Functional properties of elements
Teeth perform several functions at once. Each element has a distinctive shape according to its purpose. The main role of the units is digestive. The quality of assimilation of useful elements by the body depends on the thoroughness of grinding the products. Only after chewing and moistening with saliva will the food be ready for subsequent processing by the digestive organs.
Chewing one piece lasts on average 10-20 minutes. The force exerted by the teeth on food sometimes reaches 80 kg. Incomplete dentition can lead to disturbances in the digestive system.
Another function of the elements is aesthetic. With malocclusion, a person may develop psychological problems, since the first thing others pay attention to during a conversation is a smile. Teeth also play a role in the formation of syllables. In the absence of one or more elements, the pronunciation of syllables changes: a lisp appears, speech is distorted.
Grinding food
The human stomach is capable of fully digesting only finely ground food, which is abundantly moistened with saliva. For this purpose, there are premolars and molars in the mouth, which act like millstones - they grind large pieces of food, while simultaneously mixing it with the secretion of the salivary glands.
The absence or loss of one of these teeth leads to the fact that unprocessed large particles of food enter the gastrointestinal tract, which are difficult to respond to enzymes and can cause various chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines.
Tooth anatomy
The structure of all units is the same, but each tooth has a distinctive shape and dimensions, depending on the functions it performs.
Internal structure of teeth in the photo
What does a tooth consist of? The top layer (enamel) is predominantly composed of minerals. It protects the inner layers of the tooth from mechanical, thermal and chemical damage. The rest of the solid surface of the elements consists of proteins and liquid involved in metabolic processes. This layer tends to wear out and wear off over time. Typically, caries first affects the surface of the tooth. For this reason, you should carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity and carry out hygiene procedures in a timely manner.
If you examine a tooth in cross-section, you can also see dentin. It also consists of mineral substances and protects the pulp with the nerve fibers located in it. Many small channels are localized in dentin, with the help of which metabolic processes in bone tissue are carried out. Through these structures impulses are transmitted between nerve endings. For 1 sq. mm of dentin there are about 70,000 microscopic tubules.
The internal cavity of the elements is represented by pulp. It consists of nerve endings and lymph nodes.
The structure of the tooth should be considered depending on its location relative to the gum. The visible part of the element is the crown. The area of contact between the tooth and the gum is called the periodontium. The root is located in a special cavity, which dentists call the alveolus. The root of the tooth ends at an apex, which is supplied with blood vessels. Through these structures, the elements are fed.
No Ads
Description, structure, functions, name and location of human teeth
It is not without reason that human teeth have different shapes, structures and sizes. Each tooth performs certain functions, and its purpose is, one way or another, reflected in the name:
- The incisors are the front teeth that fall into the smile zone. They are quite sharp as their function is to tear or cut food, hence the name. Normally, every person has lateral and central (larger) incisors.
- Canines are cone-shaped teeth that can be used to tear and hold food. They are located immediately behind the incisors.
- Premolars are the small back molars located behind the canine teeth.
- Molars are the back teeth necessary for mechanical processing of food. Wisdom teeth refer specifically to molars.
The listed types of teeth are also found in animals. But in the process of their evolution, some dental units were slightly modified:
- elephants' upper incisors became tusks;
- Poisonous snakes have poison in their fangs.
Many animals have front teeth similar to human ones, but since they are called differently, they cannot always be identified with the usual incisors and canines.
The structure of human teeth
Human teeth consist of a crown and a root part. The first is located above the level of the gum, the second is inside it. The top of the crown is covered with enamel, the strongest tissue in the body. It protects the inner layer of the tooth – dentin – from external influences. Under the dentin there is a hollow chamber with nerves and blood vessels - the pulp.
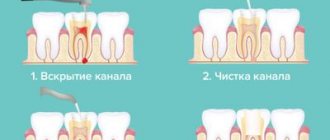
Despite its strength, enamel is vulnerable to bacteria. If left untreated, caries can affect the dentin and pulp. When the pulp chamber, which contains nerve fibers, is damaged, pulpitis develops, accompanied by acute throbbing pain. If the infection spreads to the root of the tooth, it is highly likely that it will have to be removed.
The basis of the lower part of the tooth is the root canals, which also contain arteries, veins and nerve fibers. Through the apical foramen, all of these structures are connected to the main neurovascular bundle.
The lower part of the tooth is covered with dentin and cement, which is attached to the periodontium using collagen fibers. The roots of teeth are hidden in the alveoli - depressions in the jaw bone.
Kinds
What are the units? Teeth in the oral cavity are divided into 4 types: incisors, canines, molars and premolars. The human jaw is symmetrical and each part (right and left) has the same number of elements. If this does not happen, then they talk about malocclusion development, which requires immediate correction.
