How do blood vessels bleed?
Bleeding can be mild, moderate or severe. His character may be:
- arterial - strong, jet;
- venous - blood loss occurs gradually;
- capillary - minor discharge due to damage to small vessels.
The problem itself can be stable/unstable, recurrent. Vessels of the mucosa, submucosal and intermuscular plexus, as well as those located outside the gastrointestinal tract, can bleed.
The expiration can last for several hours or days. In medicine there are:
- profuse blood loss - the patient loses more than 1 liter of blood in 1-3 hours and needs urgent medical attention;
- acute - less than 1 liter expires in 1-2 days, the patient’s vital signs are relatively stable;
- chronic - develops slowly, often over several weeks or even months, the intensity of symptoms gradually increases.
How to competently provide first aid for severe capillary bleeding?
First aid for capillary bleeding involves applying a tourniquet. The indication is extensive damage, impaired coagulation. Rules for applying a tourniquet:
- Wrap the tourniquet 2 times around the injured limb above the wound. Correct actions lead to the fact that the pulse under the wound will not be palpable.
- Place a piece of fabric under the tourniquet to avoid trophic changes.
- Be sure to record the exact time of application of the tourniquet. The skin condition is monitored.
- In the warm season, you can leave the tourniquet on the body for up to 2 hours, in winter - no more than 1 hour. Every 30 minutes you need to relax the rubber band for 30 seconds to avoid tissue death. If everything is done correctly, the limb does not turn blue or swell. And vice versa.
After applying a rubber tourniquet, the victim is quickly sent to the hospital for diagnosis and treatment. If you don’t have a rubber band at hand, use a belt, scarf, or tie.
Why is there a problem?
Medicine knows about 200 causes of bleeding in the digestive tract. At the first symptoms, you should seek professional help from a doctor and under no circumstances self-medicate, as this will only worsen the condition.
Ulcer
The most common reason. With an ulcer, the integrity of the mucous membrane of the organ is disrupted, and the main difference of the disease is deep tissue damage. The disease is chronic - with remission and exacerbations. On the mucous membrane of the stomach, esophagus or duodenum, areas of inflammation are formed, in which the protective function (mucus secretion) is reduced. Gradually, the mucosal tissues, including the walls of blood vessels, become thinner, which leads to their rupture.
Phlebeurysm
The problem may occur in the esophagus or stomach due to increased pressure in the portal vein. The most common cause is cirrhosis of the liver. Rupture of a large vessel with varicose veins is extremely dangerous, since at this moment there is a copious outflow of blood. According to statistics, in 40% of cases it stops spontaneously. And the activity of bleeding depends on the degree of liver damage.
Colon diverticulosis
With this disease, the lining of the colon bulges, forming diverticula. The reasons for their formation in medicine are not completely clear; they are mainly associated with increased intraluminal pressure. Basically, the pathology is typical for adult patients over 50 years of age. In the acute course of the disease and rupture of intrawall blood vessels in the area of diverticula, intestinal bleeding occurs.
Tumors and polyps
They occur in the small and large intestines and are benign neoplasms that grow into the intestinal lumen. Most often, bleeding is minor and chronic. The danger lies in possible degeneration into malignant tumors.
Haemorrhoids
This is the formation of venous nodes around the rectum in the anal area. The main causes are thrombosis or tissue inflammation. The disease can be acute or chronic, and its common causes are a sedentary lifestyle, excessive exercise, and obesity. Bleeding (the color may be scarlet or dark) is minor and occurs most often after bowel movements.
More rarely, esophagitis, acute hemorrhagic gastropathy, erosive duodenitis, and Mallory-Weiss syndrome are found as causes of bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract. In the lower part, bleeding can be caused by tumors, vascular malformations, and various inflammations.
How to quickly stop bleeding?
Small injuries can be easily localized by applying pressure to the wound for 5 minutes with a hand or cloth to form a blood clot. For cut wounds, the edges will stick together after some time. The skin around the wound is carefully wiped with the available antiseptic, then a bactericidal patch or sterile bandage is applied.
If a deep venous injury with drip bleeding is detected, it is necessary to sit or lay the victim down in order to elevate the damaged area above the heart. A hemostatic sponge is applied to painful large wounds, securing it with a bandage. The sponge gradually dissolves on its own; there is no need to remove it. In the absence of a sponge, apply a pressure bandage to the wound. Gauze folded in 2-3 layers and a bandage for fixation are suitable. If blood has leaked through the bandage, apply a piece of cotton wool and bandage again over the first bandage.
