Causes
The exact causes of the pathology are not fully understood. The disease is not an independent disease; it appears against the background of other diseases. Most often, this phenomenon occurs in men over 40 years of age, but is sometimes observed in women. This disease is very rare in children.
The pathology is most often observed in people with gastrointestinal dysfunction, ulcers and gastritis. The development of the disease is greatly facilitated by poor oral hygiene, smoking habits and excessive coffee consumption.
The main causes of the development of the disease are considered:
- long-term use of medications, especially antibiotics;
- fungal infections;
- dehydration;
- chemotherapy;
- metabolic disease;
- weakened immune system;
- Regular rinsing of the mouth with solutions containing astringents.
The risk group also includes people with dental defects and the absence of a large number of teeth, since in this case they are forced to eat only soft food, which does not have the proper abrasive effect on the surface of the tongue.
Geographical language. What kind of disease is this and how to deal with it?
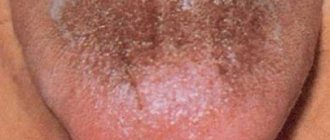
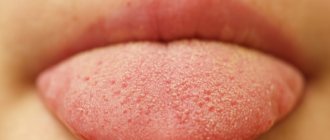
Geographic tongue (benign migratory glossitis) is an inflammatory disease that manifests itself as lesions on the back and sides of the tongue.
Typically, the affected tongue has a "bald" red area of varying sizes that is partially surrounded by an irregular white border.
The appearance of the affected part of the tongue is the result of the loss of finger-shaped projections (papillae) that cover the surface of the tongue. From time to time, similar lesions appear in other parts of the mouth - the palate, cheeks, under the tongue or on the gums. This is called geographic stomatitis or erythema migrans.
Geographic tongue can vary in color, shape and size - hence the name. Manifestations can persist for different periods of time - days, months and even years. They often disappear completely on their own. But they may appear again later.
What causes geographic language?
The causes of this disease are not fully known. Factors suspected include emotional stress, bad habits, allergies, diabetes and hormonal imbalances. An association between geographic tongue and psoriasis has been reported. However, none of these factors have been conclusively linked to geographic language.
Who gets geographic language?
Geographic tongue is a fairly common condition. Some reports in the medical literature indicate that geographic tongue affects women slightly more often than men. This can happen at any age, including in childhood. It is estimated that it may occur in 1-2.5% of the population.
Is it possible to get infected with it?
No, geographical language is not contagious. There is no evidence that the disease is transmitted in any way.
How is geographic tongue diagnosed?
Based on clinical examination and detailed history.
Are there any complications?
Geographic tongue is a disease that does not pose a threat to general health.
Does geographic tongue require treatment?
In most cases, there is no need to treat this condition.
Apart from appearance, geographic language in most cases does not manifest itself in any way. Sometimes it can cause unpleasant sensations: burning, tingling of the tongue, most often associated with eating spicy or sour foods.
If discomfort persists, your pediatrician may recommend anti-inflammatory medications (topical corticosteroids, such as triamcinolone in toothpaste applied several times a day as needed) or pain medications (local analgesics) applied directly to the affected areas. Antiseptics and anesthetics may also be effective.
Some authors have reported that the use of cyclosporine, topical and systemic antihistamines, and topical retinoids can sometimes produce beneficial results.
Can geographic tongue transform into cancer?
There are no documented cases of geographic tongue causing cancer.
Should you see a doctor if you suspect geographic tongue?
Geographic tongue is an uncomfortable condition but does not cause health problems. However, tongue damage can be a sign of other serious illnesses.
If you or your child has tongue lesions that do not go away within 10 days, be sure to contact your primary care physician/pediatrician or dentist.
Symptoms
Pathology is immediately detected during a visual examination by a dentist. In the initial stages of the disease, the presence of a foreign object in the mouth is felt, other unpleasant signs gradually appear, then the upper part of the tongue noticeably turns black. In advanced cases, the affected area occupies two-thirds of the tongue. The disease is accompanied by unpleasant odor from the mouth, changes in taste sensations, a metallic taste appears in the mouth, a feeling of tickling and soreness on the surface of the tongue, as well as causeless nausea. In rare cases, there is a burning sensation and severe itching.