Incisors
Incisors are the elements located in the center of the jaw. There are 8 such units in total - 4 at the bottom and 4 at the top. The peculiarity of the anatomy of the incisors is that they have a flat crown with a sharp cutting surface. There are 3 tubercles on the cuts of the incisors, which wear off over time. The centrally located elements are usually larger than the lateral incisors, since they bear more load when chewing food.
The upper central teeth are most susceptible to damage in the form of cracks in the enamel and chips. It is in these areas that aesthetic defects associated with improper placement of elements in the oral cavity and trema are usually noted.
Crown – part of the tooth protruding above the gum
It should be noted the main functions of the incisors are the primary capture of food, cutting pieces and chewing them. The central elements are the first to begin to chop the food and pass it further. Due to the sharp cutting edge, units and twos crumble and crush food for further normal absorption. The incisors protect the remaining elements from severe damage during chewing loads. In addition, they protect the digestive organs from the development of chronic diseases associated with insufficient absorption of nutrients by the intestines.
On the upper jaw, the units have impressive dimensions - up to 23 mm including the root system. Unit width is from 4 to 6 mm. Thanks to the flat crown, the chewing load is distributed evenly between all areas of the tooth. The thinnest enamel of the incisors is in the area of contact with the gum. It is this part that is most vulnerable to carious processes.
Several features of incisors should be noted:
- rounded root shape;
- the presence of grooves on the surface of the root;
- chisel shape;
- greater curvature of the incisors located on the sides.
Fangs
A person has 2 fangs on each jaw. They resemble a triangle in shape and are easily recognized among other elements of the series. With the help of fangs, a person can bite off pieces of hard foods - apples, carrots, crackers. The elements have only one long root. The upper units are larger than the lower ones. Some patients resort to extension procedures to give greater effect to the canines on the upper jaw.
No ads 2
Premolars
The first premolar is also called a quadruple. The main function of the tooth is transitional and exciting. Due to the wider crown, the elements take part not only in biting off pieces of food, but also in grinding it to the desired state.
On the chewing surface of the element there are several types of chewing tubercles - flat and vestibular. The first tubercle is located closer to the cheek, and the last one is directed towards the oral cavity. In rare cases, three-tubercle or four-tubercle teeth are found. An anomaly is observed if the palatine tubercle passes into the median tubercle.
Due to the many grooves and fissures, pathogenic bacteria can accumulate on the surface of premolar teeth, especially if oral hygiene is insufficient. For this reason, these segments should be given the most attention when brushing your teeth. The second premolar of the upper and lower rows has larger dimensions, but is shaped like a quad.
Molars
Molars have the same structure as the rest of the series. But, despite this, several features can be identified that are characteristic only of sixes and sevens. The main function of molars is to grind and grind food during chewing. They play an important role in the formation of an anatomically correct bite.
Each half of the jaw has 4 molars below and above. Molars have several chewing surfaces. The buccal surface of the tooth is convex. There is a groove on it, which is a place where pathogenic flora accumulates. These areas also need to be given special attention when brushing your teeth, since the salivary glands are located near the buccal surface, which are affected during the development of carious processes.
There are 3 tubercles on the chewing surface: paracone, protocone and metacone. On the buccal side there is also the most important morphological structure of bone tissue - the Carabelli tubercle. The degree of expression of the structure is varied.
In some cases, the Carabelli tubercle may have its own process
The mesial border of the molars has a slightly convex shape. The root system on this side varies in shape among different patients. It can be cylindrical or barrel-shaped. The structure of the distal surface of the molars is similar to the mesial one. The only difference is inaccessibility during hygiene measures. For high-quality cleaning of the last elements, it is better to use floss or irrigator.
Wisdom tooth
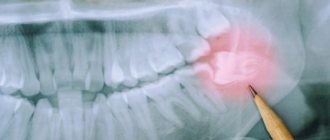
Eight, or wisdom teeth, usually appear on the surface of the gums in adulthood. The shape of the element is similar to 6, but has more powerful roots. The number eight is considered the most problematic tooth: it is difficult to break through to the surface and quickly collapses. Dentists may have difficulty removing figure eights due to their abnormal position in the mouth and crooked roots, which can be diagnosed using x-rays. In such cases, the problem area is immediately extracted, otherwise purulent inflammation of the soft tissues may develop. Another serious complication of improperly positioned wisdom teeth is the destruction of the roots of adjacent units.
No ads 3
Grabbing and biting
In the front part of the dentition there are incisors, four each on the upper and lower jaws.
