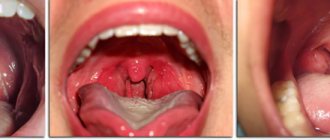
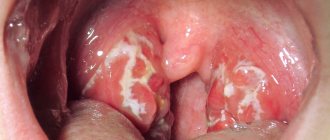
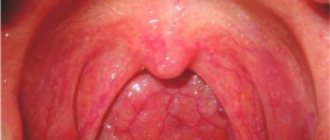
Why do you still need to remove your tonsils?
According to the results of many different studies, a large number of different pathogens have been identified, including streptococci, staphylococci, Haemophilus influenzae, lymphotropic viruses, etc., which contribute to the development of chronic tonsillitis.
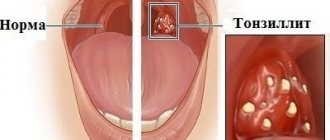
But the leading role in the development of chronic changes in the palatine tonsils, as well as local and general complications of chronic tonsillitis, is played by beta-hemolytic streptococcus from group A (S. pyogenes) - a microorganism that also uses anaerobic respiration for its vital functions. This bacterium is more often found in the deep sections of the recesses (crypts) of the palatine tonsils, since they contain the least amount of oxygen, which is the most favorable environment for the proliferation of anaerobic microorganisms.
Chronic tonsillitis becomes a focus of infection, a chronic infectious-allergic disease with a local inflammatory reaction in the palatine tonsils - all this is a consequence of the activity of not only beta-hemolytic streptococcus, but also its antigens and various pathogenicity factors, namely streptolysins.3
As a source of infection, chronic tonsillitis causes intoxication of the body. A separate problem is caused by various complications of chronic tonsillitis, for example paratonsillitis and paratonsillar abscess are quite common.
The treatment of such complications may require not only outpatient care, but also inpatient treatment with surgical intervention.
Common complications of chronic tonsillitis are: tonsillogenic sepsis (life-threatening condition), rheumatoid arthritis, endocarditis, glomerulonephritis. These conditions significantly reduce the quality of life of patients and can lead to disability.4
In connection with the above, the main treatment tactic is sanitization of the source of infection, in other words, elimination of the pathogen. There are two treatment methods - conservative or surgical.
The choice of method is currently clearly regulated and based on the classification of B.S. Preobrazhensky and V.T. Palchuna.5
This classification is based on the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis, as well as the presence and severity of toxic-allergic reactions and the presence of complications. The classification identifies 2 forms of chronic tonsillitis:
- simple (characterized by the presence of only local signs of chronic tonsillitis and tonsillitis no more than 1–2 times a year)
- toxic-allergic: toxic-allergic form I and toxic-allergic form II6
Indications for tonsillectomy
The main indications for tonsil removal are:
- Frequent exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis (more than twice a year)
- Purulent complications (peritonsillar abscess, neck phlegmon)
- Development of complications - rheumatism, heart disease, kidney disease, nervous system disease, skin disease
- Severe hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils, which can interfere with the normal act of swallowing, and also lead to severe snoring and periodic episodes of breathing apnea during sleep (obstructive apnea syndrome)
- Ineffectiveness of conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis, carried out in a complex of 2-3 courses
- Neoplasms of the palatine tonsil
Tonsillectomy is performed during the period of remission of the inflammatory process, that is, without an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis.
If a complication such as a peritonsillar abscess develops, the removal of the tonsils is carried out simultaneously with the opening and drainage of the purulent focus. This operation is called abscessonzollectomy.
Treatment methods
Therapy is prescribed by a doctor only after determining the root cause
What to do if there is bleeding from the tonsil - it depends on the cause of the bleeding. In case of acute infectious process (sore throat):
- rinse your throat with antiseptics;
- take antibiotics prescribed by your doctor;
- use antiseptic sprays and lozenges to reduce pain.
In this case, the blood is caused by inflammation and is only a symptom. Treatment is aimed at suppressing the bacterial infection.
In case of peritonsillar abscess:
- hospitalization is required;
- surgical opening of the abscess;
- taking antibiotics;
- gargling with antiseptic solutions.