Cracks in the tongue
Causes
The causes of cracked tongue are:
- Glossitis is an inflammation of the tongue that occurs either as an independent disease or as a symptom of systemic pathologies.
- Viral and bacterial infections, especially often glossitis is caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1.
- Mechanical injuries of the tongue, serving as an entry gate for infectious agents. Provoking factors leading to damage to the tongue are low-quality elements of orthopedic structures (prostheses, braces), sharp edges of damaged teeth.
- Constant consumption of hot, hot, spicy food, strong alcoholic drinks, having an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the tongue, violates its integrity, which leads to the penetration of pathogenic microflora into cracks with the development of inflammation.
Other reasons - why is the tongue cracked?
- An allergic reaction to various food and drug allergens, to denture material, to components included in toothpaste or hygienic mouth rinses.
- Deficiency of vitamins (especially groups B, A) and microelements (iron, zinc) increases the sensitivity of the tongue mucosa to adverse external influences.
- Failure to comply with hygienic rules for oral care.
- Severe dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue, caused by disruption of the salivary glands, dehydration or elevated body temperature.
- Diseases of the digestive system, cardiovascular, endocrine system, collagenosis, metabolic disorders.
- Helminthic infestation leads to the fact that some nutrients are not absorbed in the body, local immunity decreases, and the condition of the mucous membranes, including the tongue, worsens.
Folded glossitis is a congenital abnormality of tongue development. It is characterized by an increase in the size of the tongue and the appearance of grooves, cracks and folds on its surface. As a rule, a folded tongue does not cause discomfort, but with poor oral hygiene, food debris can accumulate in the deep folds, which serve as a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacterial or fungal microflora. As a result, inflammation develops: redness, swelling. The patient experiences pain, burning of the tongue, and bad breath.
Desquamative glossitis is called “geographic tongue” due to the presence on the surface of the tongue of numerous red, smooth lesions surrounded by a whitish border, which create a bizarre pattern reminiscent of a geographical map. In places where the epithelium peels off unevenly, furrows and cracks appear on the tongue. In areas of desquamation (desquamation) of the epithelium, there is increased sensitivity of the tongue to thermal and food irritants (hot, cold, sour, salty), burning and tingling, and impaired taste sensations.
The appearance of desquamative glossitis is most often associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as endocrine disorders, and pathologies of the hematopoietic system.
Diamond-shaped glossitis is characterized by the appearance on the back of the tongue of an atrophic area of red, sometimes bluish color, on the surface of which filiform papillae are completely absent. Diamond-shaped, oval lesions are flat or protruding above the surface of the tongue (tubercular, papillomatous form). In the tubercular form, the affected area consists of tubercles separated by folds and cracks.
The disease is asymptomatic and is discovered by chance at a dentist's appointment. In rare cases, the patient is bothered by a burning sensation and sometimes pain on the back of the tongue if inflammation develops.
Symptoms
Cracks in the tongue can be combined with other symptoms of glossitis.
- Glossitis, caused by bacterial microflora, is manifested by symptoms of acute inflammation: swelling, hyperemia, local pain, local fever.
- With glossitis of a viral nature, bubbles appear on the surface of the tongue, which, after opening, leave behind painful erosions.
- When affected by fungi, the tongue is covered with a cheesy coating, under which the hyperemic mucosa is visible.
- Unpleasant sensations in the mouth: itching, burning.
- Change in color of the mucous membrane of the tongue.
- The appearance of cracks, erosions, ulcers.
- Taste sensations become dull and sometimes disappear completely.
- Swelling of the tongue interferes with correct sound pronunciation, speech becomes slurred.
In the absence of treatment, glossitis becomes chronic with a persistent change in the structure of the tongue in the form of the development of hyperplastic processes.
Treatment
If cracks appear in the tongue that cause discomfort to the patient, this is a reason to consult a dentist.
For pathologies of the dental system, the following is prescribed:
- Sanitation of the oral cavity: treatment of caries, professional teeth cleaning (removal of plaque and tartar), correction of malocclusions, installation of new fillings to replace outdated ones, replacement of dentures.
- Thorough oral hygiene - proper brushing of teeth, tongue, use of an irrigator, rinsing the mouth after meals.
