will hold the seams. Before this, all foreign bodies are removed and areas that have undergone necrosis are excised. The manipulation is performed under x-ray control to make sure that there is no foreign body. If penetration of a foreign body into the cavity occurs, then it is necessary to perform surgery in a hospital setting.
Operation stages:
- Opening of the main sinus of the upper jaw.
- Removal of a tooth from the maxillary sinus (its fragments) and other foreign bodies.
- Excision of necrotic areas.
- Closing the defect.
How to treat?
The tactics for eliminating the problem depend on exactly what causes led to the perforation and what the general clinical picture is. Almost always, repairing a perforation requires surgery, the only exception to this rule is when a hole was created during a tooth extraction, provided that the dentist found it immediately and no foreign objects or infection got inside. If the problem is identified immediately, it is important to keep the blood clot in the place where it formed and prevent it from becoming infected - it will become a natural barrier to the infection entering the sinus. Protecting a blood clot from infection is carried out using a tampon with an iodine solution, which will have to be kept for at least a week.
In some cases, the doctor chooses the tactic of suturing the gum tissue. Another alternative is to install a compact plastic plate that is attached to adjacent teeth and acts as a barrier between the oral cavity and the sinus until the septum is restored.
For obvious reasons, physical barriers cannot provide a 100% guarantee that infection will not penetrate the hole, so the doctor additionally prescribes vasoconstrictors and anti-inflammatory drugs. They can be taken at home, but sometimes require the patient’s outpatient presence.
Penetration of any foreign objects into the maxillary sinus is regarded as a serious complication, which automatically means the need for surgical intervention and hospital treatment. In such a situation, the sinus is opened, removing foreign objects and tissues that cannot be restored, after which the fistula is covered with the patient’s tissues.
Consequences of perforation of the maxillary sinuses
If the presence of a defect is not noticed and the patient, despite the symptoms, does not consult a doctor, this threatens the onset of serious and dangerous consequences for health.
Possible consequences:
- Severe inflammatory reaction.
- Formation of osteomyelitis.
- Generalization of infection.
- Development of abscess and phlegmon.
- Loss of healthy teeth in the fistula area.
- Chronic sinusitis.
- Meningitis.
- Encephalitis.
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis.
To avoid the formation of complications, the patient should visit the dentist in case of any problems after tooth extraction.
What are the dangers of sinus injury?
Since the complication does not always manifest itself immediately, symptoms of sinusitis that arise after a few years force the patient to consult a regular ENT doctor. Treatment, as a rule, does not bring results - in most cases the cause is not found. You start going from one doctor to another, and precious time is lost. The longer a foreign body is in the sinus, the higher the risk of tumor formation. If sinus perforation is left unattended, it can lead to:
- chronic sinusitis and sinusitis
- inflammation of the roots of adjacent teeth
- osteomyelitis of the jaw
- encephalitis and meningitis
Old sinus perforation
If the defect is not detected and eliminated in a timely manner, acute inflammation will subside. Within a month, the patient develops a fistula. It connects the gum surface and the sinus cavity. Signs of a chronic inflammatory process appear. This will be a serious complication.
The patient has complaints:
- The presence of dull pain in the upper part of the cheek, of a constant nature. They radiate to the eye area and temporal region.
- Feeling of nasal congestion on one side.
- Separation of pus from the nose and from the fistula on the upper jaw.
- Swelling of the middle third of the face on the affected side.
- Air movement through the defect.
- Difficulty speaking.
- Getting fluid from the mouth into the nose.
Therapy of old processes is associated with significant difficulties. Patients are indicated for surgical treatment in a hospital.
Operation stages:
- Opening of the main sinus of the upper jaw.
- Removing foreign bodies.
- Excision of necrotic areas and granulations.
- Excision of tissues forming the fistula.
- Closing the defect.
After the operation, drug therapy with the use of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and decongestant drugs is mandatory for a course of two weeks.
Signs if perforation was left without the attention of a doctor
Symptoms of inflammation after unsuccessful treatment occur in different ways - after a few days, weeks or even years. Depends on the sterility of the foreign body in the sinus, its ability to cause inflammatory processes, and the characteristics of the patient’s immune system. The following manifestations are possible:
- feeling of heaviness;
- pain when chewing;
- purulent and serous discharge from one nostril;
- elevated temperature;
- impaired sense of smell;
- pain when lightly tapped under the eye and in the nose area.
