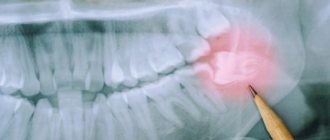
According to statistics, the 6th tooth implant is installed more often than others, which is due to the characteristics of this first molar. Sixes are the first of all permanent teeth to erupt, they are used more, and therefore deteriorate faster and more often than others. The procedure for implantation above and below differs in the choice of implant and timing of prosthetics. Implantation of a six on the upper jaw takes longer - 4-6 months, on the lower jaw - 2-4 months. Osseointegration occurs with differences due to the structural features of the jaws and different bone densities. The total duration of treatment depends on the volume of bone tissue; if there is a deficiency, bone grafting or sinus lifting is performed first.
Why do sixth teeth deteriorate more often than others?
The sixth teeth (first molars according to dental classification) are molars. The rudiments are laid at the 5th month of fetal development, and at the 9th month their mineralization occurs, which continues throughout the first month after the birth of the child. Their final formation with enamel occurs only by the age of 2-3 years. Therefore, the condition of the root and crown depends on the course of pregnancy and childbirth.
Sixes do not erupt in early childhood, since the function of chewing is not yet needed. When they erupt, they do not have predecessors in the form of milk teeth, so they essentially grow from scratch. Of the permanent molars, they begin to erupt first at 5-6 years, so they last longer than others. Frequent diseases, removals and the need for implants are associated with this.
Root canal treatment
The treatment plan for dental canals consists of several stages:
- First, access to the problem area is freed: using a special dental instrument, the filling or the area of the crown damaged by caries is removed.
- Then the contents of the pulp are removed, and the canals are cleaned mechanically using antiseptic drugs.
- After this, the root is prepared for filling. At this stage, the dentist can form the correct conical shape of the canal passage.
- Then the canals are carefully sealed. If baby teeth are treated, the dentist uses a special filling paste, which gradually dissolves as the root dissolves.
- After this, a filling is placed on the crown.
This treatment regimen is standard and does not depend on exactly how many canals there are in the diseased tooth. The main thing is that all dental canals are cleaned, treated with an antiseptic and carefully closed. If treated incorrectly, it may be necessary to remove the tooth and visit an oral surgeon.
Teeth can be single-channel, two-channel, three-channel and even eight-channel. If one of the ducts becomes inflamed, it is necessary to clean and seal not only it, but also all other canals, since the infection could penetrate into them.
Is it worth getting an implant?
The absence of the sixth tooth threatens:
- displacement of neighboring units;
- advancement of antagonists on the opposite jaw.
Neighboring and antagonist teeth will slowly shift, which threatens to expose the roots, the appearance of wedge-shaped defects at the gum itself, exposure of the neck, which is sensitive to changes in temperature of water and food, and pain. In addition, there will be a change in the bite, since the teeth will be out of place. Therefore, it is necessary to place an implant to maintain healthy teeth and correct bite.
Tips from dentists for disease prevention
The development of dental pathologies can be prevented only by following the advice of qualified doctors and observing the rules of oral hygiene.
So, for prevention purposes, dentists recommend:
- do not abuse the rules of hygiene, brush your teeth only in the evening and in the morning. More frequent exposure to tooth enamel contributes to its wear;
- hygiene procedures should be carried out half an hour after eating;
- use rinses to destroy germs remaining in the mouth after brushing;
- Cleaning should be carried out for at least 3 minutes, performing circular movements.
The main rule is that if the first signs of the disease are detected, you should immediately contact your dentist. This will help prevent further development of pathology and preserve teeth.
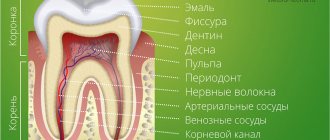
Video: tooth anatomy
Operation stages
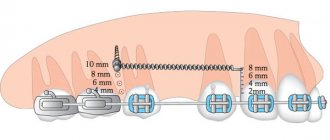
The six implant is installed in the classical way, as for all other lost teeth. Includes stages:
Preparation
Identification of contraindications, assessment of bone tissue and study of its size and density. Sanitation of the oral cavity, removal of plaque, treatment of gums and adjacent teeth. The stage lasts from several days to a month.
Bone tissue augmentation
If necessary, it is carried out as a preliminary stage in case of lack of bone tissue. The operation lasts an hour. After the planted material has fused with the bone (4-5 months), the artificial roots themselves are installed.
Installation of implants
The gum is peeled off, a bed is formed in the bone, an implant is placed, a plug is fixed, and sutures are applied. On the lower jaw, the implant takes 2-4 months to take root, on the upper jaw - 4-6 months.
Temporary prosthetics
At the patient’s request, lightweight plastic removable Butterfly immediate dentures are installed, which are attached to adjacent teeth.
Permanent prosthetics
The implant is opened, the plug is removed, the gum former is fixed, and after 10-14 days the abutment is installed. Impressions are taken and crowns are installed.
The sixth tooth implant can be placed immediately after removal into the resulting socket, but with a sufficient amount of bone tissue and under the following conditions:
- a pre-planned operation with the possibility of conducting diagnostics and assessing the immediate installation of an implant;
- atraumatic removal without damaging the alveolar process;
- absence of inflammatory and purulent processes at the root.
Why do you need to build bone tissue?
Increasing bone volume (osteoplasty) is necessary for the primary stabilization of the titanium root. If the height and width of the alveolar ridge are insufficient, the implant simply will not stay in the bone. The method of osteoplastic intervention depends on the clinical picture.
The following methods are used to build bone in the lower jaw:
- Guided bone regeneration.