They have a relatively sharp edge that, when pressure is applied, can cut even fairly dense food. Also in the oral cavity there are fangs - pointed teeth, inherited by humans from predatory ancestors. They are involved in holding food and tearing small pieces from it.
The loss of incisors and fangs leads to the fact that without its correction a person can only eat liquid or pre-cut foods into small pieces.
Classification of dental surfaces
To conveniently describe the localization of the pathological process, dentists use a term such as “crown surface”. There are 4 types of such surfaces:
Where is the eye tooth + photo
- Chewable. This part of the tooth faces the elements on the opposite jaw. In canines and incisors, this area is represented by the cutting edge.
- Vestibular. Located in the vestibule of the oral cavity. The vestibular surface of the anterior teeth has an area of contact with the lips. In the molars, this part is in contact with the inner shell of the cheek and is called the buccal surface.
- Lingual or lingual - the area of elements facing the tongue. It is in this area that the largest amount of plaque accumulates due to the difficulty of carrying out hygiene measures. The lingual side of the elements is not visible to others during a conversation, so many patients seek to install corrective systems on the inside of the tooth.
- Approximal. This type of surface is divided into medial and distal. In the first case, the area is located closer to the middle of the dentition, in the second case, closer to the edge of the arch.
Tooth surfaces
Features in adulthood
Patients in the older age group also often face problems caused by the development of canine teeth. Some of the most common questions that prompt a visit to the dentist include:
- At what age does the change from milk units to permanent ones occur? As a rule, the maxillary canines are fully formed by 11-13 years, the lower units - a little earlier, at 9-10 years.
- What is the order in which the molars erupt, and what to do if they emerge earlier than the frontal incisors?
According to the order determined by the physiology of the human body, permanent canines appear fifth - immediately after the molars, central and lateral incisors, as well as the first chewing units. In this case, a violation of the order can either be a consequence of the structural features of the jaw region in a particular case, or indicate the development of a pathological process - therefore, in such cases, it is recommended to consult a dentist and undergo a comprehensive examination.
- What causes pain in the “eye” teeth? In normal condition, teeth should not be a source of pain, so the presence of discomfort is most likely a sign of pathology. The development of gumboil, pulpitis, periodontitis, or another disease is a reason for full treatment, since the consequences can cause adentia, as well as infection of adjacent units.
- What to do if the fang grows crookedly? Abnormal position of dental elements is a common case. The choice of technique to solve the problem depends on the degree of its severity. If the defect is barely noticeable and does not cause inconvenience, doctors recommend not resorting to orthodontic treatment. In situations where the canine has erupted at a great distance from the socket, corrective devices are used - braces or mouthguards, and extraction of the unit may also be recommended.
Features of milk elements
Milk units act as precursors of permanent elements. They usually appear in the first year of a baby's life. Usually the period of eruption of the first incisors is accompanied by painful symptoms for the baby. About 2-3 years may pass between the appearance of the first and the eruption of the last milk tooth. A 3-4 year old child has 20 fully formed baby teeth in his mouth.
The structure of teeth in children
The change of the primary occlusion to a permanent one is carried out from 6-7 years of age. The shape of the permanent elements will differ little from their predecessors. The only difference is the more massive crown part and dense enamel.
In children, the degree of mineralization of enamel and dentin is weaker than in adults. Therefore, their dental care should be carried out with special care. The milk tooth is designed in such a way that most of its volume is occupied by the pulp, so caries in children becomes more complicated faster.
Another difference between milk units and permanent ones is short roots. For this reason, tooth loss in children sometimes occurs unnoticed and painlessly.
Correct names of baby teeth
In Latin, baby teeth in a child are called the same as permanent teeth in an adult. But children do not have all the dental units characteristic of older people. Milk teeth are divided into:
- central incisors;
- lateral incisors;
- fangs;
- first and second molars.
There are different names for teeth, but it is better to focus on Latin terms and serial numbers. In this way, you can identify teeth even without serious knowledge of dentistry.
Malocclusions
With a correct bite, the teeth of the upper jaw protrude onto the elements of the lower jaw by no more than 1/3. This position will make it easier for the jaws to chop food. Malocclusions are usually associated with the following conditions:
- The upper units overlap the lower ones by more than ½. This type of bite is usually called a deep bite.
- Certain groups of teeth may not fit together at all. In this case, they talk about an open bite.
- Distal bite. What it is? The problem is said to occur when the upper jaw is overdeveloped.
- If the lower jaw is pushed forward, then there is a mesial deviation.
- When the structures are displaced relative to each other, a cross anomaly occurs.
If not treated promptly, malocclusions can cause toothless jaws. For this reason, it is important to contact an orthodontist at the first sign of a problem.