Teeth are hard tissue formations with high strength that last for a long period of time. The shape and location of individual units affects their functions:
- primary mechanical processing of food is carried out with the help of saliva (chewing, formation of a food bolus);
- formation of sounds (diction);
- protection of the body (prevent harmful microorganisms from entering internal organs).
Many external and internal factors influence when a person’s teeth begin to erupt and until how many years they grow. Among them are the nature of nutrition, the quality and composition of drinking water in the region of residence, hot (cold) climate.
The structure of the dentition
The total number of primary teeth is 20, each jaw has 4 incisors (the central part of the upper and lower rows), as well as 4 molars (“chewing” 4th and 5th units). Adults normally have between 28 and 32 dental units. So, on the upper and lower jaws there is a symmetrical location:
- 4 incisors each;
- 2 fangs;
- 4 premolars;
- 6–8 molars.
Until what age do wisdom teeth grow? You may never wait for the “birth” of the notorious “eights” - congenital adentia of the third molars is considered the norm. Another clinical picture may develop: the wisdom tooth is “embedded” in the jaw, but does not erupt due to a lack of space in the dentition. If “eights” are still born, then this usually happens until they reach a maximum of 25 years of age.
No Ads
Read also
What to do if your tooth aches
Sometimes aching pain in a tooth can appear for no apparent reason at first glance.
Why do teeth crumble?
Tooth decay in general, and crumbling in particular, is not an aesthetic problem.
General principles of growth
Baby teeth begin to grow from 6-8 months of age. As a rule, by the first anniversary of his life, the baby has already “acquired” four upper and lower units. By the age of 2 years, the first canines and molars “come into the world”; after another six months, the second molars are added. The final appearance of the primary dentition (20 units) can be observed in three-year-old children.
As a rule, by the end of the first year of life, the baby “acquires” 4 anterior milk units
What to do if by 9 months the baby has not yet acquired a single tooth:
- carefully examine the oral cavity; the gums, as a rule, look slightly swollen and reddened; upon palpation, the tooth edge can be felt;
- in order to speed up the process of “birth” of the first units, pediatric dentists recommend that young parents purchase growth stimulants for baby teeth at the pharmacy - rubber ring toys;
- A light massage of the gums with a clean finger or a cold tablespoon will also only benefit the baby.
Important! Delayed growth of primary teeth can be either a variant of the physiological norm (for example, in boys this process usually begins later than in girls) or a symptom of various pathologies associated with growth retardation (in particular, rickets).
No ads 2
In the latter case, parents should seek help from a pediatrician - perhaps he will prescribe vitamins or calcium supplements to the child to normalize “healthy” mineral metabolism and improve metabolism in general. In rare cases, the absence of signs of teething up to a year indicates edentia (the rudiments of the milk units have simply not formed). In such a situation, the help of a pediatric dentist is required - he will send the child for an x-ray, based on the resulting image, he will make a diagnosis and select treatment.
Starting from the age of 5, baby teeth are gradually replaced by permanent units
To what age do a person’s teeth grow: throughout life, 20 units are replaced at a time (deciduous – permanent), and 8–12 units initially grow as molars. General cutting scheme:
- medial lower incisors – 6–9 months;
- medial upper incisors – 7–10 months;
- lateral upper and lower incisors – 9–12 months;
- first upper permanent teeth – 12–18 months;
- first lower molars – 13–19 months;
- upper (16–20 months) and lower (17–22 months) canines;
- second lower (20–33 months) and upper (24–36 months) root units.
These figures are very relative; it all depends on the individual characteristics of a particular organism. As a rule, by the age of 3, a child has already grown all his milk teeth, and from the age of 5 they begin to gradually be replaced by molars. Why teething may be disrupted: type of feeding (instead of breastfeeding - artificial), genetic factors, loss of baby teeth due to dental problems.
Answers to frequently asked questions about x-rays of baby teeth in children
We offer expert answers from specialists from the Smile Factor network of clinics to frequently asked questions by parents.
Can an x-ray be prescribed to a child “just in case”?
Unfounded medical (and dental) research is prohibited by SanPiN.
But, most often, diagnosis according to indications is at the discretion of the attending physician. Any parent can ask clarifying questions and learn more about the assigned test and what it is for. What is better - 2D or 3D scanning result?
It all depends on the goals of the diagnosis.
In some cases, a 2D image is sufficient, while in others a CBCT scan is required to obtain a 3D image. Taking into account how CT scans of the jaw and teeth are done, the procedure is not much different from a simple x-ray in terms of safety and is indicated for obtaining more extensive data about the child’s dental system in the images. Are x-rays harmful to a child?
Modern X-ray machines (and most often these are ultra-modern tomographs) produce the minimum possible radiation dose during operation, which does not cause any harm to the child’s body. To achieve the maximum recommended radiation exposure of 1000 µSv per year, a child needs to undergo about 400 x-ray examinations. It becomes clear that so much research is simply not needed. And the radiation that a baby receives during a CT scan is equal to what he receives after a week of watching TV.
Growth of milk units
How to find out that your baby is getting his first teeth:
Viburkol for teething
- the gums become red, swell, a white ball can be visually identified, from which the milk unit will later “be born”;
- the child’s cheeks are burning;
- the baby becomes capricious, whiny, refuses to eat and sleeps poorly, and the body temperature may “jump” slightly.