With internal bleeding, the victim feels drowsiness, weakness, and wants to drink. The pulse quickens, the pressure drops, the head is dizzy. Damage to the stomach is indicated by vomiting blood, intestines - tar-like stool, rectum - scarlet blood in the stool, ureters - red urine. If internal capillary bleeding is suspected, first aid will be to lie the victim down and apply cold to the damaged area. Then the doctors who arrived to the call act.
Who is at risk?
Basically, diseases that lead to bleeding are observed in adults. Moreover, according to statistics, men are 2 times more likely than women to be diagnosed with problems with the gastrointestinal tract - the stomach, duodenum. As we noted above, ulcerative pathologies hold first place in terms of the number of diseases. The peak age for diseases is 40-45 years.
However, the problem is not limited to adults. The diagnosis associated with ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract is often made to adolescents who uncontrollably consume junk food and drinks. Cases of the formation of intestinal polyps are also common.
Gastric and intestinal bleeding is increasingly being detected even in newborns. Basically, they are caused by intestinal volvulus. In 3-year-old children, leakage can be caused by the formation of a diaphragmatic hernia, as well as abnormalities in the development of the organs of the lower gastrointestinal tract.
Possible complications
Complications can arise in the presence of deep wounds, as well as in the absence of the necessary treatment and standard hygiene. Otherwise, purulent and infectious processes may occur that will require long-term treatment.
If pustules appear, you cannot squeeze them out yourself; this must be done by a surgeon under sterile conditions.
When nerve fibers are damaged, part of the tongue may lose sensitivity, but with adequate treatment this function can be restored.
What symptoms to look out for
Patients with the diagnoses we listed above should be especially monitored for the appearance of alarming symptoms. If you are taking medications for the liver and gastrointestinal tract, carefully monitor your well-being. If you are concerned about the changes discussed below, consult your doctor. However, knowing these signs is useful for every person, since many diseases of the lower and upper gastrointestinal tract develop without obvious painful sensations. Often their first manifestation may be the symptoms of bleeding.
Weakness
This is the main sign of any prolonged bleeding. Weakness gradually increases, the patient's skin turns pale, he feels cold sweat, a ringing in the ears, and trembling of the limbs. The weakened state may last for several minutes, after which it passes and returns periodically. If blood is bleeding actively, fainting or semi-fainting and even shock are possible.
Vomit
This symptom accompanies severe blood loss - more than 0.5 liters. If the vomit is dark cherry in color, it is most likely coming from a vein near the esophagus. If unchanged blood is clearly visible in the vomit, the integrity of the artery in the esophagus is most likely compromised. If the patient vomits so-called “coffee grounds” of brown color, the problem lies in the gastric vessels. Only a doctor can accurately determine the nature, location and intensity of blood loss.
Chair
Traces of blood in the stool may appear within a few hours or 1-2 days after the integrity of the blood vessels is damaged. With significant problems with the stomach or duodenum, as well as blood loss in a volume of more than 0.5 liters, you can observe melena - loose stools that resemble tar in color and consistency. If the blood loss is smaller, which often happens, for example, with intestinal bleeding, then the stool remains formed, but its color darkens.
Please note that darkening of the stool can occur due to eating foods that contain dark coloring substances, for example, blueberries and cherries. Dark stools are not an absolute sign of the presence of blood in the stool and problems in the upper or lower gastrointestinal tract. The diagnosis can only be made by a qualified specialist.
Measures to stop bleeding
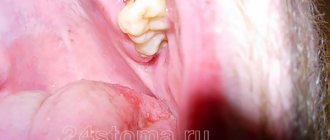
If you accidentally bite your tongue, don't panic. You need to stop the bleeding immediately, taking care to disinfect the oral cavity. To successfully stop bleeding, you should hold ice or cold water in the bite area. This will help narrow the blood vessels. When an organ is severely injured, you cannot hesitate; you must urgently visit a doctor.
- It is important to prevent pathogens from entering the wound. This will prevent infection and the development of complications.
- Before the doctor arrives, the patient must organize the free passage of the substance. To do this, tilt your head over the sink and open your mouth slightly. It is necessary to ensure that liquid does not flow down the larynx into the respiratory organs or esophagus.
- The blood will quickly stop if you press on the affected area. To do this, you need a sterile napkin or bandage. The bandage should be kept on until the bleeding stops.
