Content:
- How long does it take to bleed after tooth extraction?
- Why is it important how long it takes to bleed after tooth extraction?
- Types of violation
- Why does it take a long time to bleed after extraction?
- Possible consequences of bleeding
Extraction is one of the most difficult operations performed by dental surgeons. During the recovery period after it, serious complications may develop, one of them is bleeding. Therefore, the gum healing process requires close monitoring by the doctor and vigilance of the patient himself.
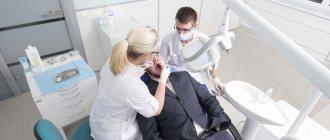
What does a dentist do?
First of all, the doctor will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis. In accordance with it, the dentist will carry out treatment.
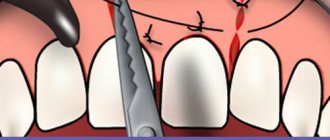
First aid is to stop blood loss. To do this, local anesthesia is performed, blood clots are removed, the wound is dried and the place where the blood is coming from is determined.
Methods to stop alveolar bleeding depend on its cause and location:
- if there is a rupture of the gums or mucous membrane, they are sutured;
- a ligature (a special thread for ligating blood vessels) is applied to the bleeding vessel;
- If there is bleeding from the alveoli (socket), a tampon of iodoform gauze is placed on it. It is left in the wound for several days.
Tamponation is used as a prophylactic measure if there is a risk of bleeding. The tampon is left in the hole for several days. Then they take it out and see how well the wound has healed.
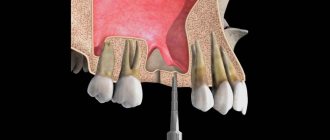
Removing wisdom teeth is potentially dangerous. Such operations are often difficult. Sometimes you have to cut the gum, saw the roots or the tooth itself and remove it piece by piece. Bleeding after such complex operations occurs more often than after ordinary ones.
Measures taken when a hole bleeds after wisdom tooth removal are the same as after regular removal. If there is a history of blood diseases, preparations are made for such an operation in advance. A blood test is carried out, in some cases calcium chloride injections and vitamin C
and
K.
_
If the cause of alveolar bleeding is systemic diseases, general hemostatic agents are used (calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, aminocaproic acid, dicinone, vikasol).
For hypertension, antihypertensive therapy is prescribed. After the pressure normalizes, the bleeding usually stops.
Why is it important how long it takes to bleed after tooth extraction?
Stopping bleeding indicates the beginning of the formation of a dense clot. It is needed to protect the wound surface from the penetration of bacteria and microbes. It also serves as a mechanical barrier for particles of food and drinks.
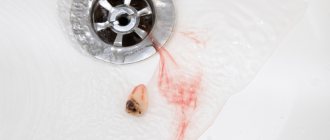
If the blood does not clot, the socket will be unprotected. Pathogenic microorganisms will begin to penetrate into the bare bed. It will secrete ichor (this is indicated by the salivary fluid acquiring a characteristic pink hue). In this case, recovery after surgery will take a long time and, most likely, will be accompanied by various complications.
When should the bleeding stop?
It is absolutely normal for blood to appear immediately after a tooth is removed from its socket. However, dentists and surgeons unanimously claim that bleeding should stop after a few minutes, that is, while the patient is in the dental chair. But this does not always happen so quickly; many patients experience the appearance of blood from the socket even after the end of the operation.
The reason for this may be several factors, the main of which are the characteristics of a particular person’s body and the complexity of the manipulations performed. Even when a wisdom tooth is removed, which is usually accompanied by severe dissection of soft tissue, the bleeding should stop flowing after 30-40 minutes. All other manifestations are not normal and require consultation with a professional.
Why is it important for the bleeding to stop? Immediately after the operation, it turns into a dense clot, which will have to protect the exposed bed from infection and bacteria until it is completely healed. After the blood has clotted, ichor may begin to ooze from the operated area, causing the salivary fluid to take on a slightly pinkish tint. This process can last 2-4 days.