These are typical signs of odontogenic sinusitis caused by poor quality dental treatment. The key difference from rhinogenic sinusitis (when sinus infection occurs from the side of the nasal passages as a result of ARVI or influenza) is that signs of the inflammatory process are detected only on one side, where treatment was carried out.
Advantages of treatment in our clinic
Summing up, we can understand that it is very easy to get a septal defect in the cavity of the upper jaw. This depends both on the actions of the dentist and on the individual anatomical characteristics of the patient.
When seeking treatment at our clinic in Moscow, you can be sure that you are guaranteed not to have such complications. We prevent complications.
To do this, we prescribe a mandatory set of preventive measures to prevent them:
- We conduct a complete examination of patients before performing any dental procedures.
- We perform a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s anatomical and topographical features.
- We follow all stages of dental procedures.
You will be satisfied with the quality of dental services if you contact us at the clinic. Our clinic has the most modern equipment at the level of the standards of the best European and American dental clinics. We can offer you a full range of all diagnostic procedures in one place. Our doctors have been trained in the world's leading dental centers and are proficient in the latest treatment and prosthetic techniques. We will help even in the most difficult cases. We develop an individual course of treatment taking into account all the characteristics of the patient. We use only proven treatment methods and materials of the highest quality. Our clinic has made the highest quality dental services available. You can view the full range of our treatment and diagnostic capabilities on our website.
Causes and mechanisms of fistula development
The oral cavity, due to the peculiarities of its anatomical structure and physiological load (food intake and salivation), is aseptic. The presence of microorganisms creates conditions in which the penetration of infection into all kinds of wounds and surgical incisions is almost inevitable. Despite the fact that during bone grafting surgery the most sterile conditions are created to prevent bacteria from entering the wound, their infection cannot be ruled out both during the intervention and in the postoperative period. Most inflammatory processes after sinus lifting develop due to the patient’s violation of the dentist’s recommendations, namely: ignoring disinfectant rinses, antibacterial ointments and oral baths, eating on the side of the bone graft.
Once in tissues that have recently undergone surgery, bacteria find themselves in ideal conditions for reproduction. The presence of minor blood clots, tissue detritus, pieces of food, if hygiene requirements are not followed and the optimal temperature is present, create a breeding ground for them. In the process of life, microorganisms destroy the structures surrounding them, and the release of leukocytes from the bloodstream to destroy hostile microflora leads to the release of pus and inhibition of healing processes.
The fistula after sinus lifting and bone grafting is not able to heal on its own due to the presence of a defect in the bone tissue. The development of such a pathological course leads to the appearance of a focus of chronic infection, the penetration of bacteria into the maxillary sinus with the formation of sinusitis and other complications. In this case, the fistula after an open sinus lift can be located not only at the implant site, but also on the lateral surface of the gum. The appearance of a fistula tract more often occurs after closed bone grafting due to worse fixation of the denture.
Among other things, the formation of a fistula can occur when the tooth root is not completely removed during a sinus lift.
Preventive measures before and after sinus lift to prevent the development of a fistula
Fistula after sinus lifting and bone grafting is quite easy to prevent by taking certain groups of medications before and after surgery, as well as observing the rules of oral hygiene.
Rules of conduct after surgery
The protective regimen should last from 5 to 7 days after the sinus lift. It includes a number of behavioral features:
- When brushing your teeth, special dental pastes with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties are used: Solcoseryl, Lakalut, Sensodyne. Oral hygiene procedures should be carried out twice a day (in the morning and before bedtime). It is necessary to brush your teeth on the operated side with great care so as not to disturb the condition of the tissues and implant after surgery.
- When eating, chewing movements should be carried out exclusively on the healthy side. Drinking all kinds of liquids through a straw is strictly contraindicated. You should also give up sweet foods for a week.
- During the first two weeks, you must stop playing any sports. This is especially true for athletics, gymnastics, cycling, swimming and martial arts. You should avoid the latter for a month.
- Try, if possible, not to sneeze or cough, avoid head injuries and bruises, and shaking.
- When sleeping, do not lie on your operated side.