Increasing the height and width of the alveolar process by replanting osteoplastic material. The surgeon peels off the gum, fills the jaw bone with osteoplastic material, closes it with a barrier membrane and applies sutures. - Splitting of the alveolar process.
Increases bone width. The doctor makes a cut in the center of the ridge, alternately screws spreaders of different diameters into it (from smaller to larger), and fills the resulting space with bone granules. - Bone block transplantation.
An autogenous (taken from the patient) bone block is screwed to the bone, covered with a collagen membrane and sutured. The 6th tooth implant is installed after the block has healed. - Increasing the volume of the maxillary bone.
Because the maxillary structures are located close to the root system of the first molars, a sinus lift is required in 90% of cases. It can be closed or open. The essence of the operation is that the doctor carefully lifts the lower part of the maxillary sinus, fills the resulting space with osteoplastic material and installs a six implant.
Features of implantation of the 6th lower tooth
The six of the lower jaw bears more loads during chewing than the upper jaw. Therefore, implants are selected taking this fact into account - wide and of sufficient length. The nuances of implantation from below:
- easier to carry out than on the top;
- implants take root faster - in 2-4 months, since the jawbone is denser and anatomically higher;
- but there is a risk of damage to the trigeminal nerve if the protocol is not followed, which is complicated by numbness of the chin and lips.
If the bone is small in height, then a preliminary operation is performed to increase it. The gum is peeled off, bone material is added, and a resorbable membrane is applied to secure it. Recovery takes up to six months.
Without preliminary bone grafting, surgery is possible if the atrophy is moderate. In this case, our Center uses bone growth stimulants. They are fixed to the neck of the artificial root during its installation and trigger the processes of bone tissue regeneration. In this case, implant healing and bone tissue growth occur simultaneously.
Indications and contraindications for molar tooth extraction
Reasons for removing a molar tooth may be:
- purulent periostitis;
- abscess;
- phlegmon;
- large tumor in the tooth area;
- purulent periodontal disease;
- the presence of a cyst in the area of the diseased tooth;
- exposed pulp;
- longitudinal tooth fracture;
- critical tooth decay;
- critical tooth curvature;
- disease of the dental bone tissue;
- sinusitis.
The following reasons are contraindications to the removal of molars:
- acute heart diseases;
- acute viral diseases;
- flu;
- angina;
- renal failure;
- pancreatitis;
- hepatitis;
- acute diseases of the nervous system;
- oncological diseases
- initial and final stages of pregnancy;
- stomatitis;
- gingivitis
- general degeneration of the body;
- alcohol poisoning.
Price
Our Center has a case payment system, which means that the case includes all materials and necessary manipulations.
The cost of implant installation includes:
- implant and superstructures;
- work of an implantologist;
- anesthesia;
- basic bone building complex;
- primary and repeat CT.
The price of implants varies depending on the type of bone. Nobel Biocare PMC (cheaper) is intended for weak tissue, and Nobel Biocare Conical Parallel CC (more expensive) is intended for dense tissue.
The cost of the crown includes:
- production of a prosthesis by a technician;
- taking impressions;
- installation of a crown.
Tooth extraction (for simultaneous implantation), bone grafting or sinus lifting are paid separately. Prices for services can be found here.
Guarantees
In our Center, implants are installed with a lifetime warranty from the manufacturer - Nobel Biocare. We provide guarantees:
- lifetime for the installation of implants;
- 1 year for crowns.
The warranty program includes a complex for the implant, surgery, bone reconstruction and prosthetics.
The guarantee is valid provided that the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, care rules and regularly visits the dentist.
Alternatives
An alternative method for restoring sixes is a bridge prosthesis. This is a structure consisting of crowns tightly connected to each other. To restore one tooth, the bridge consists of 3 crowns. The two outer ones are fixed on the teeth on both sides of the defect. The supporting teeth are ground down to form the internal cavity of the outer crowns of the prosthesis. The middle crown is hinged and imitates the lost six.
This option is cheaper than implantation, but has disadvantages - grinding the enamel of living teeth leads to a reduction in their service life. Another important point is that the bone under the hinged crown does not receive stress during chewing, so bone tissue atrophy is inevitable.
Haderup system
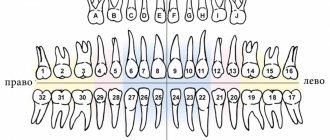
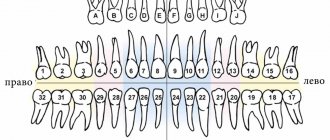
Some believe that this is the Zsigmondy-Palmer system, which has been improved. It involves the use of numeric symbols from one to eight. The numbering goes from the midline of the jaw to the edge. As additional signs there are plus and minus to indicate the top or bottom row.
Baby teeth are numbered from one to five. Each number must be preceded by a zero. This system has a number of shortcomings. For example, one of them is to indicate the location of the dental element on the jaw.
Zsigmondy-Palmer system
The scheme is not very popular in the world because it has errors. The exception is Great Britain. When created, the idea of Adolf Zsigmondy (a dentist from Hungary) was taken as a basis. It was he who came up with the Zsigmondy cross, that is, dividing the dentition into quadrants.
Each dental element has a specific serial number. The calculation starts from the midline. However, there are no exact indications of the location. Permanent teeth are marked with Arabic numerals - from 1 to 8, and milk teeth - with Roman numerals from 1 to 5. Subsequently, the American dentist Palmer made additions to the system. He changed Roman numerals to Latin letters.
The scheme is mainly used in orthodontics and maxillofacial surgery. For their specific work, it is most suitable.