Types of violation
Dentists distinguish several types of postoperative bleeding:
- Early or primary. The blood does not stop flowing for a long time immediately after the unit is pulled out. The dentist has to take various measures to stop it.
- Later or secondary. The bleeding quickly stopped at the clinic, but reappeared at home. In such a situation, many people are lost and do not know what to do. There is only one rule - if a negative symptom persists for more than an hour, you should immediately visit a dental surgeon.
Generally speaking, the appearance of blood at the site of the hole should be taken calmly. During extraction, soft tissues and blood vessels are damaged. Therefore, there is nothing strange about bleeding. You need to look at its dynamics. Every day a person’s condition should improve, as should the appearance of the hole in the oral cavity. If this does not happen, then there is some problem. It needs to be identified and eliminated.
Causes of bleeding
As a rule, hemorrhage (hemorrhage) occurs as a response to damage during soft tissue surgery or as a result of exposure to certain medications. Such problems usually go away within a few hours after the procedure.
If an ordinary tooth can be pulled out without much difficulty and a cotton swab applied to the wound, then removing third molars is much more difficult. During the manipulation process, it is often necessary to saw the crown of the tooth and pull it out in parts. With deep and curved roots, it is almost impossible to extract them without damaging bone and soft tissue.
In addition, there are also other reasons why the bleeding does not stop after a wisdom tooth has been removed:
- high blood pressure;
- mechanical injuries of a large vessel;
- the patient is taking blood thinning medications, for example, Heparin, Aspirin and others;
- low blood clotting;
- the use of anesthetics, after which the blood vessels dilate. This increases bleeding and slows down the process of clot formation;
- the presence of concomitant diseases can cause heavy bleeding. These include hepatitis, scarlet fever, leukemia, hemophilia and others;
- Overheating of the body or high physical activity immediately after removal increases the risk of hemorrhage.
If immediately in the postoperative period the patient abuses alcoholic beverages or smoking, bleeding can occur as complications.
If wisdom tooth extraction cannot be avoided, then the patient needs to understand that bleeding after such a procedure is a natural and normal process. But even with relative safety, the release of blood requires careful monitoring by both the doctor and the patient himself.
Why does it take a long time to bleed after extraction?
The reasons may be different, there are many of them. The most common:
- A sharp increase in blood pressure. Occurs in response to stress experienced during dental surgery.
- Vascular injuries. It is impossible to remove a unit without damaging them.
- Hormonal imbalance or increased levels of estrogen in the body. This reason only applies to women.
- Taking medications containing acetylsalicylic acid on the eve of a visit to the dentist. Aspirin helps thin the blood and prevents its rapid clotting. Some other medications work similarly. Therefore, it is important to be cautious about using any medications in the days leading up to the extraction.
- Gum injuries. The patient himself is usually to blame. The desire to touch the blood clot with your hands, tongue, eating too hard foods and chewing them on the inflamed side of the jaw, rinsing the mouth, drinking hot drinks or dishes are all causes of postoperative bleeding.
The wound heals worse if the gum in the area of the extracted tooth has been affected by gumboil or a cyst. In this case, the patient should be constantly monitored. Most likely, he will have to take anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and applications with antibacterial compounds for some time.
Anemia, hemophilia, alcoholism, diabetes mellitus, and atherosclerosis also increase the likelihood of postoperative complications. You must inform your doctor about the presence of these diseases. It is possible that he will prescribe hemostatic drugs.
A tooth was pulled out and the bleeding doesn’t stop: what to do?
A tooth was pulled out and the bleeding doesn’t stop: what to do?
Contents: • Bleeding is a complication after dental surgery • What should not be done after tooth extraction?
• What can you do at home? • Professional help from a dentist Tooth pulled out
– the bleeding doesn’t stop, why does this happen? Tooth extraction is a dental surgery that is performed in a clinic. Any operation is accompanied by some blood loss. Tooth extraction is no exception, as damage to gum tissue and periosteum occurs.