- Maintaining a mechanically and chemically gentle diet during inflammation means excluding hot, spicy, sour, salty foods and strong alcoholic drinks from the diet.
- Treating the tongue with antiseptic solutions.
- For pain, local anesthetics are used.
- Prescription of wound-healing, softening agents for the mucous membrane of the tongue.
If dental reasons for the development of pathology are not confirmed, you should consult a therapist. When identifying the causes of cracks in the tongue, the patient undergoes treatment from specialized specialists: gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, hematologist and others.
Published: 11/25/2021 Updated: 12/02/2021
Information verified by an expert:
Rykova
Tatyana Viktorovna,
expert doctor, co-founder of the VitaDent clinic, dentist-therapist
Back to the list of articles
Treatment
It is necessary to contact a dentist or maxillofacial surgeon with such a problem. To obtain a complete clinical picture, it is necessary to undergo examination by a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist and neurologist. Since the pathology develops against the background of other diseases, a comprehensive treatment regimen is used.
Only treatment of concomitant diseases, professional cleaning and treatment of the oral cavity, taking multivitamin complexes, antifungal medications and, if necessary, sedatives will help eliminate this unpleasant defect. Removal of heavily overgrown papillae can be carried out by cryodestruction (exposure to the pathological focus with liquid nitrogen). It is also necessary to adjust your diet, enriching it with foods with fiber, vitamins and minerals.
The prognosis for black hairy tongue is usually favorable. Elimination of causative factors, as well as appropriate comprehensive treatment of the disease, leads to complete restoration of the surface of the tongue.
Types of spots on the tongue and the reasons for their appearance
The spots can be of different colors: red, white, yellow, pink, brown and even black. The location of the spots also varies widely: at the tip, at the root, under the tongue or on the sides. Even the relief of the formations may differ from the relief of healthy tissues, which is associated with atrophy of the taste buds.
Photo: white spot on the tongue of an adult
There may be several spots or just one. They come in big and small, round and dotted. It is important to remember that any spots on the tongue indicate problems in the body. All of them are a deviation from the norm and necessarily require a doctor’s diagnosis.
Why do red spots appear on the tongue?
The tongue may become covered with red spots for the following reasons:
- A red spot or blister that does not go away for a long time may indicate such a terrible disease as cancer. Therefore, if it is detected, you should immediately seek medical help.
Scarlet feverAnother reason for the appearance of red spots on the tongue is scarlet fever. Children are most often affected by this disease. In the early stages of the disease, the spots are surrounded by bubbles; when they burst, small ulcers form in their place.
- Another terrible disease in which red spots form on the mucous membrane of the tongue is AIDS. Such spots are localized at the tip or at the root of the organ; they usually protrude above the general surface, reach 7–8 mm in width and are covered with a pale gray coating. Lymph nodes with this disease are always enlarged.
StomatitisStomatitis is far from the least important cause of the appearance of red spots. Most often, dental red spots are located on the root of the tongue, sometimes they are only surrounded by a red halo, but inside are covered with a white coating.
- If red dots and a white coating appear on the tongue, this is the so-called geographic tongue. This disease often occurs in children and pregnant women.
- Hemorrhages can also cause spotting. However, they are usually accompanied by the appearance of red dots on the tip of the tongue, and not full-fledged spots. Hemorrhage may indicate a disease such as mononucleosis.
- The mucous membrane of the taste organ may become colored after eating food with dyes.
- Allergic reaction.
- Mechanical or chemical damage (burns, wounds).
Brown spots on the tongue
There are few reasons why brown spots may appear on the tongue:
Smoking. This bad habit contributes to the formation of an unaesthetic brown dark plaque on the mucous membranes of the mouth and teeth.- Eating food with dyes, chocolate, large amounts of tea or coffee gives a spotty effect.
- The light brown color of the spot indicates problems with joints or diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
- Brown spots with a yellow tint indicate dependence on alcohol, diseases of the lungs and bronchi, as well as drug intoxication.
A dark spot on the tongue is an alarming sign. In this way, the body reflects problems with the gastrointestinal tract, “talks” about kidney and liver diseases, and problems with the gallbladder. If a dark spot is detected, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination in the clinic, identify the cause of the disease and eliminate it.