Peritonsillar abscess is very dangerous and can be treated in a hospital setting. It must be removed surgically. The operation consists of cutting the abscess and draining the cavity to remove pus. Antibacterial therapy and symptomatic treatment are required. It is important to prevent pus from entering the general bloodstream and infecting the entire body.
In case of mechanical damage:
- eliminating the cause of bleeding in case of foreign object penetration;
- gargling;
- treatment of tonsils with a wound healing agent.
For severe injuries, it is recommended to use antibacterial agents, as there is a high risk of infection and the development of an abscess. Wound healing drugs are selected by a doctor, since they are not always necessary, because the mucous membranes are restored quite quickly.
For candidiasis of the tonsils:
- gargling with antiseptics;
- taking antimycotics;
- strengthening the immune system.
In case of fungal infection of the tonsils, it is necessary to take special medications, otherwise it will not be possible to defeat the causative agent of the disease and the disease will become chronic. Throat candidiasis can be diagnosed by analyzing a throat smear.
Blood in chronic tonsillitis: treatment methods
Bleeding from the tonsils in chronic tonsillitis is caused by hard deposits in the lacunae. First of all, professional cleaning of the gaps is carried out. The manipulation involves removing the plugs with a vacuum apparatus, followed by irrigating the gaps with an antiseptic or antibacterial agent that prevents the re-formation of plaque. To effectively get rid of traffic jams, a course of procedures is required.
Then a comprehensive treatment is prescribed - taking antibiotics, regular gargling, strengthening the immune system.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, complete or partial removal of the tonsils is indicated. To preserve the tonsils, cryodestruction is used. The method allows you to remove the source of infection and hypertrophied tissue, but does not affect the entire organ. The cryodestruction procedure involves applying liquid nitrogen to the tonsils.
Antiseptic treatment of tonsils
Before use, you should read the instructions for any individual contraindications and allergic reactions.
In case of bleeding caused by inflammation or mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, it is necessary to provide antiseptic treatment of the tonsils, otherwise there is a high risk of secondary infection. For this purpose, gargling and the use of special means are indicated.
For rinsing use:
- Furacilin solution;
- Chlorhexidine or Miramistin;
- salt and soda;
- iodine solution.
At home, it is preferable to use Furacilin, since this drug is an antibiotic. To prepare the solution, grind one tablet into powder and dissolve in a glass of water.
Gargling is done 4 times a day. Additionally, you can apply Lugol's solution to the tonsils - this will provide a long-term antiseptic effect.
Tonsil hypertrophy
Palatine tonsil hypertrophy is a persistent enlargement of the tonsils that interferes with breathing through the mouth. With hypertrophy, breathing during sleep occurs with episodes of stopping, and snoring intensifies. There may be difficulty swallowing food, and speech becomes difficult.
To determine the degree of enlargement of the tonsils, the pharynx is examined. The doctor focuses on the edge of the anterior arch and the midline of the pharynx (uvula-uvula). The distance is divided into three conventional parts .
There is a classification in which several stages of tonsil hypertrophy are distinguished:
- I degree of hypertrophy - an increase in the tonsil by 1/3 of the distance from the arch to the uvula (the tonsils look behind the arches in the larynx)
- II degree of hypertrophy - tonsils are enlarged by 2/3 of the space from the arch to the uvula
- III degree of hypertrophy - the tonsils are greatly enlarged, reach the uvula and can even touch it
Contraindications to tonsillectomy
Contraindications can be absolute, when surgery is completely excluded for the patient, and relative, when there are reasons that postpone surgery until these reasons are completely eliminated.
Absolute contraindications to tonsillectomy:
- blood diseases
- some heart diseases
- tuberculosis
- cirrhosis of the liver
Relative contraindications to tonsillectomy:
- ARVI and influenza
- exacerbation of chronic diseases
- menstruation
- pregnancy
Tonsil removal methods
In modern otorhinolaryngology, there is a wide choice of tonsillectomy techniques.8
Classic method of removing tonsils
Removal of tonsils occurs by bluntly separating the tonsil tissue along with the capsule from the surrounding tissues using a rasp.