Increased excitability is another “identifying sign” of the onset of teething. The child begins to put foreign objects into his mouth - chewing minimizes discomfort on the oral mucosa. A typical symptom is increased salivation - when the secretion gets on the skin of the face (in the cheeks, chin), it causes the appearance of foci of irritation (rash). Many parents notice limited hyperemic areas on the child’s neck (on the side where the tooth is cut).
Teething is a difficult period for a child’s body; against the background of restructuring and weakened immunity, children can be “attacked” by ARVI. So, if a child has attacks of nausea and vomiting, cough, abdominal pain, runny nose, appetite has disappeared or the body temperature has risen, it is recommended to immediately show him to a pediatrician.
After the appearance of the first milk units, young parents should take care of proper hygienic care for them
Important: you should not additionally stimulate (try to speed up) the process of eruption of baby teeth. Some parents scratch their gums with bread crust, a piece of sugar, and other irritants. Such measures will not have any effect on the “birth” of milk units, but they can provoke injuries to the oral mucosa or “contribute” to the development of a local inflammatory process.
No ads 3
Bookmarking teeth
The formation of baby teeth occurs at approximately 4-6 weeks of fetal development. At the same time, the formation of the fundamental elements occurs much later - during the first months of the child’s life. For this reason, new mothers who are bottle-feeding are strongly recommended to supplement their baby’s diet with calcium. This substance promotes the proper formation of tooth enamel.
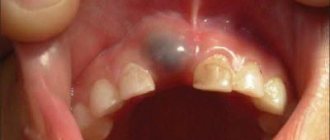
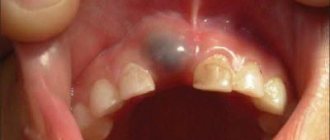
At an early age, unprotected baby teeth are extremely susceptible to carious lesions. Parents should monitor this closely, as infection can subsequently cause destruction of permanent teeth. The fact is that the rudiments of permanent teeth are in close proximity to the roots of milk teeth, so as soon as you discover dark spots on your child’s enamel, immediately go to pediatric dentistry.
How to relieve your baby's condition
Many young parents are wondering how to relieve the unpleasant symptoms that accompany the “birth” of milk units. The simplest measure is to apply cold (a piece of ice) to the “working” gum. Dental gels or ointments can also come to the rescue, relieving pain, swelling, and stopping the inflammatory process. Important: any medications should be used only with the permission of a pediatrician (pediatric dentist).
Thus, pharmacies sell special gels with lidocaine and inert fillers (menthol, astringents, flavorings) intended for use exclusively during teething. Examples of such tools:
- Kalgel (contraindicated for diathesis).
- Dentinox.
- Kamistad.
- Holisal.
- Mundizal.
General recommendations for use: a small amount of the local drug should be applied to the “working gums” 3-4 times a day for no longer than 3 days in a row.
Nature has provided for everything
Losing baby teeth is a natural and inevitable process that everyone goes through in childhood. Most often it begins at 5-6 years of age and passes painlessly. Sometimes the replacement of temporary teeth may begin earlier or, conversely, late. Some deviations from the usual indicators are not always considered a violation, since much depends on the health and physiological state of the child. When he begins to change his teeth, we recommend making an appointment with the dentist, as this is a very important period for the formation of your baby’s bite.
How do “eights” erupt?
It is impossible to give an unambiguous answer to the question of when wisdom teeth begin to grow and until what age do they grow. Third molars “come into the world” in the period from several months to 2-3 years, causing a lot of unpleasant sensations. When the “eights” begin to grow is influenced by many factors - in particular, the number of bone buds, heredity, and the anatomical features of the jaw (its shape). Due to the fact that third molars often create a certain discomfort - they affect the functioning of the TMJ, provoke sinusitis, and “displace” neighboring units of the dentition - they are often removed.
The main indications for extraction are:
- persistent hyperthermia (2–3 days) during the growth of wisdom teeth;
- acute inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) at the site of eruption;
- severe pain that makes eating difficult.
Anatomical features (shape) of the jaw, heredity and a number of other factors determine the timing of teething
Why can a 7-14 year old child sometimes experience pain when all his teeth are intact?
Yes, this can happen, but in this case the pain occurs not in the tooth itself, but in the jaw, which is growing rapidly at this age. Since permanent teeth are almost twice as large as baby teeth, they need much more space. Therefore, large new teeth can sometimes overlap each other or grow at an angle, getting out of the dentition. As the jaw grows, they align and settle into place. But a qualified specialist can competently assess this situation, as well as the risk of anomalies and developmental defects. That is why in this case you will need to consult an orthodontist.
How safe is an X-ray of a child's jaw?
X-rays of the jaw for children, including infants, are a relatively safe procedure. The radiation exposure during imaging is negligible and cannot negatively affect the further development of the dental system. At the same time, it must be said that taking X-rays without indications, for prevention, is still not worth it.
Contraindications for
Contraindications to X-raying a child’s jaw are:
- unsatisfactory general condition of the child;
- bleeding;
- pathologies in the thyroid gland.
Decoding the results
The finished images must be deciphered by a specialist. It is possible that several doctors will be present during the decoding, for example a radiologist
, dentist, otolaryngologist.
The photographs are used to assess how symmetrically the teeth and jaws are positioned. If a focus of any pathology is detected, it is important to determine its exact location and size.
When diagnosing a jaw fracture, you need to determine its complexity, consider whether there are fragments and how they are located.
If a tumor-like neoplasm is detected, it is important to assess its size, consider its boundaries (clear or blurred), and determine its location.