Bleeding is a complication after dental surgery
Socket bleeding can be quite difficult to stop. This problem occurs not only immediately after the operation, it can appear within a day.
Let's look at the reasons for this condition:
1. If the problem occurs immediately after removal, then this may be due to the fact that adrenaline has stopped working, and this provokes vasodilation. 2. If bleeding began after a certain time, then a common cause is the patient’s incorrect actions, which caused damage to the clot in the socket.
Local reasons include:
• damage to a wound or gum; • violation of the integrity of the interroot septum; • inflammation that has begun in the gum area at the site of the extracted tooth; • damage to the blood vessels located under the tongue. Common causes are mainly the patient's diseases, such as: scarlet fever, sepsis, blood diseases, hepatitis, hypertension.
What should you not do after tooth extraction?
After any surgical intervention, certain rules should be followed so as not to cause undesirable consequences.
For several hours it is prohibited:
• drink alcoholic drinks of any strength, because alcohol promotes vasodilation; • smoke; • Eating; • rinse your mouth with any liquid; • steam or take a hot shower, bath; • engage in physical labor or exercise in the gym.
How long does it take for blood to bleed from the socket?
A full-fledged clot is formed within 20 - 30 minutes.
If the bleeding continues when the patient is already at home, then there is cause for concern, so it is better to call the doctor and follow his recommendations. It is worth noting that some people confuse bleeding with ichor, which can be released from the wound for several hours after the removal procedure. If the secreted liquid is colorless or yellowish with a small amount of blood mixed in, then this is ichor. In this case there is nothing to worry about.
What can you do at home?
If bleeding begins after tooth extraction, and for some reason it is not possible to contact the dentist, then you need to help yourself.
The following manipulations may help solve the problem:
• A sterile swab should be placed on the resulting depression, then clamped with your teeth and held for approximately half an hour.
• If the bleeding does not stop, the tampon should be changed to one moistened with a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution, which helps stop the bleeding. • You can try applying cold to the cheek from the side of the extracted tooth. Cold constricts blood vessels, which helps eliminate this problem. Just remember: you can’t apply anything cold directly to the wound, as these actions can cause complications. • If the pain in the gum area is severe, then you can take painkillers, but without aspirin. This medicine thins the blood, which may cause bleeding. If the listed remedies do not produce results, and a person develops weakness or dizziness, then a visit to the dentist should not be postponed.
Professional dental care
The doctor will assess the situation and take action to stop the bleeding. What should a patient be prepared for? If there is bleeding from the soft gum tissue, the dentist may use sutures to close the wound.
If blood flows out of a blood vessel, then a tampon soaked in a special agent is placed into the tooth wound, the vessel is compressed, and the tampon is left in the hole for 5 days.
If the use of local remedies is ineffective and the bleeding does not stop, then the doctor may prescribe general medications that accelerate blood clotting. But the use of these medications is possible only after examination and testing.
Prevention of bleeding
To reduce the risk of all kinds of complications, you must adhere to some rules before tooth extraction: • Approximately two days before surgery and after, you should definitely stop smoking. • If the patient has hypertension, it is necessary to take medications to stabilize blood pressure, and also measure it before and after this dental procedure. • If the patient is taking blood thinning medications, they should be stopped a few days before surgery as they reduce blood clotting.
Prevent bleeding
Tooth extraction is considered a complex procedure, despite the minor amount of damage. Therefore, the patient should follow some of the doctor's instructions to prevent uncontrolled bleeding and minimize the risk of soft tissue inflammation:
- Do not touch or remove the formed blood clot from the wound. In the first 24 hours after surgery, it is not recommended to rinse the mouth.
- Do not touch the injury site with your hands or tongue. This can help break up the blood clot, even if the instruments are sterile.
- During the day after the procedure, you should avoid drinking drinks through a straw, as the vacuum provokes the removal of the blood clot from the socket. If the rule is ignored, the patient experiences increased pain after surgery and the gums swell even more.