Painful sensations are relieved with painkillers. For acid burns, use a weak alkali solution. Areas of damage caused by chemicals are immediately washed with running water. Do not ignore contacting your doctor. Only a specialist can determine the cause and prescribe the correct treatment.
How to make a diagnosis
The doctor examines the patient, assessing his external condition, the shade of the skin and mucous membranes. Then he measures blood pressure - often it is low.
In the clinic, the patient undergoes a general blood test. Using it you can quickly get an idea of the level of hemoglobin and the volume of other blood cells. Additionally, the diagnosis is made by biochemical analysis, but it is usually prescribed several days after the onset of blood loss, since the chemical composition of the blood changes only over time.
The main diagnosis concerns the detection of the very cause of the violation of the integrity of blood vessels. To do this, doctors use the following hardware examinations.
- Endoscopy - examination of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum using a flexible tube with a miniature camera allows you to quickly detect a problem area;
- Contrast radiography - an effective method for detecting bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract involves injecting a safe contrast solution into the organ, followed by an X-ray;
- Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern method that allows you to obtain comprehensive information about the condition of all tissues of a particular organ of the gastrointestinal tract.
First aid
To stop bleeding, you need to do the following:
- Wash well with soap (preferably household soap); it is recommended to treat them with an antiseptic solution or use rubber gloves in order to achieve maximum sterility. Such actions minimize the risk of pathogenic microorganisms and infections entering the wound, since all kinds of inflammatory processes in this organ are very difficult to treat. Often, with such phenomena, patients are practically unable to talk, eat, or even drink.
- Take the proper position: while sitting, bow your head forward, which will prevent blood from entering the throat, while the blood will come out, so you need to prepare some kind of vessel for spitting or place yourself near the sink.
- Remove from your mouth anything that can further injure or irritate the mucous membranes: chewing gum, piercings, dental braces, cigarettes. Provide the tongue with a state of complete rest. If the person is conscious, it is advisable to provide a constant stream of clean water to cleanse the mouth.
- The bleeding can be stopped by covering the damage; to do this, take a sterile material (bandage, gauze, cotton swab) and press firmly to the affected area. You need to hold it until the blood stops completely, that is, at least 15 minutes. Change the material periodically. It can be removed only after the bleeding has stopped.
- Rinse your mouth with water and treat with an antiseptic solution to prevent the penetration of bacteria and infections.
- If bleeding is accompanied by a painful symptom, you can apply a piece of ice or use a drug from the analgesic group.
- For the first few days after bleeding, avoid physical overload, as it can provoke a second reaction.
- After a strong blow or fall that leads to bleeding, you must contact a traumatologist or dentist.
- If the blood flows heavily, immediately call a team of doctors.
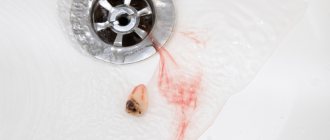
Let's find out what to do if a tooth is pulled out and the bleeding doesn't stop
Moreover, there is a list of restrictions that cannot be carried out during bleeding:
- Do not drink hot drinks (tea, coffee).
- Do not treat the affected area with alcohol solutions, as such actions can cause burns.
- Do not cover the wound with your fingers or press your tongue to the roof of your mouth.
Main causes and symptoms
Capillaries are the smallest vessels, and in normal cases, their superficial damage to the skin does not pose any danger. Stopping the bleeding occurs on its own and does not require special action. The main sign of damaged capillaries is bright red blood. It flows slowly, there is no pulsation. The blood clotting system will work quickly. The vessel contracts, the blood flow slows down and stops due to the formation of a blood clot from platelets and fibrin fibers. Typically the process lasts up to 5 minutes.
Causes of capillary bleeding:
- abrasions, scratches and cuts;
- burns;
- low platelet concentration (thrombocytopenic purpura);
- decreased coagulability (hemophilia);
- pseudohemophilia - increased vascular permeability, causing spontaneous bleeding;
- oncology;
- purulent inflammation of the skin affecting the capillaries;
- atherosclerosis;
- hormonal imbalance, etc.
External bleeding is noticeable immediately, but internal bleeding (from the vessels of the stomach, uterus, intestines) is determined by the person’s condition. The main signs are weakness and drowsiness for no particular reason, pale skin, severe thirst, rapid pulse, decreased blood pressure. Sometimes the listed symptoms are accompanied by severe shortness of breath, nausea, fainting and dizziness. If first aid is not provided in time, internal capillary bleeding can be fatal.