The separation of the tonsil is completed using a wire loop. The bleeding is stopped, the vessels are cauterized using an electrosurgical method (electrocoagulation). This operation takes from 15 to 40 minutes.9 Today, this operation is used in ENT practice more often than others. The operation can be performed under general or local anesthesia.
The only disadvantage of this method, unlike others, is the highest risk of bleeding. However, the operation is fairly routine and, relative to the number of operations performed, the risks of complications are low.
Laser method for tonsil removal
When removing tonsils, a laser beam is used to destroy and coagulate tissue. The laser beam coagulates the blood at the incision site and seals the blood vessels, which prevents bleeding. The laser method is less traumatic and has a lower risk of complications. Also, in this way it is possible both complete removal of the palatine tonsils and their partial excision.
Radio wave method for removing tonsils (using the Surgitron device)
Tissue excision occurs using a radio signal, which is transmitted by an electrode and causes the evaporation of intracellular fluid and tissue dissection.
The advantage of this method is that thermal damage to tissue is several times lower than when using laser or electrosurgical methods. There is less tissue injury, as a result of which the patient experiences less pain in the postoperative period; the level of tissue regeneration is maintained. Complete tissue healing occurs without the formation of a rough scar.
Cryodestruction
This method of removing tonsils involves local exposure to liquid nitrogen using a special nozzle.
The nozzle is selected individually, taking into account the peculiarities of the anatomy, since its contact with the palatine tonsil must be especially clear and dense for a more effective effect. Cryotherapy causes microcirculation disturbances, which ensures the absence of bleeding during and after surgery. This method is painless and bloodless, and does not form a rough scar. The method is recommended for patients with an increased risk of bleeding, severe heart failure and pathology of the endocrine system.
When is it necessary to remove tonsils?
If bleeding is not observed for the first time and is caused by regular damage to the tonsils due to pronounced proliferation of the organ’s lymphoid tissue, a decision is made on complete or partial resection of the tonsils. In this case, the operation poses less of a threat to health than regular damage and the constant risk of infection of the organ.
Removal is indicated if a malignant process is suspected. Lymphoma of the pharyngeal ring (cancer of the tonsils) is a fairly rare, but very dangerous cancer pathology with a high mortality rate.
The difference between tonsillotomy and tonsillectomy
Tonsillotomy is an operation in which enlarged tonsils are removed not entirely, but partially. This type of surgical intervention is indicated for patients with grade III hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils, when they occupy the entire space from the anterior palatine arch to the uvula. During a tonsillotomy, part of the enlarged tonsils is removed. Tonsillotomy, in contrast to the more radical method of complete removal of the tonsils, allows them to preserve their protective functions. This method is also recommended for treating children.
Anesthesia for tonsillectomy
Tonsillectomy is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia.
With local anesthesia, the tonsil and surrounding tissues are injected with anesthetic drugs, while the patient is conscious and sitting in a chair.
The second method uses inhalation incubation anesthesia, in which the patient is put into medicated sleep. After surgery, the patient wakes up immediately in the room.
Both methods of pain relief have their advantages and disadvantages, so only the doctor who will perform the operation, as well as the anesthesiologist, can choose the right method. The patient's health status and wishes are also taken into account.
What to do if there is bleeding after tonsil removal?
Bleeding after tonsillectomy is quite rare. This complication is typical only for an operation during which the tonsils were removed with a scalpel.
In the first week after removal of the tonsils, isolated drops of blood may appear, which is explained by mechanical damage to the tissue during chewing and swallowing food. This is explained by the fact that a wound remains at the site of the removed organ, which heals within several weeks. To avoid bleeding, in the first week you need to eat soft foods, giving preference to various purees.
If heavy bleeding occurs 7 or more days after surgery, a person should urgently seek medical help. The patient is hospitalized, the bleeding is stopped surgically. The patient must remain in the hospital for 3-5 days after the incident.
Recovery in the postoperative period
The operation requires the patient to remain in the hospital for several days. After the operation, the patient is transferred to a ward for further medical supervision.