Red spots and dots on the tongue with a white coating
In both adults and children, red spots on the tongue can appear in tandem with a white coating. Red spots with plaque appear on the tongue against the background of such pathologies:
- Constipation. Prolonged constipation causes intestinal problems, which in turn affects the entire body and can lead to red circles on the tongue.
- Poisoning. This disease can cause small red dots and plaque to appear on the tongue.
- Lack of vitamins and nutrients. With vitamin deficiency, the color of the surface of the tongue often changes to pale with small specks. Weakness, lethargy, and pallor of the skin are added to spotting.
- Kidney dysfunction. Round pink spots form on the tongue.
- Inflammation. Redness of the taste organ may be accompanied by burning, pain, irritation and increased sensitivity to hot and cold.
The tongue becomes covered with a white coating due to many diseases. Even a common cold, poor diet, or the wrong medication can lead to the formation of plaque in the mouth.
Causes of a “bald” tongue
“Bald” spots on the tongue indicate atrophy of the taste buds. With this pathology, some areas of the tongue become completely smooth, as if polished, and acquire a pinkish or bright red color.
Causes of pathology:
- Burns that quickly pass, and the “bald spot” is again overgrown with papillae. A burn is always accompanied by a burning sensation.
- Lack of vitamins and nutrients: B1, B2, B12, PP, proteins.
- Chronic malnutrition.
- Anemia.
- Smoking.
- Infections.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Dehydration.
Redness of the entire surface of the tongue and its “baldness” are often caused by chemotherapy. Smooth pink spots appear with psoriasis.
Other pathologies
Black, blue, green, yellow spots and plaques on the tongue are not as common as those listed above. What do they mean:
- Black spots occur due to fungal infection or iron oxidation - in the presence of piercings.
Photo of plaques on the tongue with leukoplakiaYellow is a common symptom of jaundice. With this disease, the skin of the body also acquires a yellow tint.
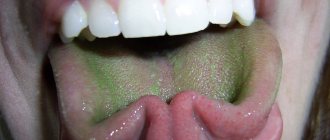
- Green - can be either a symptom of candidiasis (fungal infection) or a consequence of smoking, damage to the mucous membrane or oxidation of the piercing.
- Blue ones are often harbingers of more serious pathologies, such as cancer or pneumonia. The tongue is blue in case of sepsis, bronchial asthma, all kinds of heart defects or poisoning. Most often, the reason for the appearance of blue spots on the tongue is problems in the functioning of the human respiratory system.
- Formations in the form of plaques appear on the mucous membranes of leukoplakia due to too rapid growth of benign cells.
Prevention
As such, there is no prevention of black villous tongue. Even with good oral hygiene, you can encounter a similar phenomenon, but with timely treatment of diseases that lead to the development of such a complication, you can minimize the likelihood of the disease occurring.
The following rules must also be observed:
- thoroughly brush your teeth, gums and tongue with a soft brush;
- It is necessary to drink enough water, because if there is a lack of hydration in the oral cavity, it begins to develop; bacteria;
- reduce coffee consumption and quit smoking and alcoholic beverages.
The disease recurs quite rarely. During an exacerbation, the patient is advised to follow a gentle diet; food should be warm and soft in consistency.
When and which doctor to contact about a coating on the tongue
As a rule, tongue coating is not the main symptom.
And it is other symptoms that tell you which doctor you should see. If plaque on the tongue is accompanied by symptoms of ARVI, you should consult a physician. If you have symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases, contact a gastroenterologist. If there are no such symptoms, and the cause of your concern is plaque, in case of white plaque you can consult a dentist, in case of yellowish or gray plaque, you can consult a gastroenterologist. And in any case, you can consult a general practitioner - family doctor or therapist. A child with a persistent coating on the tongue should be shown to a pediatrician.
What it is
In a healthy child, the tongue has a uniform pink color without spots or plaque. But in the presence of any pathology, spots of various colors and sizes may appear, which represent:
- An uneven accumulation of plaque on the surface of the tongue, which consists of exfoliated epithelium, tiny food particles, and microorganisms.
- Excessive proliferation of epithelium in certain areas of the mucous membranes.
- Limited inflammation.
- Benign or malignant neoplasms.
Let's look at the main reasons for the appearance of various spots and methods of treating them.