- Do not engage in active sports and avoid excessive physical activity for 2 days after removing the wisdom tooth from the socket. Simple housework is acceptable - washing floors, dusting.
- For 24 hours after surgery, avoid going to the sauna or bathhouse, and do not take a hot bath or shower.
- Do not apply warm compresses to the sore area in order to minimize pain or swelling of the cheek. This provokes the spread of the inflammatory process into the deep tissues of the gums.
- For 2 days after the intervention, do not eat too cold or hot food. Otherwise, the pain symptoms intensify.
- You should stop taking spicy foods and carbonated drinks for a while. Dishes with a sour or strong taste provoke a recurrence of the problem.
- Do not chew food on the affected side for 3-7 days.
- If food debris gets into the wound, wash it off with water. Do not use toothpicks or fingers.
- In the first three days after surgery, stop drinking alcohol and smoking. Nicotine and alcohol dry out the mucous membranes of the mouth, thereby increasing pain and increasing the risk of infection of damaged tissues.
24 hours after the intervention, the damaged area of the gum is regularly treated with antiseptic compounds or salt water. After wisdom tooth removal, it is not recommended to carry out hygiene procedures for 8 hours. After this, the teeth are brushed 2 times a day, but all movements are performed with extreme caution so as not to damage the blood clot.
A cold compress is applied to the cheek only in extreme cases, for example, when it is not possible to stop the bleeding for a long time. On the one hand, this procedure helps relieve swelling and reduce pain, but on the other hand, it negatively affects the state of local immunity.
All measures to stop bleeding after wisdom tooth removal are performed within a limited period of time from 7 to 14 days from the date of surgery.
After regeneration of damaged tissues, a person can lead a normal life, since further healing of the hole will occur independently without taking preventive measures. Following the specialist’s recommendations helps to minimize the clinical picture of the problem and accelerate wound healing.
Professional help
The patient requires medical attention if there is prolonged bleeding, even if a small amount of biological fluid is released.
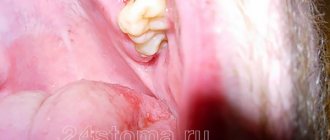
Smell after wisdom tooth removal
Despite the speed of implementation and modern techniques, removal of a dental unit is a surgical procedure that leads to injury to the mucous membrane.
An open bleeding hole is a constant source of infection. As a result, the socket cavity can fester and cause complications in the form of exacerbation of chronic pathologies and more serious consequences - sepsis or death.
In the hospital, the patient will be offered several procedures to stop the bleeding as quickly as possible.
Electrocoagulation
The dentist cauterizes the damaged vessels using an electrode shaped like a sharp needle. The manipulations are performed quickly and, as a rule, patients tolerate the procedure well.
Electrocoagulation is prescribed to patients who suffered severe soft tissue damage during the removal of a wisdom tooth or to people who inadvertently injured their gums. If the bleeding is associated with high blood pressure, then the procedure in question will not have an effect.
Putting stitches on the wound
This method is suitable for problems associated with high blood pressure or dry socket syndrome. Without additional surgical intervention, the wound will not heal on its own.
After suturing, the doctor gives several recommendations to the patient on caring for the oral cavity. These include antibacterial treatment of the damaged area at home, regular visits to a specialist to monitor the healing process of the hole.
Taking medications
This method of stopping blood is used if the patient has problems with the formation of a blood clot. In addition to drug therapy, the patient will have to regularly visit a specialist to monitor the wound healing process.
What to do after wisdom tooth removal
The body perceives the removal of a wisdom tooth as an injury and reacts to it accordingly.
If significant pain symptoms occur, the dentist prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to patients. Antihistamines may be prescribed to reduce swelling and sensitivity of nerve endings. The medication is taken for 7-10 days according to the standard regimen.
If the removal of a wisdom tooth occurred against the background of inflammatory diseases of the gums - phlegmon or gumboil, then after the procedure antibacterial drugs are prescribed. They are taken for 5-7 days, depending on the severity of the infectious process.