The first day is the most unpleasant for the patient, since it is not recommended to swallow, eat or drink, and the patient may also experience severe pain. Bed rest is observed for 2-3 days. If the tissues heal well and there are no signs of bleeding, the patient can be discharged for further outpatient observation. On average, a patient is discharged from the hospital within a week. The tissues finally heal within three weeks. All this time, the patient may experience pain and discomfort in the throat, as well as periodic fever.
For 10-20 days after the operation, that is, throughout the recovery period, the patient is recommended to follow a diet: hot, cold, sour, spicy foods should be excluded, as well as the consumption of rough food in the form of cookies, gingerbread, crackers, since such food can irritate the injured area. It is recommended that the food be soft: in the form of baby food, cereals, and various soufflés.
In the postoperative period it is prohibited:
- play sports, lift weights, as exercise can lead to bleeding
- visit baths, saunas, take a hot bath
- consume hot foods and drinks
As noted above, pain is the most unpleasant ailment that accompanies the patient throughout the recovery period from the first day after surgery. The pain may bother the patient at rest, or may intensify when swallowing and talking. To improve the patient's well-being and reduce pain in the postoperative period after tonsillectomy, drugs for general and local anesthesia are used. The local drugs used must also have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Causes of blood appearing on the tonsils
Blood on the tonsils is an alarming symptom that should not be ignored. It may appear against the background of existing inflammatory diseases of the tonsils, or for no apparent reason. It is possible to determine exactly whether this symptom is dangerous only after examination by an otolaryngologist. At home, accompanying symptoms will help suggest a diagnosis.
Chemical burn as a cause of bleeding
You can burn your tonsils by accidentally overdosing the dosage of medications when rinsing
Blood on the tonsils can occur due to a chemical burn. You can get it at home if household chemicals and other irritating substances accidentally come into contact with your tonsils.
Chemical burns are most often work-related injuries, but can also occur as a result of self-medication for sore throat.
Quite often, damage to the mucous membrane occurs when gargling with iodine, vinegar or other potent substances when the recommended dosages are exceeded.
A chemical burn is a reason to immediately go to the hospital. Chemicals deeply affect the mucous membrane, causing deep erosions and non-healing ulcers to form at the burn site.
Thermal burn
If blood comes from one gland after a burn with hot food or boiling water, we are talking about a serious injury. Thermal burn of the tonsils can also be caused by inhalation of steam, for example, due to home inhalations according to folk recipes.
As a rule, after receiving a burn, a person strives to immediately cool the affected area. Use cold water or pieces of ice. This is effective for skin burns, but has a different effect on the mucous membrane of the tonsils, resulting in blisters and bleeding erosions.
Thermal burn itself is not dangerous, but only if treated in a timely manner. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will treat the tonsils with a wound-healing agent and prescribe adequate therapy for speedy tissue restoration.
Mechanical damage to the tonsils
Children constantly put everything in their mouths and can easily injure their mouth and throat.
If there is bleeding from the tonsils, the cause may be mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. This happens due to:
- eating hard foods that scratch the tonsils;
- getting a foreign object into the throat;
- attempts to independently rinse the lacunae of the tonsils;
- removing plaque from the tonsils using improvised objects.
No one is immune from damage to the tonsils by solid food. Usually the cause is snacking on the go and hastily eating crackers and other solid foods.
Note! Those with a sweet tooth can be injured by regular candy, whose sharp edges can scratch the throat and tonsils.
Blood on a child's tonsils may be due to the fact that young children like to put small objects into their mouths. Careless movement can cause injury to the tonsils. Caution must be exercised with children - before diagnosing mechanical damage to the throat by a foreign object, symptoms of tonsil disease and other causes should be excluded.
Perhaps the most common cause of bleeding from the tonsils is an attempt to independently clean the lacunae professionally. A person purchases a special syringe with a curved tip, inserts the tip into the lacuna to remove the plug, and as a result scratches the delicate mucous membrane. Bleeding from the tonsils is often observed when trying to remove plaque, characteristic of chronic tonsillitis, with improvised objects, such as a cotton swab.
Blood due to tonsillitis
Acute tonsillitis can cause bleeding from the tonsil. This occurs due to swelling of the tissue of the tonsils and an acute inflammatory process, during which small capillaries are damaged. If there is bleeding from the tonsil, you must first rule out acute tonsillitis. Symptoms of the disease:
- severe pain in the throat when swallowing;
- hyperemia and swelling of the throat;
- high body temperature;
- symptoms of intoxication.
In chronic tonsillitis, drops of blood may also be found on the tonsils. This is due to plugs in the gaps. The deposits in the recesses of the tonsils harden over time. During meals, they can move due to the pressure of hard food, as a result of which dense deposits scratch the mucous membrane of the lacunae, causing bleeding.
Necrotizing tonsillitis is especially dangerous. This is an acute infectious process caused by pyogenic bacteria, which lead to necrosis of the affected tissues. As a result, blood appears on the tonsils, a gray-green coating is observed, under which large ulcers are identified. The disease occurs in an acute form and is accompanied by high body temperature.
Peritonsillar abscess
The disease is accompanied by a bright fiery throat color
The disease is an advanced acute bacterial tonsillitis and is manifested by the formation of a large cavity filled with pus. The abscess occurs in a severe form - cutting and tearing pain, body temperature above 39 degrees, severe symptoms of intoxication. If the disease is not treated, after 5-6 days the abscess will open on its own. As a result, a wound is formed from which pus and blood ooze.
Opening an abscess is very dangerous, as it can lead to blood poisoning (sepsis) if purulent masses enter the bloodstream. If you suspect an abscess, you should consult a doctor. Urgent hospitalization is indicated when an abscess is opened.
Blood after tonsillectomy
Bleeding after removal of tonsils or tonsillectomy is quite common. Moreover, if on the first day after the operation the appearance of droplets of blood is considered normal, then blood a few days after tonsillectomy is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Important! The risk of bleeding continues for 14 days after surgery.
Bleeding from the tonsils after a patient has had their tonsils partially removed may indicate an infection. Since the tonsils are very sore in the first days after surgery, a person may not notice a deterioration in well-being. Infection of a postoperative wound is very dangerous and requires urgent medical attention.
Malignant neoplasms
Another reason why blood bleeds from the tonsils may be malignant neoplasms of the tonsils and larynx. This disease does not have any associated symptoms and can only be diagnosed by a doctor.
If blood appears, and other causes have been excluded, you should undergo a comprehensive examination by an otolaryngologist in order to exclude benign and malignant neoplasms.
Candidiasis of the tonsils
A rare cause of blood on the tonsils is candidiasis or thrush. This is a disease of a fungal nature, manifested by the formation of a thick yellow plaque on the tonsils. Under the plaque, which is a waste product of yeast, ulcers form that can bleed. Candidiasis can only be diagnosed by performing a smear.
Complications of tonsillectomy
The most serious complication during and after removal of the tonsils is bleeding from the site of the surgical intervention - the tonsil niche. Bleeding can be vascular, parenchymal, arterial, venous, and the cause may also be invisible.
Bleeding in the postoperative period was observed in 1.5-13% of patients. A favorable outcome of the operation depends on knowledge of the location of the large tonsillar vessels of the palatine tonsils and the use of modern, less traumatic surgical methods.12
It is worth noting what may bother the patient after surgery:
- Small blood clots
- Pain and discomfort at rest and swallowing
- Scar changes on the palate
Tonsillectomy is a serious surgical intervention that requires an integrated approach, starting from indications for surgery, preparation, and ending with strict adherence to all recommendations. Precise execution of each step can contribute to a favorable outcome of the operation and minimize the risks of complications.
Diagnostics
The first thing to do if you find blood from the tonsil is to consult a doctor. Even minor mechanical damage to the tonsil is fraught with dangerous complications.
The otolaryngologist will perform a pharyngoscopy and interview the patient. You may also need ultrasound diagnostics, a throat smear, a general and biochemical blood test. To establish the cause, it is important to take into account the medical history, as well as recent surgery or other manipulations of the tonsils, for example, washing the lacunae. Based on the results of the examination and examination, the doctor will select the optimal treatment regimen.